HOME CALENDAR NETWORK FUNDING CONTACT RESOURCE TOURS SACRED GEOMETRY ANTHROPOCOSM EARTH GRID VORTEX SITES SILK ROAD GEOMANCY HARMONICS ANTI-GRAVITY
[under construction]
see also: QIGONG VORTEX SITE TOURS
VORTEX SITES:

When one seeks healing, one also receives messages from spiritual guides.
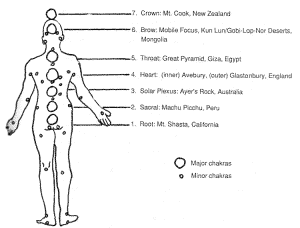
PRIMARY ENERGY CENTERS: EARTH CHAKRAS
(see also Becker and Hagen's Planetary Grid System)
Mountain Chakras (Energy centers): (eg.vile vortices)
Root: Ararat
Navel: Neblina
Solar Plexus: Kilamanjaro
Heart: Haleakala
Throat: Shasta
Brow: Everest
Crown: Fuji
Other Interpretations of Chakra Sites:
The planetary chakra system alternates/changes according to a predetermined/particular timing (eg.celestial influence; Earth spin); (sim.vile vortices).
Central Hermetic Site: (primary electro-magnetic geo-cosmic connection)
Etheric Heart Center [sim.Tantric: Anahata Chakra] (internal and external operates in tandem):
· Internal: Avebury Circle, Wiltshire, England (according to Richard C. Hoagland: site design geometry parallels megalithic site geometry at Cydonia, Mars)
· External: Glastonbury Tor; current Mobile Focus (see geomancy)
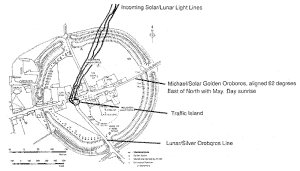
Avebury Round Table of the Sun:
Avebury is considered a condensed planetary Round Table of the Sun, which is a model for understanding the independent/differentiated activities of the 12 tones (solar royal court) in one sound (ie.solar logos; sun king; individual component of galactic logos). The planetary Round Table is the central receptor complex for cosmic (solar system) energy, contributing to Gaia's star evolution paradigm (on the threshold of transcendence, attaining 4th dimensional awareness of anti-gravity). According to Sumerian cosmology/astrology, the solar system comprises of 12 planetary/celestial (revolving, rotating, interrelating) bodies, or cosmic notes, influencing 12 zodiac houses; establishing a triangular influence (stars-planets-geo points) upon life via Dragon (Knight) Lines (12) [sim.Babylonian: "dragon" (sir); British: title for knight (sir)] and the Avebury Round Table of the Sun.
In summary, Avebury is calibrated by 12 tones, which are induced by solar (Earth's ecliptic through the 12 zodiac houses; 12 months) and galactic (Sun's ecliptic through zodiac; zodiac age = 2160 years; precession of equinoxes) ecliptics.
Cradle of Civilization:
Ante-Diluvial Landing Corridor:
In the land [Sumerian: “home of the righteous ones” (Edin); Akkadian: “plain” (edinu); Biblical: Eden] between the two rivers (Tigris and Euphrates) [Biblical: “abundant” (Pishon) and “which gushes forth” (Gihon)], the landing corridor was laid out like an arrow (45° NW), entering from the headwaters of the Persian Gulf (most abundant source of petroleum; Sumerians had names for the 9 bituminous substances: petroleum, crude oils, native asphalts, rock asphalts, tars, pyrogenic asphalts, mastics, waxes, pitches), and pointing to the twin peaks of Mount Ararat, the Near East’s most conspicuous landmarks. Five cities with specific function were established in five perfect places. The cities on the centerline of the flight corridor are separated at intervals of 6 beru (60km/37 mi.).
Earth Stations (Reflective with Seven Stations of Heaven on Nibiru’s Path):
1) Eridu (Home in Faraway Built): first gold extracting facility at the edge of the Persian Gulf; abode of Ea; third ring from center [1r.Ea/Enki] (An Nasiriyah)
2) Bad-Tibira (Bright Place Where the Ores are Made Final): metallurgical smelting and refining center; second ring from center on flight path [1r.Nannar]
3) Laraak (Seeing the Bright Glow): beacon city to guide landing shuttlecraft; first ring from center on flight path, triangulating with the other paired beacon cities [1r.Ninurta]
4) Sippar (Bird City): landing place; space port; second ring from center on flight path [1r.Utu]
5) Shuruppak (Place of the Utmost Well-Being): medical center; first ring from center on flight path [1r.Ninhursag]
6) Laarsa (Seeing the Red Light): beacon city; second ring from center [1r.Ea/Enlil]
7) Nibiruki (Earth Place of Nibiru): mission control center (duranki); center [1r.Enlil]
8) Lagash: beacon city paired with Laarsa; second ring from center [1r.Ninurta]
First established was Home in Faraway Built (Eridu), which functioned as the first gold extracting facility at the edge of the Persian Gulf, and abode of Enki. The spaceport was built at Bird City (Sippar), which was aligned on center with the flight corridor. Bright Place Where the Ores are Made Final (Bad-Tibira), the smelting and refining center, and Place of the Utmost Well-Being (Shuruppak), the medical center, was laid out on center, from the landing corridor’s entrance. Earth Place of Nibiru (Nibruki) [Akkadian: Crossing Place on Earth (Nippur)], served as the mission control center, located in the exact center of the landing corridor. At Nibiruki was a raised platform, Place of Earth’s Root (Kiur), with antennas, ascending to a secret communication chamber (from Earth to the Igigi), the holy of holies, the Dark, Glowing Chamber (Dirga) [sim.Hebrew: Ark of the Covenant], where vital star charts and orbital data panels, the Tablets of Destinies, were installed, and the Bond of Heaven and Earth (Duranki), a true axis mundi, was maintained. The structure became the prototype for all ziggurats and pyramids (eg.Tower of Babel) to come.
POST-DILUVIAL FLIGHT CORRIDOR: Triangulations of the Divine Grid (see fig.)
The post-Diluvial flight corridor adopted the same principles of triangulation as the antediluvial flight corridor. The masterful yet simple Divine Grid precisely arrayed by the Anunnaki, artfully combined basic geometry with natural landmarks. Mount Ararat is the northern landmark that anchors the flight corridor on center with mission control (Jerusalem) and the spaceport in Tilmun (Sinai). The southern line of the landing corridor connects the twin peaks of Ararat with the twin peaks of St. Katherine (Harsag) and Umm Shumar (Mount Moses), while the upper line of the landing corridor connects through landing platform at Baalbek and the pyramids (artificial twin peaks) of Giza and Heliopolis. Due the flat terrain of Egypt, artificial twin peaks were constructed where the northern line of the flight corridor crossed the 30th parallel (30° N Lat), which delineated a sacred division of air space. The Three Ways delineated the airspace (each spanning 60° Lat) between Enlil in the north (northpole to 30° N Lat), An in the middle over the equator (30° N Lat to 30° S Lat), and Ea in the south (southpole to 30° S Lat). The outer and inner perimeter circles about Mission Control (Jerusalem) designated the equidistant pairs of radial sites which utilized oracle stone installations for communication.
Diluvial Pivot for Focal Point of Central Flight Corridor:
1) Mount Ararat: focal point of central flight corridor
· Highest Mount in Near East
· Post-diluvial landing place
Outer Circle:
2) Giza/Heliopolis (An): Geodesic Beacon
· Outlines flight corridor
· Giza Pyramid, two companion pyramids, and sphinx situated on Baalbek-Ararat line
· Equidistant with Mount St. Katherine to Baalbek and Jerusalem
3) Mount St. Katherine/Mount Umm Shumar: Geodesic Beacon
· Outlines flight corridor
· Highest peaks of Sinai
· Distinctive twin peaks
· Equidistant with Giza Pyramid to Baalbek and Jerusalem
Inner Circle:
4) Baalbek (Cedar Mountain): Landing Place
· Antediluvial platform of immense size
· Equidistant with Mount Sinai to Jerusalem
5) Mount Sinai: Spaceport (see ‘Tilmun’ above)
· Situated in the intersection of central flight path and 30th parallel (gaze of the sphinx)
· Equidistant from Heliopolis and Umm Shumar
· Equidistant with Baalbek to Jerusalem
Center:
6) Jerusalem (Mount Zion): Mission Control
· Crossing point where the Baalbek-Mount St. Katherine line intersects with the flight path’s center line leading to the focal point of Mount Ararat
· The angle drawn from Jerusalem to Heliopolis and Mount Umm Shumar is exactly 45º
The Bible has glorified the divine connections between Jerusalem (Mount Zion), Baalbek (Crest of Zaphon), and Giza (Memphis). According to the Book of Jubilees, there were four Places of the Lord on Earth, which were created as holy places facing each other. Three of them were in the lands of Shem.
1) Garden of Eternity in the Cedar Mountain (Baalbek): the most sacred; dwelling of the Lord
2) Mountain of the East (Mount Ararat): not in the lands of Shem
3) Mount Sinai (Tilmun): center of the Sacred Desert
4) Mount Zion (Jerusalem): center of the Navel of the Earth
The ancient oracle sites of the Cedar Mountain, Mount Sinai, and Mount Zion, are situated at equal angles (11.5º) from the oracle site at Delphi, Greece. Furthermore, the oracle sites of Jerusalem and Siwa to Delphi correlate angularly (45º) with the oracle site arrangement of Mount St. Katherine and Heliopolis to Jerusalem, respectively.
GAZE OF THE SPHINX (30th N parallel): Silk Road
Heliopolis (Giza)
Eridu
Persopolis
Harappa
Lhasa
see also video on Atlantis: http://www.forbiddenknowledgetv.com/videos/atlantis--lemuria/atlantis-the-lost-continent-.html
http://www.forbiddenknowledgetv.com/videos/ancient-civilizations/atlantis---documentary.html
http://www.forbiddenknowledgetv.com/videos/archeology/the-pyramid-code.html
SACRED SITES OF PREHISTORIC ANTIQUITY:
[Archeological and/or ancient religious/spiritual/sacred sites listed by continent, country, and then state/province, alphabetically. The data-list compilations were dependent on the information available/discovered.]
The following list catalogs archeological and/or ancient religious/spiritual/sacred sites, as possible candidates for electro-magnetic technologies via earth grid site position and celestial orientation (vortex site), listed by continent, country, and then state/province/city, alphabetically; nearby rivers, sacred mountain peaks, modern city/town/village location, and associated buildings are also incorporated. The data-list compilations were dependent on the information available/discovered.
Sacred site candidate-types include:
· Megalithic sites (eg.ante-diluvian ziggurats/pyramids, temples, stone circles, standing stones, dolmens, cairns, brochs, rune/picture stones, stone ships, talayots, kurgans, nuraghe, underwater megaliths, petroglyphs, etc.; emphasized sacred site type- see [note 93])
· Painted caves (European Neanderthal/Australian aboriginal)
· Sumerian ziggurats (cradle of civilization)
· Pyramids, mounds and cliff dwellings (eg.kiva)(Africa, Asia, Europe, Americas)
· Phoenician-Greco-Roman stone pantheonic temples (Mediterannean, Europe)
· Hindu-Buddhist temples (eg.mandirs, wats, candis, stupas, grottoes, caves) (Asia)
· Muslim mosques (early Islamic world: Asia, Africa, Europe)
· Judeo-Christian synagogues, churches, cathedrals, monasteries (Holy Land and Europe)
· Fortifications (Celtic-Roman castrum)/medieval castles (Asia, Europe)
· crop circles
[NOTE 86] Most pyramids, monuments, and megaliths were built on earth’s energy grid (aka. “ley lines”), which was known and considered in the ancient world. <it is a scientific fact that> Ley Lines (ie. Chinese geomancy called them “dragon lines”) are straight fault lines in the earth’s tectonic plates, which release powerful electro-magnetic energy <not recognized by science>. Ley Lines generate telluric currents in the land; certain geological topologies will magnify telluric current- where megalithic builders preferred to position their structures-technologies; where ley lines cross (conductivity discontinuities: place where one area of ground which has good electrical conductivity meets another area with lesser capacity for conductivity)- where ancient megalithic sites were established; the pre-dawn hours have heightened telluric wave energy, due to the daily changes in the earth’s geo-magnetic field (strongest in day, weakest at night; pre-dawn is the most dramatic change, or increase in the strength of telluric electro-magnetic energy; weaker field changing to stronger field); Induction physics: wherever there is a changing magnetic field, there is the generation of electric current; megalithic structures were technologies used to concentrate electro-magnetic energy; power-plants
This Vortex Site work in progress, an overwhelming task, intends to compile a data-list of archeological sacred sites of prehistoric antiquity, and superimpose their collective locations over various earth grid networks (which may vary in scope), in order to study their functional, geometrical, and harmonic relationships.
AFRICA:
ALGERIA:
· Carthage (Tunis)
· El Wad/Oued [Arabic: “the river”] (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; oasis town watered by underground river; Guemar)
· Great Mosque of Algiers (1097 CE: Almoravid Islamic; Casbah, Bab el Oued, Algiers)
· Great Mosque of Tlemcen (1082 CE: Almoravid Islamic; Tlemcen)
· Ketchaoua Mosque (1612 CE: Moorish-Byzantine Islamic; Algiers)
· Serquenout (Ideles; Mt.Telerhteba)
BOTSWANA:
· Tsodilo (70000 BCE: first known human ritual; 4500 rock paintings; rock carvings; Kalahari desert; Shakawe)
CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Bouar [MA](3140 BCE: Neolithic: megaliths, cairns, settlements; star stones- Cepheus, Draco)
CHAD:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Agoza [MA](Neolithic; Lake Chad)
EGYPT: [MA: pyramids]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
[NOTE 75] Great Pyramid is the reduced embodiment of the dimensions <scale model> of the Earth (see Giza below): the base measurement (cubit) used in ancient navigation, taking into account the Earth’s wobble and the Precession of the Equinoxes (or Lunar-Solar Precession, or the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth’s equator causing its wobble) reflects in the Great Pyramid of Giza; Plato refered to the Earth as the “sphere within the sphere” (precession of constellations); the rate of precession was measured <in calibrations of 12> with an instrument which resembles a ringed cross; Plato described the Earth as a “12 pathced leather ball”; a zodiac age (2160 years) = 1/12 the Platonic Year (25920 years), or one complete Earth wobble cycle
[NOTE 76] Thoth is the patron deity of weights and measures, and the <measurement of the> moon; Essenes measured the lunar cycle; the moon is the only celestial body with a retrograde rate measurable with the human eye; according to Plato (descriptions within the works, Timaeus and Critias), Atlantis was destroyed 9000 years (or lunar cycles/months) before his time (ie. solar calendar: 10000 BCE; lunar calendar: c. 1500 BCE; perhaps used more widely in ancient world; actual time designation <solar/lunar> could have been lost in the translation of 4 historical renderings coming to Plato); Antikythera mechanism (dated- 1st c.BCE?) was recovered in the Antikythera ship wreck; it is an ancient analog computer (w/bronze gears; 2 concentric scales: Greek solar cycle and Egyptian Lunar-Sothic cycle) designed to calculate astronomical <solar, lunar, planet> positions (Crichton Miller)
[NOTE 79] The invasion of the Sea Peoples (Atlanteans? seemed to come from northern and western Atlantic- Germany, Denmark, Holland), fighting major naval battles against Egypt, during the New Kingdom; who the Sea Peoples were and where they came from is considered a mystery to academia; their naval migrations (through the Straight of Gibraltar) were prompted by rising sea levels (3’/year for 100 years); the Egyptians defeated the Sea Peoples, and consequently settled around Greece, Turkey, and Lebanon; submerged port cities off the coast of Egypt near Alexandria: Heracleon and Menuthias (another son of Poseidon); the sons of Poseidon- Atlas, Menuthias, Gades, etc. were building port cities of their maritime trade empire around the world (from Sidon to Gibraltar and beyond), with the ancient mapping knowledge <of Atlas>
[NOTE 85] 25,000 mi. circle alignment (100km wide) of ancient megalithic sites (pyramids): Peru- Paracas drawing, Nazca track, Ollantaytambo, Machu Picchu, Cusco, Sacsayhuamnan, Paratoari; Africa- Mali- Dogon lands; Algeria- Tassili N’ajjer; Egypt- Siwa oasis, Giza Great Pyramid, Petra; Mesopotamia- Ur, Persepolis; Pakistan- Mohenjo Daro; India- Khajuraho; Burma- Pyay; Thailand- Sukhothai; Cambodia- Angkor Wat, Preah Vihear; Easter Island; alignment: is at an angle of 30° from the equator; similarly, Giza is located on the 30°N Lat parallel, the line defining the Neutrality Zone; eventhough the sites are from different historical periods, most were built upon more ancient sites; the circle is equal in length to the equator; if the line is taken as the equator, then the north pole would be in present day Alaska; distance matching: Giza-Nazca = Giza-Teotihuacan; Angkor Wat-Nazca = Mohenjo Daro-Easter Island; Giza-Easter Island = 10000 x F; (Angkor Wat-Giza) x F = Giza-Nazca; (Giza-Nazca) x F = Nazca-Angkor Wat;
[NOTE 86] Submerged Cities: there are 200+ sunken cities in the Mediterranean alone (Childress); 10,000,000 sq. miles (approx. size of Europe and China) of <costal> land was flooded; and rubbed from the record (Hancock)
[NOTE 87] Atlantis was an urban civilization with large naval forces that conquered other parts of the world; accd to Greek texts, Atlantis was connected with extra-terrestrial beings; founded by Poseidon (Sumerian: Ea/Enki), who built Atlantis to protect his demigod lineage
[NOTE 91] mythological thinking for astronomical reality
[NOTE 92] Band of Peace sites: all on the ancient Nile river bed; all visible from one site to the next; black granite floor tiles at the E part of site; astronomical ritual- Sirius drops below horizon (out of sight) for 70 days, which coincides with the flooding of the Nile; Star-Site correspondences: Orion’s Belt- Giza, Pleiades- Abu Sir, Leo- Heliopolis; sound healing harmonic resonance- site chambers harmonize w/human body cavities; older constructions are built of larger megaliths, while newer constructions are built of smaller megaliths;
[NOTE 93] megalithic temple sites (ie. pyramids, henges, etc.; usually in a series having star correspondence in plan; placed on ground where an unusual type of geology concentrates (magnifies intensity several fold) the regular daily natural electro-magnetic fluctuations that occur everywhere) are typically located on <global> ley lines (and where they cross- conductivity discontinuities: where greater line of current meets a lesser line of current), which conduct telluric waves/current of subtle Earth <electro-magnetic> energy (qi; prana); in Chinese tradition, only the emperor (illegal for commoners) could be buried on a dragon line (aka. ley line); megalithic temple function- power plant; key hours are the pre-dawn hours (ie. 3-5am; hour of Lung-tiger; when the weaker <magnetic> field changes to the stronger field most quickly; induction- changing magnetic fields generate electric current); the energy field fluctuates with the daily changes in the geomagnetic field (strongest during the day, and weakest at night); the orientation of temples changed to match the precessional drift of the stars; alignment to stars indicates the tracking of the seasons (monsoons)- to arrive at a location when the lakes have water; temples are geometrical metaphors for the human body; sacred sites along W shore of the Nile, mark the position of the old Nile, and hence measure the migration of the Nile, about 8 mi. W-E;
· Abu Garab (band of peace; quartz base for largest obelisk once standing in Egypt; laser cut round disc base and holes)
· Abu Haggag Mosque (Islamic; built on 14th c.BCE Egyptian temple; Luxor)
· Abu Rowash [MA] (band of peace; pyramid open to air; top of mountain)
· Abu Simbel [MA](1224 BCE; Egyptian; Kushite; ruins)
· Abu Sir (band of peace; star correspondence- Pleiades; )
· Abydos (Predynastic; cult center of Khentiamentiu, Osiris and Isis; relief depictions- helicopter-like and flying machine objects; Asyut-Luxor)
· Ahmad Ibn Tulun Mosque (884 CE: Abbasid Islamic; Cairo)
· Aksha
· Al-Azhar Mosque (969 CE: Islamic; Cairo)
· Al-Hakim Mosque (928-92 CE: Islamic; Cairo)
· Al-Hussein Mosque (1154 CE: Islamic; Cairo)
· Alexandria acropolis
· Amarna/Akhetaten (1346 BCE: city of Akhetaten; El Minya)
· Amr ibn al-As Mosque (642 CE: Islamic; oldest mosque in Africa; Fustat)
· Aqsunqur/Blue Mosque (1347 CE: Mamluk Islamic; Cairo)
· Armant/Hermonthis (Middle k.: Hatsheput; mortuary temples; Thebes)
· Beni Hassan (21st-17th c.BCE: Old-Middle k.; ancient Egyptian-Hatsheput cemetery; 39 tombs: tombs of Jhety and Baket/Artemis; Asyut-Memphis)
· Bubastis/Tell Basta/Per-Bast/Phibeseth [Bibl.: House of Bastet”] (943 BCE: Shoshenq I; Cairo)
· Buto/Per Wadjet (Paleolithic; 3100 BCE: 305 BCE: Ptolemaic; Alexandria)
· Dashur/Dashour (Old Kingdom: royal necropolis: smooth sided pyramids (sim. Giza)- Snorfu’s Bent Pyramid (white); Red Pyramid- interior: giant crack/fissure, chemical burns; Black Pyramid; band of peace; Cairo)
· Deir el-Madinah (1600 BCE: Thebes)
· Deir el-Bahri (2100 BCE: Old-Middle k.: Hatsheput; mortuary temples; Luxor)
· Dendera (2613 BCE: temple foundations; complex: Temple of Hathor; Roman-Ptolemaic: birth houses; Coptic church of Isis; Hancock: duat model; zodiac-constellation ceiling; relief depictions of light bulb like objects; Qina)
· Edfu/Behdet (Ramses II; 237 BCE; Lato)
· El Ashmunein/Hermopolis/Khmun [Egyptian: “eight town;” Ogdoad “8 deities”](Old-Middle k.: Hatsheput; Al Minya)
· El Dakka (Hyksos-Hatsheput; 3rd c.BCE: Meroitic-Kushite: temple to Thoth; near Kuban)
· El-Mursi Abul-Abbas Mosque (1775 CE: Islamic; Alexandria)
· El-Tabia Mosque (Islamic; Aswan)
· Elephantine/Abu/Yebu (1650 BCE: Hyksos-Hatsheput: temple/abode to Khnum; Ptolemaic; Greco-Roman; Tropic of Cancer)
· El Kab/Nekhab/Nekhen/Hierakonpolis (10000 BCE: Paleolithic; 5500 BCE: Neolithic; 3100 BCE: Early Dyn.temples; 1550 BCE: Hyksos-Hatsheput: rock cut temples, necropolis; 332 BCE: Ptolemaic settlement; Coptic monastery; Wadi Hillal; Luxor)
· Esna (1493 BCE: Thutmose II; Lato)
· Faras (Hyksos-Hatsheput; Meroitic: temple; Nubian border; l.Nasser)
· Gerf Husein (rock-cut temple of Ptah: Ramses II; Lake Nasser)
· Giza/Great Pyramid [MA] (2560 BCE?; 25000-36000 BCE (1.5 precessional cycles ago): and Khafre’s Pyramid Giza; marked ancient prime meridian (indicating ancient world mappers); Earth commensurate measurement: Earth dimensions embodied in the Great Pyramid; factor 43200- circumference of Earth = 21600 nautical miles = 43200 pyramid base perimeter lengths; base side = ½ nautical mile (1 NM = 1.15 mi or 6076.12 ft) or 440 cubits (cubit = 20.632 in.); 440 x 4 = 1760; 1760/half nautical mile = 20.632 in. (Egyptian cubit); perimeter of bases x 43200 = equatorial circumference of Earth; height of Great Pyramid x 43200 = polar radius of earth (distance from earth center to north pole); (John Anthony West; Graham Hancock); half perimeter/height = golden mean (F2); also found in ‘king’s chamber’ (F); elevation found in façade of Strassburg cathedral; pi and phi derive the value of the cubit: p (3.1416) - F2 (2.618) = .5236 (cubit); height of Great Pyramid x 1 billion = approx. distance from earth to the sun; perimeter of pyramid base / 2 x height = p; Hancock: Pyramid of Sneferu; complex connected w/Heliopolis; the pyramid is a model of the sky (stars); the pharaoh represents heaven as the son of Osiris (aka.Orion); 1872: Robert Baval: the celestial river is the milky way galaxy); discovered shaft from Queen’s chamber inclining towards the star Sirius <of Isis, divine mother, wife or Osiris, lord of Duat>; 2 shafts from the King’s chamber target stars: N- Orion’s belt; mirror of heaven; model of Duat; 10500 BCE: three pyramids aligned with the three stars of Orion’s belt- due S; gaze of the sphinx: due E- captures view of sunrise during the spring equinox; rising constellation on E horizon was Leo, in 10500 BCE; band of peace; 2nd pyramid maybe older than the Great pyramid w/older foundation platform; center of largest trans-continental land mass on Earth- Africa, Europe, Asia; inner core made of dolemite limestone-high magnesium content, stronger conductor; outer whiter limestone (closer to pure calcium carbonate)-low magnesium content, therefore a weaker conductor of electricity than dolemite, an insulator; granite lined passage ways and shafts is slightly radioactive, releasing radon gas, and will ionize or electrify the air; transmission stone; limestone aquifers fill with water after rainfall and river flooding (rise and fall of the Nile) causing the generation of an electric current/charge (sim. Eng. mounds and stone circles; Tihuanacu; Abydos); concentration of negative charge from the ground at the peak of pyramid (or mound), and concentration fo positive charge above; if 2 charges become strong enough, brush discharge may be produced- glow effect on pyramid; power plant for Earth during a golden age/sattya yuga;
· Heliopolis/An (3100 BCE; star correspondence- Leo)
· Henen-Nesut/Herakleopolis Magna [Egy.:”House of the Royal Child”](Old-Middle: cult center of Heryshaf-Herakles; Nubian; Coptic)
· Jabal Yu Alliq/Mount Gebal [MA](Neolithic Age; highest peak in N Sinai)
· Karnak [MA](2100 BCE; Hancock: winter solstice axis alignment- “gateway to the heavens”; Big Dipper and Orion alignments (sim. Nabta Playa); architectural Hyksos-Hatsheput; Fibonacci series and Golden Section found in architecture; consecrated to Amun-Ra, the animator of form; ram-sphinxes; horn spirals; 4D-growth architecture; realm of Neter- invisible science; Philae)
· Temple of Kom Ombo (Ptolemaic)
· Kom el Ahmar (Middle k.: Hatsheput; N Edfu)
· Kuban (Hyksos-Hatsheput; near El Dakka)
· Luxor Temple (1400 BCE: Thebes)
· Medinet Habu (Hyksos-Hatsheput; New k.: Ramses III; mortuary temple; Luxor)
· Colossi of Memnon [MA](1400 BCE: Thebes)
· Memphis (3100 BCE: f.Menes k.; 2600 BCE: Old Kingdom capital; Hatsheput; Nubian; Mit Rahina)
· Menkaure’s Pyramid [MA](Giza)
· Miam
· Nabta/Napta Playa [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic: star stones- Taurus, Pleaides, Vernal Equinox; 3 layers of sediment: 1- Aswan calendar stone circle (oldest); 2- “cow stone” megalithic sculpture buried beneath; 3- further beneath, older bedrock sculpture; alignments: summer solstice calendar?; 6270 BCE-Sirius, Arcturus, Alpha Centauri; <Wendorf and Malville; Brophy and Rosen>, 6400-4900 BCE-Orion <Brophy>; Big Dipper (represented by cow leg by later Egyptians); necropolis-human, cattle; could be source of Egyptian civilization; SE Egyptian desert)
· Ninsu (El Faiyum)
· Oxyrhynchus (300 BCE: Greek; El Minya)
· Pi-Ramses/Avaris/Hit-waret [Egy.: “House of the Department”] (1783 BCE: Hyksos trading capital; Nile Delta)
· Pyramid of Amenemhet III [MA] (Hawara)
· Pyramid of Nyuserre Ini [MA](2400 BCE)
· Pompei’s Pillar [MA](293 CE: Alexandria)
· Qasr Ibrim/Primis (Hyksos-Hatsheput; 750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Byzantine; Wadi Halfa)
· Qis (Middle k.: Hyksos-Hatsheput; Al Minya)
· Quseir/Leucus Limen (3000 BCE; Ramses II; Al Qusair; Red Sea)
· Osireion [MA](1294 BCE: Abydos)
· Rameses obelisk [MA](Luxor)
· Rameses IV quarries [MA](Wadi Hammamat)
· Rameses IV tomb [MA](Thebes)
· Ramesseum [MA](1300 BCE: Thebes)
· Sahure’s pyramid [MA](Saqquara)
· Saint Katherine’s Monastery, Mount Sinai (1450 BCE: where Moses saw the burning bush and received the Ten Commandments; 381 CE: monastic life recorded by Egeria; 527-565 CE: monastery; 800 CE: monks discovered remains of St.Katherine; Achtiname document therein stating the monastery’s protection by Muhammad; Fatimid mosque built within walls of monastery; Mount Saint Katherine)
· Saint Mark’s Coptic Orthodox Cathedral (60 CE: founder: St.Mark the Evangelist martyred and buried under church in 68 CE; 311 CE: little chapel on grave of St.Mark; 321 CE: church enlarged; 641 CE: ruined by Arabs; 680 CE: rebuilt; 828 CE: body of St.Mark robbed by Italians, but head remained; 1219 CE: destroyed during crusades; 1547 CE: new church founded; 1819 CE: church rebuilt; 1950 CE: rebuilt; Coptic Orthodox; Alexandria)
· Sais/Zau (pre-Diluvial town: survived; 1100 BCE; 8th c.BCE: 24th d.: Nubian; Alexandria)
· Sakara/Saqqara (4300 BP: Pyramid complex; Step Pyramid of Zoser; Pyramid of Unas: interior- inscribed text, sacred spell-astronomical code?, legacy of lost civilization?; star ceiling; describing journey in the duat, near constellation Orion, image of their god Osiris; symbol for duat: 5 pointed star within a circle; band of peace; sophisticated mechanistic disc discovered by Walter Emory; concave quartz floor; Isis is connected to Sirius, and Osiris to Orion)
· Serabit el Khadim (ancient Egyptian-Hatsheput turqoise mine; Sinai pen.; Wadi Matula)
· Speos Artemidos/Grotto of Artemis (Middle k.: Hyksos-Hatsheput; S Beni Hassan; Al Minya)
· Mount Sinai/Horeb/Musa/Gabal Musa (post-diluvial flight corridor; St.Katherine City)
· Sultan Hassan Mosque (1356 CE: Mamluk Islamic; stones harvested from Giza necropolis; Cairo)
· Tanis/Djanet (1600 BCE; Nile Delta)
· Thebes (capital of New Kingdom-Hatshepshut: necropolis; Luxor)
· Tjeny (Nubian-Merotic; Coptic; Girga)
· Valley of the Kings (1600 BCE: Theban Necropolis; Hancock: Burial place of Seti I; astronomical ceiling- star gods, constellation symbols; made astronomical-afterlife)
ETHIOPIA:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Addis Ababa, Sodda Megaliths [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; Addis Ababa)
· Axum [MA](400 BCE; Adwa mts.)
· Dire Dawa (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
GAMBIA:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Senegambian stone circles [MA](Neolithic; 8th c.CE; stone circles; erected over earlier graves; star stones- Hydra, Virgo; N of Janjanbureh/Georgetown)
LIBYA:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Haua Fteah (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Qusayr [Arabic: “castle”] Ad Daffah [MA](Neolithic; marked ancient border between Egypt and Libya)
· Tobruk [MA](Neolithic; Greek colony: Antipyrgus; Roman: fortress; Al Butnan)
MALI:
[NOTE 94] Many Dogon glyph drawings (cosmological) match meanings with Egyptian heiroglyphs; it seems as though there was a priest class that left ancient Egypt and preserved heiroglyphic usage and meaning in Mali; <Laird Scranton- Sacred Symbols of the Dogon>
· Djinguereber Mosque (1327 CE: Islamic; Timbuktu)
· Great Mosque of Djenne (13th c.CE: Sudano-Sahelian Islamic; Djenne)
· Sidi Yahya Mosque (1440 CE: Islamic; Timbuktu)
· Timbuktu (10th c.CE: Tuareg)
MAURETANIA:
· Chinguetti Mosque (13th c.CE: Islamic; second oldest minaret still in use; Chinguetti)
MOROCCO:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Ifri N’Ammar [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic cave: rock drawings; star stones- Hydra, Ursa Major, Leo, Virgo, Serpens Caput, Lyra, Aquila; Nado, Rif; near Afso)
· Jebel Irhoud
· Lixus (7th c.BCE: Phoenician; megalithic cyclopean ruins are similar to Mayan and Aztec ruins; Larache)
· Koutoubia Mosque (1158 CE: Islamic; Marrakech)
· Mzora/Msoura [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle-167 monoliths surrounding 55m dia. tumulus; megalith star stones- Ophiuchus; 25km S Asilah)
· Mogador/Essaouira (5th c.BCE: Phoenician; Carthaginian navigator Hanno)
· Sidi Abderrhaman (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Tamuda (3rd c.BCE: Mauretanians; Tetouan)
· Volubilis (Neolithic; 3rd c.BCE: Carthaginian; Roman)
NIGER:
· Agadez Mosque (1515 CE: Islamic; Agadez)
SOUTH AFRICA: [Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site (CHWHS)]
· Blombos Cave (80000 BP: ochre engravings, bone tools, shell beads; 140000 BP: fishing; Mosselbay)
· Cango Caves (Oudtshoorn)
· Coopers Cave [CHWHS](1.8m BP; Gauteng)
· Duinefontein (400000 BP: stone tools, animal bones; Cape Town)
· Gladysvale Cave [CHWHS] (1.8m BP; Gauteng)
· Hoedjiespunt (Middle Pleistocene; Saldanha Bay)
· Klasies River Caves (Paleolithic; Mesolithic; Humansdorp)
· Kromdraai [CHWHS] (Gauteng)
· Makapansgat (2.6-3 m BP; Mokopane)
· Mapungubwe (1075 CE: pre-colonial state)
· Motsetsi [CHWHS] (Gauteng)
· Plovers Lake [CHWHS] (Gauteng)
· Saldanha Bay (250-28k BP: tropical-Neanderthal; Capetown)
· Sterkfontein [CHWHS] (Gauteng; Krugersdorp)
· Swartkrans [CHWHS] (Sterkfontein)
· Sibudu Cave (72000 BP; Tongaat)
· Taung
SUDAN:
· Buhen (1860 BCE: 12th d.Senusret III; settlement; fortress; Hyksos-Hatsheput; Egyptian border)
· Jebel Barkal (1450 BCE: Thutmose III; Merowe; swastikas in pottery)
· El Kadada Dolmen (4000 BCE; Shendi; Khartoum)
· El Kurru (750 BCE: royal Kushite tombs; Tangasi)
· Kawa (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; stelas; Dongola)
· Kerma (7500 BCE: Meso-Neolithic; 2500 BCE: Kushite ruins; 3rd cataract of Nile)
· Meroe [MA](Neolithic; 800 BCE: Kushite pyramids; 5-6th cataract of Nile; Khartoum)
· Musawwarat es-Sufra (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Shendi)
· Naga (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Shendi)
· Napata [SM] (1345 BCE: royal Kushite tombs; cult center ruins; Temple of Amun; Egyptian; Jebel Barkel; Karima)
· Nubian pyramids at Meroe (4000-300 BCE: Kushite Kingdoms: royal tombs)
· Nuri (750 BCE: royal kushite tombs)
· Sai (Hyksos-Hatsheput; Kushite; Nubian desert)
· Sanam (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Merowe)
· Seddenga (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Kosha)
· Semna/Amara West (1965 BCE: Senusret I; fortress; Hyksos-Hatsheput; Kushite; Nubian desert)
· Soleb (750 BCE: Egyptian ruins; Kosha)
· Tebu/Pnubs (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Kerma)
· Wad Ban Naqa (750 BCE: Kushite ruins; Pyramid of Amanishakheto; Shendi)
TUNISIA:
[NOTE 67] The central city of Atlantis (destroyed c.10000 BCE? during global <deluge> cataclysm, or 1450 BCE? during the time of Moses and the Exodus), from the descriptions of Plato, is known to have 3 concentric canal rings, with a cross intersecting and canal emerging from the center point; which is symbolized by the ringed cross in Celtic and Christian traditions (sim. symbols: zodiac, sun; 2D symbol represents a 3D vortex experience- a stargate technology?); (William Henry)
[NOTE 68] Atlantis was a global <circum-navigating> civilization distributed all over the world, established on islands and coast lines; most active in the Mediterranean and Atlantic Ocean (outside and inside the Strait of Gibraltar, aka. “Pillars of Hercules”; see also NOTES on s. Spain); the deluge submerged Atlantis and its evidence for existence; an earlier phase of Atlantean prehistory was rooted in Mesopotamia; (Graham Hancock)
[NOTE 69] Atlantean trans-ocean ships (sim. 2500 BCE: Khufu’s ship; Greeks, Phoenicians), were more advanced than clipper ships, with navigator priests who read the stars to guide their path (eg.Atlas’s mapping method); Plato tells about a maritime war between the Atlanteans and the Greeks
[NOTE 74] <East-West> Navigation was possible through the measurement of time, or taking into account the Earth’s wobble, and the Precession of the Equinoxes; the Earth spinning on axis gave the appearance of the zodiac constellations moving along the horizon- the ancient navigator-priests knew the rate of zodiac movement, and hence knew longitudinal distances and designated measuring systems (see Giza, Egypt as an encoding of geometry, earth measurement)
· Carthage [Phoen.: “New City” (Qart-hadast); New Atlantis?] (Sea Peoples?; 1st m. BCE: Phoenician; Roman; Tunis; replica of central city of Atlantis? w/concentric ringed canals)
· Kerkouane (4th-3rd c.BCE: Phoenician; Roman; Kelibia; Cape Bon)
· Mosque of Uqba (670 CE: Islamic; Kairouan)
· Utica (1100 BCE: Phoenician; Roman; Tunis)
ZAMBIA:
· Broken Hill (250-28k BP: tropical-Neanderthal)
ZIMBABWE: (Rhodesia)
· Great Zimbabwe [t.Shona: ”huge stone buildings”] (1200 CE; Masvingo/Ft.Victoria)
ASIA:
ABKHAZIA: (former USSR; approximately 3000 megalithic monuments are known in the western Caucasus w/more constantly being found)
· Gelendzhik [MA](4000-2000 BCE: Neolithic: 3 dolmens in a row on a hill above Zhane r.; near pyramidal dolmen in Mamed Canyon; Black Sea coast; Gelendzhik)
AFGANISTAN:
· Buddhas of Bamyan [SR](507/554 CE: Hazarajat; destroyed)
· Chakhil-i-Ghoundi Stupa (2nd-3rd c.CE: Greco-Buddhist/Hellenistic-Indian; Hadda; Jalalabad)
· Dargah Pir Rattan Nath (5th c.CE: Hindu-Ganesh; Kabul)
· Hadda (2nd-1st c.BCE: Greco-Buddhist artifacts; Jalalabad)
ARMENIA: (p.USSR) (301 CE: world’s first Christian nation)
· Akhtala monastery (8th c.BCE: bronze, clay, iron items; 576 rectangular stone sepulchers; 5th c.: aka.Agarak; 10th c.CE: Bagratunis-Gurgen fortified Armenian Apostolic Church; St. Astvatsatseen/Holy Virgin church; Akhtala, Yerevan)
· Aramus (Kotayk, Armenia)
· Garni Temple (3rd m.BCE: first settlements; 8th c.BCE: Urartian; 3rd c.BCE: summer residence for Armenian Orontid and Artaxiad royalty; 1st c.CE: Roman temple- Tethys, Oceanus, Thetis; last refuge of k.Mithridates; Azat r.; Goght, Yerevan, Kotayk)
· Geghard [“spear” which had wounded Jesus during the Crucifixion]/ Ayrivank [“monastery of the cave”] monastery (f. Saint Gregory the Illuminator; 4th c.CE: monastery complex; 9th c.: d.by Arabs- burned manuscripts; earthquake dmg.; 12th c.: relic- spearhead that wounded Christ on the cross allegedly brought by Apostle Thaddeus; relics of the Apostles Andrew and John; 1215: Armenian; Katoghike tympanum, Gavit, rock-cut church with spring, Jhamatun, tomb, Chapel of S.Grigor; Azat r.; Goght, Yerevan, Kotayk)
· Goshavank [“monastery of Gosh”] (older monastery- Nor Ghetik d.earthquke in 1188; 12-13th c.CE: Armenian; complex- 3 churches: Saint Astvatsatsin, Saint Gregory, Saint Gregory the Illuminator, double chapel, single chapel, gavit, bell tower, book depository, school, gallery; Khachkars; Gosh)
· Haghartsin monastery (13th c.CE: Armenian; complex- 3 churches: Saint Astvatsatsin, Saint Gregory, Saint Stepanos, refectory; Bagratuni sepulcher; Dilijan, Tavush)
· Haghpat monastery (10th c.CE: Armenian; Alaverdi, Lori)
· Harich (2nd c.BCE: fortress town)
· Harichavank/Harich monastery (7th c.CE: Armenian; Harich, Shirak)
· Hovhannavank Karapet/Saint John the Baptist monastery (f.Saint Gregory the Enlightener; 4th c.CE: Saint Karapet; single nave basilica; 1216-21 CE: Gandzasar-Armenian centerpiece; Kasagh r.; Ohanavan, Aragatsotn)
· Kecharis monastery (1003 CE: 1st structure- Saint Grigor church; 11th c.CE: Surb Nshan church; 13th c.CE: Katoghike church; 1220: Surb Harutyun; Armenian; 2 chapels, gavit; Tsarkhadzor)
· Khor Virap monastery (642 CE: orig.church: Saint Gevorg Chapel; 17th c.CE: Saint Astvatsatsin; where Saint Gregory the Illuminator was incarcerated for 13 yrs by the pagans; Mt. Ararat, Lusarat)
· Metsamor [MA](5000 BCE: Neolithic: stone circles; Metsamor; nuclear power plant)
· Noravank monastery (f.1205 CE: Armenian; complex- churches: S.Karapet, S.Grigor, S.Astvatsatsin; Vayots Dzor)
· Sanahin monastery (10th c.CE: Armenian; Alaverdi, Lori)
· Sevanavank monastery (874 CE: Armenian; l.Sevan; Sevan, Gegharkunik)
· Tatev monastery (4th c.CE: 1st chapel; 8th c.CE: Armenian; complex- 895-906: St.Paul and St.Peter church; 836-48: early constr.- rebuilt St.Gregory in 1295; 905: Gazavan- 8m pendulous pillar; 11th c.CE: Astvatsatsin; earthquake in 1931; Tatev, Syunik)
· Zorats Karer [MA](7600-4500 BCE: Neolithic: Karahunj stone circle observatory; temple ded.to Armenian sun-god Ari?; star stones- Cygnus-Deneb; Bronze-Iron Age: necropolis: 223 large stone tombs; 300 BCE-300 CE: Hellenistic-Roman: place of refuge; Sisian, Syunik)
· Zvartnots (Yereven, Armavir)
· Zvartnots Cathedral (642-53 CE: Armenian Apostolic; Echmiatsin, Vagharshapat, Yereven)
AZERBAIJAN:
· Ateshgah of Baku [“Fire Temple”](17th-18th c.CE: Hindu/Zorastrian temple-castle; 1883 CE: abandoned; pentagonal complex; Surakhani; Baku)
· Bibi-Heybat Mosque (1281 CE: Shirvan Islamic; Baku)
· Gandzasar monastery (1216-38 CE: Armenian; relics of Saint Zaechariah; bas-reliefs- crucifixion, adam and eve; Vank, Martakert, Nagorno-Karabakh)
· Gobustan [MA](20000 BCE: rock painting; petroglyphs; btwn.Pirsagat and Sumgait r.; 40 mi. SW Baku)
BAHRAIN:
· Khamis Mosque (692 CE: Islamic; Khamis)
BANGLADESH: [Buddhist/Jain/Hindu temples (mandir), monasteries]
· Chandranath Temple (accd.to Hindu sacred texts, where the arm of Goddess Sati fell; Sitakunda)
· Comilla Jagannath Temple (16th c.CE: Hindu)
· Dhakeshwari Temple (12th c.CE: Hindu; Dhaka)
· Dhamrai Jagannath Rath (19th c.CE: chariot temple; Dhamrai)
· Jagannath Temple/Handial Mandir (1300 CE: Hindu; Pabna)
· Jeshoreshwari Kali Temple (13th c.CE: Hindu; Ishwaripur; Satkhira)
· Kal Bhairab (19th c.CE: Shaivite-Hindu; giant Shivalinga; Medda; Brahmanbaria; Chittagong)
· Kantajew Temple (1702-52 CE: Hindu; terracotta; earthquake dmg; Dinajpur)
· Khan Mohammad Mridha Mosque (1704-5 CE: Islamic; Dhaka)
· Puthia Temple Complex (1815 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Rajshahi)
· Ramna Kali Mandir (1000 BP: Kali-Hindu; 1971 CE: destroyed by Pakistan Army; Dhaka)
· Somapura Mahavihara (810 CE: monastery; Naogaon)
· Taherpur Temple (1480 CE: Hindu; Rajshahi)
BHUTAN: [Buddhist temples, stupa, fortress (dzong)]
· Chagri Dorjeden Monastery (1620 CE)
· Choedrak Monastery (1234 CE; near Tharpaling monastery)
· Chorten Charo Kasho (19th c.CE: stupa; Trongsa)
· Chorten Kora (18th c.CE: stupa; Trashiyangtse; Kulong Chu r.)
· Dungtse Lhakhang (1421/1433 CE: monastery; Paro)
· Gangkhar Puensum [SM] [“Three Mountain Siblings”]
· Gangtey Monastery (1450 CE: Wangdue Phodrang d.)
· Jambay Lhakhang (659 CE: monastery; Bumthang/Jakar)
· Jomolhari/Chomolhari [SM] [aka.”the bride of Kangchenjunga”](Tib.: abode of Jomo protector goddess bound by Guru Padmasambhava; Jomolhari Temple, meditation caves of Milarepa and Gyalwa; Thangthangkha; Jangothang; Jomo Lharang holy lake)
· Kongchogsaum Lhakhang/Tsilung (8th c.CE: central Bhutan)
· Kungzandra (8th c./1488 CE: monastery; Tang valley)
· Kurjey Lhakhang (monastery; Bumthang)
· Kyichu Lhakhang (7th c.CE: Paro)
· Lhuentse Dzong (1543)
· Nalanda Buddhist Institute (1754 CE: Punakha Dzongkhag)
· Simtokha Dzong (1629 CE; Thimphu)
· Taktsang Dzong (1692 CE: Paro)
· Tamshing Lhakhang (1501: Bumthang)
· Tango Monastery (13th c.CE; Thimphu)
· Thowadra Monastery (1238 CE; Tang v.)
· Trongsa Dzong (1543 CE; Trongsa)
· Zugne (7th c.CE; Bumthang)
BURMA/MYANMAR: [1431 CE: Arakanese; Buddh. pagoda = kyaik; stupa = paya]
· Amarapura (1816 CE: Pahtodawgyi Buddh. stupa; 1847 CE: Kyautawgyi Paya Buddh. stupa)
· Ananda Temple (1105 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Andaw Thein (1515; Mrauk U; Rakhine)
· Bandoola Kyaung Monastery
· Bawbawgyi Pagoda (Pyay)
· Bawbawlay Pagoda (Pyay)
· Botataung Pagoda [“1000 military officers”](2500 BP?: Buddh.; Yangon)
· Bupaya Pagoda (2nd or 11th c. CE: Buddh.; Ayeyarwady r.; Bagan)
· Dhammayangyi Temple (1167 CE: largest Buddh.temple in Bagan)
· Dhammayazika Pagoda (1121 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Five Mahn Pagodas (Mingala-Mahn-Aung; Ratna-Mahn-Aung; Sakya-Mahn-Aung; Lawka-Mahn-Aung; Zina-Mahn-Aung)
· Gawdawpalin Temple (1211 CE: Buddh.; 1975 CE: earthquake dmg; Bagan)
· Hpaung Daw U Pagoda (Inle l.; Shan)
· Htilominlo Temple (1105 CE: Buddh.; 1975 earthquake dmg; Bagan)
· Htukkanthein Temple (1571; Mrauk U; Rakhine)
· Koe-thaung Temple (1553; Mrauk U; Rakhine)
· Kuthodaw Pagoda (1857 CE: Theravada Buddh.; 729 kyauksa gu/stone inscription caves w/Tipitaka in Pali; Mandalay)
· Kyaikpun Paya (Bago)
· Kyaiktiyo Pagoda [“pagoda; to carry on the hermit’s head;” aka.“Golden Rock”](Kyaiktiyo m.; Mon)
· Le-myet-hna Temple (1535: Shite-thuang; Mrauk U; Rakhine)
· Mahabodhi Temple (1200s CE: Buddh; modeled after Mahabodhi, Bihar; Bagan)
· Maha Kalyani Paya (Bago)
· Mahamuni Buddha Temple (1785 CE: Buddh.; Mandalay)
· Mahazedi (Bago)
· Manuha Temple (1067 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Mawai-daw Kucku Pagoda (Shan)
· Mingalazedi Pagoda (1284 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Mingun Pagoda
· Nanpaya Temple (Brahma-Hindu; Myinkaba; Bagan)
· Nathlaung Kyaung Temple (1000s CE: Vishnu-Hindu; Bagan)
· Payathonzu Temple [“Group of Three Buddhas”](middle ages: Buddh.; Mahayana-Tantric interior frescoes; Bagan)
· Pindaya Caves (1773 CE: Buddh.; 8000 images of Buddha; Shan)
· Ratana-pon (1612; Mrauk U)
· Sanda Muni Temple
· Shite-thaung Temple (1535; Mrauk U; Rakhine)
· Shri Kali Temple (Hindu; Yangon)
· Shwedagon Pagoda (2500 BP: legend; 6th c.CE: stupa; Yangon)
· Shwegugale Paya (Bago)
· Shwegugyi Temple (1131 CE: Buddh.; stone slabs in Pali; Bagan)
· Shenandaw Monastery (1800s CE: Buddh.; Mandalay)
· Shwemawdaw Paya [aka.”Golden God Temple”](10th c. CE: pagoda; Bago)
· Shwesandaw Pagoda (1057 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Shwesandaw Pagoda (Buddh.; Paya)
· Shwethalyaung Buddha (994 CE: reclining Buddha temple; Bago)
· Shwezigon Pagoda (1102 CE: Buddh.; Nyaung Oo; Bagan)
· Sulamani Temple (1183 CE: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Sule Pagoda (2500 BP: Buddh.stupa; Yangon)
· Tharabha/Sarabha Gate (middle ages: Buddh.; Bagan)
· Thatbyinnyu Temple (mid-1100s CE: Buddh.; adj.Ananda Temple; Bagan)
CAMBODIA: [Angkor; derived from Sanskrit: “city” (nagara); wat/pagoda]
· Angkor Thom (900 CE: Hindu temple complex: Angkor Wat (head of Draco), Bayon (center = galactic hub; heart of Draco), Phimeanakas, Preah Pithu, Preah Palilay, Phnom Bakheng; Preah Khan, Ta Keo, Prasat Kravanh, Prasat Kok Po, Prasat Phnom Rung, Prasat Roluh, Prasat Ak Yom, Prasat Kas Ho, Western Mebon, Prasat Ta Noreay, Prasat Trapeang Ropou, Baphuon, Neak Pean, Ta Som, Eastern Mebon, Pre Rup, Ta Prohm, Banteay Kdei, Sras Srang, Banteay Samre, Khleangs, Terrace of the Elephants, Terrace of the Leper King, Thommanon; irrigation system; Hancock: 5 ‘churning of the milky ocean’ sculpture bridges: 54 asuras and 54 devas = 108 churners x5 bridges = 540; each bridge leads to a portal; Draco star mapping: temple complex layout on site plan matches the Draco constellation orientation from 10500 BCE Siem Reap)
Phnom Bok [SM] (900 CE: Hindu hill temple; Siem Reap)
Phnom Dei [SM] (900 CE: Hindu hill temple; Siem Reap)
Phnom Krom [SM] (9th c.CE: Shiva-Vishnu-Brahma hill temple; Siem Reap)
Phnom Kulen [SM] (Siem Reap)
· Angkor Wat [MA](9th c.CE: Hindu cosmological temple symbolizing Mount Meru; Angkor Thom; Graham Hancock: 2x/annum- on March 21st and September 21st, equinox alignments; scaled to Hindu cycles of time (cycle 1/<age>- 1,728,000 years/1728 cubits; cycle 2-4 <ages> also; relief: ‘churning of the milky ocean’; ocean = whole universe; represents the law of precession of the zodiac constellations based on the Earth’s revolution and wobble; encoded precessional numbers: 72 temples; causeway: 3/4° from due E, representing 54 precessional years; offset gave a 3 day warning before the spring equinox; on equinox the Sun aligns with the central tower; star mirroring- Draco’s heart; temple complex layout on site plan matches the Draco constellation orientation from 10500 BCE- due N; Siem Reap)
[NOTE 90] (HANCOCK): 3 ancient civilizations (in Mexico, Egypt, and Cambodia), from different time periods, share commonalities- pyramidal, god-king, cult of immortality, astronomer-priests, sacred poisonous snake, contain hidden image of heavens (Orion’s belt; Draco); sky maps on the ground
· Bakong (881 CE: Hindu-Shivaite temple; Hariharalaya, Ruluos)
· Baksei Chamkrong [“Bird who Shelters Under Its Wings”](968 CE: Shiva temple; Siem Reap)
· Banteay Prei Nokor (SE Kompong Cham)
· Banteay Samre (Hindu; Angkor)
· Banteay Srei (967 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Angkor)
· Banteay Chhmar (12th c.CE; Thma Puok)
· Baphuon (11th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Angkor Thom)
· Bat Chum (10th c.CE; Srah Srang, Angkor)
· Bayon (1200 CE: Mahayana Buddh.; Hindu-Theravada temple; Angkor Thom; Siem Reap)
· Beng Mealea (12th c.CE: Vishnu temple; E Angkor)
· Chau Say Tevoda (12th c.CE; Thommanon)
· Drukhsh (12th c.CE: Vishnu-Hindu temple; Theravada Buddh.; Siem Reap)
· East Baray (900 CE; near Angkor Thom)
· Kbal Romaas (Neolithic)
· Kbal Spean (11-13th c.CE: 1000 lingas; Kulen hills)
· Koh Ker (928 CE; NE Angkor)
· Koulen
· Krol Ko (12th c.CE: Buddhist temple; Angkor)
· Lolei (9th c.CE: Shivaite; Ruluos)
· Phimeanakas (910 CE: royal marriage rite naga temple; Angkor Thom; Siem Reap)
· Phnom Bakheng [SM](900 CE: 1st Angkor Shiva-Hindu temple; Angkor Thom; Siem Reap)
· Phnom Chisor (11th CE: Hindu; S Phnom Penh)
· Phnom Laang (Paleolithic)
· Prasat Andat (7th c.CE: Hindu; Kampong Svay; Kampong Thom)
· Prasath Kasaouit
· Prasat Kravanh (921 CE: Hindu temple; Angkor Thom; Siem Reap)
· Prasat Kuh Nokor (10th-11th c.CE: Buddhist temple; Baray)
· Prasat Phum Prasat (706 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Kampong Thom)
· Preah Khan (1191 CE: Buddhist temple; Angkor Thom; Siem Reap)
· Preah Ko (879 CE: Shivite; Hariharalaya)
· Preah Vihear (11th-12th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Dangrek m.; Preah Vihear)
· Ruluos [“Temples”] (9th c.CE: temples: Bakong, Lolei, Preah Ko; Hariharalaya)
· Sambor Prei Kuk (7th c.CE; Kompong Thom)
· Spean Thma [ka.“bridge of stone”](Ta Keo; Angkor; between Angkor Thom and Eastern Baray)
· Ta Keo (1000 CE: Shiva-Hindu temple mountain; Angkor Thom)
· Ta Nei (12th c.CE; Angkor)
· Thommanon (12th c.CE: Vishnu-Shiva-Hindu; Siem Reap)
· Tonle Bati (12th c.CE; S Phnom Penh)
· Wat Athvea/Prasat Vat Althea (12th c.CE: Hindu-Buddh.; Angkor)
· Wat Bakan (1200 CE)
· West Baray (713 CE/11th c.CE; W Angkor Thom)
· West Mebon (11th c.CE: Hindu; Angkor)
· Yasodharapura [“Holy/Capital City”] (899-917 CE; Phnom Bakheng)
CHINA: [Taoist and Buddhist temples (si/gong); Tibetan monasteries][SM]
Expansion of Bronze Age sites (2200-256 BCE: Xia-Shang-Zhou d.; near copper and tin ores):
19-16th c.BCE: Shang d.; Yellow r.- Anyang (epicenter), Zhengzhou, Dengfeng, Erlitou, Luoyang, Xia Xian
16-14th c.BCE: Shang d.; Yellow r.- Anyang, Zhengzhou, Erlitou, Luoyang; Yangzi r.- Panlongcheng
15-11th c.BCE: Shang d.; Yellow r.- Anyang, Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Hui Xian, Xun Xian, Lingbao, Yonghe, Shilou, Suide, Baode, Xin Xian, Gaocheng; Huai r.- Jiashan, Funan; Yangzi r.- Changxing, Feixi, Panlongcheng, Chongyang, Changsha, Ningxiang, Liliing, Changning; Qingjiang; Wuming
13-11th c.BCE: Shang d.; High Yinxu, Anyang phase; Yellow r.- Anyang, Zhengzhou, Wen Xian, Luoyang; Huai r.- Tianmen
11-10th c.BCE: Western Zhou d.; Lingyuan, Kezue; Yellow r.-Xingtai, Anyang, Changzhi, Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Lihtong, Chang-an, Jingyang, Fufeng, Qishan, Baoji, Lingtai, Shilou; Yangzi r.- Peng Xian
1000-771 BCE: Western Zhou d.; Yellow r.- Feicheng, Anyang, Luoyang, Fufeng, Meishan, Qishan; Huai r.- Sui Xian, Jingshan
770-476 BCE: Spring and Autumn period of Eastern Zhou d.; Tangshan, Hunyuan/Liyu; Yellow r.- Luoyang, Hui Xian, Feicheng, Xinzheng, Shangcunling/Shan Xian, Houma, Changzhi; Huai r.- Shou Xian; Yangzi r.- Wujin, Yandunshan, Tunxi, Tonglushan, Jingshan, Sui Xian, Jiangling, Hengshan, Gongcheng
475-221 BCE: Warring States period; Eastern Zhou d.; Yellow r.- Pingshan, Hui Xian, Jincun, Luoyang, Shan Xian, Xianyang, Xingping; Yangzi r.- Sui Xian, Jiangling, Changsha, Xiangxiang, Fuling, Chengdu, Shizhaishan, Jiangchuan; Zhaoying
206 BCE-8 CE: Western Han d.; Yellow r.- Mancheng, Luoyang, Wuwei, Anxi, Dunhuang; Yangzi r.- Changsha, Shizhaishan, Jiangchuan
· Ani Tsankhung Nunnery (7th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Badachu [“Eight Great Sites”] (Eight Buddhist temples; Shijingshan, Beijing)
1) Changan Temple (Temple of Eternal Peace)
2) Dabei Temple (Temple of Great Mercy)
3) Dragon Spring Nunnery
4) Lingguang Temple (temple of Divine Light)
5) Pearl Cave (The Cave of Precious Pearl)
6) Sanshan Nunnery (Three-hill Nunnery)
7) Xiangjie Temple (The Temple of the Fragrant World)
8) Zhengguo Temple
· Bailin Temple [“Monastery of the Cypress Grove”](1347 CE: Yuan d. Buddhist temple; Beijing)
· Baimasi [“White Horse Temple”] [SR](Eastern Han d.: 1st Buddhist temple in China?; Luoyang)
· Banpo (4500 BCE: Yangshao)
· Bao’ensi (1440 CE: Buddhist monastery complex; Sichuan)
· Baoguangsi (Tang d.Buddhist temple-pagoda; Chengdu)
· Baoguosi/Lingshan Temple (880 CE: Tang d.Mahayana Buddhist; Jiangbei, Ningbo, Zhejiang)
· Bashidang (5540 BCE: Pengtoushan culture: Lixian, Hunan)
· Beifudi (7-8000 BCE: Cishan-Xinglongwa cultures: pottery masks, carved relief, altars, evidence of burned burials on raised platforms; stone tools, ceramic pots, subterranean cave shelters, sacrificial sites, jade pieces; Yi, Baoding, Hebei)
· Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves [SR](5th c.CE; Turpan-Loulan)
· Bingling Temple cave (420 CE: giant Buddhas; Lanzhou, Gansu)
· Beiyuemiao [“Northern Peak Temple”] (2nd c.BCE: Han; Northern Wei/Tang; Quyang, Heibei)
· Bozikeli Qian Fo Dong/Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves [SR](5th-9th c.CE: 77 rock-cut caves; arched ceilings; Buddhist murals; Turpan-Shanshan; near Gaochang ruins; Mutou valley; Taklamakan desert)
· Buchasergyi Lakang (Nyingchi, Tibet)
· Buchu Sergyi Lhakhang (7th c.CE: Buddh. Monastery; Bayi, Tibet)
· Chang’an/Xian [SR](1 CE: ancient capital)
· Changchun Temple (1592 CE: Ming d. Buddhist temple; Xuanwu, Beijing)
· Cheng’en Temple (Sui d.; 1510 CE: Ming d. Buddhist temple; Beijing)
· Chenghuangmiao [“City God Temple”]/Jinshan God Temple (1403 CE: Ming; Taoist temple; Shanghai)
· Chengling Pagoda (540 CE; Zhengding)
· Chengtoushan (4500 BCE: earliest rice field- Changde, Hunan)
· Chengxu Temple (1086 CE: Song; Taoist temple; Zhouzhuang)
· Chengziya AS (2500 BCE: Longshan settlement; Jinan, Shandong)
· Chokorgyel Monastery (1509 CE: Buddhist; Metoktang v. Tibet)
· Dabeilou (1500 BP: Buddhist-part of Zhantanlin Temple; Jiuhuashan)
· Dafosi (1000+ BP: Buddhist; Xinchang, Zhejiang)
· Dahuisi [“Temple of Great Wisdom”](1513 CE: Ming d.Buddhist temple; Beijing)
· Dajue Temple [“Great Awakening Temple/Temple of Enlightenment”] /Qingshui [“Clear Water Temple”](1068 CE: Liao d.Buddhist temple; 1428 CE: Ming d.rebuilt; Haidian, Beijing)
· Daxiangguosi (555 CE: Buddhist; Kaifeng, Henan)
· Dazhaosi (1579 CE: Buddhist temple; Hohhot; Inner Mongolia)
· Dazhong Temple [“Big Bell Temple”]/Juesheng Temple (1733 CE: Qing d.Buddhist temple; Beijing)
· Dazu Shike/Rock Carvings (7th c.CE: Buddhist-Confucian-Taoist; 75 sites; 50000 statues, 100000 inscription carvings; Dazu, Chongqing, Sichuan; Baodingshan and Beishan)
· Donglinsi [“East Wood Temple”](Tang d.: Pure Land Buddhist monastery; Jiujiang, Jiangxi; Lushan)
· Drepung Monastery [“Rice Heap”](1416 CE: Buddhist; m.Gephel; Lhasa)
· Drigung Monastery (1179 CE; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Dunhuang [“Blazing Beacon”](Han d.: pilgrimage site; Gansu)
· Erligang (Shang d. bronze settlement; Henan)
· Erlitou (Shang d. bronze settlement; Henan)
· Fahai Temple [SR](1439 CE: Ming d.Buddhist temple; Shijingshan, Beijing)
· Famensi (Northern Zhou d. Buddhist temple and pagoda; Fufeng; Xian, Shaanxi)
· Fawangsi (Tang d.: Buddhist temple; 2 pagodas; Dengfeng, Henan; Songshan)
· Fayusi/Stone Temple (1699 CE: Qing d.Buddhist temple; Zhejiang; Putuoshan)
· Fayuan Temple (645 CE: Tang d.Buddhist temple; Ming d.rebuilt; Beijing)
· Five Sacred Mountains of Taoism: [SM]
1) E-Taishan [“Leading Peaceful Mountain”](Paleo-Neolithic; 3000 BP: religious worhip; Shang d.-Qing d.; Qin d.: Daimiao Temple; Dongyue Temple; Zengfu; Yellow r.; Tai’an, Shandong)
2) W-Huashan [“Splendid Mountain”](2nd c.BCE: Taoist temple-Shrine of the Western Peak; immortality herbs- Kou Qianzhi; Chen Tuan revelations; Cloister of the Jade Spring dedicated to Chen Tuan; Quanzhen School; Weinan; Huayin; Yellow r.; Xian, Shaanxi)
3) S-Nan Hengshan/Nan Yue [“Balancing Mountain”](8th c.CE: Buddhist monastery- Zhushengsi; Zhurong Gong; 725 CE: Heaven Governor Huo King Temple/South Heaven Genuine Master Temple/Grand Temple of Mount Heng; Hengyang, Hunan)
4) N-Bei Hengshan [“Permanent Mountain”](Han d.: Beiyue Miao, “Shrine of the Northern Peak”; 491 CE: Xuankongsi/Buddhist Hanging Monastery; Xinzhou-Yuanping; Hongdao-Dingxiang, Shanxi)
5) C-Songshan [“Lofty Mountain”](477 CE: Shaolin Temple- birth of Zen Buddhism, largest collection of stupas in China; Pagoda Forest; 523 CE: Songyue Pagoda; Tang d.: Fawang Temple pagodas; Dengfeng; Yellow r.; Zhengzhou, Henan)
· Foguangsi (857 CE: Tang d.Buddhist temple; East Hall; 1137 CE: Hall of Grand Temple of Mount Heng/Heaven Governor Huo King Temple/South Heaven Genuine Master Temple (725 CE: Buddhist temple; Hengyang, Hunan; Nan Hengshan)
· Forbidden City (1406 CE: Ming d.capital; Beijing)
· Foshan Ancestral Temple (Song d.; 1372 CE: Ming d.: Taoist temple; Foshan, Guandong)
· Four Sacred Buddhist Mountains: [SM]
1) Emeishan [“Delicate Eyebrow Mountain”](1st c.CE: 1st Buddhist temple built in China; Ming-Qing d.: 76 Buddhist monasteries; Baoguosi; Leiyinsi; Qingyinge; grottoes; Yangzi r; Leshan, Sichuan)
2) Jiuhuashan/Lingyangshan [“Nine Glories Mountain”](Temples: 1500 BP: Huacheng; 598 CE: Guoqing; Dabeilou; Baisuigong; Qiyuansi; Roushen; Tianchi; Zhantanlin; Zhiyuan; Yangzi r.; Chizhou, Anhui)
3) Putuoshan [“Potalaka Mountain”](Temples: Puji; Fayu; Shanghai; Zhoushan is., Zhejiang)
4) Wutaishan [“Five Terrace Plateau Mountain”](53 sacred monasteries; Major Temples: Yuan d.: Nanshan <lower 3 terraces-Jile; middle-Shande; upper 3-Youguo; Xiantong; Tayuan; Pusading; Inner Temples: Shouning; Bishan; Puhua; Dailuo Ding; Shuxiang; Guangzong; Yuanzhao; Guanyin Dong; Longquan; Luomuhou; 767 CE: Jinge; Zhenhai; Wanfo-ge; Guanhai; Zhulin; Jifu; Gufo “Old Buddha”; Outer Temples: Jin d.: Yangqing; 782 CE: Nanchan; Tang d.: Mimi; 857 CE: Foguang; 1158 CE: Yanshan; Tang d.: Zunsheng; Jin d.: Guangji; Tang d.: oldest existing wooden buildings; Shanxi)
o Everest Mount [Tibetan: “Saint Mother” (Qomolangma Peak); Chinese: “Earth Mother” (Zhumulangma Feng/Shengmu Feng)](highest mountain on Earth; Rongbuk monastery)
o Huangmeishan (Chan/Zen- East Mountain Teaching; Yangzi r.; Hubei)
o Jizu Mount/Nine Stratta Cliffs (Temples: Shu k.: nunneries; Tang-Ming-Qing d.: Zunsheng Tower, Xitansi, Shizhongsi, Huayansi, Jindingsi, Zhushengsi, Lengyan pagoda, Jiguansi, Dajuesi; Dali, Yunnan)
o Kailash Mount [Skt.:”crystal”] (sacred place of five religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Ayyavazhi, Bon; Manasarowar and Rakshastak Lakes; Tibet)
o Lushan (402 CE: Hui-yuan founded Pure Land Buddhism here; Yangzi r.; Jiangxi)
o Miaofengshan (Grand Canal; near Beijing; Hebei)
o Nan Wutaishan (Yellow r.; Shaanxi)
o Tiantaishan (Zhejiang)
o Wangtan (Zhejiang)
· Ganden Monastery (1409 CE; Lhasa, Tibet): first school of Tibetan medicine (5th Dalai Lama); later a medical school and hospital was built at Chagpori, near Lhasa; sMan-rtsis-khan (r.13th Dalai Lama; where Dr.Yeshi Donden trained) new college of astrology and medicine was built in Lhasa
· Gaochang Ruins [SR](1st c.BCE; Turpan, Xinjiang)
· Guanghuasi (558 CE: Buddhist temple; Fujian)
· Gufosi (Qing d.: Buddhist temple; Wutaishan)
· Guiyuansi (1658 CE: Qing d.Buddhist temple; Wuhan/Hanyang City, Hubei)
· Guoqingsi (598 CE: Sui d.Buddhist temple; Taizhou, Zhejiang; Tiantaishan)
· Manasarovar/Manasa Sovara Lake (Hindu sacred lake; Kailash m.; Chiu Gompa; Tibet)
· Manjusri; Zushi Pagoda; 6th c.CE: Songyue Pagoda; Wutaishan)
· Giant Wild Goose Pagoda [SR](652 CE; Xian)
· Great Mosque of Xian [SR](700 CE: Islamic; Xian, Shaanxi)
· Great White Pyramid [SR](210 BCE: mound, subterraneanean burial chambers, necropolis; stepped-pyramidal mausoleum (open to sky) buried beneath earthen mound, w/E-W passages leading to the emperor Qin Shihuangdi’s tomb; rivers and seas of quicksilver/mercury; connected w/buried terra cotta army; Xian)
· Great White Pagoda/Sarira Stupa of Tayuan Temple (1582: Ming Dynasty; Mt.Wutai)
· Guanghan (Shang d. bronze settlement; Sichuan)
· Guanghuasi (Buddhist temple; Xicheng, Beijing)
· Guangjisi (Jin d.Buddhist temple; Wutaishan; Beijing)
· Guangxiaosi [“Temple of Bright Filial Piety”](206 BCE: Buddhist; Guangzhou)
· Guoqingsi (598 CE: Buddh.; Tiantai m.; Hangzhou, Zhejiang)
· Gyang (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Lhatse, Tibet)
· Hanshansi [“Cold Mountain Temple”](502 CE: Buddhist temple-monastery; Fenqiao, Suzhou)
· Haxiu (4000 BCE)
· Hongluo Temple (Tand d.Buddhist Temple; Beijing)
· Houjiazhuang (Shang d.; large tombs: 72 bronzes in 1004; 460 bronzes, 750 jades, 560 bone objects, 5 pottery obj., stone and ivory sculpture in tomb of Fu Hao; 191 burial pits; 1330 human and animal sacrifices; bone oracles; Xibeigang; Anyang)
· Hua Pagoda (Tang d.; Zhengding)
· Huaisheng Mosque (650 CE: Islamic; Guangzhou)
· Huangpi Panlongcheng (Shang culture bronze settlement; Hubei)
· Huqiusi [“Tiger Hill Temple”](327 CE: Buddhist; Suzhou, Jiangsu)
· Id Kah Mosque [SR](1442 CE: Islamic; Kashgr, Xinjiang)
· Jiahu (7000 BCE: Peiligang culture; Luoyuan, Fujian)
· Jianfusi [SR](684 CE: Tang d.Buddhist temple hosting Small Wild Goose Pagoda; ancient bells; Xian, Shaanxi)
· Jiaohe Ruins [SR](108 BCE: Anterior Jushi capital; Turpan, Xinjiang)
· Jietai Temple (Tang d.Buddhist temple; Mentougou, Beijing)
· Jimingsi (557 CE: Liang d.Buddhist temple; 1387 CE: rebuilt; Nanjing)
· Jing’ansi [“Temple of Peace and Tranquility”](247 CE: Wu k. Buddhist temple; 1216 CE: relocated; Shanghai)
· Jinci Temple/Huiri Yongming Temple (954 CE: Buddhist; Hangzhou, Zhejiang)
· Jingesi [“Golden Pavillion Temple”](767 CE: Buddhist; Shanxi; Wutaishan)
· Jinsha (1000 BCE: Baodun culture; ivory, jade, bronze, gold, stone objects; Chengdu)
· Jiaohe Ruins [SR](108 BCE: Jushi k.; Han d.; Turpan)
· Jietai (Tang d. Buddhist temple; Mentougou, Beijing)
· Jokhang/Tsuklakang (605-650 CE: early geomantic Tib.Buddh. temple; Barkhor Square, Lhasa)
· Jonang (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Phuntsholing, Tibet)
· Kachu (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Chimpu, Tibet)
· Karma Gon Monastery (12th c.CE: Karma Kagyu sect, Tibetan Buddh.; Chamdo)
· Katok Monastery (1159 CE: Tib.Buddh; Nyingma, Tibet)
· Khorzhak Monastery (996 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Burang; Ngari, Tibet)
· Kizil Caves [SR](3rd-8th c.CE: Buddhist frescoes; Baicheng, Xinjiang)
· Kumbum (1427: Palcho Monastery; Gyantse Kumbum; Tibet)
· Kyangbu (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Gyantse, Tibet)
· Lamaling Monastery (7th c.CE: Nyingmapa sect. Tib.Buddh.; Buchu, Burqug, Nyingchi, Tibet)
· Linggusi (515 CE: Liang d. Buddhist temple-pagoda; Nanjing, Jiangsu; Zhongshan)
· Lingxiao Pagoda (762 CE; Zhengding)
· Lingyansi [“Temple of the Understanding Rocks”](357 CE; 11th c.CE: Buddhist; 1056 CE: Pizhi Pagoda; 167 stupa forest; Tai’an, Shandong; Taishan)
· Lingyinsi [“Temple of the Soul’s Retreat”](328 CE: Eastern Jin d. Chan Buddhist temple; monastery; pagoda; Feilai Feng grottoes; Hangzhou, Zhejiang; Wulinshan)
· Liuhe Pagoda (10th c.CE; d.1121 CE; r.1165 CE: Hangzhou, Zhejiang)
· Liurongsi [“Six Banyan Trees Temple”](537 CE: Buddhist temple-pagoda; Guangzhou)
· Longhuasi [“Luster of the Dragon Temple”](242 CE; 977 CE: rebuilt Chan Buddhist temple; pagoda; 500 Lohan; Shanghai)
· Longmen Grottoes [“Dragon’s Gate”](316-907 CE: Cave/Grottoes: Northern Wei d.: Guyang, Middle Binyang, Lotus-flower, Weizi, Huangfugong; Sui d.: South Binyang; Tang d.: Fengxiansi, 10000 Buddha Cave, Hidden Stream Temple, Kanjingsi, Dawanwufo, North Binyang; Luoyang, Henan)
· Longxingsi (1052 CE: Song d. Buddhist monastery; Zhengding, Hebei)
· Louguantai (Taoist temple; where tradition says Laozi composed the daodejing; Ta Yu village; Zhouzhi, Shaanxi; Xian)
· Manasarovar Lake (highest fresh water lake in world; 1200 mi. from Lhasa; Mount Kailash)
· Melikawat ruins [SR](300 BCE; Hotan)
· Menri Monastery [“medicine mountain”](1405 CE: Bön; Tibet)
· Miaoying Temple (Liao-Yuan d. Buddhist temple; Xicheng, Beijing)
· Milarepa’s/Namkading Cave (1052-1135 c.CE: Milarepa; Nyalam, Tibet)
· Mimisi (Tang d. Buddhist; Wutaishan)
· Mindroling Monastery (1676 CE: Nyingma school; Zhanang, Shannan, Tibet)
· Mogao Caves/Grottoes/Caves of the Thousand Buddhas/Dunhuang Caves [SR] (366-1366 CE: Buddhist cave shrines and art; 406-1002 CE: manuscripts; Dunhuang, Gansu)
· Muru/Meru Nyingba Monastery (7th c.CE: Buddh; Barkhor, Lhasa, Tibet)
· Nanchansi (782 CE: Buddhist temple; Xinzhou; Wutaishan)
· Nanhuasi (502 CE: Chan Buddhist monastery; near Caoqi; Shaoguan, Guangdong)
· Nanputuosi (Tang d.: Buddhist temple; Xiamen, Fujian)
· Narthang Monastery (1153 CE: Buddh.; Shigatse, Tibet)
· Nechung Monastery/Sungi Gyelpoi Tsenkar [“the smaller dwelling;” “Demon Fortress of the Oracle King”](8th c.CE: Buddh.; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Niujie Mosque (996 CE; r.1622-1722 CE: Islamic; Beijing)
· Niya/Jingjue [SR](1800 BCE: 100 dwellings, sickles, clubs, urns, human remains)
· Ngor Ewam Choden (1429 CE: Sakyapa Tib.Tantric Buddh.; Shigatse, Tibet)
· Nyethang Drolma Lhakhang (9th c.CE: Atisha Buddh. Monastery; Nyethang, Tibet)
· Palcho/Pelkor Chode Monastery/Shekar Gyantse (1418 CE: Tib. Buddh.; Gyangze, Shigatse, Tibet)
· Palpung Monastery (1727 CE: Tibetan Buddhist monastery; Dege, Sichuan)
· Palyul (1665 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.)
· Potala Palace (637 CE: Tib.Buddh. Songsten Gampo; res. of Dalai Lama; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Pujichansi [“Chan Temple of Universal Salvation”] (916 CE: Chan Buddhist temple; Putuoshan)
· Puningsi (1755 CE: Buddhist temple; Chengde, Hebei)
· Putuo Zongchengsi (1767 CE: Buddhist temple; Chengde, Hebei)
· Qianfoshan [“Thousand Buddha Mountain”](Sui d. carved Buddha relief in hill rock; Xingguochan Temple; Jinan, Shandong)
· Qixiasi (489 CE: Buddhist temple; 1000 Buddha Caves grottoe; Nanjing, Jiangsu)
· Ralung Monastery (1180 CE: Drukpa Tib.Buddh.; Tsang, Gyantse, Tibet)
· Ramoche Temple (7th c.CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Rongbuk Monastery (1902 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.; Everest m.; Dingri, Xigaze, Tibet)
· Sakya Monastery [“pale earth”](1073 CE: Sakyapa Tib.Buddh.; Shigatse, Tibet)
· Salu Monastery (1040 CE: Sakya Tib.Buddhist; Shigatse, Tibet)
· Samding Monastery [“Temple of Soaring Meditation”](13th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Tibet)
· Samye Gompa (775 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Shannan, Tibet)
· Sanga Monastery (1409 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Sanxingdui [“Three Stars Mound”](1200 BCE: Baodun culture; bronze artifacts and mound; Guanghan, Deyang, Sichuan)
· Sera Monastery (1419 CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.; Wangbur m.; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Shalu (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Gyantse, Tibet)
· Shanhuasi (11th c.CE: Buddhist temple; Datong, Shanxi)
· Shaolinsi (477 CE: Buddhist temple-monastery; 791 CE: Pagoda Forest; Dengfeng, Henan; Songshan)
· Shechen Monastery (1695 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.; Derge, Tibet)
· Shelkar [“crystal white”] Chode Monastery (1266 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Tingri, Tibet)
· Shixianggou (Shang d. bronze settlement; Henan)
· Shuanglinsi (6th c.CE: Buddhist temple; Pingyao, Shanxi)
· Simbiling Monastery (Bon-Gelug Tib.Buddh.; Taklakot, above Purang, Ngari, Tibet)
· Simenta [“Four Gates Pagoda”](523 CE: Buddhist pagoda; Shandong)
· Small Wild Goose Pagoda (707 CE; Xian)
· Tanzhe Temple [“Temple of Pool and Zhe Tree”](1700 BP: Jin d.Buddhist; Beijing)
· Tashilhunpo Monastery (1447 CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.; Shigatse, Tibet)
· Temple of Azure Clouds (1331 CE: Yuan d.Buddhist; Haidian, Beijing)
· Temple of the Six Banyan Trees (537 CE: Buddhist; Guangzhou)
· Terracotta Army (246 BCE: Xian)
· Three Pagodas (824 CE; Yunnan)
· Tianningsi (1100 c.CE: Liao d.Buddhist pagoda; Beijing)
· Tomb of King Wen (122 BCE: Guangzhou)
· Tradruk Temple (8th c.CE: early geomantic Tib.Buddh.; Nedong, Shannan, Tibet)
· Tsi Nesar (7th c.CE: early geomantic Tib.Buddh. temple; near Drongtse monastery; Gyantse, Tibet)
· Tsomon Ling (17th c.CE: Tib.Buddh. temple; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Tsozong Gongba Monastery [“Castle in a Lake”](1400 CE: Nyingma/Red Hat Tib.Buddh.; Assam Himalaya; Tibet)
· Tuoshan [“Camel Mountain”](Northern Zhou-Tang d.: 638 Buddhas, 5 main grottoes: Tianhe “Sky River,” Tianqiao “Sky Bridge,” Tianquan “Heavenly Spring,” Wulong Pool, Tiannanmen “Gate of Southern Heaven gate;” Haotian Temple; Qingzhou, Shandong)
· Tsurphu Monastery (1159 CE: Kagyu/Karmapa Tib.Buddh.; Gurum, Lhasa, Tibet)
· Wanfusi (Chan-Zen temple; Huangbo m., Fujian)
· Wanshou Temple (1577 CE: Ming d.Buddhist; Beijing)
· Wofo Temple/Doulu temple (7th c.CE: Buddhist)
· Wolongsi (168 CE: Buddhist; Xian)
· Wulongmiao [“Five Dragons Temple“]/King Guangren’s Temple (833 CE: Tang d.; Taoist temple; contains China’s 2nd oldest wooden building; Ruicheng, Shanxi)
· Wutasi [“Five Pagoda Temple”]/Zhenjuesi [“Temple of the Great Righteous Awakening”](1727 CE: Buddhist; Hohhot, Inner Mongolia)
· Wusutu Zhao Monastery (1606 CE: Buddhist; Hohhot, Inner Mongolia)
· Wuyang (7500-8500 BP: earliest bone oracle incriptions; Henan)
· Xilitu Zhao (1585 CE: Lamaist temple; Hohhot; Inner Mongolia)
· Xiaotun (Shang d.; village; sacrifice burials; source of oracle bones at Yinxu; Anyang)
· Ximingsi (Tang d.Buddhist temple; Xian)
· Xingjiaosi (669 CE: Buddhist temple-pagoda; Xian)
· Xingtai <CC: 500 BCE: 20 patterns match modern crop circles in other countries>(1500 BCE: Shang dyn.; Qinghe co., Hebei)
· Xuankongsi [“Hanging Temple”](1500 BP: Buddhist-Taoist-Confucian hanging monastery; Datong, Shanxi; Hengshan)
· Xuanmiaoguan (276 CE: Western Jin d. Taoist temple; Suzhou)
· Xumi Pagoda (636 CE; Zhengding)
· Yan’an/Yanzhou (military stronghold; pilgrimage site; Shaanxi)
· Yangqingsi (Jin d. Buddhist temple; Wutaishan)
· Yanshansi (1158 CE: Buddhist temple; Wutaishan)
· Yanshi (Shang d. bronze settlement; Henan)
· Yaowangshan Stone Sculptures (Northern Wei d.-Tang d.: 200 stone tablets; 7 grottoes; statues; Yaoxian, Shaanxi)
· Yemar (11th c.CE: Tibetan Buddh.; Gyantse, Tibet)
· Yerpa (7th c.CE: Tib.Buddh. monastery; Lhasa, Tibet)
· Yinxu [“Remains of Yin”] (1400 BCE: Longshan; oracle bones; ancient Shang capital; necropolis?: 185 ceremonial pits, buried 852 human and animal sacrifices, 15 horses, 10 oxen, 18 sheep, 35 dogs, 5 chariots; Anyang)
· Yonghe Temple [“Palace of Peace and Harmony Lama Temple”](1695 CE: Qing d.Buddhist; Beijing)
· Youguosi (Song d. Buddhist monastery- Iron Pagoda; Kaifeng, Henan)
· Yuantongsi (8th c.CE: Buddh.temple; Kunming)
· Yungang Grottoes [SR](460-525 CE: 252 grottoes, 51000 Buddha statues and statuettes; Datong, Shanxi)
· Yunju Temple (616 CE: Buddhist; Fangshan, Beijing)
· Zhenguosi (963 CE: Buddhist temple; Pingyao, Shanxi)
· Zhengzhou (Shang d. bronze settlement; Henan)
· Zhenjue Temple [“Temple of the Great Righteous Awakening”]/Five Pagoda Temple (Ming d. Buddhist; Beijing)
· Zhihuasi [“Temple of Wisdom Attained”](1443 CE: Buddhist; Beijing)
· Zhuhuasi [“Temple of Wisdom Attained”](Ming d.Buddhist; Beijing)
· Zunshengsi/Shanzhugeyuan/Zhenrongchanyuan (Tang d.Buddhist temple; Wutai)
HONG KONG:
· Lei Cheng Uk Han Tomb (25-200 CE: Eastern Han)
· Stone Circles (Neolithic):
o Lo Ah Tsai (Lamma is.)
o Fau Lau (Lantau is.)
· Wong Tei Tung (Palaeolithic; Sham Chung)
GEORGIA: (p.USSR)
· Armazi (100 BCE; Mtskheta)
· Bagrati Cathedral/Gelati Monastery (11th c.CE; d.1692 in explosion by Ottoman troops; Kutaisi, Imereti)
· Dmanisi (600 CE; Kvemo Kartli)
· Jvari monastery (4th c.CE: Saint Nino wooden cross over pagan temple; 586-605 CE: Great Church of Jvari; Mtskheta)
· Kutaisi (2nd m.BCE: capital of k.Colchis; Rioni r.)
· Mtskheta (1000 BCE: capital of k.Iberia: Armaztsikhe acropolis; 1st c.BCE: Roman: Pompey’s bridge; confluence of Aragvi and Kura r.)
· Nokalakevi (1000 BCE; Senaki)
· Samtavro Monastery (4th c.CE: Nunnery of Saint Nino; 11th c.CE: reconstructed; Mtskheta)
· Sioni Cathedral of the Dormition (5th c.CE: initial church; 575-639 CE: new structure; 1112 CE: rebuilt; 1226 CE: Mongol destruction; 13th c.CE: current; 1386 CE: damaged and repaired; 17th c.CE: damaged by Persians; Mtkvari r.; Tbilisi)
· Svetitskhoveli/Living Pillar Cathedral/Cathedral of the Twelve Apostles (1st c.CE: Elias brought Jesus’s robe here?; 4th c.CE: original church of Saint Nino; location chosen at confluence of Mtkvari and Aragvi r.; damaged by Arabs, Persians, earthquakes; 5th c.CE: tomb of King Vakhtang I Gorgasali; 1010-29 CE: Georgian Cross-Dome; Mtskheta)
· Tsalenjikha Cathedral (12-14th c.CE; Byzantine Palaeologan; Tsalenjikha, Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti)
· Vani (800 BCE: gold objects)
INDIA: [Hindu temple (mandir); cave (bilam); Buddhist temple/shrine (stupa)/monastery (vihara; gompa)]
· Aasfi Masjid (1784 CE: Shia Islamic; Lucknow)
· Adichanallur (1800 BCE: 160 clay urns containing human skeletons; Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu)
· Adi Kumbeswarar Temple (700 CE: Shiva-Hindu; festival: Mahamaham; Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Aghoreshwara Temple (Hoysala-Kadamba Shiva-Hindu; Ikkeri; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Ahobilam (Hindu: 108 Vaishnava Divyadesams; 9 temples Nallamala forest; Narasimha Swamyin Cave; Accd. to the Puranic legend, this is where Narasimha blessed Prahlada to kill demon Hiranyakashipa; Kurnool; Nandyal; Andhra Pradesh)
· Aihole (450 CE: Hindu; temples: Lad Khan- Shiva, Huchappayya, Huchimalli, Galaganatha, Durga; Chalukya style; Bagalkot; Karnataka)
· Airavatesvara Temple (12th c.CE: Dravidian-Chola Shiva-Hindu; Darasuram, Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Ajanta Caves (200 BCE; Ajintha, Aurangabad)
· Alampur
· Alathiyur Hanuman Temple (1000 BCE: Hanuman Hindu; Alathiyur; near Tirur; Malappuram; Kerala)
· Alchi Monastery (1000 c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Amararama (Shiva-Hindu; Pancharama Kshetra; Shivalinga; Krishna r.; Guntur; Andra Pradesh)
· Amaravati/Dhanyakataka (500 BCE: Buddh. stupa; Buddha preaches kalachakra; Guntur, Andra Pradesh)
· Amarnath Temple (5000+ BP: Shiva-Hindu: cave temple of Amarnath-Shiva; stalagmite-linga; 1990s-2000 massacres; heavily secured w/military; Srinagar; Himachal Pradesh)
· Ambalappuzha Sri Krishna Temple (790 CE: Hindu; Kerala)
· Ambika Mata Temple (961 CE: Durga-Hindu; inscription; Udaipur, Rajastan)
· Ammachiveedu Muhurthi (1400 CE: Krishna Hindu; Ambalappuzha; Kerala)
· Ammathiruvadi Temple (1000 CE: 108 Durga Hindu; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Ambaji (Ambaji Mata-Shakti-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peetha; Abu m.; Banaskantha; Gujarat)
· Amrutesvara Temple (1196 CE: Hoysala Hindu; vimana, mandapa, kirthimukhas-demon faces; Ramayana sculptures, Mahabharata, Kanada poems by Janna; Chikmaglur; Karnataka)
· Anajaneya Temple Gotluru (400 BP: Hindu; Gotluru; Andra Pradesh)
· Ananta Vasudeva Temple (13th c.CE: Vaishnava-Hindu; Bhubaneswar, Orissa)
· Ananthanatha Basadi (1250 c.CE: Chalukya Jain; Lakshmeshwara; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Annamalaiyar Temple (10 BCE: Kovil Annamalaiyar/Shiva-Unnamalaiyaal/Parvati-Hindu; Annamalai hill; Thiruvannamalai, Tamil Nadu)
· Annamanada Mahadeva Temple (800 CE: Shaivite Hindu; Annamanada; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Annapoorneshwari [“feeding one and all”] Temple (400 BP: Hindu; Horanadu; Chikmaglur; Karnataka)
· Annigeri (1050 CE: Chalukya Hindu; Temples: Amruteshwara- 76 pillars, Banashankari, Gajina Basappa, Hire Hanuman, Puradhireshwar; Annigeri; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Antara Gange [“Ganges from deep”][SM] (Shathashrunga m.; Kolar; Karnataka)
· Arambol Caves (Buddh.; Goa)
· Aranmula Parthasarathy Temple (1000 CE: Krishna Hindu; Mahabharata; Aranmula; Kerala)
· Arasavalli (7th c.CE: Surya-Narayana Swami-Hindu; Srikakulam; Andra Pradesh)
· Arattupuzha Sree Sashta (2000 BCE: Rama Hindu; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Ardhagiri Sri Veeranjaneya Swamy Temple (12th c.CE: Hanuman-Hindu; Aragonda; Andra Pradesh)
· Ashtabujakaram (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesam; legend: Sarabeswaran; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Avantipur
· Avudayar Koil (2nd c.CE: Chola Shiva-Hindu; origin of sacred book of Saivism, Thiruvasakam; Pudukkottai, Tamil Nadu)
· Aurangabad Caves (6-7th c.CE: 12 artificial rock-cut Buddhist shrines; Maharashta)
· Babri Mosque (1528 CE; d.1992 CE: Islamic; built over large Hindu complex; Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh)
· Badami Caves (600 CE: Karnataka)
· Badoli
· Badrinath Temple/Sapta Badri (Jain: 1st Trithankar- Adinath/Rishabdev = Lord Badrinath; 9th c.CE: f.Shankara; Himalayan-north branch for Advaita Vedanta; Badrinarayan-Vishnu-Hindu: Alaknanda r.; Badrinath; 4-Chota/Char Dham; Uttarakhand)
· Baijnath Temple (1000+ BP: Shiva-Hindu; Himachal Pradesh)
· Bakthavatsala Perumal Temple (6th c.CE: Pallavas Bakthavatsala/Vishnu-Hindu; Thirunindravur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Baleshwar Temple (10-12th c.CE; 16th c.CE: Chand d. Baleshwar/Shiva-Hindu; location of Vishnu turtle incarnation, Kurmavtar; Champawat, Uttarakhand)
· Balligavi (birth place of Virashaiva saint Allama Prabhu; 685 CE: Satavahana-Kadamba, Chaturmukha linga-4 faced linga; 7-8th c.CE: Chalukya-Hoysala Hindu: Kedaresvara temple: trikuta vimana; mandapa, Brahma linga, Vishnu statue; legend: capital of Asura king Bali- Balipura [“city of Bali”]; Shikaripura; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Bambleshwari Temple (2200 BP: Shiva-Parvati-Hindu; legend of Raja Veersen puja; Dongargarh; Rajnandgaon; Chhattisgarh)
· Banashankari Temple (7th c.CE/18th c.CE: Banashankari-Parvati-Hindu; near Badami; Cholachagudd; Bagalkot; Karnataka)
· Banashankari Temple (13th c.CE: Chalukya Hindu; Amargol; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Bandora Caves (Buddh.; Goa)
· Banke Bihari Temple (16th c.CE; moved 1864: Krishna-Hindu; Vrindavan, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh)
· Barabar Caves (3rd c.BCE: Buddh.; oldest surviviing rock cut caves of India; Nagarjuni caves; Jehanabad, Bihar)
· Bardan Monastery/Gompa (17th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Padum; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Basgo Monastery/Gompa (1680 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Basco; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Basistha Temple (2nd-1st m.BCE: Shiva-Hindu; Brahmaputra r.; Guwahati; Assam)
· Becharaji Temple (Shakti-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peetha- hands; Bahucharaji; Mehsana; Gujarat)
· Bedse Caves (1st c.BCE: Buddhist vihara; Pune; Maharashtra)
· Beechupally (Hanuman-Anjaneya Swamy-Hindu; Krishna r.; Mahaboob Nagar; Andhra Pradesh)
· Belur
· Bhadrachalam Temple (1674 CE: Rama-Hindu; Andhra Pradesh)
· Bhadrakali Temple (1163 CE: Grand Mother Goddess-Hindu; Bhadrakali l.; 8 major, 12 minor temples; Warangal; Andhra Pradesh)
· Bhairabi Temple (9th c.CE: Durga-Hindu; Brahmaputra r.; Tezpur; Assam)
· Bhavani Temple (12th c.CE: Parvati-Hindu; 52 Shakti Pithas; Tuljapur, Maharashta)
· Bhaja Caves (200 BCE: Buddh. vihara; Karli, near Lonavala; Maharashtra)
· Bharhut (3rd c.BCE: Maurya-Buddhist stupa; Satna, Madhya Pradesh)
· Bhima Devi Temple Complex (8-12th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; 13th-15th c.CE: destruction by Muslim and Mongol invasions; Pinjore; Panchkula; Haryana)
· Bhimakali Temple (Hindu: 52 Shakti Peethas- ear of Sati; Sarahan; Himachal Pradesh)
· Bhirrana (Harappan; Fatehabad)
· Bhitargaon (6th c.CE: Gupta Hindu; Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh)
· Bhoramdeo Temple (7-11th c.CE: Hindu; Kawardha; Chharrisgarh)
· Bhramaramba Mallikarjuna Temple (Shiva-Hindu; one of 12 Jyotirlinga; Srisailam; Andhra Pradesh)
· Bhubaneshwar (2nd c.BCE: Chedi Kalinga temple city; Orissa)
· Bhuleshwar (13th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Kailash; Mahashivatri; Maharashtra)
· Bhumara
· Bhutanatha group (7th-11th c.CE: Bhutanatha-Hindu; Kalyani Chalukya style; Shivalinga, Makara, Yamuna riding a tortoise, Vishnu, Nandi; Badami; Karnataka)
· Bhuteshwar Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Jind; Haryana)
· Bhutia Busty Gompa (1879 CE: Buddh.; Darjeeling)
· Bijjat Maharaj Temple Sarain (7th c.CE: Bijjat Maharaj-Hindu; Sarain; Shimla; Himachal)
· Bijli Mahadev (Shiva-Hindu; shivalinga; lightning temple; Kullu valley; Himachal Pradesh)
· Biraja Temple (13th c.CE: Shiva-Durga-Hindu; Jajpur, Orissa)
· Bishnupur
· Boiyakonda Gangamma Temple (Hindu; pilgrimage; Chittoor; Andhra Pradesh)
· Brahma Temple, Pushkar (14th c.CE: Brahma-Hindu; Pushkar, Rajastan)
· Brahmeswara Temple (9th c.CE: Hindu; Bhubaneswar, Orissa)
· Brihadeeswarar Temple (11th c.CE: Chola Brihadeeswarar/Shiva-Hindu; Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu)
· Chamba
· Chamunda Mata Temple (Chamunda-Shakti-Hindu; Chotila; Gujarat)
· Chamundeshwari Temple (12th c.CE: Hoysala Chamundeshwari/Durga-Hindu; Chamundi hills; Mysore, Karnataka)
· Chandi Devi Temple (8th c.CE: Chandidevi/Shakti-Hindu; Panch Tirth; Siddh Peetha; Haridwar, Uttarakhand)
· Chandi Mandir (Chandi-Hindu; Navratras festivals; Shivalik hills; Chandigarh; Haryana)
· Chandramouleshwara Temple (900 BP: Chalukya Hindu; Unkal Hubli-Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Charbhuja (1444 CE: Vishnu-Hindu; Kumbhalgarh, Rajsamand, Rajasthan)
· Charminar [“Mosque of the Four Minarets”](1591 CE: Islamic; Hyderbad, Andhra Pradesh)
· Chaturbhuja Temple (875 CE: Gurjara Pratihara d.; Vishnu-Hindu; Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh)
· Chaudayyadanapura Mukteshwara temple (11-12th c.CE: Kalyani Chalukya Hindu; 7 Kannada inscriptions; Haveri; Karnataka)
· Chausath Jogini Temple [“64 Joginis Temple”](9th c.CE: Bramh d.Hindu; near Bhubaneshwar, Orissa)
· Cheluvanarayana Swamy Temple (1098 CE: Cheluvanarayana/Tiruanarayana-Hindu; Melkote; Mandya; Karnataka)
· Chemrey Gompa (1664 CE: Tib.Buddh.; 40kmE Leh; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Chennakeshava temple (1117 CE: Hoysala Hindu; Belur; Hassan; Karnataka)
· Chennakeshava Temple (1268 CE: Hoysala Vishnu-Hindu; trikurta vimana; legends: Mahabharata, Ramayana; yalis, makara, hansas; Somanathapura; Mandya; Karnataka)
· Cheraman Juma Masjid (629 CE: Islamic; 2nd oldest mosque in the world; Kodungallur, Kerala)
· Chettikulangara Devi Temple (800 CE: Sree Devi Hindu; Mavelikkara; Kerala)
· Chidambaram Natarajar Temple (400 CE: Pallava-Chola Shiva-Nataraj-Hindu; 5 Pancha Bootha Sthalams- Aether; Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu)
· Chilkur Balaji Temple (1500s CE: Lord Venkateswara-Visa Balaji-Hindu; Osman Sagar l.; Gandipet; Hyderbad; Andhra Pradesh)
· Chintaman Ganesh (Hindu; Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh)
· Chirakkadavu Sree Mahadevar Temple (1000 CE: Shaivite Hindu; Kottayam; Kerala)
· Chitorgarh
· Chudamani Vihara (1006 CE: Buddh. vihara-monastery; 3rd c.BCE: Nagapattinam; Tamil Nadu)
· Dadhimati Mata Temple (4th c.CE: Gupta Laxmi-Dadhimati-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peethas; Nagaur, Rajasthan)
· Daksheswara Mahadev Temple (1810 CE: Shiva-Hindu; legend of Daksha; Kankhal, Haridwawr, Uttarakhand)
· Danteshwari Temple (14th c.CE: Danteshwari-Shakti-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peetha-tooth of Sati fell here; Dantewada; Bastar; Chhattisgarh)
· Da Parbatia (4th c.CE: Hindu; Tezpur; Assam)
· Darasuram
· Deogarh
· Deur Kothar (3rd c.BCE: Maurya king Asoka; Buddhist stupas; Rewa; Madhya Pradesh)
· Devi Jagadambi/Jagadambika Temple (10-12th c.CE: Chandella d. Hindu; -25 temples @Khajuraho; Madhya Pradesh)
· Devi Temple, Kadampuzha (Sree Devi Hindu; Mahabharata; Malappuram; Kerala)
· Dhanop Sheetla Mata Temple (900 CE: Shiva-Parvati-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peeth; Bhilwara, Rajastan)
· Dharmaraya Swamy Temple (12th c.CE: masonry; 16th c.CE: Hindu; Bangalore, Karnataka)
· Dharmasthala (968 CE: Shiva-Hindu-Jain; gold linga; legend of Annappa; Anna Daana [“free food”]- 10000 pilgrims/day; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Dharmrajeshwar (4-5th c.CE: Buddhist-Hindu cave temple; Mandsaur; Madhya Pradesh)
· Dhankar Gompa (12th c.CE: Buddh.temple and monastery; ancient capital of Spiti; Lahul; Himal Pradesh)
· Dholavira (2900 BCE; Harappan civilization; Gujarat)
· Dilwara (11-13th c.CE: Jain temple complex: Vimal Vasahi, Luna Vasahi, Pittalhar, Parshvanatha, Mahavir Swami; Sirohi, Rajastan; Mt. Abu)
· Diskit Gompa (14th c.CE: f.Tsong Khapa; Gelugpa-Yellow Hat Tib.Buddh.; Dosmoche “Festival of the Scapegoat;” Nubra v.; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Doddabasappa Temple (12th c.CE: Chalukya Hindu: 24 pointed vimana; Gadag; Dambal; Karnataka)
· Dodda Ganeshana Gudi/Bull Temple (Nandi-Hindu; Basavanagudi; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Draksharama (800 CE: Shiva-Surya-Hindu; Shiva-linga; Godavari r.; Kakinada; Andhra Pradesh)
· Dubdi Gompa (1701 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.; Yuksom; Sikkim)
· Durga Mandir (1500 CE: Durga-Hindu; Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh)
· Durga Parameshwari Temple (8th c.CE: Durga-Hindu; Mundkur; Udupi; Karnataka)
· Durgiana Temple (Durga-Hindu; Amritsar, Punjab)
· Dwaraka [MA] [GP12] (32000-9000 BP: submerged <70’> sandstone walls, cobblestone streets sea port evidence; Hindu texts- dwelling place of Lord Krishna; King Shalva <from sky; gods = extra-terrestrials?> attacked <with energy weapons?> Krishna on Earth <who responded with thunder arrows>; Krishna eventually departed Earth, and ocean consumed Dwaraka; Sangam <assembly of sages; included extra-terrestrials> literature: 1st two sangams took place at Kumari Kandam <naga kingdom that “sank beneath the waves”>; near Gulf of Khambhat submerged <170’> complex- 2001: Oceanic Institute researchers detect anomolies 7 miles from shore; commisioned to survey pollution, the site scan sonar detected regular structures- network of stone buildings, shrouded in mud and sand, covering 5 sq.mi.; remains of 2 cities situated on ancient rivers; 32000 BP: dozens of wood and pottery artifacts; 9000 BP: covered by ocean; Gulf of Khambhat; Gujarat)
· Dwarakadheesh Temple (400 BCE; 8th c.CE: f.Shankara; western branch for Advaita Vedanta; 16th c.CE: Krishna-Hindu; 4 Char Dham; Mahabarata mention; near Dwaraka- submerged complex; Gujarat)
· Dzongkhul Monastery (10th c.CE: f.Naropa; Kagyu Tib.Buddh.; Zanskar; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Ekambareswarar Temple (600 CE: Ekambareswarar-Shiva-Hindu; 5 Pancha Bootha Sthalams- Earth; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Eklingji (8th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Udaipur, Rajasthan)
· Elephanta Caves (5-8th c.CE: Chalukyan-Hindu; Mahabharata; Pandava; Banasura; Mumbai, Maharashtra)
· Ellora Caves (500 CE: Hindu-Buddh.-Jain; Aurangabad, Maharashtra)
· Enchey Gompa (200 BP: Tib.Buddh.; Gangtok; Sikkim)
· Eravikulangara Temple (400 CE: Shaivite Hindu; Ernakulam; Kerala)
· Eri Katha Ramar (5th c.CE: Pallavas Rama-Hindu; Thirunindravur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Ettumanoor Mahadevar Temple (1542 CE: Shiva Hindu; Kottayam; Kerala)
· Evoor (Sree Krishna Hindu; Alappuzha; Kerala)
· Ezhumanthuruthu Poonkavil Devi Temple (17th c.CE: Devi Hindu; Kottayam; Kerala)
· Gadag (1050-1200 CE: Chalukya Hindu: temples: Trikuteshwara complex- Shiva-Brahma-Surya, Veeranarayana- where Kumara Vyasa composed Mahabharatha; Gadag; Dambal; Karnataka)
· Galageshwara Temple (11th c.CE: Kalyani Chalukya Hindu; shivalinga; Kannada inscription; Ganesha; Galaganatha; Haveri; Karnataka)
· Galtaji (18th c.CE: Surya-Balaji-Hindu; Jaipur, Rajasthan)
· Gandhola Monastery (8th c.CE: f.Padmasambhava; Tib.Buddh.; sacred junction of Chandra and Bhaga r. to form the Chenab r.; Lahaul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Gangaikondacholapuram
· Gavi Gangadhareshwara/Gavipuram Cave Temple (9th c.CE: Shiva-Agni-Hindu; astronomical arch.: Makar Sankranti Day-light shines on cave shivalinga for 1 hr.btwn. Nandi horns; solstice temple at an earlier time; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Gaya (600 BCE: Magadha k.; Hindu/Buddh.: ancient city; Gayasisa/Brahmayoni hill- where Gautama Buddha taught Fire Sutta; Vishnupadh Temple; Bodhgaya; Bihar)
· Gemur Monastery (11th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Kullu; Himachal Pradesh)
· Ghorawadi/Ghorawdeshwar caves (3rd-4th c.CE: 9 Buddh. meditation rooms carved out of a single rock; Pune, Maharashtra)
· Ghum Gompa (1875 CE: Buddh.; Darjeeling)
· Gnana Saraswati Temple (Saraswati-Hindu; Godavari r.; Basar; Andhra Pradesh)
· Godachi (Vijayanagar: Hindu; Ramdurg; Belgaum; Karnataka)
· Gokarnanatheshwara Temple (1908 CE: Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Gomateshwara [MA](1000 CE; Shravanabelagola, Karnataka)
· Gongotri Temple (18th c.CE: Ganga-Hindu; 4-Chota Char Dham; near source of Ganges r.- Bhagirathi r.; Rishikesh; Uttarakhand)
· Gop
· Gopinath Mandir (12th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Gopeshwar, Chamoli, Uttarakhand)
· Gorakhnath Math (11th c.CE: Yogi Gorakshanath-Hindu shrine; Gorakhpur, Uttar Oradesh)
· Gozzangwa Monastery (10th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Khardong; Lahul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Grishneshwar (1000 CE: r.16th c.CE: 12 Jyotilinga; Shiva-Hindu; Aurangabad, Maharashtra)
· Gwalior
· Guptakashi (Shiva-Hindu; legend: Pandavas, Mahabharata; Garhwal, Uttarakhand)
· Guru Ghantal Monastery (11th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Tupchiling; Himachal Pradesh)
· Guruvayur Temple (1000 CE: Krishna Hindu; 4000 BCE: deity; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Halasi (980 CE: 2nd Kadamba capital; Vaishnavism-Shaivism-Hindu-Jain; temples: Bhuvaraha Narasimha, Suvameshwara, Kapileshwar, Hatekeshwara, Kalmeshwara, Gokameshwara; 11th c.CE: Jain temple; Belgaum; Karnataka)
· Halasuru Someshwara Temple (12-13th c.CE: Someshwara-Shiva-Hindu; 16th c.CE: Hoysala-Chola-Vijayanagara styles added; Halasuru; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Halebid
· Hampi (Mahabharata legend: Kishkindha and Vanara-monkey kingdoms; 1 CE; 1336-1565 CE: Vijayanagara ruins; naga temples: Virupaksha; elephant stables; stone chariot at Vittala complex, Stepped Tank near Underground Temple, Bukka Aqueduct near Anegondi; Anjeyanadri hill; Bellary; Karnataka)
· Hangal Tarakeshwara (12th c.CE: Kalyani Chalukya Shiva-Hindu-Jain; dome; shivalinga; Veerabhadra temple; Billeshwara temple; Hangal; Haveri; Karnataka)
· Hanle Gompa (17th c.CE: Drugpa-Kagyu “Red Hat” Tib.Buddh.; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Hanuman Temple (1724 CE: Bala-Hanuman-Hindu; 5-Mahabharata Delhi; Connaught Place, New Delhi)
· Hariharashwara Temple (1223-4 CE: Hoysala Vishnu-Shiva-Hindu; mantapa, vimana, Kannada inscriptions, hero stones; legend: Guhasura vs. Harihara; Harihar; Davanagere; Karnataka)
· Hari Parbat (1590 CE: Muslim fort; Sharika Temple; Makhdoom Sahib; accd.to legend, this hill was once a large lake inhabited by the demon Jalobhava, then Parvati dropped a pebble, becoming the hill, to crush the demon; Srinagar; Himachal Pradesh)
· Hatimura Temple (1667 CE: Durga-Hindu; human sacrifice; Brahmaputra r.; Silghat; Nagaon; Assam)
· Hemis Gopma (1672 CE: f.Sengge Namgyal; Drukpa Tib.Buddh.; Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Hidimba Devi Temple (1553 CE: Hidimbi Devi-Hindu; Mahabharata; cave temple; Manali; Himachal Pradesh)
· Hooli Panchalingeshwara temple (Hindu; temples: Andhakeshwara, Bhavnisankhara, Kalmeshwara, Kashi Vishwanatha, Madaneshwara, Suryanarayana, Tarkeshwara, Beerdevar; Belgaum; Karnataka)
· Hoysaleswara Temple (1121 CE: Hoysala Shiva-Hindu; sculptures: Shiva-Parvati, dancing Ganesha, Garuda pillar; Halebidu; Hassan; Karnataka)
· Hridayaleeswarar Temple (6th c.CE: Hridayaleeswarar/Shiva-Hindu; Thirunindravur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Hulimavu Cave Temple (15th c.CE: Hindu; shivalinga; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Hundur Gompa (Tib.Buddh.; Nubra v.; Ladakh; Himachal Pradesh)
· Idagunji Devasthana (1500 BP: Vaisnava-Krishna-Hindu; Lord Ganesha temple; Manki; Uttara Kannada; Karnataka)
· Ishvara Temple (1220 CE: Hoysala Shiva-Hindu; hero stone; Kannada inscription; Arasikere; Hassan; Karnataka)
· Itagi Bhimambika temple (1000 CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu; Gadag; Gajendragad; Karnataka)
· Jagannath [“Lord of the Universe”] Temple (11th c.CE: Jaganath-Krishna-Vishnu-Hindu; 4 Char Dham; Rath Yatra festival; Puri; Orissa)
· Jagannath Temple (1691 CE: Vishnu-Hindu; 1990: collapsed; 1992: restored; Ranchi; Jharkhand)
· Jagannatha Gattu Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Shivalinga; Kurnool; Andhra Pradesh)
· Jagdish Temple (1651 CE: Aryan-Hindu; Udaipur, Rajasthan)
· Jageshwar (9-13th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; temple city of 124 stone temples; Jageshwar, Almora, Uttarakhand)
· Jag Mandir/Lake Garden Palace (1515-1652 CE: water palace; Lake Pichola; Udaipur, Rajasthan)
· Jakhoo (Hanuman-Hindu; Ramayana; Shimla; Himachal Pradesh)
· Jama Masjid (1617-56 CE: Islamic; Delhi)
· Jama Masjid (1400 CE: Islamic; Jaunpur)
· Janardanaswamy Temple (2000 BP: Vishnu-Hindu; Varkala; Thiruvananthapuram; Kerala)
· Jarai-ka-Math (860 CE: Pratiharas Durga-Hindu; Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh)
· Jayanti Devi Temple (Jayanti Devi-Hindu; Jind; Haryana)
· Jaugada fort (300 BCE; Bhubaneshwar)
· Jogeshwari Caves (520-550 CE: Buddh. cave temple; Maharashtra)
· Jyotisar [“core meaning of light”] (banyan-vat where Krishna preached Bhagavad Gita; Kurukshetra/Dharmakshetra; Haryana)
· Kadalayi (5000 BP: Vishnu-Hindu; Chirakkal; Kannurl; Kerala)
· Kadri Manjunath Temple (968 CE: Lokeshwara-Shiva-Hindu; bronze statue; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Kailasnatha Temple (8th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Kailasanathar Temple (8th c.CE: Kailasanathar-Shiva-Hindu; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Kailash/Kailasanatha Temple (8th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; rock cut temple; linga; Ellora caves; Maharashtra)
· Kalahasti Nathar (5 Pancha Bootha Sthalams- Wind;)
· Kalakaleshwara temple (Shiva-Hindu; Gajendragad; Gadag; Karnataka)
· Kalasa (Shiva Hindu; legend: Skanda Purana- myth of Sage Agasthya and marriage of Shiva-Parvati; Bhadra r.; Chikmaglur; Karnataka)
· Kalghatgi (Hindu-Jain; Temples: Mahalakshmi, Shantinatha Basadi Jain, Tamboor Basavanna; Kalghatgi; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Kalighat Kali Temple (Kali-Hindu; 52-Shakti Peethas; Hooghly r., Adi Ganga r.; Calcutta, West Bengal)
· Kalika/Maha Kali Temple (300 BP: Kali-Hindu; legend: Kalika Mata came into dream of Pandit Jagat Ram Sharma revealing Pindi stone within hill; Reasi; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Kalika Mata Temple (Bhadrakali-Kali-Hindu; Chittorgarh, Rajasthan)
· Kalikambal Temple (relocated 1640 CE: Kalikambal-Hindu; Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Kalka Mandir (3000 BP; 3rd c.BCE: Ashoka Kali-Hindu; 5-Mahabharata Delhi; New Delhi)
· Kalpeshwar (Shiva-Hindu; 5-Panch Kedar; legend: Pandava, Mahabharata; Garhwal, Uttarakhand)
· Kamakhya Temple (1565 CE: Kamakhya-Hindu; human sacrifice; Nilachal hill; Guwahati; Assam)
· Kamakshi Amman Temple (6 CE: Pallava kings; Kamakshi-Parvati-Hindu; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Kamala Narayana Temple (12th c.CE: Hindu; Kadamba style: Degaon; Kittur; Belgaum, Karnataka)
· Kambagiri Swami (Vishnu-Hindu; Kurnool; Racherla; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kanaka Durga Temple (Durga-Hindu; Krishna r.; Vijayawada; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kanakagiri (Mauryan capital; Gangavati; Koppal; Karnataka)
· Kandariya Mahadeva Temple (1000 BCE?; 1050 c.CE: Chandela Mahadeva-Shiva-Hindu; largest temple @Khajuraho; Madhya Pradesh)
· Kangra
· Kanheri Caves [SR](3rd c.BCE: Maurya Empire; Mumbai)
· Kanipakam Vinayaka/Sri Varasidi Vinayaka Swamy Temple (11th c.CE: Chola Ganesha-Hindu; Kanipakam; Chittoor; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kapaleeshwarar Temple (7 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Mylapore, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Kapila Theertham (11th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Kapila Maharishi cave; near Tirupati-Tirumala; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kapilash Temple (1246 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Dhenkanal, Orissa)
· Kappil Bhagavathy Temple (1000 BP: Shaivite-Hindu; Kappil; Kerala)
· Kardang Monastery (12th c.CE: Drukpa Tib.Buddh.; Lahul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Karkala Sri Venkataramana Temple (14th c.CE: Venkateshwara-Hindu; Karkala; Karnataka)
· Karla Caves (2nd c.BCE-2nd c.CE: Buddhist rock-cut vihara-stupa; Karli; Maharashtra)
· Karmanghat Hanuman Temple (11th c.CE: Hanuman-Hindu; Karmanghat; Hyderbad; Andhra Pradesh)
· Karni Mata (15th c.CE: Durga-Hindu; Deshnoke, Rajasthan)
· Karpaka Vinayakar Temple/Pillaiyarpatti (4th c.CE: Karpaka Vinayakar-Ganesha-Hindu; rock-cut cave shrine; Madurai, Thiruppatthur, Tamil Nadu)
· Karppillikkavu Sree Mahadeva Temple (2000 BCE?: 108 siva kshethras; Shaivite-Hindu; Ernakulam; Kerala)
· Kartikeya Temple (5th c.BCE: Kartikeya/Kumara/Skanda-Hindu; Skanda Purana; Peshawar; Kurukshetra; Haryana)
· Kashi Vishwanath Temple/Golden Temple (11th c.CE; r.1780 CE: Vishwanath/Shiva-Hindu; Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh)
· Kasivisvesvara Temple Gadag (1087 CE: Chalukya Hindu; Kannada inscriptions; Gadag; Lakkundi; Karnataka)
· Kaviyoor Mahadevar Temple (10th c.CE: Shiva-Vishnu Hindu; Kaviyoor; Kerala)
· Kayavarohan [“body descent”] Temple (2nd c.CE: Lakulisha-Shiva-Hindu; Shivalingas; accd. Shiva Purana: 68 pilgrimage-tirtha of Shiva; Shivratri festival; Vadodara; Gujarat)
· Kedareswar Temple (Hanuman-Shiva-Hindu; 8 Astasambhu; near Ramachandi; Dhenkanal, Orissa)
· Kedarnath Mandir (Kedarnath-Shiva-Hindu; 4-Chota Char Dham; 5-Panch Kedar; accd.to Puranas, where Pandava brothers performed penance to Shiva; lingum; Garhwal Himalayan range; Mandakini r.; Kedarnath; Uttarakhand)
· Kesaria (where Gautama Buddha preached Kesaputtiya Suttas; 200 CE: stupa; Bihar)
· Keshava temple (1268 CE: Hoysala Hindu; Somnathpur; Mysore; Karnataka)
· Kesava Deo Temple (2500 BCE?; 400 CE; d.1017 CE; r.1150 CE: Krishna-Hindu; Mathura, Uttar Pradesh)
· Ketakeshwar Dewal (Hindu; one of the largest shivalinga; Tezpur; Assam)
· Key Monastery (11th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Khajuraho [MA](950 BCE; Madhya Pradesh)
· Kharligarh ancient fort (300 BCE; Bhuampada)
· Kheer Bhawani (Bhawani-Maharagya Devi-Hindu; linga; legend: Hanuman retrieved linga from Sri Lanka-Ravana and brought here; Tula Mula; Srinigar; Kashmir)
· Khrew (Jawala Bhagvati-Hindu; Pulwama; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Kiradu
· Kodandarama Temple (14th c.CE: Kodandarama/Rama-Hindu; Hiremagalur, Karnataka)
· Konark/Konarak Sun Temple [MA](1250 CE; Orissa)
· Kondagattu (300 BP?: Anjaneya Swamy-Hanuman-Hindu; Karimnagar; Andhra Pradesh)
· Koodakmanikyam Temple (854 CE: Ramayana-Hindu; Irinjalakuda; Trissur; Kerla)
· Koodal Azhagar Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 devyadesams; Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Kopineshwar Mandir (810-1240 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Nandi; linga; Thane, Maharashtra)
· Korzok Gompa (17th c.CE: Drukpa Tib.Buddh.; Leh; Ladakh; Himachal Pradesh)
· Kosambi (5th c.BCE: Muaryan city; Gautama Buddha holy site; Uttar Pradesh)
· Kottarakkara Sree Mahaganapathi Kshethram (Ganapati-Siva-Hindu; Kottarakkara; Kerala)
· Koti Lingala (Shiva-Hindu; lingas; Godavari r.; Karimnagar; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kotilingam (15th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; 12 rows x 85 lingams; Panchadharala; Visakhapatnam; Andhra Pradesh)
· Koulutla Chenna Kesava Temple (11th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Kurnool; Andhra Pradesh)
· Krauncha Giri (15th c.CE: Chalukya Hindu; 1st abode of Subramanya/Murugan; Kumaraswami temple; legends: Mahabharata, Skanda Purana, Agastya, Parasuram; Bellary; Karnataka)
· Kshreerarama (Shiva-Hindu; Shivalinga-Vishnu; Pancharama Kshetras; Palakollu; W.Godavari; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kudalasangama (12th c.CE: Lingayat-Hindu; temples: Sangamanatha, Aikya linga of Basaveshwara, Sabha Bhavana; Chalukya style; Bagalkot; Karnataka)
· Kudargarh (17th c.CE: Maa-Hindu; Surguja; Chhattisgarh)
· Kudroli Bhagavathi (800 BP: Hindu; festivals: Nadavali, Bharani; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Kukke Subramanya Temple (968 CE: Subramanya-Hindu; Garuda pillar; idols: Shesha, Vasuki; Sarpa Samskara/Sarpa Dosha; Kumaradhara r.; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Kuknur (8-13th c.CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu: Navalinga temple; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Kumararama (892-922 CE: Kumara-Murugan-Shiva-Hindu; Shivalinga; Pancharama Kshetras; Samarlakota; E.Godavari; Andhra Pradesh)
· Kumara Swami Devasthana (Kumara Swami/Subrahmanya/Parabrahman-Hindu; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Kungri Monastery (1330 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.; Lahul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Kursha Gompa (1000 c.CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.; Doda r.; Zanskar; Ladakh; Himachal Pradesh)
· Kurudumale temple (Chola Hindu; Kolar; Karnataka)
· Kushinagar (ancient city where Siddartha Gautama Buddha died; 3rd c.BCE-5th c.CE: ruined Buddh.stupas and viharas; Uttar Pradesh)
· Kuttankulangara Sri Krishna Temple (300 BP: Hindu; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Kuttumuck Siva Temple (300 BP: Hindu; Kerala)
· Lakkundi (10th c.CE: Kalyani-Chalukya Shiva-Hindu: 50 temples: Kasivisvesvara, Halagunda Basavanna, Laxminarayana, Mallikarjuna, Nadayadeva, Nagaradeva, Neelakanteshwara, Suryanarayana, Someshwara, Virabhadara, Vishwantha, Virupaksha; 11th c.CE: Jain temples: Brahma Jinalaya Basadi, Kaishivishanatha, Nanneshwara, Stepped wells; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Lakshmi Devi Temple (1114 CE: Hoysala Shiva-Hindu; Doddagaddavalli; Hassan; Karnataka)
· Lakshmi Narasimha Temple (13th c.CE: Hoysala Vishnu-Hindu; Bhadravathi; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Lakshmi Narasimha Temple (1246 CE: Hoysala Shiva-Hindu; Sadashiva temple; Nuggehalli; Hassan; Karnataka)
· Lakshminarayana Temple (1250 CE: Hoysala Vaisnava-Hindu; trikurta vimana; makara and hansa friezes; Hindu epics, Mahabharata, Ramayana, Puranas/Myths, Mandya; Karnataka)
· Lamayuru Gompa (11th c.CE: oldest Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Kargil; Himachal Pradesh)
· Lankeshwar Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Guwahati; Assam)
· Latiyal Mata Temple (1500 CE: Hindu; Phalodi; Jodhpur, Rajasthan)
· Laxminarayan Temple/Birla Mandir (1622 CE: Laxmi-Vishnu-Hindu; Janmashtami and Diwali festivals; New Delhi)
· Lenyadri, Shri Girijatmaj (1st c.CE: Ganesha-Girijatmaja-Hindu; cave temple; festival: Jayanti; Pune, Maharashtra)
· Lepakshi (Shiva-Vishnu-Virabhadra-Hindu; Kurma Saila-tortoise shaped hill; Lepakshi; Anantapur; Andhra Pradesh)
· Lhalung/Sarkhang [“Golden Temple”] Monastery (10th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.; Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Likir Gompa (1065 CE: Gelugpa Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Indus r.; Saspol; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Lingaraj Temple (11th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Bhubaneswar, Orissa)
· Lokanarkavu Temple (1500 BP: Durga-Hindu; Memunda; Vatakara; Kerala)
· Lothal (2400 BCE: Dholka, India)
· Maa Taratarini Temple (Mahabharata; Hindu; 4 major 52 Shakti Peetha; Taratarini hill; Berhampur/Brahmapur, Orissa)
· Madai Vadukunda Shiva Temple (5-8th c.CE: Kolathiri Kings; Shiva-Hindu; Madai; Kannur Taluk; Kerala)
· Madhyamaheshwar (Shiva-Hindu; 5-Panch Kedar; legend: Pandava, Mahabharata; Mansuna, Garhwal, Uttarakhand)
· Madurai (500 BCE: Hindu temple town)
· Mahabaleshwar Temple (Dravidian Shiva-Hindu; festival: Shivaratri Rathyatra; Gokarna, Karnataka)
· Mahabalipuram
· Mahabhairav Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Tezpur; Assam)
· Mahabodhi Temple (250 BCE: where Siddhartha Gautama Buddha attained enlightenment; Bodhgaya)
· Mahadev Temple (1112 CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu; based on Amruteshwara temple at Annigeri; Itagi; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Mahadev Temple Tambdi Surla (12th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; garbhagriha, antarala, nandi mandapa, Trimurti carvings; Goa)
· Mahadeva Temple, Kalanjoor (1100 BP: Shiva-Hindu; Kalanjoor; Kerala)
· Maha Ganapathi Mahammaya Temple (500 BP: Ganesha-Hindu; Lord Ganesha temple; Shirali; Uttara Kannada; Karnataka)
· Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga (12 Jyotirlinga; Shiva-Hindu; Nandi; Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh)
· Mahakali Caves (1st c.BCE-6th c.CE: Buddh. vihara-chaitya, monastery; Mumbai)
· Mahakuta (6th c.CE: Shaivite-Hindu; Mahakuta Pillar script; Dravidian, Vesara, Nagara temples: Mallikarjuna, Sangamesvara, Vishnu; Bagalkot; Karnataka)
· Mahalakshmi Temple, Kolhapur (700 CE: Kannada Chalukya Lakshmi-Vishnu-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peetha; Kolhapur, Maharashtra)
· Mahamaya Dham (Sati-Hindu: 52 Shakti Peetha; Bilasipara; Assam)
· Mahamaya Kalika Devasthan Kansarpal (12th c.CE: Kali-Hindu; Goa)
· Mahanandiswara Swamy Temple (1500 BP: Shiva-Hindu; fresh water pools: Kalyani, Pushkami; 9 Nandi shrines; Nallamala Hills; Kurnool; Andhra Pradesh)
· Mahasu Devta Temple (9th c.CE: Huna Mahasudevta-Hindu; Hanol, Dehradun, Uttarakhand)
· Mahavinayak Temple (12th c.CE: Ganesha-Hindu; 5 Kshetras; sculpture; Jajpur, Orissa)
· Mandher Devi Temple (1600 CE: Hindu; Mandhradevi; Satara; Maharashtra)
· Mangaladevi Temple (9th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Mangla Gauri (15th c.CE: Vaishnavite-Hindu; mentioined in Purana legends and tantric works; Gaya; Bihar)
· Mangueshi Temple (1600 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Mangeshim; Goa)
· Manikaran (17th c.CE: Hindu-Sikh; Ramachandra, Shiva, Rama-Krishna-Vishnu temples; legend: Manu recreated human life here after deluge; hot springs; experimental geothermal energy plant here; 1905: earthquake; Beas and Parvati r.; Kullu; Himachal Pradesh)
· Mankiala stupa (Rawalpindi); Sialkot (2500 BCE)
· Mansa Devi Temple (Mansa/Shakti-Hindu; Panch Tirth, 5 Pilgrimages; Siddh Peetha; festival: Navratri; Haridwar, Uttarakhand)
· Manyamkonda (Venkateshwara-Hindu: hill shrine; Mahabubnagar)
· Markandeshwar (3rd m.BCE: original temple, pre-Mahabaharata; Shiva-Hindu; Kurukshetra; Haryana)
· Martand
· Marudamalai (800 CE: Murugan-Hindu; 6-Arupadaiveedu; Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu)
· Marundeeswarar Temple (7th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Thiruvanmiyur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Mashro Gompa 16th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Indus r.; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Masrur
· Mata Mansa Devi (1811-15 CE: Shakti-Hindu; Navratri festival; Panchkula; Haryana)
· Matho Gampo (16th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar m.; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Mathura (1600 BCE?- legend: birth place of Krishna; 6th c.BCE: ancient capital; Uttar Pradesh)
· Maya Devi Temple (11th c.CE: Mayadevi/Shakti-Hindu; Panch Tirth; Siddh Peetha; Haridwar, Uttarakhand)
· Mecca Masjid (1617-94 CE: Islamic; Hyderbad)
· Meenakshi Amman Temple (500 BCE: Madurai center; 1600 CE: Meenakshi-Parvati-Shiva-Hindu; Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Melukote/Thirunarayanapuram (12th c.CE: Cheluva-Narayana Swamy Temple; Sri Ramanujarya residence; Hindu; Yadavagiri rocky hills; Mandya; Karnataka)
· Modhera
· Mookambika (1200 BP: Shiva-Shakti-Hindu; Adi Shankara; Kollur; Karnataka)
· Morgaon Ganesha Temple/Shri Moreshwar Mandir (17th c.CE: Ganesha-Hindu; Pune; Maharashtra)
· Moteshwar Mahadev (Bhimashankar/Shiva-Hindu; Bheem Shankar Jyotirlingam; festival: Maha Shivratri; Kashipur, Uttarakhand)
· Moti Masjid (1660 CE: Islamic; Delhi)
· Mukteswar Temple (900 CE: Hindu; Bhubaneswar, Orissa)
· Mulbekh (Drukpa-Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Mundkur (700 CE: Durga-Hindu; Karkala Taluk, Udupi, Karnataka)
· Mutathura Mahadever Temple (800 CE: Shiva-Vishnu-Hindu; Thiruvattar, Tamil Nadu)
· Mylara Lingeshwara Temple (Shaivite-Hindu: legend: Mallasura demon quelling; Karnika Utsava prophecy utterance; Goravara Kuinita dance; Mylara; Bellary; Karnataka)
· Nachiyar Koil (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Tirunaraiyur, Tamil Nadu)
· Nachna
· Nagarjunakonda (2nd c.CE: Mahayana Buddhist settlement; near Hyderbad; Andra Pradesh)
· Nageshwar Temple (Shiva-Hindu; 12-Jyotirlinga; Dwaraka, Gujarat)
· Naina Devi (Hindu: 52 Shakti Peeths; 2008 stampede- 123 died; Gobind Sagar l.; Bilaspur; Himachal Pradesh)
· Nalanda (427-1197 CE: Mauryan-Gupta Buddh. University; Bihar)
· Namgyal Monastery (1575 CE: Tibetan Buddh.assoc.w/Dalai Lamas; 1959 CE: relocated to Dharamshala; Himachal Pradesh)
· Nanda Devi [SM] [Hindi: “Bliss Giving Goddess”](Uttarakhand)
· Nandeeswarar Temple (Chola Shiva-Hindu; Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Nandi [“joyful”] Temple (1537 CE: Shaivite-Hindu; Vijayanagara style; Bangalore; Karnataka)
· Narasimha temple Narasapura temple (11-12th c.CE: Kalyani Chalukya Hindu; Haveri; Karnataka)
· Narasingam Yoga Narasimha Perumal Temple (770 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Narasingam, Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Navagraha Temples (7-12th c.CE: Chola Navagraha-Shiva-Hindu; Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Navalinga Temple (9th c.CE: Dravida Shiva-Hindu; 9 lingas; Kannada inscriptions; Koppal; Karnataka)
· Neelkanth Mahadev Temple (Nilkanth/Shiva-Hindu; legend: where Shiva consumed poison Halahala, originating from the sea when Devas and Asuras churned the sea to obtain Amrita, Samudramanthan; Pauri Garwal, Uttarakhand)
· Negheriting Shiva Doul (8-9th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; shivalinga; Dergaon; Golaghat; Assam)
· Nellaiappar Temple (700 CE: Chola Nellaiappar/Shiva-Hindu; Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu)
· Nellitheertha Cave temple (1487 CE: Somanatheshwara-Shiva-Hindu; Sage Jabali penance to Durga Parameshwari; Dakshina Kannada; Nellitheertha; Karnataka)
· Nerul Balaji Temple (Hindu; Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra)
· Omkareshwar (12 Jyotirlinga Hindu; Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh)
· Osian
· Padayanivettom Devi Temple (1200 BP: Devi-Hindu; Mavelikkara, Kerala)
· Padmanabhaswamy Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 divya desam; Thiruvananthapuram; Kerala)
· Palani Murugan Temple (2nd-5th c.CE: Chera Dandayudhapani Swami/Murugan-Hindu; Pandavas; Arupadaiveedu; Palani, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu)
· Pancha Rathas [MA](7th c.CE: Hindu; Pandavas; rock-cut temple; Mamallapuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Pandavleni Caves (1st c.CE-12th c.CE: Hinayana Buddh.rock-cut vihara-chaitya; Nashik; Maharashtra)
· Pandrethan
· Paraheda Shiv Mandir (1000 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Banswara, Rajasthan)
· Paramekkavu Bagavathi Temple (1000 CE: Bagavathi-Vishnu-Hind; Thrissur; Kerala)
· Parsurameswar Temple (650 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Bhubaneswar, Orissa)
· Parthasarathy Temple (8th c.CE: Vaishnavite-Hindu; 108 divyadesams; Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Pataleshwar (753 CE: Rashtrakuta Shiva-Hindu; rock-cut cave; Pune, Maharashtra)
· Pathiyoor Devi Temple (b.Parasurama; 108 Durga Hindu; Kerala)
· Patna/Pataligrama (450 BCE: ancient capital; Gautama Buddha holy site; Bihar)
· Pattadakal (8th c.CE: Shaivite-Hindu-Jain; Mahakuta Pillar script; Chalukya, Dravidian, Vesara, Nagara temples: 725 CE: Sangameshvara, Kashivishvanatha, 733-45 CE: Virupaksa, 740 CE: Mallikarjuna, Papanatha, Jain Naryana; Bagalkot; Karnataka)
· Patteswaram (Shiva-Hindu; Patteswaram, Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Pava (ancient city; Gautama Buddha holy site; Uttar Pradesh)
· Pemayangtse Gompa (1721 CE: Nyingmapa Tib.Buddh.; Sikkim)
· Pillars of Ashoka (300 BCE: Vaishali, Lumbini, Meerut (Delhi), Topra (Delhi), Kaushambi (Allahabad), Lauriya-Areraj, Lauriya-Nandangarh, Rampurva, Sankissa, Sanchi, Sarnath, Nigalisagar)
· Phensang Gompa (1705 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Pelling; Sikkim)
· Phodang Gompa (Kagyu Tib.Buddh.; Chaam Dance Festival-10th mo., 28-29th day; Gangtok; Sikkim)
· Phugtal Gompa (12th c.CE: Drukpa Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Phyang Gompa (1515 CE: Drikung Kagyu Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Poonkunnam Siva Temple (1000 BP: Hindu; Thrissur, Kerala)
· Pulimukham Devi Temple (400 BP: Bhadra Bhagavathi-Hindu; Thazhava, Kollam, Kerala)
· Punrasar Balaji (Hanuman-Hindu; Punrasar, Rajasthan)
· Puri: 8th c.CE: f.Shankara; eastern branch for Advaita Vedanta;
· Raghunath Temple (1835-60 CE: Rama-Vishnu-Hindu; 2002: suicide bombers; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Ragigudda Anjaneya Temple (Hanuman-Hindu; Shivalinga; Ganesh, Surya and Tajarajeshwari temples; Bangalore)
· Rajarajeshwara Temple (11th c.CE: 108 Shiva-Parvati-Hindu; 64 Shakti-Peetham-head of Sati fell here; 1000s BP: linga; 18th c.CE: d.7-story Gopuram by Tipu Sultan; Taliparamba, Kannur, Kerala)
· Rajgir (1000 BCE: Mauryan-Gautama Buddha pilgrimage site; Bihar)
· Ramachandi Temple (Surya-Hindu; Kusabhadra r.; Puri, Orissa)
· Rama Giri (12th c.CE: Hindu; Krishna r.; Mahbubnagar; Andhra Pradesh)
· Ramanathaswamy/Rameswaram/Ramalingeswarar Temple (Ramanathaswamy-Shiva-Hindu; 11/12 Jyotirlingas; 4-Char Dham; legend: where Rama prayed to Shiva for sins committed against Ravana; Rameswaram/Pamban i.; Tamil Nadu)
· Ramappa/Ramalingeswara Temple (1213 c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Warangal; Andhra Pradesh)
· Ramatheertham/Rama Temple (Ramachandra Swamy-Sita Devi-Lakshmana-Hindu; Ramatheertham; Andhra Pradesh)
· Ramgarh
· Rameshwara Temple (Vijayanagara Hoysala-Dravida Hindu; Keladi; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Ramnathi (16th c.CE: Ramnath-Shiva-Hindu; Goa)
· Ranganathaswamy Temple (16th c.CE: Ranganathaswamy-Vishnu-Hindu; Vijayanagara style; Bangalore)
· Rangdum Gompa (18th c.CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Suru v.; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Rangnath Dol (Shiva-Hindu; Joysagar Tank; Brahmaputra r.; Assam)
· Rani Sati Temple (1600 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan)
· Ratnagiri (6th c.CE: Gupta; Buddh. mahavihara; Jajpur, Orissa)
· Ratnagiri Murugan Temple (14th c.CE: Murugan-Hindu; Vellore, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Ravalnath (Shaivite-Hindu; Goa)
· Rektha Kanda Swamy Temple (8th c.CE: birthplace of Sri Ayyappan-Hindu; Omallur, Pathanamthitta)
· Rizong Gompa (1831 CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Roda
· Rozabal Shrine (Tomb of Jesus?; Shrinagar; Kashmir)
· Rudranath (Shiva-Hindu; 5-Panch Kedar; legend: Pandava, Mahabharata; Garhwal, Uttarakhand)
· Rudreswar Temple (1744 CE: Hindu; Brahmaputra r.; Guwahati; Assam)
· Rumtek Gompa (16th c.CE: Kagyu Tib.Buddh.; Gangtok; Sikkim)
· Salsette
· Sanchi (3rd c.BCE: Buddh. Stupa; Besnagar; Madhya Pradesh)
· Sangameswara Temple (Shiva-Hindu; shiva linga; confluence of Krishna and Bhavanasi r.; Kurnool; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sani Gompa (2nd c.CE: Kagyu Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Sankar Gompa (Gelugpa Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Sankissa (accd. to commentaries of Tipitaka; ancient city where Siddartha Gautama Buddha returned to earth; Fatehgarh, Uttar Pradesh)
· Sannihit Sarovar (meeting point of 7 sacred Saraswatis; Kurukshetra; Haryana)
· Saptakoteshwar (12th c.CE: Shaivite-Hindu; Narve; Goa)
· Saptharishiswarar (4600 BCE?: Saptharishiswarar/Shiva-Hindu; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sarangapani Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Sarnath/Mrigadava/Isipatana/Rishipattana (5th c.BCE: ancient city where Siddhartha Gautama Buddha taught the dharma; 2nd c.BCE: Buddh.monastery complex; Dhamekh Stupa; Ashoka Pillar; Chaukhandi Stupa- Islamic; Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh)
· Saundatti fort (875-1230 CE: Hindu-Jain; Ratta d.capital; inscriptions; Renuka Sagara reservoir, Yallammagudda temple, Navilatirhta dam, Savadatti Chalukya temples: Puradeshwara, Ankeshwara; Belgaum, Karnataka)
· Sekhareswar Temple (1000 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Lathanga, Paradip, Jagatsinghpur, Orissa)
· Shambhulinga temple (11th c.CE: Chalukya Shiva-Parvati-Hindu; Kundgol; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Shamlaji/Dhodi Dhwaja Vada (Vishnu-Hindu; Sabarkantha; Bhiloda-Modassa; Gujarat)
· Shanka Basadi (8th c.CE: Kalyani-Chalukya Jain; Lakshmeshwara; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Shankaracharya/Jyesteshwara Temple (200 BCE/9th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Srinagar; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Shankaragaurishvara Temple (883-902 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Patan; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Shanta Durga Temple (12th c.CE: Shantadurga-Hindu; Kavalem; Goa)
· Shashur Monastery (17th c.CE: Drugpa Tib.Buddh.; Lahul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Shey Gompa (1655 CE: Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Shitla Mata Temple (Durga-Hindu; 52 Shakti Peeth; Patna, Bihar)
· Shivkhori [“Shiva’s cave”] (Shiva-Hindu; cave temple; legend of Bhasmasura; Reasi; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Shringeri (8th c.CE: f.Shankara; southern-Shringeri branch for Advaita Vedanta-Hindu; Sringeri Sharada Peetham matha est. by Adi Shankaracharya; legend of Adi Shankaracharya: site where the cobra shaded the frog during spawning; 14th c.CE: Sharadamba temple, Vidyashankara temple, inside Rashistambhas- zodiac pillars; Tunga r.; Chikmaglur; Karnataka)
· Shringapuram Mahadeva Temple (10th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; 5 linga; inscriptions; Thrissur, Kerala)
· Shringeri Sharadamba temple (8th c.CE: Sharada/Saraswati-Hindu; Sree Sharada Suprabhata Stotram compostion; Tunga r.; Chikmaglur; Karnataka)
· Siddhesvara Temple (11th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Haveri; Karnataka)
· Sidi Saiyyed Mosque [SR](1573 CE: Islamic; Ahmedabad)
· Sikkal Singaravelan Temple (Muruga-Singaravelan-Hindu; Arupadaiveedu- 6 abodes of Muruga; legend: Kamadenu; Sikkal, Kumbakonam, Tamil Badu)
· Simhachalam [“Lion Hill”]/Simhadri (1098 CE: avatar Narasimha-Vishnu-Hindu; Visakhapatnam; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sirsangi Kalika Temple (1148 CE: Hindu; festivals: Ugadi, palenquins of Kalamma; near Saundatti; Belgaum; Karnataka)
· Sisupalgarh (300 BCE; Khurda); Takht Bhai (100 BCE: Buddhist monastic ruins; Mardan)
· Sita Mai Temple (Sita-Hindu; Sitamai; Karnal; Haryana)
· Sivadol (1734 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Sivasagar; Assam)
· Sogal (Hindu: Someshwara temple; near Munavalli and Saundatti; Belgaum; Karnataka)
· Someshwara temple complex (11th c.CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu; Nandi and Shiva idols, 8th c.CE: Kannada inscriptions; Lakshmeshwara; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Someshwara (11th c.CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu; Kolar; Karnataka)
· Somarama (Shiva-Hindu; Pancharama Kshetras; Sivalinga; Ramachandrapuram; E.Godavari; Andhra Pradesh)
· Somnath
· Sonana Khetlaji (1200 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Sonana, Pali, Rajasthan)
· Spituk Gompa (11th c.CE: Gustor Festival-11th mo.27-29th day; Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Sravasti (5th c.BCE: Siddartha Gautama Buddha pilgrimage site; Angulimala stupa, Anathapindika stupa, Jain Tirthankara, Gandhakuti- Buddha’s hut, Anandabodhi tree; Rajagaha; Uttar Pradesh)
· Sree Indilayappan Temple, Marayikkodu (1500 BP: Shiva-Vishnu-Hindu; Kottarakkara, Kerala)
· Sree Poornathrayesa Temple (Dwarpara Yuga?; Vishnu-Santhana Gopala Moorthy-Hindu; Tripunithura, Kochi, Kerala)
· Sri Adikesavaperumal Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 devyadesams; Kanyakumari, Thiruvattar, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Appakkudathaan Perumal Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Azhagiya Manavala Perumal Temple (Chola Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Devaadi Raja Perumal Temple/Thiruvazhunthoor (Chola Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Therazhunthoor, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Hara Saabha Vimocchana Perumal Temple/Thirukkandiyur (Chola Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Kandiyur, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Jagan Mohini Kesava Swamy Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Ryali; E.Godavari; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Kalahasthi (12th c.CE: Vayu-Shiva-Parvati-Hindu; Kalahasthi; Andhra Pradesh)
· Srinivasa Perumal Temple (1600 CE: Srinivasa-Vishnu-Hindu; Kodavasal, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Pundarikashan Perumal Temple/Thiruvellarai (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Purushothaman Perumal Temple/Thirukkarambanoor (Brahma-Shiva-Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Uttamar Kovil, Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Rajiv Lochan Mandir (Vamana-Narasimha-Vishnu-Hindu; 3 river confluence/Triveni Sangam- Mahanadi, Pairi, Sondur; Rajim; Chhattisgarh)
· Sripada Sri Vallabha Samsthanam (14th c.CE: Hindu; Pithapuram; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Raja Rajeshwara Kshetram (Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple (12th c.CE: Ranganatha-Vishnu-Hindu; Nellore; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple/Srirangam (2000 BP: Ranganatha-Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; 8 Svayam Vyakta Ksetras; largest functioning Hindu temple in world; Srirangam, Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Sri Nookambika Ammavari Temple (renovated 1611 CE: Hindu; Gavarapalem; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Ujjaini Mahakali Temple (17th c.CE: Mahankali-Hindu; Secunderabad; Andhra Pradesh)
· Sri Vadivazhagiya Nambi Perumal Temple/Thiru Anbil (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Pancharanga Kshetrams; Kollidam r.; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Venkatesa Perumal Temple (16th c.CE: Vishnu-Hindu; Tirupur, Tamil Nadu)
· Srivilliputhur Divya Desam (788 CE: Andal-Vatapatrasayee-Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Srivilliputhur, Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Vishnumurthy Temple (600 BP: Vishnu-Hindu; shrine; Mangalore; Karnataka)
· Sripuram (Hindu; Vellore, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Chandramouleeswarar Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; ruins: 108 Shiva temples; Hariharan Kundram hill; Arungundram, Tamil Nadu)
· Sri Raghotham Peeta (1300 BP: Hindu monastery; Ashoka; Gokarna; Karnataka)
· Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple (Ranganatha-Vishnu-Hindu; Shivanasamudra; Mandya; Karnataka)
· Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple (9th c.CE: Ranganatha-Vishnu-Hindu; Srirangapatna; Mandya; Karnataka)
· Stakna Gompa (16th c.CE: Drugpa Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Sthaneswar Mahadev (Shiva-Hindu; holy water tank; linga; Kuru penance; Thanesar; Kurukshetra)
· Stok Gompa (14th c.CE: Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Stongdey Gompa (1052 CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar v.; Padum; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Sudi (11th c.CE: Chalukya Shiva-Hindu; temples: Twin Towered Shiva, Mallikarjuna, Naga Kunda-well; Sudi; Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Sukreswar Temple (1744 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Brahmaputra r.; Itakhuli hill; Guwahati; Assam)
· Sundha Mata Temple (1100 CE: Hindu; inscriptions describing the victory of Chauhans over the Parmaras; Sundha, Bhinmal, Rajastan)
· Sun Temple (1026 CE: Surya-Hindu; Modhera; Gujarat)
· Surya Sadashiva Temple (700 BP: Surya-Shiva-Hindu; Nada; Dakshina Kannada; Karnataka)
· Suryanar Kovil (1000 CE: Chola Surya-Navagraha-Hindu; Navagraha temple; Suryanarkoil, Tamil Nadu)
· Swamimalai Murugan Temple (Muruga-Hindu; Arupadaiveedu- 6 abodes of Muruga; Kumbakonam, Tamil Badu)
· Tabo Monastery (996 CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.; Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Talagunda (Kadamba village; 5th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu: Pranaveshwara temple; Talagunda pillar Kannada inscriptions; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Talakad (350-1050 CE: Gangas; 11th c.CE: Chola; 12 c.CE: Hoysala Hindu; 5 Lingam temples: Pathaleshwara, Maruleshwara, Arkeshwara, Vaidyanatheshwara, Mallikarjuna, Keethinarayana; Kaveri r.; Mysore; Karnataka)
· Tangyud Monastery (11th c.CE: Drugpa Tib.Buddh.; Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Tanjore
· Tashiding Gompa (1717 CE: Nyingma Tib.Buddh.; Sikkim)
· Tayul Monastery (17th c.CE: Drugpa Tib.Buddh.; Lahul, Spiti; Himachal Pradesh)
· Tawang Monastery (1680 CE: Buddh.; Arunachal Pradesh)
· Thikse Gompa (15th c.CE: Gelug Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Leh; Jammu-Kashmir)
· Thiruchendur Murugan Temple (Senthilandavan/Muruga-Hindu; 6-Arupadaiveedu; Tiruchendur, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruchsirupuliyoor/Arulmaakadal Perumal Temple (Chola Vishnu-Hindu; Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruchuzhial (Advaita Vedanta-Hindu; 12th Tevara Stalam; birthplace of Ramana Maharishi; Manamadurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirumuruganathaswamy Temple (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Sivastalam in Kongu Nadu; Tiruppur, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirunadhikkara Cave Temple (7th c.CE: Jain-Hindu; 9-10th c.CE: frescoes depict Ramayana and Mahabharata; Thiruvattar, Kanyakumari, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruevvul (Chola Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Tiruvallur, Arakkonam, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirukadalmallai (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirukkadigai (Vishnu Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Sholinghur, Vellore, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirukutralam (Shiva-Trimurti-Hindu; 64 Shakti Peetham; Tenkasi, Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirukkadaiyur Mayanam/Thirumeignanam (11th c.CE: Chola Shiva-Hindu; Thirukkadaiyur, Kumbakonam, Tamil Badu)
· Thirumeyyam (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Pudukottai, Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirunana (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Sivastalam in Kongu Nadu; Bhavani, Tamil Nadu)
· Thirunarayanapuram (legend: Dasavataram-Vishnu; Vaishnavite-Hindu; 40 sacred ponds- kulams; Melkote; Karnataka)
· Thirunelli Temple (962 CE: Chola-Vishnu-Hindu; Narasimha Purana, Padma Purana; Brahmagiri hill; near Manathavady; Kerala)
· Thiruppandikodumudi (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Sivastalam in Kongu Nadu; Khaveri r.; Tamil Nadu)
· Thirupparamkunram Murugan Temple (8th c.CE: Jain rock-cut cave temple; Murugan-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Thirupparamkunram, Madurai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruppullani (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruppunavayil (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Tevara Stalams; 14 lingams; Pudukkotai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruputkuzhi (Vijayaraghavaswamy/Moolavar-Rama-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruthani Murugan Temple (Murugan-Hindu; festival: Krittikais; Thiruthani, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruvambadi Sri Krishna Temple (1000 BP: Krishna-Hindu; Thrissur, Kerala)
· Thiruvanaikaval (2nd c.CE: Chola Jambukeshwara/Shiva-Akilandeswari/Parvati-Hindu; 5 Pancha Bootha Sthalams- Water; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruvannamalai Arunachaleswara (5 Pancha Bootha Sthalams- Fire;)
· Thiruvanchikulam (7th c.CE: Mahadeva Temple; Siva-Hindu; Kerala)
· Thiruvidandai (Pallava Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Varaha Kshetram; Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thiruvotriyur Temple (Aadhipureeswarar/Shiva-Hindu; Thiruvotriyur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Thotlakonda (2000 BP: Hinayana Buddhist monastery complex; Visakhapatnam; Andra Pradesh)
· Thottipal Bhagavati Temple (108 Devi temple; Hindu; Thrissur, Kerala)
· Thousand Pillar Temple (1163 CE: Shiva-Vishnu-Surya-Hindu; Hanamakonda-Warangal; Andhra Pradesh)
· Thrikkavu Temple (108 Durga Hindu; Malapuram; Kerala)
· Thrikodithanam Mahavishnu Temple (800 CE: Chera Vaishnava-Hindu: inscriptions; 5 Pandava; Mahabharata; Changanassery, Kerala)
· Tigawa
· Tirumala Venkateswara Temple (300 CE: Venkateswara-Vishnu-Hindu; Chittor; Tirupati; Andhra Pradesh)
· Tiruppukkozhiyur (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Shivastalam in Kongu Nadu; Avinasi, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu)
· Tiruttalinathar Temple (Shiva-Hindu; 7-Tevara Stalam; Thiruputhur, Tamil Nadu)
· Tiruvadanai (Shiva-Hindu; 8-Tevara Stalam; Tiruvadanai, Tamil Nadu)
· Tiruvaikavur Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Tiruvaikavur, Tamil Nadu)
· Tiruvekkaa (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Tiruvelukkai (Rama-Hindu; 108 Divyadesams; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Trikuteshwara (1050-1200 CE: Chalukya Hindu; Gadag; Hubli-Dharwad; Karnataka)
· Trilokpur (1573 CE: Bala Sundri-Durga-Hindu: triangle of 3 Durga Temples, or faces; Dhyanu Bhagt Temple, Shiva Temple, Lalita Mata Temple; Trilokpur; Himachal Pradesh)
· Trimbakeshwar Shiva Temple (Hemadpanthi Shiva-Hindu; Jyotirlinga; Godavari r.; Trimbak; Nashik; Maharashtra)
· Tripurantaka Temple (1070 CE: Chalukya Hindu: 80 inscriptions- Shaiva, Vaishnava, Jain, Buddhist; Kamasutra relief on friezes; Ganda-Bherunda- 2 headed mythical bird sculpture; naga door figures; dikpala-guardians; sculptures- Brahma, Shiva, Vishnu; Shimoga; Karnataka)
· Tripura Sundari Temple (1501 CE: Hindu; 52-Shakti Peethas; Udaipur, Tripura)
· Triyuginarayan/Akhand Dhuni Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; where Shiva married Parvati with Vishnu as witness; Rudraprayag, Uttarakhand)
· Tsuklakhang Palace (Tib.Buddh.; Pang Lhabsol, Kagyad, Losar festivals; Gangtok; Sikkim)
· Tungnath (Shiva-Hindu; 5-Panch Kedar; legend: Pandava, Mahabharata; Garhwal, Uttarakhand)
· Ucchi Pillayar Temple/Rockfort/Thayumanaswamy (7th c.CE: Shiva-Ganesha-Hindu; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Udayagiri (Buddh. complex: stupa/viharas; Orissa)
· Udupi Sri Krishna Matta (13th c.CE: Vaisnava-Krishna-Hindu; Udupi; Karnataka)
· Umamaheshwaram (Shiva-Hindu; Hyderbad; Andhra Pradesh)
· Uma Nanda Temple (1681 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Peacock i.; Brahmaputra r.; Guwahati; Assam)
· Undavalli caves (4-5th c.CE: Brahma-Vishnu-Shiva-Trimurti-Hindu; rock-cut caves; Vijayawada; Andhra Pradesh)
· Uppiliappan/Thiruvinnagar Temple (Vishnu-Hindu; 108 Devyadesams; Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu)
· Uttamar Kovil (Trimurti-Hindu; Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu)
· Vadakkunnathan Temple (b.Parashurama; Shiva-Hindu; Mahabharata murals; Thrissur, Kerala)
· Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga (Shiva-Hindu; 12 Jyotirlingas; 52 Shakti Peeths; Deoghar; Jharkhand)
· Vaishali (6th c.BCE: ancient city; Ashokan pillar; where Gautama Buddha preached last sermon; Bihar)
· Vaishno Devi (Vaishnavi-Shakti-Hindu; Katra; Reasi; Jammu and Kashmir)
· Vaitheeswaran [“Lord Doctor”] Temple (Shiva-Navagraha-Hindu; 9-Navagraha; Vaitheeswaran, Tamil Nadu)
· Vajreshvari/Vajrayogini (Mahabharata times: Vajreshvari-Vajrayogini-Parvati-Hindu; legend of Vajrayogini; Nagarkot; Kangra; Himachal Pradesh)
· Vallabhapuram (Sri Vallabha-Hindu: Andhra Pradesh)
· Valluvan Kadav Sree Muthapan (400 BP: Hindu; Kerala)
· Vajreshwari Temple/Shree Vajreshwari Yogini Devi Mandir (1739 CE: Hindu; legend: Puranas; Thane; Mumbai; Maharashtra)
· Vanniappar Temple (1000 CE: Hindu; Azwarkuruchi, Tirunelveli)
· Varadavinayaka (1725 CE: Ganesha-Hindu; Ashtavinayak Ganesh temple; Mahad, Raigad, Maharashtra)
· Varadharaja Perumal Temple (1053 CE: Pallavas; Vishnu-Hindu; Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu)
· Varaha Cave Temple (7th c.CE: Hindu; rock-cut temple; Mamallapuram, Chennai, Tamil Nadu)
· Varanasi/Benares [d.after the confluence of rivers Varuna and Assi](accd.legend-Ramayana, Rigveda, Purana, Mahabarata: 8000 BP f.Shiva/3000 BP: sacred city; Uttar Pradesh)
· Vayalur Murugan Temple (800 CE: Chola Muruga-Hindu; Trichy, Tamil Nadu)
· Veera Narayana Temple (1200 CE: Hoysala Vaishnava-Hindu; mantapa, vimana, parapet wall relief; Chikmagalur; Karnataka)
· Veezhinathar Kovil (Veezhinathar-Shiva-Hindu; Thiruveezhimizhalai, Tamil Nadu)
· Venkateshwara Temple at Ramenahalli (250 BP: Hindu; Gadag; Karnataka)
· Venjamakoodal (800 CE: Shiva-Hindu; 7-Shivastalam in Kongu Nadu; Karur, Tamil Nadu)
· Vijayanagara [MA](1200 CE; Bellary, Karnataka)
· Vikramasila (8th c.CE: Buddh.university; Bihar)
· Virupaksa Temple (7th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Virupaksa consort of Pampa; Vijyanagar ruins; festivals: chariot, Virupaksa-Pampa marriage; Tungabhadra/Pampa r.; Hampi; Bellary; Karnataka)
· Vishalakshi Temple (Sati-Hindu; 52-Shakti Peethas; Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh)
· Vishnupad Mandir (1787 CE: Vishnu-Hindu; Gaya, Bihar)
· Vishnu Temple, Deogarh (500 CE: Gupta-Hindu; Deogarh, Madhya Pradesh)
· Viswanatha Swamy Temple, Palakkad (1464 CE: Siva-Hindu; Palakkad, Kerala)legend: Rama resting place on way to Ravana;
· Vithoba Temple, Pandharpur (12th c.CE: Vithoba-Krishna-Vishnu-Hindu; Pandharpur, Maharashtra)
· Walkeshwar Temple (1127 CE: Shiva-Hindu; Banganga tank; Malabar hill; Walkeshwar, Mumbai, Maharastra)
· Yadagirigutta/Sri Lakshminarasimha Swamy Temple (Narasimha-Hindul Nalgonda; Hyderabad; Andhra Pradesh)
· Yaganti/Sri Yaganti Uma Maheswara Temple (15th c.CE: Shiva-Hindu; Pushkarini holy baths; Agastya caves; Venkateswara cave; Veera Brahmam cave; Yaganti; Kurnool; Andhra Pradesh)
· Yamunotri (19th c.CE: Yamuna-Hindu; 4-Chota Char Dham; where sage Markandeya wrote Markandeya Purana; Uttarkashi; Uttarakhand)
· Yelluru Sri Vishweshwara Temple (Shiva-Hindu; Devaayathana style; Udupi; Karnataka)
· Zangla Gompa (1823 CE: Sandor Korosi Csoma made first Eng-Tib dictionary here; Tib.Buddh.monastery in Ladakh; Zanskar v.; Jammu-Kashmir)
INDONESIA: [Javanese-Hindu temple (candi)]
· Arca Bugisan (7 Buddha and Bodhisattva statues; Yogyakarta; S Prambanan Plain)
· Arca Dwarapala (1222 CE; Malang; E.Java)
· Arca Totok Kerot (Kediri, Java)
· Borobudur (9th c.CE: Magelang, Java)
· Candi Agung (Hindu k.: Negara Dipa; Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan)
· Calon Arang (site inspired Balinese Leak dance; Kediri, Java)
· Candi Bacem (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Badut (8th c.CE: Shivaite temple; Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Batu Jaya (6th c.CE: Buddhist stupa compound; Karawang, W.Java)
· Candi Biaro Bahal (South Tapanuli, Sumatra)
· Candi Boro (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Brahu (Buddhist temple; Trowulan, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Canggal (8th c.CE: Buddhist complex; Yogyakarta)
· Candi Cangkuang (Shiva temple; Garut, W.Java)
· Candi Cetho [V](15th c.CE: Javanese-Hindu temple; Surakarta; Mount Lawu)
· Candi Dorok (Kediri, Java)
· Candi Gambar Wetan (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Gana (reliefs, statues; Yogyakarta; W Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Gentong (Yuan-Ming ceramics; Trowulan, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Jago (13th c.CE: scenes of Mahabharata epic w/underworld demons; Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Jawi (13th c.CE: Buddhist funerary temple, terraced sanctuaries, meditation grottoes, sacred pools; 80 sites; Tretes, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Kalasan (8th c.CE: Buddhist temple; Yogyakarta; W Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Kalicilik (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Karangnongko (Yogyakarta; Klaten Regency)
· Candi Kedulan (temple foundation; Yogyakarta; W Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Kidal (1248 CE: Javanese-Hindu temple; Malang)
· Candi Kotes (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Laras (Buddhist k.: Tanjung Puri; Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan)
· Candi Lumbung (Buddhist temple complex: 1 central, 16 smaller surrounding; Yogyakarta; N Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Mendut (8th c.CE: Mahayana Buddhist temple; Kedu plain, Java)
· Candi Merak (10th c.CE: 2 Hindu temples w/reliefs; Yogyakarta; Klaten Regency)
· Candi Muara Takus (11-12th c.CE: Sriwijaya e.; Buddhist temple complex; Kampar Regency, Riau, Sumatra)
· Candi Muaro Jambi (11-13th c.CE: Melayu k.; Buddhist temple complex; Jambi, Riau, Sumatra)
· Candi Muteran (Trowulan, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Ngawen (8th c.CE: Hindu-Buddhist: 5 aligned sanctuaries; lion sculptures; Yogyakarta)
· Candi Pawon (8th c.CE: Buddhist temple dedicated to Kuvera, god of wealth; Kedu plain, Java)
· Candi Penataran (12-15th c.CE: Majapahit k. Javanese-Hindu temple complex; stepped pyramid; Blitar)
· Candi Plaosan (9th c.CE: Hindu-Buddhist temple complex: 2 main w/reliefs; Yogyakarta; N Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Plumbangan (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Rambut Monte (Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Sajiwan (Buddhist temple w/reliefs; Yogyakarta; S Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Sambisari (10th c.CE: underground Hindu temple buried by eruptions from Mount Merapi; Yogyakarta)
· Candi Sari (8th c.CE: Buddhist sanctuary w/9 stupas; Yogyakarta; W Prambanan Plain)
· Candi Sawentar (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Segaran (pond; Trowulan, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Sewu (8th c.CE: Buddh.; Prambanan; Java)
· Candi Simping (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Singosari (1304 CE: Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Songgoriti (Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Sukuh [V](15th c.CE: Javanese-Hindu temple; linga-yoni relief; Surakarta; Mount Lawu)
· Candi Sumberawan (Malang, E.Java)
· Candi Sumbernanas (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Surawana (1390 CE: Majapahit k.; Kediri, Java)
· Candi Tegowangi (Kediri, Java)
· Candi Tepas (Blitar, Java)
· Candi Tikus (13th c.CE: Majapahit capital; irrigation system; Trowulan, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Candi Tondowongso (Kediri, Java)
· Candi Wringin Branjang (Blitar, Java)
· Dieng Plateau [“Abode of the Gods”](7-8th c.CE: originally 400 Hindu temples-only 8 remain; oldest Candi in central Java: Abiyasa, Arjuna, Bima, Darawati, Dwarawati, Gatotkaca, Pandu, Parikesit, Puntadewa, Magersari, Nakula, Sadewa, Sembadra, Senjaka, Srikandi; Wonosobo, Java)
· Gapura Bajang Ratu (Trowulan, Java)
· Gedong Songo(8-9th c.CE: Hindu complex; Semarang)
· Gerbang Wringin Lawang (Trowulan, Java)
· Gua Selomangleng (Kediri, Java)
· Gunung Sari (ruins of three secondary temples and primary foundations remain; Yogyakarta)
· Gunung Wukir (oldest Javanese incriptions; ruins of three secondary temples and primary foundations remain; Yogyakarta)
· Kidal
· Maros (Paleolithic)
· Masjid Agung Demak (15th c.CE: Islamic; Demak, Java)
· Masjid Sultan Ssuriansyah (1700 CE: Islamic; South Kalimantan)
· Pura Besakih [“Mother Temple of Besakih”] (14th c.CE: Agama Hindu Dharma; Bali; Mt. Agung-Mt. Meru replica)
· Prambanan Plain/Roro Jonggrang (850 CE: Mataram k.: 237 Shivaite temple complex; flanked by Vishnu and Brahma temples; Ramayana relief; Yogyakarta, Java)
· Pura Luhur (11th c.CE: Hindu Balinese Sea Temple; Pecatu village, Kuta South; Uluwatu)
· Ratu Boko (8-9th c.CE: Hindu-Buddhist temple w/royal garden and bathing pool; surrounding temples: Arca Gopolo, Banyunibo, Barong, Dawangsari, Ijo, Watugudig, Abang, Gampingan, Sentono, Situs Payak; E Yogyakarta; S Prambanan)
· Sangiran (Meganthropus: Surakarta, Java)
· Singasari
· Tanah Lot (15th c.CE: Hindu Balinese Sea Temple; Tabanan; Denpasar)
· Tirtha Empul Temple (926 CE: Warmadewa d. Hindu; purifying pool; Bali)
· Lake Tondano (Neolithic)
· Trowulan (13th c.CE: Majapahit capital; Candi: Tikus, Brahu, Gentong, Muteran, Kolam Segaran, Gapura Bajang Ratu, Gerbang Wringin Lawang; Mojokerto, Java; Mount Penanggungan)
· Ngandong (250-28k BP: tropical-Neanderthal)
IRAN:
· Adur Gushnasp (3rd-4th c.BCE: Zoroastrian fire temple; believed to have been created by Ashura Mazda; Mount Khajeh; Lake Hamun; Sistan)
· Apadana (500 BCE: Persepolis)
· Bisitun [SR](transitional Neanderthal; 6th c.BCE: earliest epigraphical reference to “ariya” (sim.Aryan); 400 BCE; Jeyhounabad; Kermanshah)
· Choqa Zanbil (2400 BCE: Elamite; 1200 BCE; Dezfoul; Susa; Ahvaz)
· Darband (cave)
· Do-Ashkaft (cave)
· Ecbatana [SR](600 BCE; Hamadan)
· Fatima al-Masumeh Shrine (17th c.CE: Shia Islamic; Qom)
· Firuzabad (224 CE: Sassanid)
· Ganj Par (Paleolithic; Gilan)
· Ganj Dareh (Neolithic)
· Ghagha Shahr (3rd-4th c.BCE: citadel complex w/Zoroastrian fire temple, Adur Gushnasp; believed to have been created by Ashura Mazda; Mount Khajeh; Lake Hamun; Sistan)
· Gorgan (600 BCE)
· Imam Reza Shrine (818 CE; ruined 993 CE; r.1009-1310 CE: Shia Islamic; contains mausoleum of 8th Imam of Twelver Shi’ites; Mashhad)
· Jameh Mosque of Isfahan (771 CE: Shia Islamic; Isfahan)
· Jamkaran Mosque (984 CE: Shia Islamic; Jamkaran, Qom)
· Jiroft Civilization (3000 BCE)
· Jondi Shapur (271 CE; Gundeshapur)
· Ka’ba-i Zartosht (Cube of Zoroaster; 5th c.BCE: Persepolis)
· Kashafrud (Lower Paleolithic)
· Konar Sandal (3rd m.BCE: Bronze Age; Jiroft)
· Kunji Cave
· Mar Tarik
· Naqsh-e Rustam (1000 BCE: Darius tombs; Persepolis; Marv Dasht)
· Pasargadae (Batrakatas; 6th c.BCE: Tomb of Cyrus the Great; Persepolis; Marv Dasht)
· Persepolis/Takht-e Jamshid [MA](515 BCE; Marv Dasht)
· Qal’a-e Kafaran/Qal’a-e Sam (3rd-4th c.BCE: double citadel complex consisting of Kok-e Zal and Chehel Dokhtaran w/Zoroastrian fire temple; believed to have been created by Ashura Mazda; Mount Khajeh; Lake Hamun; Sistan)
· Qaleh Bozi Caves
· Saint Stephanos Monastery (9th c.CE: Armenian church; Arax r.; Jolfa)
· Saint Thaddeus Monastery (68 CE: 1st church dedicated to Saint Jude; 10th c.CE: apse; earthquake damage in 1319; 1329 CE: rebuilt; Maku)
· Shah Mosque/Masjed-e Shah (1611 CE: Shia Islamic; Isfahan)
· Shahr-e Sukteh/Burnt City (3200 BCE: Jiroft; Bronze Age; Zahedan)
· Soltaniyeh (1312 CE)
· Susa (7000 BCE; Ahvaz)
· Takht-i-Suleiman (5th c.BCE; Phraaspa; Takab)
· Tangeh Bolaghi (5000 BCE: skeleton near Pasargadae)
· Taq-e Bostan [SR](226 CE: Sassanid Empire; Kermanshah)
· Tepe Musyan
· Warwasi (Middle Paleolithic)
IRAQ: [25,000 AS][step pyramid (ziggurat)]
· Al Abbas Mosque (680 CE: Islamic; Karbala)
· Al Askari Mosque (944 CE: Shia Islamic; shrine of 10th and 11th twelver; Samarra)
· Al-Kadhimiya Mosque (7th c.CE: Shia Islamic; tombs of 7th and 9th twelve; Baghdad)
· Al-Mada’in (Taq-I Kisra ruins) (312 BCE: Seleucia and Ctesiphon; Salman Pak)
· Al-Qurnah (Euphrates r. and Tigris r. junction; possible site for Garden of Edin)
· Arbela
· Ashur
· Babylon (3000 BCE: capital of Babylonia for millennium; 689 BCE: sacked by Assyrian Nebuchadnezzar; Al Hillah)
· Baghdad [SR](762 CE; Bagdad museum contains a galvanized cell battery made w/ clay pot)
· Balawat
· Barda Balka
· Borsippa
· Colossal Bulls [MA](Nimrud; 713 BCE: Dur-Sharrukin/Khorsabad; Nineveh/Mosul)
· Ctesiphon
· Dur Kurigaizu
· Dur Sharrukin [“Fortress of Sargon”](706 BCE: Khorsabad)
· Eridu (5000 BCE: artifacts; traditional birthplace of Abraham; Basra)
· Great Mosque of Samarra (848-51 CE: Islamic; Malwiya tower; Samarra)
· Hassuna
· Hatra (300 BCE)
· Imam Ali Mosque (977 CE: Shia Islamic; Najaf)
· Imam Husayn Mosque (680 CE: Shia Islamic; Karbala)
· Isin (2000 BCE; Ishan al-Bahriyat)
· Jarmo (7000 BCE: Kirkuk)
· Kish
· Lagash
· Nimrud (1300 BCE; 883-859 BCE: Assyrian capital under Ashurbanipal II; Mosul)
· Nineveh (1800 BCE; oldest city of Assyria; 704-681 BCE: capital under Sennacherib; Mosul)
· Nippur (Sumerian capital; cuneiform archive)
· Nuzi
· Palagawra
· Samarra (6000 BCE)
· Shanidar cave (Neanderthal; 80,000 BP; Kurdistan)
· Sippar
· Shuruppak
· Tepe Gawra
· Ubaid (3500 BCE: terra-cotta figurine w/cone head and large eyes now in Iraq Museum)
· Ur (3000 BCE; Tell el-Mukayyar)
· Uruk (Ubaid culture; legendary walls built by Gilgamesh)
· Zarzi
Ante-Diluvial Flight Corridor (Sitchin): (see “vortex sites”)
1) Eridu (Home in Faraway Built); (c.5400 BCE; Tell Abu Shahrain; An Nasiriyah)
2) Bad-Tibira (Bright Place Where the Ores are Made Final) (Tell al-Madineh)
3) Laraak (Seeing the Bright Glow); (2800 BCE; Tell Sankarah)
4) Sippar (Bird City); (Tell Abu Habbah)
5) Shuruppak (Place of the Utmost Well-Being) (3000 BCE; Tell Fara; Al-Qadisiyyah)
6) Laarsa (Seeing the Red Light); (2800 BCE; Tell Sankarah)
7) Nibiruki (Earth Place of Nibiru) (Nuffar; Nippur)
8) Lagash (2800 BCE; Tell Sankarah)
ISRAEL:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Ahwat [MA](Bronze age: 1160 BCE: Shardana sea-people; sim.nuraghe; Caesarea, Manasseh)
· Al-Aqsa Mosque (705 CE: Mamluk Islamic; Dome of the Rock/Temple Mount; Jerusalem)
· Al-Khadra Mosque (1288-90 CE: Mamluk Islamic; Nablus)
· Alexandrium (104 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress)
· Amathus (1100 BCE: Iron Age; 141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress)
· Amud (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Ashkelon (2000 BCE)
· Atlit Yam [MA](6900-6300 BCE: Neolithic: submerged stone semicircle; 8-12m beneath sea level; findings: ground fills containing flints, 2 layers animal bones, wells, megaliths w/cup marks, 10 flexed burials w/human skeletons revealing earliest known cases of TB, fish=hooks, anthropomorphic stone stelae, stone arrowheads, sickle blades, axes, plant remains-seeds, granary weevils; Bay of Atlit at mouth of Oren r.; off coast of Atlit; 8500 BP: possible Etna m. eruption caused 10-storey/40m tsunami to engulf Mediterranean coastal cities w/in hrs.)
· Avdat (3rd c.BCE; Ramon; Negev)
· Bethsaida (Jesus fish and loaves; Golan)
· Beit She’an (1500 BCE: Scythopolis; Jezreel v.)
· Caesarea Maritima [MA](25 BCE)
· Cathedral of St.James (12th c.CE: Armenian church; Old Jerusalem)
· Capernaum (150 BCE)
· Church of the Holy Sepulchre/Chirch of Resurrection (2nd c.CE: Temple of Aphrodite; 4th c.CE: Constantine’s church: great basilica/Martyrium, colonnaded atrium/Triportica/Golgotha/where Jesus was crucified, rotunda/Anastasis-“Resurrection”/remains of rock-cut-room/burial site of Jesus; kokhim-tombs; damaged by fire in 614; repaired in 630; destroyed 1009; reconstruction in 1027-8; 1099 CE: taken by knights of the 1st Crusade; 1149 CE: Romanesque; 1187 CE: captured by Saladin; third Crusade treaty; 1244 CE: captured by Khwarezmians; renovations in 1555; fire damage 1808; Old Jerusalem)
· Cyprus (141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; Dead Sea; Jericho)
· Docus (141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; Jericho)
· Dome of the Rock (691 CE: Islamic; oldest Islamic building in the world; on the Temple Mount; Jerusalem)
· Esbus (Bronze Age; 141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress)
· Es Skhul (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; Haifa)
· Galilea (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Great Mosque of Gaza/Great Omari Mosque (1340 CE: Mamluk Islamic; site of ancient Hellenic temple and 5th c.CE Byzantine church; Gaza)
· Ibrahimi Mosque/Sanctuary of Abraham/Cave of the Patriarchs/Cave of Machpelah [“Cave of the Double Tombs”] (21st-19th c.BCE: Abraham; Islamic; Christians and Muslim tradition: burial place of Abraham and Sarah, Isaac and Rebekah, Jacob and Leah; Hebron)
· Jezzar Pasha Mosque (1781 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Acre)
· Mosque of Omar (1193 CE: Islamic; Jerusalem)
· Mount Carmel/Karem El (600000 BP: Neanderthal-Homo Sapiens; 1500 BCE: Canaanite sacred site; grotto of Elijah; Haifa)
· Mount Ebal [SM] (1220 BCE: ruins: Al-Kalah, Kunaisah, el Burnat; Nablus; Jerusalem)
· Gebae (141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; Caesarea)
· Ezion-Geber/El Kheleifeh (8th c.BCE; Aqaba; Eilat)
· Mount Gerizim [SM](Greco-Roman: Zeus temple; 6th c.BCE: Hadrian castle; Nablus; Jerusalem)
· Et-Tell (1400 BCE; Beitin/Bethel)
· Gaza (2500 BCE: Egypt-Canaanite: sea port)
· Gezer (1350 BCE: Gezer Calendar; Abu Shusheh)
· Gibeon (700 BCE; al-Jib)
· Haluza (Halasa/Elusa)
· Har Karkom [“Mount Saffron”]/Jabal Ideid/Mount Gerizim [geri=kar; zim=kom] [MA](Paleolithic cult center: 40000 rock engravings/drawings; megaliths; possible Mount Sinai/Horeb; Petra-Kadesh Barnea; Negev desert)
· Hayonim
· Herod’s Temple/Temple Mount [MA] [SM](19 BCE: Jerusalem; Mount Moriah [Hbr: “ordained/considered by God”]: Temple of Solomon?)
· Herodium (40-4 BCE: Herodian fortress; Herod’s burial site; Bethlehem)
· Hippos (300 BCE; Horbat Susita)
· Hyrcania (141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress)
· Jericho (9000 BCE: Tell es-Sultan)
· Kebara Cave (60-48k BP: Neanderthal; Caesarea; Wadi Kebara; Hadera; Mt.Carmel)
· Lachish (701 BCE)
· Machaerus (104 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; Dead Sea)
· Malatha (141 BCE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; Dead Sea)
· Mamshit (Negev)
· Masada (72 CE: Hasmonaean-Herodian fortress; palaces; Dead Sea)
· Mount of Olives [SM](Jerusalem)
· Mugharet ez-Zuttiyeh
· Neve David (15000 BCE: Mt.Carmel)
· Qafzeh-Skhul/Mugharet et-Skhul (100-90k BP: human remains; Nazareth; Mt.Precipice)
· Ramat Rahel
· Shivta (Negev)
· Shuqba (250-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· Sultan Ibrahim Ibn Adham Mosque (958 CE: Islamic; Beit Hanina)
· Tabun Cave (250-45k BP: Mesolithic-Neolithic; Ramallah; Mt.Carmel)
· Tel Arad (4000 BCE; Negev)
· Tel Be’er Sheva (4000 BCE; Beersheeba)
· Tel Dan (Golan)
· Tel Hazor (1800 BCE; near Kadesh)
· Tel Megiddo (7000 BCE)
JAPAN: [Buddhist temples (ji); Shinto shrines]
· Adashino Nenbutsuji (811 CE: Buddh.; stupa; Kyoto)
· Aizawa Tadahiro
· Asuka-dera (588 CE: Buddh.; Asuka, Nara)
· Byodo-in (998 CE: Fujiwara Palace; 1052 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Chion-in (1234 CE: Jodoshu Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Daianji (716 CE: Buddh.; Nara)
· Daitokuji (1315 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Enryakuji (767 CE: Tendai Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Eiheiji (1244 CE: Soto Zen Buddh.; f.Eihei Dogen; Fukui)
· Eihoji (1313 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Gifu)
· Engakuji (1282 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; 2nd -5 Mountains; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Fujiyama [V][SM](Chubu)
· Futaiji/Narihira-dera (847 CE: Buddh.; Nara)
· Gangoji (718 CE: Buddh.; Nara)
· Ginkakuji [“Temple of Silver Pavillion”](1490 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Gionzan An’yo-in (1225 CE: Jodoshu Buddh.; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Gokokuji (1681 CE: Shingon Buzan Buddh.; Tokyo)
· Hasedera (686 CE: Buzon-Shigon Buddh.; Sakurai, Nara)
· Hiei, Mount [SM](NE Kyoto; Shiga)
· Higashi Honganji (1602 CE: Shin Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Hokkeji (745 CE: Komyo Buddh.; Nara)
· Hokkiji (638 CE: Shotokushu Buddh.; Nara)
· Horinji (622 CE: Shotokushu Buddh.; Nara)
· Horyuji (607 CE: Shotokushu Buddh.; Ikaruga, Nara)
· Inamurayama [SM](Amanouzume fertility goddess Shinto shrine: divine phallus; Tosa, Kochi)
· Ishibutai kofun [MA] (Asuka, Nara)
· Iwajuku (10000 BCE; Jomon: Kakasake, Midori, Gunma)
· Jochiji (1450 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; 4th -5 Mountains; Kita-Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Jozaiji (717 CE: Tendai Buddh.; Gifu)
· Jufukuji (1200 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; 3rd -5 Mountains; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Kaneiji (1625 CE: Tendai Buddh.; Tokyo)
· Kannoji (827 CE: Shinto-Buddh.; Kabutoyama; Hyogo)
· Kenchoji (1253 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Kinkakuji [“Temple of the Golden Pavilion”] (1397 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Kofukuji (669 CE: Hosso Buddh.; Nara)
· Kiyomizu-dera (798 CE: Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Kotoku-in (1252 CE: Jodoshu Zen Buddh.; Daibutsu; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Mampukuji (1661 CE: Obaku Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Meigetsu-in (1383 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Mieji (1450 CE: Nichiren Buddh.; Gifu)
· Miwayama [SM][Jpn: “August/beautiful room”](250 CE: Shito: shrines, 6 tumulus/mounds: Hashihaka, Nishitonozuka, Chausuyama, Mesuriyama, Andonyama, Shibutani-muko; mirrors, weapons, ornaments, coffins; Yamamato k.; Nara)
· Myoshiji (1342 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Nantaiyama [V](pre-Jomon: phallic stone rods; 500 BCE: Yayoi: Shinto shrines; 767 CE: Futarasan Shrine; Nikko)
· Nanzenji (1291 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Ninnaji (888 CE: Shingon Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Nishi Honganji [“Western Temple of the Original Vow”](1602 CE: Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Ominesan [SM](8th c. CE: Shinto; Tenkawa, Nara)
· Ryoanji [“Temple of Peaceful Dragon”](Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Saidaiji (765 CE: Shingon Buddh.; Nara)
· Sagamiji (745 CE: Shingon Buddh.; Kasai; Hyogo)
· Saihoji (8th c. CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Sanjusangendo (1164 CE: Tendai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Sannai Maruyama (Jomon: Sannai, Aomori)
· Senshoji (628 CE: Sho-Kannon-Tendai Buzan Buddh.; Tokyo)
· Shinyakushiji (747 CE: Kegon Buddh.; Nara)
· Shohoji (1638 CE: Obaku Buddh.; Gifu)
· Sofukuji (1390 CE: Rinzai Buddh.; Gifu)
· Sojiji (740 CE: Soto Zen Buddh.; 2nd -5 Mountains; Noto; 1911 CE: rebuilt in Yokohama)
· Taisekiji (1290 CE: Nichiren Shoshu Buddh.; Shizuoka)
· Tateyama [SM][V][Jpn.: “Standing Mountain”](Shinto: Oyama shrine; Hida Mts.)
· Tenryuji (1339 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Todaiji (8th c. CE: Kegon Buddh.; Nara)
· Toji (796 CE: Shingon Zen Buddh.; Kyoto)
· Toshodaiji (759 CE: Ritsu Buddh.; Nara)
· Yakushiji (680 CE: Hosso Buddh.; Nara)
· Yoshinogari (300 BCE; Yayoi: Yoshinogari and Kanzaki, Saga, Kyushu)
· Zenkoji (16th c. CE: Shingon Buddh.; Gifu)
· Zenyomitsuji (Shingon-Mahayana Buddh.; Tokyo)
· Zuiryuji (1468 CE: Rinzai Buddh.; Gifu)
· Zuisenji (1327 CE: Rinzai Zen Buddh.; Kamakura; Kanagawa)
· Pyramids of Japan: Motoyama
OKINAWA:
· Sunabe Sunken Pyramid [MA] [GP14](14000+ years ago; 1987: diver Hichiro Oritaki discovered submerged (60-100’) pyramidal complex- tools, engravings, stepped pyramid (2 football fields), cooridors, tunnels, human face (resembling Moa faces on Easter i., and sphinx), stacked megaliths; off coast of Yonaguni i.); western edge of Dragon’s Triangle in Pacific o.; Utsurobune [Jpn.: “hollow ship”]legend: woman found in hollow saucer-shaped craft off coast of Japan; 5 different drawings in different form resembling modern UFO reports; 14,000-300 BCE: Jomon period- 15000 Dogu figurines (resembling Hopi Kachina) resembling humanoid in a space/underwater diving suit; culture spawned from beings represented by Dogu; E-W trench; orientated S; on Tropic of Cancer; tilt of Earth has shifted 1°/last 10,000 years; )
[NOTE 88] 3/4 submerged sites are vile vortices- Bimini is. [GP18], Yonaguni i. (Sunabe) [GP14], Dwarka [GP12]; <non-vile vortice> Titicaca (Huanacu) [GP35]
JORDAN:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Ain Ghazal (7250 BCE: Neolithic; Amman)
· Jerash (3200 BCE: Bronze Age)
· Petra [SM](100 BCE: Nabateans; Jebel al-Madhbah)
· Tall al-Umayri [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic Age; planisphere; standing stones; star stones- Andromeda, Vernal Equinox, Winter Solstice; Madaba Plains; S of Amman, E of Jerusalem)
KAZAKHSTAN: [kurgan-mounds]
· Berel cemetery (300 BCE: kurgan 11: tomb: dozen sacrificed horses preserved w/skin, hair, harnesses, saddles, on birch bark, next to funeral chamber containing 2 Scythian nobles- sim.Ashvamedha; Bukhtarma r.)
· Issyk kurgan (4th c.BCE: skeleton, silver cup, gold ornaments, Scythian animal art objects and headdress- Kazakh bridal hat; near Talgar)
· Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasavi [SR](1389-1405 CE: Islamic; Hazrat-e Turkestan)
· Novovelichkovskaya kurgan (2000 BCE: Yamna-Novotitorovka culture nomad tomb: 11 people, embracing couple, bronze tools, stone carvings, jewelry, ceramic vessels, red ochre; Ponura r.; Krasnodar)
· Turkistan [SR](2nd c.BCE)
KOREA: [dolmens (1000 BCE)][MA]; [Buddh. temple (sa)]
· Baekdudaegan Mountain/Changbaishan [“Long White Mountain”][V](2333-108 BCE: Gojoseon; Later d.: Buyeo-Goguryeo-Goryeo-Joseon; sacred ritual site; Jurchen-Jin d.; Manchu; Ryanggang, North Korea; Jilin, China; Heaven Lake)
· Beomeosa (678 CE: Hwaeom Buddh.; national treasures: stone pagodas; Busan; South Gyeongsang)
· Beopjusa (653 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Songnisan m.; Boeun; North Chungcheong)
· Bongeunsa (794 CE: Buddh.; Seoul)
· Bongseonsa (969 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Seoul; Gyeonggi)
· Bongwonsa (889 CE: Buddh.; Seoul)
· Bulguksa (528 CE: Jogye Buddh.; 7 national treasures: Dabotap, Seokgatap stone pagodas; North Gyeongsang)
· Donghwasa (493 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Palgongsan; Daegu; North Gyeongsang)
· Ganghwa
· Geumsansa (600 CE: Jogye Buddh.; national treasures; Moaksan m.; Gimje; North Jeolla)
· Gochang
· Guinsa (1945 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Sobaek m.; Danyang; North Chungcheong)
· Haeinsa (802 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Three Jewels Temple; 1398 CE: Tripitaka Koreana; Gaya m.; South Gyeongsang)
· Hwaeomsa (544 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Three Jewels Temple; d.1590s; Jirisan m.; Gurye; South Jeolla)
· Hwangnyongsa [“Golden/Yellow Dragon Temple”](553 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Gyeongju; North Gyeongsang)
· Hwasun
· Jikjisa (418 CE: Jogye Buddh.; d.1590s; r.1610; Hwangaksan; Gimcheon; North Gyeongsang)
· Jogyesa (1395 CE: Buddh.; Seoul)
· Magoksa (640 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Gongju; South Chungcheong)
· Miruksa (602 CE: Buddh.; Iksan; North Jeolla)
· Musangsa (Zen Buddh.; Jogye m.; Daejeon)
· Naksansa (671 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Naksan m.; Sokcho; Gangwon)
· Oseam (643 CE: Buddh.; Seorak m.; Gangwon)
· Pohyonsa (11th c. CE: Buddh.; Myohyang m.; Hyangsan; Jeollabuk)
· Seonunsa (6th c. CE: Jogye Buddh.; Dosolsan m.; Gochang; North Pyongan)
· Silleuksa (580 CE: Buddh.; Yeoju; Gyeonggi)
· Sinheungsa (653 CE: Seon/Zen Jogye Buddh.; Seoraksan m.; Sokcho; Gangwon)
· Songgwangsa (Zen Jogye Buddh.; Three Jewels Temple; Jogye m.; Suncheon; South Jeolla)
· Ssanggyesa (722 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Jirisan m.; Hadong; South Gyeongsang)
· Sudeoksa (1308 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Deoksungsan; South Chungcheong)
· Tongdosa (646 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Three Jewels Temple; Chiseosan m.; Yangsan; South Gyeongsang)
· Woljeongsa (643 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Odaesan m.; Pyeongchang; Gangwon)
· Yongjusa (854 CE: Jogye Buddh.; Hwaseong; Gyeonggi)
KYRGYZSTAN:
· Issyk Kul Lake [SR](500 BCE)
· Gazzalakonda cairn
· Sulayman Mountain [SM] (several millennia: place of worship; Muslim; Osh)
LAOS:
· Oum Moung (13th c.CE; Angkorian temple; near Wat Phou)
· Plain of Jars [MA](500 BCE; Xieng Khouang)
· Pha That Luang (3rd c.CE: stupa; national symbol; Vientiane)
· That Dam/Black Stupa (stupa; according to legend: protected by seven-headed naga; Vientiane)
· Wat Phou (5th c.CE/11th-13th c.CE: Khmer temple; Mekong r.; Champasak)
LEBANON:
· Anjar (c.600 CE: Umayyads)
· Baalbek [MA](2900 BCE)
· Byblos (3000 BCE: oldest port; cedar)
· Fakhredine Mosque (1493 CE: Islamic; Deir el Qamar)
· Khatem Al-Anbiyaa Mosque (Beirut)
· Mansouri Great Mosque (1294-1314 CE: Norman-Mamluk Islamic; Tripoli)
· Sayyida Khawla Mosque (Beirut)
· Sidon (6000 BCE: Neolithic; 4000 BCE: Egypt-Canaanite; Phoenician capital)
· Tyre (2750 BCE: Egypt-Canaanite; sea port)
MALAYSIA:
· Batu Caves (1891 CE: Murugan-Hindu; Gombak, Selangor, Kuala Lumpur)
· Bujang (Dragon) Valley (300 CE: Hindu-Buddhist)
· Cheng Hoon Teng [“Temple of Green Cloud”](1645 CE: Taoist; Malacca)
· Dhammikarama Burmese Temple (1803 CE: Theravada Buddh.; Penang)
· Kek Lok Si [“Temple of Supreme Bliss”](1890 CE: Buddh.; Air Itam; Penang)
· Kota Tampan (300000 BP: Paleolithic; Lenggong)
· Niah Caves (40000 BP; Sarawak; Miri)
· Snake Temple (1850 CE: Buddh.; Penang)
· Sungai Tingkayu
· Wat Chaiya Mangkalaram (1845 CE: Thai Buddh.; Penang)
MONGOLIA: [kurgans; Tib.Buddh. temples/monasteries]
· Amarbayasgalant Monastery (1727 CE: Buddh.; Baruunburen Sum; Selenge)
· Erdene Zuu Monastery (1585 CE: Buddh.; Kharkohin; Ovorkhangai)
· Gandantegchinlen Gompa [“Great Palace of Complete Joy”](1835 CE: Tib.Buddh.; Ulaanbaatar)
· Karakorum (13th c.CE: Mongolian e.; Hujurt)
· Noin-Ula kurgans [SR](2nd c.BCE: 200 large kurgans- square footprint, timber burial chambers w/deep shafts, horse burials, lavish furnishings, Chinese coffin, Chinese Xian-ping lacquer cups, Greco-Bactrian textiles; burial tomb of Xiongnu- ruler of Hun federation; 13 CE: Kurgan 6- tomb of Uchjulu-Jodi-Chanuy; Selenga r.; N Ulan Bator)
· Shankh Monastery (1647 CE: Buddh.; Kharkohin; Ovorkhangai)
NEPAL: [Hindu-Buddhist temples, shrines (stupa)]
· Adinath Lokeshwar Mandir (15th c.CE: Chobar)
· Ashok Stupa, Pulchowk (Lalitpur)
· Ashok Stupa, Lagankhel (Lalitpur)
· Bhadgaon
· Bodhnath (500 CE: largest Buddhist Stupa in the world; Bagmati)
· Bungmati (Lalitpur)
· Changu Narayan (3rd c.CE: Vishnu Temple; Thimi)
· Devadaha (Gautama Buddha holy site of preaching; near Kapilvastu)
· Indradev Samskarita Jay Manohar Varma Mahavihara (Su Baha; Lalitpur)
· Itumbahal (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Janabahal (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Kangchenjunga [SM] [Nepali: “The Five Treasures of Snows”](Himalayas)
· Kankre Bihar (Surkhet)
· Kapilavastu (7th c.BCE: Tilaurakot- Shakya fortress founded by Gautama Buddha’s father, Suddhodana; near Lumbini)
· Kathmandu
· Kirtipunya Mahabihar (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Lokeshwar, Chobhar (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Lumbini (563-483 BCE: birthplace of Siddhartha Gautama Buddha; Rupandehi; Kapilbastu)
· Machapuchare [SM] [Nepali: “Fish’s Tail”](sacred to Hindu Shiva; Annapurna Himal)
· Mahabauddha (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Mahamanjushree (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Manakamana [“heart/soul wish”] (1600s CE: Manakamana-Hindu; Gandaki, Gorkha)
· Manjushree temple (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Muktinath (Hindu-Buddh; Beni/Dhawalagiri; Rasuwa)
· Nyatapola (1701 CE: 5 story pagoda; Bhaktapur)
· Ombahal (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Pashupatinath (5th c.CE: largest Hindu Shiva pagoda temple in the world; Kathmandu; Bagmati r.)
· Patan
· Shankerdev Samskarita Mayurvarna Mahavihara
· Sheeghal (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Swayambhunath/Monkey Temple [Tibetan: “shrine to the eternal self-existent flame”] (5th c.BCE: Buddha teaches at site; 3rd c.BCE: Emperor Ashoka built a temple later destroyed; 5th c.CE; Kathmandu)
· Tukanbahal (Buddh.; Kathmandu)
· Vajrayogini (Thimi)
PAKISTAN: [Buddhist stupa]
· Badshahi Mosque (1671 CE; Lahore)
· Butkara Stupa (2nd c.CE: Mauryan; Swat)
· Dharmarajika [SR](3rd c.BCE: Buddhist stupa; Taxila)
· Dholavira (2nd m.BCE: Harappa culture)
· Harappa (3300 BCE; Sahiwal)
· Kanishka Stupa [SR](2nd c.CE: Kushan; Peshawar; Shah-Ji-ki-Dheri)
· Katasraj Temple (6th c.CE: Hindu; legend: Mahabharata, Pandava; Katas, Chakwal, Punjab)
· Lahore Fort (4th c.CE: gold coins; 1025 CE)
· Mankiala (7th c.CE; Rawalpindi)
· Mehrgarh (7000 BCE; Balochistan)
· Mohabbat Khan Mosque (1670 CE: Islamic; Peshawar)
· Mohenjo Daro [MA](Larkana) (2600 BCE: Harappa culture/Indus Valley)
· Rakhigarhi (2nd m.BCE: Harappa culture)
· Ranikot Fort (400-836 CE; Hyderbad)
· Rohtas Fort (1500 CE; Dina)
· Sialkot Fort (2500 BCE; 2nd c.CE)
· Takht-i-Bahi (1st c.BCE; Mardan)
· Taxila [SR](600 BCE: oldest university; Islamabad)
PHILIPPINES:
· Sheik Karimal Makdum Mosque (1380 CE: Islamic; 1st mosque in Philippines; Tawi-Tawi)
RUSSIA: [cave paintings; Shang d. China (Bronze Age) influence]
(see also Russia in Europe)
· Arkaim (2000 BCE: Proto-Aryans; Earliest Chariot; Chelyabinsk)
· Avdeevo
· Gambell Sites
· Ignateva Cave (6000 BCE: microliths, cave paintings; Chelyabinsk
· Krivoye Ozero (2000 BCE: Magnitogorsk)
· Mezin (13000 BCE)
· Okladnikov (45-28k BP: Neanderthal-human)
· Orvik
· Pazyrryk culture
· Pshada r. dolmen
· Sintashta (2000 BCE: Proto-Aryans; Arkaim)
· Talitski (13000 BCE)
· Ubsunur Hollow (between Tannu-Ola and Altai mts.) (4000 BCE: 20,000 burial mounds; Tuva)
· Uelen (500 BCE)
· Yeliseevichi
SAUDI ARABIA:
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Al-Masjid al-Haram [“The Sacred Mosque”]/Grand Mosque (638 CE: Sunni-Salafi Islamic; Kaaba; Mecca)
· Rajajil Stones [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; Dumat al Jandal; in line with 30th parallel and Giza; in N-S line with Mecca; S Sakakah; Al Jawf)
SRI LANKA:
· Anuradhapura (10th c.BCE: Protohistoric; ancient sacred capital)
Eight Great Places (Atamasthana) of Veneration in Anuradhapura:
1) Abhayagiri Dagaba (2nd c.BCE; Anuradhapura)
2) Jaya Sri Maha Bodhiya (288 BCE: sacred fig tree; Anuradhapura)
3) Jetavanaramaya (2nd c.CE; Anuradhapura)
4) Lankarama (stupa; Anuradhapura)
5) Lovamahapaya (building; Mahawamsa)
6) Mirisaveti Stupa (Anuradhapura)
7) Ruwanwelisaya (dagoba stupa; Anuradhapura)
8) Thuparamaya (1862: dagoba-stupa; Anuradhapura)
Isurumuniya (5th c.CE: rock temple)
Maha Viharya
Mihinthale
Other Structures:
o Dakkhina Stupa (2nd c.BCE: stupa built over ashes of King Dutugemunu)Isurumuniya (4th c.CE: viharaya cliff temple and stupa; Tisawewa)
o Kiribath Vehera
o Kuttam Pokuna (bathing pool/tank)
o Magul Uyana (ancient garden)
o Naka Vihara (stupa; clay caskets)
o Queen’s Palace
o Rathna Prasadaya (2nd c.CE: skyscraper)
o Sela Cetiya (1st c.BCE: stupa)
o Samadhi Statue
o Toluwila Statue
o Vessagiri (rocks and caves)
· Dambulla cave temple/Golden Temple of Dambulla (2700 BP: bones; 1st c.BCE: Hindu-Buddh.; 5 caves; E Colombo, N Kandy)
· Kalutara Vihara (world’s only hollow dagoba/Buddhist shrine with 74 murals of Buddha’s life)
· Kelaniya Raja Maha Vihara (500 BCE: Buddh.; Colombo)
· Ketheeswaram Temple (7th c.CE: Dravidian Shiva-Hindu; Manthai, Mannar)
· Kothduwa Temple (1860 CE: Buddh.; 340 CE: Buddha tooth relic; Kothduwa)
· Nallur Kandaswamy Temple (1749 CE: Murugan-Hindu; Jaffna)
· Rankoth Viharaya (Buddh.; Panadura)
· Senanayake Aramaya (Buddh.; sacred hair relic; Madampe)
· Solosmasthana (16 sacred places believed to have been visited by Gautama Buddha):
1) Abhayagiri Dagaba (2nd c.BCE; Anuradhapura)
2) Dighavapi (3rd c.CE: Buddhist sacred shrine; “Long Tank;” Ampara)
3) Diva Guhava (cave where Buddha stayed; Ratnapura)
4) Jaya Sri Maha Bodhi
5) Jetavanaramaya (see above)
6) Kelaniya Raja Maha Vihara (before 500 BCE: Buddhist temple; Buddha visitation)
7) Kiri Vehera (3rd c.BCE: stupa; Kataragama)
8) Mahiyangana (543 BCE: Buddha’s clavicle bone is enshrined; 2nd c.BCE: renovated stupa)
9) Mirisavetiya (see above)
10) Muthiyangana Raja Maha Vihara (5th c.BCE: Buddhist temple; visited by Gautama Buddha; Badulla)
11) Nagadipa (built by Naga kings)
12) Ruwanwelisaya (see above)
13) Sela Cetiya
14) Sri Pada/Adam’s or Buddha’s Footprint (Ratnapura, Sabaragamuwa)
15) Tissamaharama (2nd c. BCE: large dagoba-stupa; Rahuna; Yala NP)
16) Thuparamaya (see above)
· Sri Dalada Maligawa/The Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic (1595 CE: Buddh.; Kandy)
SULTANATE OF OMAN:
· Amlah (Bronze Age: burial ground; al-Zahirah)
· Lizq (fortified mountain settlement)
· Ras al-Jins (settlement and burial area)
· Samad al-Shan (Samad culture burial area; al-Mudhaybi; Sharqiyah)
· Shir (burial ground)
SYRIA:
· Aleppo/Halab [SR](5000 BCE: Amorite; 1600 BCE: Hittite; 800 BCE: Assyrian; 333 BCE: Greek; 64 BCE: Roman)
· Al-Fadael Mosque (1062 CE: Islamic; Hims)
· Al-Nouri Mosque (1129 CE: Islamic; Hims)
· Aqsab Mosque [SR](1234 CE: Ayyubid Islamic; Damascus)
· Bosra (14th c.BCE)
· Darwish Pasha Mosque [SR](1574 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Damascus)
· Dederiyeh (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Dura Eurpous
· Ebla [t. “white rock;” Sum.: “light beer”] (2500 BCE: Akkadian/Egyptian inscriptions; 17000 cuneiform tablets written in Sumerian to record Eblaite lang. <prev.unknown Semitic lang.; 2nd oldest written lang. to Akkadian>
· Great Mosque of Aleppo [SR](1090 CE: minaret; 13th c.CE: Mamluk Islamic; said to entomb of Zechariah, father of John the Baptist; Aleppo)
· Nabi Habeel [“Abel”] Mosque [SR](1599 CE: Islamic; believed to contain the grave of Abel, son of Adam; Barada r.; Damascus)
· Nur al-Din Mosque (1172 CE: Islamic; Hama)
· Palmyra/Tadmor [Amor.: “town that repels”] (2nd m. BCE: temple of Bel; crossroads between Meditarranean and Euphrates)
· Sinan Pasha Mosque [SR](1590 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Damascus)
· Tell Abu Hureyra [SR](11500 BP: Mesolithic/Natufian culture; l.Assad; Aleppo)
· Tell Halaf (Neolithic; 750 BCE: ivory panel of tree of life; Iraq Museum; Ras al’Ayn)
· Tekkiye Mosque [SR](1544-58 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Damascus)
· Ugarit [Arabic: “cape of wild fennel”] (6000 BCE: Neolithic wall fortification; necropolis; Phoenician; Ras Shamra)
· Umayyad Mosque [SR](715 CE: Umayyad Islamic; Damascus)
· Mari (5th m.BCE: 260 room palace; 25000 Akkadian tablets; Tell Hariri; Abu Kamal)
· Qatna (3rd m.BCE: Bronze Age; Tell el-Mishrife; near Homs)
· Zenobia
THAILAND: [Buddhist temple (wat); village (ban)]
· Ban Chiang (4420 BCE: earliest Bronze Age in the world; Nong Han; near Udon Thani)
· Ban Grong Greng Rin (Buddh. village; Phitsanulok)
· Ban Laemphrathat (Buddh. village; Phitsanulok)
· Ban Non Wat (Neolithic: burials; ancient Khmer highway; Non Sung; Phimai; near Nakhon Ratchasima)
· Krue Sae Mosque (16th c.CE: Islamic; Pattani)
· Mueang Sing (1180-1219 CE; Sai Yok, Kanchanaburi)
· Muang Tum (10th c.CE: Khmer temple; Prakhon Chai)
· Phra Pathom Chedi (4th c.ce: artifacts; 11th c.CE: Khmer prang; 1870; tallest stupa in world; Nakhon Pathom; Bangkok)
· Phanom Rung (10th c.CE: Shiva temple; Buriram)
· Phra That Si Song Rak (1560 CE: Lan Xang-Ayutthaya Kingdom; stupa; Dan Sai)
· Phimai (7th/11th c. CE; end of ancient Khmer Hwy)
· Sdok Kok Thom (11th c.CE: Khmer Shiva temple; NE Aranyaprathet)
· Wat Arun [“Temple of the Dawn”](1809 CE: Buddh.; Chao Phraya r.; Bangkok)
· Wat Benchamabophit Dusitvanaram (1899 CE: Buddh; Bangkok)
· Wat Bunglam (Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Chedi Liem (13-18th c.CE: Buddh.; Ping r.; Wiang Kum Kam; Chiang Mai)
· Wat Chedi Luang (14th c.CE: Buddh.; Chiang Mai)
· Wat Chedi Yot Thong (Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Chiang Man (1297 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Mai)
· Wat Chulamani (Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Nang Phaya (1450 CE: Buddh. monastery; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Pho/Temple of Reclining Buddha (1788 CE: Buddh.; birthplace of Thai massage; Bangkok)
· Wat Phra Kaew (18th c.CE: Hindu-Theravada Buddh.; Bangkok)
· Wat Phra Kaew (940 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Rai)
· Wat See Bun Mayiga Ram (Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Phra Si Rattana Mahathat Woramahawihan (1357 CE: Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Phra Singh (1345 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Mai)
· Wat Phra Singh (1385 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Rai)
· Wat Phrathat Doi Chom Thong (940 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Rai)
· Wat Phrathat Doi Suthep (1383 CE: Buddh.; Chiang Mai)
· Wat Ratchaburana (1463 CE: Buddh.; Phitsanulok)
· Wat Ratchanadda (1846 CE: Buddh.; Bangkok)
· Wat Suthat (1807 CE: Buddh; giant swing; Bangkok)
· Wat Umong (1300s CE: Buddh.; Chiang Mai)
TURKEY:
[NOTE 94] Hittite language (Indo-European- similarities to Sanskrit, Greek, English, German) studied by Bedrick Rosney (Czech)
· Aigai (3rd-2nd c.BCE; Aeolis)
· Akdamar Is. (915 CE: Cathedral of the Holy Cross; l.Van)
· Akhisar/Thyatira (3000 BCE: Hittite)
· Alabanda (Greco-Roman; Doganyurt/Araphisar)
· Alaca Hoyuk (4th m.BCE: Hattian-Hittite: mound w/burials in fetus position facing south, gold-iron sword, sun disk, sphinx gate, dams; Hattusa; Bogazkale)
· Alalakh (2000 BCE: Amorite; Tell Atchana; near Antioch/Antakya)
· Alexandria Troas/Sigia (310 BCE: Greco-Roman; Bozcaada)
· Alinda (2nd m.BCE: Hittite; Caria; Karpuzlu)
· Alisar (4th m.BCE; Yozgat)
· Allianoi (Prehistoric: Yortan vessel, flint stones; Hellenistic; 2nd c.CE: Roman: insulae, propylon, nympheum; Bergama)
· Amuk (Antakya)
· Anastasian Wall (aka.Long Walls of Thrace)(5th c.CE: from Evcik Iskelesi to Sea of Marmara- 56km)
· Ani (5th c.CE; Kars)
· Ankara (Hittite)
· Antigonia (Syria)
· Antioch/Antakya [SR](4th c.BCE)
· Antioch on the Maeander (Pythopolis; Kuyucak)
· Antioch, Pisidia (Yalvac)
· Antiochia Lamotis (Erdemli)
· Antiochia ad Cragum (170 BCE: Cragus, Sidyma)
· Antiochia Pyramum (Cilicia; Karatas)
· Antiochia, Lydia
· Apamea (Phrygia) (Greco-Roman; Burdur)
· Apamea Myrlea (202 BCE; Mudanya)
· Aphrodisias (Hellenistic; Roman; Caria; Geyre)
· Apros (Trace; Roman-Catholic; unknown loc; near Tekirdag)
· Ararat/Mount Judi [SM](mythological landing place of Noah’s Ark; beginning place of post-diluvial civilization; Sirnak; Armenian Highland)
· Ariassos (Antalya; Dag)
· Arycanda (2nd m.BCE; Aykiricay, Antalya)
· Aspendos (1000 BCE: Greco-Roman; Serik)
· Attalia/Antalya (3rd c.BCE)
· Bayezid II Mosque [SR](1501-6 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Istanbul)
· Bogazxoy (aka. Hattusa: Hittite)
· Bursa Grand Mosque (1396-1400 CE: Seljuk Islamic; Bursa)
· Carchemish (Hittite)
· Catalhoyuk [t.Turk.: “fork mound”] (7500 BCE; Konya)
· Cayonu (7200 BCE; Diyarbakir)
· Cebrene (Greco-Roman; Alexandria; Bayramic)
· Ceramus (Oren)
· Corycus (191 BCE; Kizkalesi)
· Cremna, Pisidia (25 BCE)
· Didyma [MA]
· Digda (Tire; Odemis)
· Dorylaeum (Roman; Eskisehir)
· Edessa, Mesopotamia (2nd c.BCE; Sanliurfa)
· Eflatunpinar (Hittite)
· Ephesus/Apasas (6000 BCE: Hittite; 550 BCE: Temple of Artemis, 7 wonders; theatre; Roman; Selchuk)
· Elaiussa Sebaste [t.Gk.:”olive”] (2nd c.BCE: Roman; Silifke; Mersin)
· Emirdag (1437 BCE: Hittite; Afyon; Eskisehir)
· Epiphania, Cilicia (orig.Oiniandos; 2nd c.BCE; Cukurova; Adana)
· Euromus (6th c.BCE: temple of Zeus Lepsinos; Kyromus/Hyromus; Selimiye; Milas)
· Eyup Sultan Mosque [SR](1458 CE: Islamic; Istanbul)
· Fatih Mosque [SR](1463-70 CE: Islamic; Istanbul)
· Gavurkale (Hittite)
· Gobekli Tepe [MA] [t.Turk.: “hill with a navel”](10000 BCE; Sanliurfa)
· Gordium (12th c.BCE: Thracian; Polatli)
· Great Temple and Yerkapi rampart [MA](2000 BCE; Hattusa/Bogazkale)
· Hasankeyf (1800 BCE)
· Hacilar (7400 BCE; Burdur)
· Hagia Sophia [MA][SR](532-7 CE: Byzantine; 1453: church converted to Ayasofya mosque; Islamic; Istanbul)
· Harran [t.Akk.: Harranu, “road, path; campaign journey”](1100 BCE: Babylonian; Roman; home of moon god, Sin)
· Hattusa [MA](6th m.BCE: Neolithic; fortresses, tunnels, fountain irrigation; Hatti; Hittite capital; sphinx; Bogazkale)
· House of Virgin Mary (Ephesus)
· Hosap Castle (Guzelsu)
· Iopolis (Greek: where moon goddess Io was worshipped; mt. Silpion; Antioch)
· Ivriz (8th c.BCE; Hittite-Assyrian; Eregli)
· Jagca Koy (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Kerkenes (pre-Hellenistic; Yozgat)
· Knidos (Hellenistic: Dorian Hexapolis; Tekir)
· Kadirli/Kars [SR](Hittite; Adana)
· Kaman-Kalehoyuk (Bronze Age; 1800 BCE: oldest steel fragments)
· Karabel (Hittite)
· Karaman/Laranda (Greek)
· Karatepe [t.”black hill”] (Hittite fortress)
· Kestel (3290 BCE: Bronze Age: tin mining; Taurus mts.; Karaman)
· Kultepe/Kanesh (2000 BCE; Kayseri)
· Kusakli (16th c.BCE: Hittite; Basoren/Altinyayla)
· Kustul Monastery (752 CE; Trabzon)
· Laleli Mosque [SR](1783 CE: Baroque Islamic; Istanbul)
· Magnesia on the Maeander (Hellenistic city; Germencik)
· Metropolis (Neolithic: temple of Ares; Torbali; Izmir)
· Miletus (Neolithic; Minoan; Cretan; Achaean; Akkoy)
· Nemrud Dagi [MA](62 BCE: Armenian Highlands, Adiyaman)
· Nevali Cori (8th m.BCE: Neolithic: temples, monumental sculpture; Vedic; Urfa)
· Nuruosmaniye Mosque [SR](1749-55 CE: Ottoman Baroque Islamic; Istanbul)
· Olympos (Hellenistic; Kemer)
· Patara/Arsinoe (Hellenistic: oracle center, theatre, temple of Apollo; Gelemis)
· Perga (12th c.BCE: acropolis; Antalya)
· Pergamon/Bergama (281 BCE: Greek city; acropolis)
· Panionium (550 BCE: Ionian sanctuary of Poseidon; Soke; Izmir)
· Pednelissus, Pisidia (2nd c.CE; near Selge; Kozan)
· Pepuza (2nd c.CE: center for Christian church of Montanism; Tymion; Karahalli)
· Phaselis (700 BCE: Rhodians; Kemer)
· Pinarbasi Golu (spear heads, dagger, axes; Anatolia)
· Pompeiopolis (Roman; Taskopru)
· Rustem Pasha Mosque [SR](1561-3 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Istanbul)
· Sagalassos (8000 BCE; 14th c.BCE: Hittite; Aglasun; Isparta; Burdur)
· Sardis (472 BCE: Greek-Persian; Izmir)
· Samosata (7000 BCE: relics; 160 BCE: Hellenistic capital; Samsat; Adiyaman damn)
· Sapinuwa [t.Hattic: sapi, “god”] (17th c.BCE: Bronze Age: Hittite city; Ortakoy; Yozgat)
· Seleucia/Pamphylia (Greco-Roman: agora, mausoleum, necropolis; Side; Manavgat)
· Seleucia Pieria/Palaeopolis [SR][t.Gk.: “old city”] (300 BCE; part of Syrian tetrapolis- Apamea, Laodicea, Antioch; necropolis; Samandag)
· Seleucia Sidera (Roman: Egirdir; Isparta)
· Selge, Pisidia (Hellenistic; acropolis)
· Selimiye Mosque (1575 CE: Islamic; Edirne)
· Skepsis (Kursuntepe; Bayramic)
· Smyrna (7th-4th m.BCE: Chalcolithic-Neolithic settlements; 3rd m.BCE: Bayrakli; 1500 BCE: Hittite; 11th c.BCE: Aeolian-Greek; 610 BCE: Lydian; 545 BCE: Persian; 340 BCE: Alexander; 133 BCE: Roman; 178 CE: earthquake devastation; 1076 CE: Seljuk Turks; 1204: 4th Crusade; 1389: Ottoman Empire; Izmir)
· Stratonicea [name of Seleucid’s wives](Lydia)/Indi/Hadrianopolis (Hellenistic: Siledik; Kirkagac)
· Suleymaniye Mosque [SR](1557 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Istanbul)
· Sultan Ahmed Mosque/Blue Mosque [SR](1616 CE: Ottoman Islamic; Istanbul)
· Sumela Monastery (386 CE; Trabzon)
· Tell Tayinat [SR](Hittite/Aramean; Antioch)
· Tille (4th m.BCE: surface pottery; Adiyaman)
· Toprakkale/Rusahinili [t.Urart.: “city of king Rusa II”] (9th c.BCE; Van; Ararat)
· Tripolis (Phrygia)/Neapolis/ Apollonia/Antoninopolis (Greco-Roman: necropolis; Yenicekent; Denizli)
· Trocmades (Roman-Catholic; Eskisehir)
· Tushhan (Iron Age: Assyrian; Ziyaret Tepe)
· Tyana (2nd m.BCE: Hittite; Nigde)
· Termessos (Anatolian: necropolis, theatre, gymnasium; Gulluk Dagi)
· Troy/Wilusa/Truwisa)
· Xanthos/Arinna (Hittite; Luwian; Greco-Roman; Kinik)
· Yazilikaya [t.Turk.:”inscribed rock”](15th c.BCE: Hittite; Corum)
· Yenikapi [SR](6500 BCE; Istanbul)
· Yesil Mosque (1421 CE: Islamic; Bursa)
· Yesilova Hoyuk [t.Turk.: “mound”](6500 BCE; Bornova; Izmir)
· Zeugma [t.Gk.:”yoke”]
· Zincirli Hoyuk/Samal (10th c.BCE: Syro-Hittite)
TURKMENISTAN: (p.USSR)
· Merv/Meru/Margiana [SR](Prehistoric; 3rd m.BCE: possible origin of Hindu Mt.Meru; 12th c.CE: largest city in world; Mary)
UZBEKISTAN: (p.USSR)
· Aman-Kutan (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Bibi-Khanym Mosque [SR](1399-1404 CE; 1897 CE: earthquake; Islamic; Samarkand)
· Bukhara [t.Soghdian: “lucky place”] [SR](3000 BCE: Sapalli culture; 6th c.BCE: Persian)
· Po-i-Kalyan [SR](1514 CE: Islamic; Bukhara)
· Samarkand [SR] (700 BCE)
· Teshik-Tash (250-45k BP: Neanderthal-human)
· Ulugh Beg Madrasa [SR](Islamic; Samarkand)
VIETNAM:
· Bao Quoc Pagoda (1670 CE: Buddh.; Hue)
· Buu Phong Temple (17th c.CE: Buddh,; Ho Chi Minh; Dong Nai)
· Dong Duong (Hindu temple)
· Hoa Lai (Hindu temple)
· Keo Temple (1061 CE: Buddh.; Thai Binh)
· Mi Son [SR](4th c.CE: Champa Bhadresvara/Shiva-Hindu; linga; Duy Phu, Quang Nam)
· One Pillar Pagoda (1049 CE: Buddh.; Hanoi)
· Perfume Pagoda (1400s CE: Buddh.; Hanoi)
· Pho Minh Temple (1262 CE: Buddh.; Nam Dinh)
· Po Nagar (Hindu temple)
· Quan Su Temple (15th c.CE: Sangha Buddh.; Hanoi)
· Quoc An Temple (1600s CE: Buddh.; Hue)
· Thien Mu Pagoda (1601 CE: Buddh.; Hue)
· Vinh Trang Temple (19th c.CE: Buddh.; My Tho; Tien Giang)
YEMEN:
· Marib (2000 BCE: Sabaean capital)
· Zafar (110 BCE: Himyarite capital; Yarim)
EUROPE:
ALBANIA: (Ancient Greek)
· Antigonea (Chaonia; Saraqinisht, Gjirokaster);
· Apollonia (588 BCE: Gylakeia; Pojan, Fier);
· Berat (Bulcheriopolis);
· Butrint (1000 BCE: Bouthrotios; Sarande);
· Durres (627 BCE: Epidamnos/Dyrhacchion)
· Finiq (Phoenice: Delvine);
· Lezhe (Lissos);
· Orikum (Oricum);
· Shkoder (400 BCE: Shkodra);
AUSTRIA: [cathedrals, abbeys]
[NOTE 22] Most Austrian abbeys were dissolved by Emperor Joseph II (ruler of Habsburg dominions from 1780-90) in 1783.
· Admont Abbey (f.1074 CE: Benedictine; Baroque; art, 1400 manuscripts, 200000 vol.; fire in 1865; burials- Gebhard of Salzburg, Englebert of Admont; Enns r.; Styria)
· Aggsbach Charterhouse (f.1380- d.1782 CE: Carthusian monastery; Aggsbach)
· Altenburg Abbey (f.1144 CE: Benedictine; Baroque; Altenburg)
· Burgstallkogel (800 BCE: Urnfield culture; mounds; Gleinstatten, Leibnitz)
· Engelszell Abbey (f.1295 CE: Cistercian; fire in 1699; rf.1925: Trappist; Rococo; Engelhartszell)
· Flavia Solva (Celto-Roman; Leibnitz)
· Gaming Charterhouse (f.Albert II, Duke of Austria; 1330 CE: Carthusian; burial- Albert II; d.1782; Gaming)
· Garsten Abbey (f.Ottokar II of Styria; 1080-2 CE: Benedictine; dynastic burial place; 1110-1: independent; d.1787; 1851: prison; High Baroque; Garsten)
· Geras Abbey (f.1153 CE: daughter house of Seelau Abbey; Premonstratensian canons; Romanesque-Baroque basilica; Geras)
· Gleink Abbey (f.Arnhalm I of Glunich converted castle; 1120 CE: Benedictine; ded.Saint Andrew; fire dmg.in 1220/1275/1313; 15th c.CE: Hungarian invasions; 1532: Turk marauders; Baroque; d.1784; library; 1832: Salesian Sisters; Steyr)
· Goss Abbey (f.Adela of Leoben, wife of Count Aribo I; 1004 CE: Benedictine nunnery; 1020: imperial abbey by Henry IV; Styrian aristocracy school; d.1782; Gothic abbey church; frescoes; Romanesque crypt; Styria)
· Gottweig Abbey (1072-83 CE: Benedictine; 1580: fire dmg.; 1604: rebuilt; 1718: burned-rebuilt Baroque; Krems)
· Grossmugl (600 BCE: Kalenderberg culture; largest burial mound/tumulus in central Europe; Korneuburg)
· Gurk Abbey (f.Saint Hemma of Gurk; 1043-d.1072 CE: Benedictine double monastery; Gurk)
· Gurk Cathedral (1140-1200 CE: Catholic basilica; Gurk)
· Heiligenkreuz Abbey (f.Saint Leopold; 1133 CE: Cistercian; 1739: Baroque church; Heiligenkreuz)
· Herzogenburg Priory (1014 CE: Priory church; f.1112 CE: Augustinian; 1244: flooding- moved up river from Traismauer as Saint Georgen; 1714: Baroque; Gothic art; Herzogenburg)
· Klosterneuburg Priory (f.Saint Leopold; 1114 CE: Augustinian; 1181: Verdun Altar: burial- Saint Leopold, Kaiser of Holy Roman Empire; 1634: Habsburgs rebuilt Baroque; Klosterneuburg)
· Kremsmunster Abbey (f.Tassilo III, Duke of Bavaria; 777 CE: Benedictine; 10th c.: d.Hungarian raid; dmg.during Napoleonic wars; Mathematical Tower w/astronomical observatories; 1680-9: library- 160000 vol., 1700 manuscripts, 2000 incunabulae, 800 CE: Codex Millenarius; treasure- Tassilo Chalice; Kremsmunster)
· Lambach Abbey (f.Adalbero of Wurzburg; 1040 CE: Benedictine; Romanesque frescoes; 17-18th c.: Baroque; d.1941 by Nazis; Lambach)
· Lilienfeld Abbey (f.Leopold VI, Duke of Austria; 1202 CE: Cistercian; daughter house of Heiligenkreuz Abbey; 1683: turned into fortress to resist Turk advance; 17th c.: Baroque; 1789: suppressed; 1810: dmg.fire-rebuilt; winemaking at Lilienfelderhof-monastic grange; burials- Leopold VI; Lilienfeld)
· Mauerbach Charterhouse (f.Frederick the Handsome; 1313-d.1782 CE: Carthusian; burial- Frederick the Handsome; Baroque; Mauerbach)
· Melk Abbey (f.1089 CE: Benedictine; 12th c.: f.school; scriptorium; 15th c.: Melk Reform; 1702-36: Baroque; Danube r.; Melk)
· Michaelbeuern Abbey (736 CE: Benedicitine; 977: reconstr. After Hungarian wars; 1346: fire; 1691: Baroque; Dorfbeuern)
· Millstatt Abbey (f.Count Aribo II; 1070 CE: proprietary monastery; 1452: fell to Habsburg; 1478: dmg.Turks; 1487: Hungarian attacks; 1737: crypto-protestantism; -Habsburg; Millstatt)
· Mittelberg Hill (1600 BCE: Bronze Age: star disc; earthworks; copper mine)
· Mondsee Abbey (f.Odilo, Duke of Bavaria 748 CE: Benedictine; 800: Codex Millenarius, illustrated Latin book of the Gospels, written here; 831: King Louis the Pious gave abbey to Regensburg Cathedral; 1142: independent under Abbot Conrad II-martyred; d.1791; 1810: acquired by Bavaria during Napoleonic wars; Mondsee, former Bavaria)
· Neuberg Abbey (f.Habsburg Duke Otto the Merry; 1327 CE: Cistercian; 1330: High Gothic hall church; cloisters, chapter house; 1612: Baroque high altar; 1786: suppressed; 1850: converted into hunting lodge; Neuberg)
· Nonnberg Abbey (f.Saint Rupert; 714 CE: Benedictine; 987: independent; 1000: rebuilt; 1423: fire; 1464-1509: reconstruction; 1624: enlarged; 1880s: Baroque; Maria Augusta Kutschera/von Trapp- basis for The Sound of Music; Salzburg)
· Ossiach Abbey (est.Count Ozi; 1024 CE: Benedictine; legend: King Boleslaw II the Bold of Poland, after he was banished in 1079 for the murder of Saint Stanislaus of Krakow, worked his penance for 8 years, until his death there; 1215: Romanesque tower; 1484: fire- Late Gothic; 1641: Baroque
· Pernegg Abbey (f.w/Geras abbey; d.1783; near Geras)
· Rein Abbey (f.Leopold the Strong; 1129 CE: Cistercian; 1276: Rein Oath- Styrian-Carinthian nobility pledged allegiance to Rudolf of Habsburg, ending the rule of King Ottokar II of Bohemia; Romanesque-Renaissance; Gothic Chapel of the Cross; library- 100000 items, 390 manuscripts, 150 incunabula; Rein)
· Saint Florian’s Priory (f.Carolingian; 1071: Augustinian; 1686-1708: Baroque; 1744: library- 130000 items; 1941: monks expelled by Gestapo; 1071: f.boys choir; Sankt Florian)
· Saint Georgenberg-Fiecht Abbey (10th c.CE: 1st hermitage by Blessed Rathold/Rapoto of Aibling; f.1138 CE: Georgenberg; 1705: series of fires; f.1708 CE: Benedictine; 1741-81: Baroque; 1806: Treaty of Pressburg- Tyrol passed from Austria to Bavaria; 1941: abbey impounded by Gestapo; Tyrol)
· Saint Lambrecht’s Abbey (f.Count Markward of Eppenstein; 1076-d.1786-1805 CE: Benedictine; Gothic-Baroque; 1938: seized by Nazis; 1942-5: used as external storage for Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp; Sankt Lambrecht)
· Saint Paul’s Abbey in the Lavanttal (f.Dukes of Carinthia on site of ancestral castle; 1091 CE: Benedictine; Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; 18th c.: crypt- 13 Habsburg member coffins; d.1787; 1809: monks from Saint Blaise’s Abbey in the Black Forest moved in; d.1940: Nazis; Saint Pauls in the Lavanttal)
· Saint Peter’s Archabbey (f.Saint Rupert; 696 CE: Late Antiquity church stemming Christianization of the region; Benedictine; 784: oldest library in Austria- 800 manuscripts, 100000 vol., music archives, art; writing school; Nazis expelled monks; Salzburg)
· Saint Stephen’s Cathedral (1147-60 CE: Roman Catholic; Vienna)
· Salzburg Cathedral, Virgil and Rupert’s (774 CE; burned 842 CE; 1000-1020 CE: crypt; 1106-47 CE: towers; Romanesque basilica; severely damaged in 1598 CE; 17th c.CE: Baroque Catholic cathedral; Salzburg)
· Sandberg (300 BCE: Celtic city; Hollabrunn)
· Sausenstein Abbey (f.1336 CE: Cistercian; 16th c.: suffered during Turkish invasions; hospital for Napoleon’s troops during occupation; WWII: German experimental agricultural institution; occupied by Russians; Sausenstein)
· Schottenstift/Scottish Abbey (f.1155 CE: Henry II brings Irish monks; Benedictine; Vienna)
· Seckau Abbey (f.1142 CE: Augustinian; 1143: Romanesque-Baroque basilica; Habsburg burial ground; d.1782; 1883: Benedictine; 1940: Gestapo evicted monks; Seckau)
· Seitenstetten Abbey (f.Udalschalk; 1112 CE: settled by monks from Gottweig Abbey; Gothic; Hungarian disturbances; Turk taxes; Reformation; 16th c.CE: Baroque; Romanesque Knight’s Chapel; Benedictine; Seitenstetten)
· Viktring Abbey (f.1142 CE: Cistercian; from Weiler-Bettnach Abbey in Duchy of Lorraine, filial monastery of Morimond Abbey; 1411: fire; 1447: Frederick III of Habsburg presents altar in abbey church; d.1786; altar merged w/Heiligenkreuz Abbey; 1897: Moro textile factory; Viktring)
· Vindobona (Celtic; Vienna)
· Wettingen-Mehrerau Abbey (f.Saint Columbanus; 611 CE: 1st monastery- Mehrerau; 1097-8: rebuilt; resettled by monks from Petershausen Abbey; Thirty Years War: Swede devast.; 1738: rebuilt; 1805: Treaty of Pressburg; Mehrerau)
· Wilhering Abbey (f.Ulrich castle; Augustinian; 1146 CE: Cistercian monks from Rein Abbey; Romanesque-Gothic; high altar statue of Saint Bernard of Clairvaux; 1940: monks expelled by Nazis; Wilhering)
· Zwettl Abbey (f.Hademar I of Kuenring; 1137 CE: Cistercian; 1426: sacked by Hussites; Romanesque-Baroque; Zwettl)
BELGIUM: [megaliths; cathedrals, abbeys]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Affligem Abbey (f.repenting 6 hermit knights: Hermann II, Count Palatine of Lotharingia; 1061 CE: Benedictine; burials: Queen Adeliza of England, father Duke of Godfrey I of Leuven; 12th c.CE: Cluniac; monk John Cotton- treatise: Arte Musica; 1146: where Saint Bernard of Clairvaux had visioin of Virgin Mary; 1796: French occupation; Brussels)
· Aulne Abbey (f.Saint Landelinus; 637 CE: Benedictine; 1144: Augustinian; 1147: Cistercian from Clairvaux; 18th c.CE: burned by French; including library- 40000 books, 5000 manuscripts; Sambre r.; near Landelies)
· Averbode Abbey (f.Count Arnold II of Loon; 1134-5 CE: Premonstratensian; 1579: bubonic plague- monk reduction; 1664-72: rebuilding; 1834: reest.; 1942: burned; near Diest)
· Bonne-Esperance Abbey (f.William, son of Rainard, Knight of Croix; 1130-18th c.CE: Premonstratensian; 1792/94: occupied/pillaged by French Revolutionary Army; 1616-7: remains of Saint Frederick of Hallum brought here from Mariengararde Abbey in Netherlands to save from Calvinists; Walloon, Estinnes, Hainaut)
· Brecht Abbey/Our Lady of Nazareth (f.1236-d.1797 CE: Cistercian-Trappist nuns; closed in aftermath of French revolution; Brecht)
· La Cambre Abbey Abbey (f.Henry I, Duke of Brabant; 1196 CE: Cistercian; Ixelles, Brussels)
· Cathedral of Our Lady (1352-1521 CE: Roman Catholic; Gothic; Antwerp)
· Chimay/Saint Monegonde’s Abbey (f.9th c.CE: Benedictine; 1919: Trappist nuns; Hainaut)
· Cornillon Abbey (f.1124 CE: Premonstratensian; now occupied by Carmelite nuns; Mt.Cornillon; near Liege)
· Engis (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Floreffe Abbey (f.1121 CE: Premonstratensian; 1791: French Republican suppression; Sambre r.; Floreffe)
· Forest Abbey (f.1105-d.1796 CE: Benedictine; Seine tr.; Brussels)
· Gembloux Abbey/Saint Peter; martyr Saint Exuperius (f.Saint Guibert; 945 CE: Benedictine; 1157/85: fires-rebuilt; 1598: pillaged by Calvinists; 1793: French suppression; Orneau r.; Gembloux, Namur)
· Ghent [Celtic “confluence” (Ganda)](Stone Age; Celtic; confluence of Scheldt and Lys r.; E. Flanders)
· Grimbergen Abbey (f.1128 CE: Augustinian-Premonstratensian; 1660: Baroque; Grimbergen)
· Herkenrode Abbey (f.Count Gerard of Loon; 1182 CE: Cistercian; 1191: burial: Count Gerard; 18th c.: reconstr.; 1797: French closed; 1972: Canonesses of the Holy Sepulchre; Kuringen, Hasselt, Limburg)
· Keizersberg [“Caesar’s/Emperor’s hill”] /Mont Cesar Abbey (legend: Roman castle?; 1187: commandery of Knights Templars; 1312: abolished-Knights Hospitallers; 1782: castle d.by Emp.Joseph II; 1798: French secularization; 1888: Benedicitine; Leuven)
· Liege Cathedral/Saint Paul (Romanesque collegiate church)
· Lobbes Abbey (f.Saint Landelin; 650-d.1794 CE: Benedictine; Carolingian-Ottonian period: Church of Saint Ursmarus: Romanesque-Mosan: choir, crypt, tower; Sambre r.; Hainaut)
· Malmedy Abbey (f.685 CE: Benedictine; relics of Saint Remaclus; Malmedy)
· Munsterbilzen Abbey/Saint Amor (f.Saint Landrada; 670-d.1773 CE: Benedictine nuns; 881: plundered by Vikings- restored; Munsterbilzen, Limburg)
· Namur (Celtic-Aduatuci: Roman)
· La Naulette (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Orval Abbey (10th c.CE: chapel; 1070: Benedictine monks from Calabria; 1132: Cistercian monks from Trois-Fontaines Abbey in Champagne; Trappist beer; 1252: fire- rebuilt; 1637: Thirty Years War- pillaged by French merc.; 17th c.: Trappist-Cistercian; 1785: Augustinian; 1793: burned by French; 1887: Harenne family- Cistercian f.; Villers-devant-Orval, Luxembourg)
· Park Abbey (f.Duke Godfrey; 1129-d.1792 CE: Premonstratensian; 16th c.: Calvinist sufferings; Leuven)
· Postel Abbey (f.Duke Godfrey; 1138-d.1797 CE: Rhineland Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Premonstratensian; Mol, Antwerp)
· Rochefort Abbey/Notre-Dame de Saint Remy (f.Gilles de Walcourt, count of Rochefort; 1230-d.1797 CE: Cistercian-Trappist nuns; 1464: nuns expelled- replaced by monks; 1568: Eighty Years War- ravaged by protestant armies; 1577: and Austrian armies; 1595: f.brewery; 17th c.: war, famine, plague; 1650: Lorraine army invasions; 1789: French revolutionary army invasions; Rochefort, Namur)
· Saint Aubin’s Cathedral (1751-67 CE: Late Baroque; Roman Catholic; Namur, Wallonia)
· Saint Bavo/Baafs Cathedral (942-1038 CE: Romanesque; 14-16th c.CE: expansions; Roman Catholic; Ghent)
· Saint Bernard’s Abbey (f.Duke Henry I/II; 1243 CE: Cistercian; 1672: burned; d.French Revolution; 1811: naval hospital; 1821: prison; 1867: military prison; 1948-77: prison; Hemiksem, Antwerp)
· Saint Hubert Abbey (825 CE: Benedictine; Saint Hubert)
· Saint Martin Cathedral (1221 CE: Gothic; reconstructed; Ypres)
· Saint Michael and Saint Gudula Cathedral (1226-1276 CE: Gothic; Roman Catholic; Brussels)
· Saint Rumbold Cathedral (1200; 1452-1520 CE: Roman Catholic; Mechelen)
· Sclayn (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Scladina cave (100000 BP: Neanderthal)
· Soleilmont Abbey (f.Albert III, Count of Namur; 1088 CE: Trappist nuns; 1237: Cistercian nunnery; daughter house of Aulne Abbey; d.1796; 1837: Bernadine; 1919: Cistercian; Gilly, Charleroi)
· Spy-sur-l’Orneau (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Stavelot-Malmedy Abbey/Saints Martin, Peter, Paul (f.Saint Remaclus; 650 CE: Benedictine; relics of Saint Remaclus; 9th c.: hospital; 881: Norman invasions; 10th c.: Hungarian invasions; d.1793; Stavelot, Liege)
· Tongerlo Abbey (f.1128: Premonstratensian; Westerlo, Antwerp)
· Tournai/Our Lady of Flanders’ Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque choir; 13th c.CE: Early Gothic choir replacement; inspired by Amiens Cathedral; Roman Catholic; Tournai, Wallonia)
· Val-Dieu Abbey (f.1216: Cistercian; 1287/1574: d.-rebuilt; Aubel, Liege)
· Veldwezelt-Hezerwater (Palaeolithic; proto-Neanderthal)
· Weris I, II [MA](Neolithic: dolmens, menhirs; star stones- Virgo; Durbuy, Wallonia, Belgium)
· Westvleteren Abbey (f.9th c.CE: Cistercian-Trappist; 1610-1784: Bridgettines; brewery; West Flanders)
BOSNIA:
· Ali Pasha’s Mosque (1560-1 CE: Islamic; Sarajevo)
· Arnaudija Mosque (1594 CE; d.1993; Islamic; Banja Luka)
· Emperor’s Mosque (1462 CE: Islamic; Sarajevo)
· Ferhadija Mosque (1579 CE; d.1993; Islamic; Banja Luka)
· Gazi Husrev-beg’s Mosque (1531 CE: Islamic; Sarajevo)
· Sisman Ibrahim Pasa Mosque (1562 CE: Islamic; Pocitelj)
BULGARIA: (Ancient Thrace: kurgans)
· Alexandrovo (4th c.BCE: kurgan; Thracian tomb; Haskovo)
· Banya Bashi Mosque (1576 CE: Islamic; Sofia)
· Borovo
· Djumaya Mosque (1364 CE: Islamic; Plovdic)
· Duvanlii
· Ibrahim Pasha Mosque (1616 CE: Islamic; Razgrad)
· Tomb of Kazanlak/Kazanluk Valley (400 BCE: kurgans: Valley of the Thracian Kings-necropolis; Kazanlak)
· Kralevo
· Letnitsa
· Lukovit
· Madara Rider (710 CE; Shumen)
· Malko Turnovo
· Nesebur
· Ovcharovo [MA](megalith; Sakar m.; Haskovo)
· Panagyurishte
· Pereshchepina kurgan (660 CE: burial memorial for Great Bulgaria Khan Kubrat; golden treasure; Mala Pereshchepina)
· Perperikon [MA](5000 BCE; Kardzhali)
· Plovdiv
· Pobit Kamak [MA](megalith; Rhodopes m.; Pazardzhik)
· Pormorie
· Ravnogor
· Rogozen
· Sinemorets
· Sofia
· Tomb of Sveshtari (300 BCE: Getae: kurgan-tomb: caryatids, painted murals; Razgrad)
· Tombul Mosque (1740-4 CE: Islamic; Shumen)
· Tatul
· Varna Necropolis (4600 BCE; Varna)
· Vratsa
· Vulchitrun
· Zlatinitsa
CROATIA: [cathedrals]
· Cathedral of Saint James (1402 CE: Romanesque; 1431-41 CE: Renaissance; Catholic; Sibenik)
· Hvar/Pharos (3500-2500 BCE: Neolithic-Hvar; 384 BCE: Greek)
· Hvar Cathedral/of Saint Stephen (14-15th c.CE: Gothic; 17th c.CE: bell tower; Renaissance-Baroque-Dalmation; Catholic; Hvar)
· Krapina (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; castles; Zagreb)
· Rijeka (Celtic; Roman: arch)
· Rijeka Cathedral/of Saint Vitus (1638 CE: Baroque; Catholic; Rijeka)
· Saint Chrysogonus (Romanesque; Zadar)
· Saint Donatus (9th c.CE: pre-Romanesque; over temple of Juno; Zadar)
· Saint Francis (Gothic; Zadar)
· Saint Krsevan (Romanesque; Zadar)
· Saint Mary (1105 CE: Romanesque; Zadar)
· Split/Aspalathos (6th c.BCE: Greek colony; 229 BCE: Roman)
· Split Cathedral/of Saint Duje (3rd CE: Romanesque; 1100 CE: bell tower; 17th c.CE: chorus; Roman Catholic; Split)
· Vindija (250-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· Zagreb Cathedral/of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1093 CE; 15th c.CE; 17th c.CE: Neo Gothic; Catholic; tallest bldg.in Croatia; Zagreb)
· Zadar (4th-2nd m.BCE: prehistoric: Stone Age; Neolithic; 9th c.BCE: Liburian; 7th c.BCE: Phoenician-Etruscan-Greek; 2nd c.BCE: Roman: walls, forum, basilica, temple, amphitheatre, cemeteries, aqueduct)
· Zadar Cathedral/of Saint Anastasia (4-5th c.CE: Romanesque basilica; 12-13th c.CE: Roman Catholic; Zadar)
CYPRUS: (UK)(Ancient Greek)
· Arabahmet Mosque [SR](1571 CE: Islamic; Nicosia)
· Curium (Limassol)
· Hala Sultan Tekke (647 CE: Islamic; Larnaca)
· Kition (600 BCE: Phoenician; 450 BCE: Greek; Larnaca)
· Lala Mustafa Pasha Mosque Famagusta (1298 CE: Islamic; Famagusta)
· Salamis (1100 BCE: ancient city; Famagusta)[Cyprus Polis: Paphos, Soloi, Kourion, Chytroi, Kition, Amathus, Idalion, Ledrai, Tamassos, Kyrenia, Lapethos, Marion]
· Selimiye Mosque (1209 CE: Islamic; Nicosia)
· Temple of Aphrodite (Ktima)
CZECH REPUBLIC: [cathedrals]
· Cathedral of Saint Bartholomew (1295-16th c.CE: Gothic; Roman Catholic; Pilsen)
· Dolni Chabry [MA] (menhir)
· Dolni Vestonice (11000 BCE)
· Domica (7000 BP: cave paintings)
· Drahomysl [MA](menhir)
· Druzec [MA](menhir)
· Horomerice [MA](menhir)
· Jemniky [MA](menhir)
· Kersko [MA](menhir)
· Klobuky/Kamenny Pastyr [“stone shepherd”] [MA](tallest Czech menhir; 25km NW Prague; Klobuky, Kladno, Central Bohemia)
· Klucek [MA](menhir)
· Kulna (250-45k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Ledce [MA](menhir)
· Libenice [MA](menhir)
· Louny [MA](menhir; Louny, Usti nad Labem, Selibice)
· Mladec caves (35000 BP: cranial fragments; Olomouc, Moravia)
· Orasice [MA](menhir)
· Prague (Paleolithic; 200 BCE: Celts; 1st c.BCE” Marcomanni-Suebi)
· Saint Peter and Paul Cathedral (14-15th c.CE: Gothic; Brno)
· Saint Vitus Cathedral (925 CE: Romanesque rotunda; 1060 CE: Romanesque basilica; 12th c.CE: expansions; 1344 CE: Gothic mod.; Roman Catholic; located within Prague Castle complex; containing tombs of many Bohemian kings and Holy Roman emperors; largest church in Czech Rep.; Prague)
· Saint Wenceslas Cathedral (1131 CE: Romanesque; 13-14th c.CE: neo-Gothic mod.; Roman Catholic; 4th tallest bldg.in Czech Rep.; Olomouc)
· Sipka (250-45k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Slany [MA](menhir)
· Slavetin [MA](menhir)
· Tuchlovice [MA](menhir)
· Vinarice [MA](menhir)
· Zatec [MA](menhir; Louny, Asti nad Labem, Brezno)
DENMARK: [megaliths; rune stones/picture stones (400-900 CE); cathedrals, abbeys; stave churches]
[Note 23] After the Reformation (1535), the properties and incomes of abbeys in Denmark were reverted to the crown.
· Aalborg Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (1125-1527 CE: Benedictine nuns; Aalborg, Nordjylland)
· Aalborg Friary (1250-1530 CE: Franciscan friars; Aalborg, Nordjylland)
· Aarhus Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Aarhus; Viking settlement w/6 runestones)
· Aebelholt Abbey/Saint Thomas (1104 CE: 1st wooden abbey on Eskilso i., Roskilde Fjord; moved from Eskilso; 1167-1536 CE: Augustinian; Romanesque; Tjaereby near Hillerod, Hovedstaden)
· Alling Abbey/Saint John (1250-1536 CE: Benedictine; Svostrup, Gjern, Midtjylland)
· Stones of Askeberga
· Antvorskov/Saint John the Baptist (f.Valdemar the Great; 1164-1536 CE: Knights Hospitallers; Zealand i.; Slagelse, Sjaelland)
· Asserbo Charterhouse (1162 CE: Carthusian-Cistercian; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Baekke
· Borglum Abbey (1000: royal farm; 1086: King Canute fled in revolt; residence burned; 1134: bishopric; 1209-1536 CE: Premonstratensian; daughter house of Steinfeld Abbey- Cologne, Ger.; Romanesque; Borglum, Nordjylland)
· Budolfi (Saint) Church (1132 CE: Romanesque; near Viking burial site; Aalborg, Jutland)
· Carmelite Priory (1479-1529 CE: Carmelite friars; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Carmelite Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (1430-1536 CE: Carmelite friars; Helsinger, Zealand)
· Carmelite Priory (1418-1532 CE; Skaelskor, Sjaelland)
· Dominican Priory/Saint Nicholas (1441-1536 CE: Dominican friars; Helsinger, Hovedstaden)
· Dominican Priory (1300-1536 CE; Skaelskor, Sjaelland)
· Dueholm Priory/Saint John the Baptist (1370-1536 CE: Knights Hospitallers; Nykobing Mors, Nordjylland)
· Essenbaek Abbey (1179-1529 CE: Benedictine; Assentoft, Midtjylland)
· Esrum Abbey (pre-Christian site: wooden stave chapel; Esrum Spring; 1140: Benedictine; 1151-1536 CE: Cistercian; daughter house of Clairvaux; 1194/1204: burned-new church; Codex Esromensis; 17th c.: converted into royal hunting lodges; Zealand i.; near Hillerod, Hovedstaden)
· Franciscan Friary (1238-1530 CE: Franciscan; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Franciscan Friary /Saint Anne (1420-1537 CE: Franciscan friars; Helsinger, Hovedstaden)
· Franciscan Friary (1237-1537 CE; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Glenstrup Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (orig.Viking religious site- stave chapel?; Romanesque; 1125-1431/1441-5: Benedictine; 1432: Carthusian; 1445: Bridgettine; Glenstrup, Nordjylland)
· Grinderslev Priory (1150-1536 CE: Augustinian; Grinderslev, Midtjylland)
· Gudum Priory (1250-1532 CE: Benedictine nuns; Gudum, Midtjylland)
· Halstead Priory/Saint Samson (owned by the crown; 12th c.CE: old granite church; Gothic; 1290-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1510: sacked by Hanseatic league; Nakskov, Lolland, Sjaelland)
· Holbaek Priory/Saint Nicholas (1275-1535 CE: Dominican friars; Holbaek, Sjaelland)
· Horsens, Franciscan Friary (1261-1532 CE: Franciscan; Horsens, Midtjylland)
· Horsens, Knights Hospitallers/Saint John Baptist (1375-1536 CE: Knights Hospitallers; Horsens, Midtjylland)
· Hospital of the Holy Ghost (1296-1530 CE: Order of the Holy Ghost; 1497: Augustinian; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Hospital of the Holy Ghost (1451-1536 CE: Order of the Holy Ghost; Aalborg, Nordjylland)
· Hospital of the Holy Ghost (1475-1536 CE: Order of the Holy Ghost; Funen i.; Sonderso, Elvedgard, Sjaelland)
· Hospital of the Holy Ghost (1470-1536 CE: Order of the Holy Ghost; Nakskov, Sjaelland)
· Hospital of Saint Anthony/Blessed Virgin Mary (1470-1536 CE: Benedicitine monks; Praesto, Sjaelland)
· Hundslund Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Clement (1100: royal farm given by King Erik II Emune; 1250-1535 CE: Benedictine nuns; Romanesque-Gothic; Dronninglund Castle, Nordjylland)
· Jelling stone ship (Bronze Age/970 CE: 2 royal barrows/mounds, stone ship; runestone to Queen Thyra; Jelling)
· Kalundborg Friary (1240-1532 CE: Franciscan friars; Gothic; Kalundborg, Sjaelland)
· Kalvo Abbey (1167-1172 CE: Cistercian; Kalvo i., Skanderborg, Midtjylland)
· Koge Friary/Blessed Virgin Mary (King Hans I donated farm to Franciscans; 1484-1531 CE: Franciscan friars; Koge, Sjaelland)
· Kerteminde (Funen)
· Knardup Abbey (f.King Christopher II; 1326-1536 CE: Cistercian; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Lejre (Denmark)
· Lindhilm Hoje [Old Norse: “hill/mound” (haugr/hoje)] (Viking: 5th c.CE: N part of site; 1000-1050 CE: S part of site; 700 graves; Aalborg)
· Mariager Abbey (1446-1536 CE: Bridgettines; Mariager, Midtjylland)
· Maribo Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (1416-1536: Bridgettine; Brick Gothic; 1551-1621 CE: Lutheran women’s college; Maribo, Sjaelland)
· Naestved Priory (1265-1532 CE: Dominican friars; Naestved, Sjaelland)
· Naestved Friary (1242-1532 CE: Franciscan friars; Naestved, Sjaelland)
· Nykobing Falster Friary (1419-1532 CE: Franciscan friars; Nykobing Falster, Sjaelland)
· Nysted Friary (1286-1538 CE: Franciscan friars; Nysted, Sjaelland)
· Om Abbey (1172-1536 CE: Cistercian; 1140: nuns; Mosso, Gammel Rye, Midtjylland)
· Poor Clares’ Priory (1497-1535 CE: Poor Clares; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Ringstead Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (1020: royal mint; 1081: Benedictine priory; 1134-1536 CE: Benedictine monks; Ringstead, Sjaelland)
· Roskilde Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (1160: Benedictine nuns; 1177-1532 CE: Cistercian nuns; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Roskilde Cathedral (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Brick Gothic; 1st Gothic cathedral out of brick; main burial site for Danish monarchs since 15th c.; Zealand i.; Roskilde)
· Saeby Priory (1460-1536 CE: Carmelite friars; Saeby, Nordjylland)
· Saint Agnes Priory (prev.Viking fortress to launch naval raids; 1403-1536 CE: Dominican nuns; Gavno castle; Gavno, Sjaelland)
· Saint Agnes Priory (1263-1527 CE: Dominican nuns; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Saint Canute’s/Odense Cathedral (1100 CE: Brick Gothic; Lutheran; Abbey Hill; Odense)
· Saint Catherine’s Priory/Saint Catherine of Siena (1231-1536 CE: Dominican friars; 1699: Lutheran; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Saint Clare’s Priory/Saint Clare of Assisi (1256-1537 CE: Poor Clares; Roskilde, Sjaelland)
· Saint George’s Leper Hospital (1109; 1261-1609 CE; 1348: devast.by Hanseatic League; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Saint Gertrude’s Hospital (1397-1530 CE; Copenhagen, Hovedstaden)
· Sebber Priory/Saint Lawrence (1250-1536 CE: Benedictine nuns; Sebbersund, Nordjylland)
· Slangerup Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Nicholas (1000 CE: Viking royal residence; 1095: King Erik Ejegod replaced wooden stave church with limestone church ded.Saint Nicholas; 1170 CE: Benedictine nuns; 1187-1555 CE: Cistercian nuns; “unruly nuns;” Slangerup, Hovedstaden)
· Skovkloster Abbey/Saint Peter (1140: original Romanesque church; 1175-1536 CE: Benedictine; Herlufsholm School; Naestved, Sjaelland)
· Soro Abbey/Saint Peter (1142: Benedictine; 1161: Cistercian; Soro, Sjaelland)
· Thyra’s burial mound (Jelling)
· Vestervig Abbey (1110-1536 CE: Augustinian; Thisted, Nordjylland)
· Vitskol Abbey (1158-1536 CE: Cistercian; Ranum, Nordjylland)
· Vrejilev Priory (1110-1536 CE; Romanesque; Premonstratensian from Borglum ab.; 1200 CE: fire; nuns; Vra, Nordjylland)
· Vordingborg Priory (1253 CE: Dominican friars; Vordingborg, Sjaelland)
ESTONIA: [megaliths; stone ships (Viking); cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Haapsalu Castle (13th c.CE: castle w/cathedral; legend of the White Lady: when ther is full moon of August, an image of a white lady appears on the wall of the chapel; Haapsalu)
· Nabala [Latv.: ”navel center” (naba)] Stone [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones cup markings- planisphere; Juri Parish, Harju)
· Pulli (11000 BP; Parnu)
· Saint Mary’s Cathedral (13th c.CE: Dane; Lutheran; Tallinn)
· Saint Olaf’s Church (12th c.; 1438-1519 CE; 1549-1625 CE: tallest bldg.in the world; Tallinn)
· Salme ships (750 CE: 2 pre-Viking: ship burial; 35 skeletal remains of warriors killed in battle; weapons, artifacts, ritual sacrificed dogs; Salme, Saaremaa)
· Sooaluse Stone [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones cup markings- planisphere; Rakvere Parish, Viru)
· Tumala [Babyl.: “Pleiades” (Temennu)] Foundation Stone [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones cup markings- Pleiades, Hyades; Saaremaa)
· Viru Village Stone [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones cup markings- Perseus; Rouge Parish, Voru)
FINLAND: [megaliths; cathedrals]
· Astuvansalmi (3000 BCE: largest rock paintings in Scand.; lake Saima)
· Espoo/Esbo (9000 BP)
· Porvoo Cathedral (13-15th c.CE: Lutheran; Porvoo)
· Turku (Stone Age)
· Turku Cathedral (13-15th c.CE: Lutheran; Turku)
· Ukonkivi (Sami: Inari)
· Wolf Cave (130000 BP; Karijoki)
FRANCE: [MA] [painted caves; dolmens; megaliths; standing stones; stone circles; cairns; tumuli; cathedrals]
[NOTE 10] The occupation of Celtic oppida and/or enclosed oppida (hill-forts surrounded by earthwork mounds) by the Roman Empire, and the consequent appearance of the earliest earthwork mounds in the Mississippian cultures of the New World, suggests that the indigenous Druids of Europe escaped Roman persecution by emigrating to the New World and inserting their mound culture there.
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
[NOTE 89] Dolmens like caves served as dark meditation chambers, or penial gland activators, connecting the macrocosm within the microcosm.
· Abbey of Saint Germain (9th c.CE: crypt; most ancient murals painting in France, tomb of the bishops; Auxerre, Burgundy, Yonne)
· Abbey of Saint Martial (f.on ancient Roman cemetery of Christian martyrs-Saint Martial sarcophagus; 848 CE; 10th c.CE: crypt; developments of Gregorian chant; Limoges, Haute-Vienne)
· Agde [Gk.: “good fortune”(agathe tyche)](5th c.BCE: Greek colony settled by Phocaeans; Roman; Herault)
· Agde Cathedral/Saint Stephen (5th c.CE: predecessor Roman temple of Diana; 9th c.CE: predecessor Carolingian church; 12th c.CE: Roman Catholic; Herault r.; Agde, Herault)
· Agen Cathedral/Saint Caprasius (12th c.CE: Roman Catholic dedicated to Saint Caprasius; Agen, Lot-et-Garonne)
· Aire Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (11-12th c.CE: Roman Catholic; 17th c.CE: alterations; Aire-sur-l’Adour, Landes)
· Aire-sur-l’Adour (5th c.CE: residence of lings of the Visigoths; Landes)
· Aix-en-Provence (Cimbri-Teutone; 123 BCE: Roman: Aquae Sextiae; 477 CE: Visigoth; Frank-Lombard; 731 CE: Saracen; Anjou; Bouches-du-Rhone)
· Aix Cathedral/Holy Savior (1st c.CE: predecessor Roman forum; temple of Apollo; 6th c.CE: predecessor church f.Saint Maximinus who brought Mary Magdalene from Palestine to Aix-en-Provence; 12-19th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Aix-en-Provence, Bouches-du-Rhone)
· Albi (3000-600 BCE: Bronze Age; 51 BCE: Roman: Albigensium; Cathar-Gnostic; Tarn)
· Albi Cathedral/Saint Cecilia (4th c.CE: predecessor church destroyed by fire 666 CE; 920 CE: second church by Saint Cecilia; 1282-1480 CE: French Gothic; Albi; Tarn)
· Aleth Cathedral (9th c.CE: processor church destroyed by Normans in 10th c.CE; 1146 CE: replaced by Saint Malo cathedral, dedicated to Saint Peter; d.in 1255 CE: ruins; Saint-Servan, near Saint Malo)
· Amiens (Paleolithic: Acheulean; Roman: Samarobriva: Ambiani settlement; Frank; Norman; Somme)
· Amiens Cathedral/Blessed Virgin (1218; 1258 CE: fire destroyed archives; 1266-1406 CE: Gothic; Amiens, Somme)
· Angers (400000 bce: Lower Paleolithic: stone tool; Gallic-Andecavi; Roman: Juliomagus; 845 CE: Viking invasions; Anjou capital; Maine-et-Loire)
· Angers Cathedral/Saint Maurice (1032 CE: original bldg. burned; Gothic; Angers, Maine-et-Loire)
· Angouleme (507 CE: Visigoth: Clovis; 9th c.CE: Norman; Charente)
· Angouleme Cathedral/Saint Peter (4th c.CE: original pre-Christian sanctuary; 507 CE: destroyed; 560 CE: 2nd cathedral; 760 CE: burned by Normans/Vikings; 1017 CE: Romanesque; 12-19th c.CE: expansions and alterations; Angouleme, Charente)
· Antibes (5th c.BCE: Greek colony settled by Phocaeans from Massilia; 43 BCE: Roman; Alpes-Maritimes)
· Apt (Gallic-Vulgiente; 125 BCE: Roman: Apta Julia; Lombard; Saracen; Vaucluse)
· Arles (800 BCE: Ligurian; Celtic; Phoenician trading port; 123 BCE: Roman: Barbegal aqueduct and mill; aqueduct, Vitruvian water-wheels, watermill-tympanum; theatre, arena/amphitheatre; necropolis: The Alyscamps, cryptoporticus; Thermes of Constantine, obelisk; seat Praetorian Prefecture to Gaul; Saracens; k.Frankish Arles; Viking raids; Bouches-du-Rhone)
· Arras [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Aquila; Belgic-Atrebates: Nemetacum; Roman: Atrebatum; 9th c.CE: Viking attacks; Pas-de-Calais; near Lille)
· Arras Cathedral (1030-1396 CE: Gothic; 1833 CE: rebuilt Classical; Arras, Pas-de-Calais)
· Arcy-sur-Cure (45-28k BP: Neanderthal-human; Avallon)
· Auch (Aquitanian-Basque; 50 BCE: Roman; Gers)
· Autun Cathedral/Saint Nazarius (5th c.CE: 1st cathedral dedicated to Saint Nazarius; 1120-80 CE: 2nd cathedral dedicated to Saint Lazarus; Tomb of Lazarus; 15th c.CE: Romanesque; Autun)
· Auxerre (Gallo-Roman: Antissiodorum; Yonne)
· Auxerre Cathedral/Saint Stephen (3rd c.CE: diocese; 5th c.CE: predecessor cathedral; 1215-1540 CE: Gothic; Yonne r.; Auxerre, Burgundy, Yonne)
· Avignon (Celtic hill fort; Gallic-Cavares, Avennius clan; Greek-Phocaean colony; Roman; 5th c.CE: Goths; 12th c.CE: Saracens; Avignon Papacy; Vaucluse)
· Avignon Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Avignon, Vaucluse)
· Avranches (Abrincatui; 933 CE: Norman)
· Avranches Cathedral/Saint Andrew (1172 CE: Gothic; Avranches, Normandy, Manche)
· Baptistere Saint-Jean (4th c.CE: 2nd oldest church in France; Poitiers, Vienne)
· Barnenez [MA](ph1-4850-4250 BCE; ph2-4450-4000 BCE: Neolithic: cairn-72m long x 25m wide x 8m high, 13-14000 tons of stone w/11 chambers; tumulus; carved symbols; finds- pottery, stone axes, flint blades and arrowheads; star stones- Ophiuchus-nu, Serpens Cauda; 3000 BCE: Bronze Age: pottery, copper dagger, barbed arrowhead; Bay of Morlaix; Finistere, Britanny)
· Basilica of Notre Dame du Port (10th c.CE: Romanesque over 6th c. church of Saint Avitus; Clermont-Ferrand, Puy-de-Dome)
· Basilica of Saint Martin d’Ainay (legend: accd.to Eusebius, where 48 Christians-incl.Blandina were fed to lions in Roman amphitheatre; 859 CE: Ainay abbey: Benedictine; chapel of Saint Blandina; 11th c.CE: Romanesque; Lyon, Rhone)
· Basilica of Saint Nazarius and Celsus (11th c.CE: Romanesque; crypt; 1269-1330 CE: Gothic; Carcassonne, Aude)
· Basilica of Saint Remi (11-15th c.CE: Romanesque; royal burials; Reims, Marne)
· Bau de l’Aubesier (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Bayeux (Bodiocassi; 1st c.BCE: Gallo-Roman: Augustodurum; 9th c.CE: Viking raids; Norman; Calvados)
· Bayeux Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1077 CE: Norman-Romanesque; Bayeux, Calvados)
· Bayonne (3rd c.CE: Roman: Lapurdum; military site; 840 CE: Vikings; 12th c.CE: Basque-Gascon; Pyrenees-Atlantiques)
· Bayonne Cathedral/Saint Mary (1258; 1310 CE: Romanesque destroyed by 2 fires; 13-17th c.CE: Gothic; Bayonne, Pyrenees-Atlantiques)
· Beauvais (Roman: Bratuspantium/Caesaromagus; Oise)
· Beauvais Cathedral/Saint Peter (10th c.CE: Romanesque; 1225-1548 CE: Gothic; Beauvais, Oise)
· Besancon [MA](Neolithic: legend of La Vouivre; star stones- Andromeda; 1500 BCE: Bronze Age: Gaul; 1st c.BCE: Roman; 1034 CE: Holy Roman Empire; Besancon, Doubs)
· Besancon Cathedral/Saint John the Evangelist (11-13th c.CE: Romanesque; Besasncon, Doubs)
· Beziers (Neolithic; Celtic; 36 BCE: Roman: Colonia Julia Baeterrae Septimanorum; amphitheatre; white wine; 1209 CE: Albigensian Crusade; Herault)
· Beziers Cathedral/Saint Nazarius and Celsus; 13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; erected over ruined cathedral d.Albigensian Crusade Biache-Saint-Vaast (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal; Lille)
· Blois Cathedral/Saint Louis (12th c.CE: previous collegiate church of Saint Solenne; crypt; 1544-1860 CE: Gothic; Blois)
· Bordeaux (30-20000 BP: Neanderthal: cave Pair-non-Pair, near Bourg sur Gironde; 300 BCE: Celtic-Bituriges Vivisci: Burdigala; 60 BCE: Roman; 276/409 CE: Vandal; 414 CE: Visigoth; 498 CE: Frank; 6th c.CE:
· Bordeaux Cathedral/Saint Andrew (1096 CE: Romanesque; 13-15th c.CE: Gothic; Bordeaux)
· Boubiers [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cygnus; Picardy; near Amiens, Oise)
· Bougon, Tumulus/Necropolis of [MA](4800 BCE: Neolithic: stepped barrows/burial mounds: A-F; 90 ton capstone for Tumulus A; Bougon, near La-Mothe-Saint-Heray)
· Boulogne-sur-Mer [Celtic: “foundation,””settlement,””citadel” (bona)](43 CE: Roman: Bononia; Portus Itius; Base of Classis Britannica; Pas-de-Calais)
· Bourg-en-Bresse (Roman remains)
· Bourges (Celtic-Bituriges: Avaricon; Roman: Avaricum; Germanic: Burg; Cher)
· Bourges Cathedral/Saint Stephen (3rd c.CE: predecessor Roman church; 1195 CE: Gothic; Bourges, Cher)
· Brignogan [sim.Babylonian: “serpent” (unuk) = nogan][MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Cauda-chi; Britanny)
· Broceliande in Paimpont [MA](Neolithic: Merlin’s Grave; star stones- Serpens Caput-alpha; Rennes, Britanny)
· Cahors (Celtic; Lot)
· Cahors Cathedral (7th c.CE: predecessor church by Saint Didier; 11th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Cahors, Lot)
· Camaret-sur-Mer [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-mu; Brest, Britanny)
· Cambrai (Roman: Camaracum; Peutinger table; 4th c.CE: Frankish raids; Nord)
· Carcassonne (3500 BCE; 6th c.BCE: Celtic: Carsac; hill fort; 100 BCE: Roman: Carcasum; 453 CE: Visigoth; Aude)
· Carcassonne Cathedral/Saint Michael (13th c.CE: Gothic basilica; Carcassonne, Aude)
· Carnac [MA](4500/3117 BCE: Neolithic: tumuli-St.Michael; dolmens- Er-Roc’h-Feutet, La Madelaine, Kercado, Mane Brizil, Kerlescan, Kermarquer, Mane-Kerioned/Pixies mound, Crucuno, Crucuno stone rectangle-3, 4, 5 rectangle of 21 menhirs; single menhirs; star alignments, planisphere; 3000+ standing stones; star stone rows/alignments- Libra Bootes <sim.Arabic: nakkar>, Virgo; Plouharnel- Scorpio, Autumn Equinox; La Trinité-sur-Mer- Leo; Locmariaquer- Hydra; Gavrinis- Hydra; El Lannic- Procyon-Lance Star; Kerguntuil; Kerlescan-555 stones, 13 lines, 800m long, stone circle-39 stones in W, stone circle in N; Kermario/House of the Dead-1029 stones in 10 columns, 1300m long; Manio-quadrilateral arrangement, giant menhir; Menec-11 menhir rows, 1165m x 100m long, stone circle/cromlech ruins at ends; local petrifaction legend: Roman legion turned to stone by Merlin/Saint Cornelius; Hancock: myth of deluge; passage way aligned with winter solstice sunrise; Saint Barbe; Bay of Quiberon; Carnac; btwn. Vannes and Quiberon, Britanny)
· Carpentras (Greek; Roman: Carpentoracte Meminorum/Forum Neronis; triumphal arch; Vaucluse)
· Castres [Lat.: “fortified place” (castrum)](Roman: fort; Tarn)
· Chalons Cathedral/Saint Stephen (1147 CE: Gothic; Chalons-sur-Saone)
· Cham des Bondons [MA](menhir; Lozere)
· Menhir du Champ Dolent [MA](Neolithic: largest menhir in Brittany-10m high; star stones- Serpens, Ophiuchus-beta/Cebalrai; near Mt. St. Michel; Dol-de-Bretagne, Britanny)
· Chartres [MA](3117 BCE: Central Loire Valley- North Celestial Pole; Carnute; Roman: Autricum; 858 CE: burnt by Normans; Autura/Eure r.; Eure-et-Loir; Orleans)
· Chartres Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (876 CE: Church of St.Mary housing the tunic of the Virgin Mary, 1st c.CE, gifted by Charles the Bald, grandson of Charlemagne; 858; 962; 1020; 1134; 1194 CE: 5 successive cathedrals destroyed by war/fire; 1200 CE: Gothic; Chartres, Eure-et-Loir; Orleans)
· Chateauneuf [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus-gamma; St. Malo, Britanny)
· Chateau-Ville-Visille [MA](Neolithic; red megalith; star stones- Taurus-Aldebran; French Riviera; near Queyras)
· Chauvet Cave/Chauvet Pont-d’Arc (32000 BP: Upper Paleolithic: oldest known cave paintings-13 different species: horses, cattle, reindeer, cave lions, panthers, bears, owls, cave hyenas, rhinos, Venus figure?, chimera?; Ardeche cave wall paintings from S-N: Entrance- Milky Way end; Brunel Chamber/Mammoth Stalagmite Cascade- Hole in the Milky Way; Brunel Chamber Panel of the Sacred Heart- Canis Minor; Vestible of red bears Puppis; Dotted Animal Panel- Canis Major; group of dots, Wall of Domiminos- Orion; Alcove of the Yellow horses- Hydes; Chamber of the Bear Hollows Rinoceros Head- Taurus; Cactus gallery Red Bear- Menkar, Pisces; Gallery of Hands, Hanging Rock with one large and one small butterfly sign- Perseus, Pleiades; Panel of the Panther (and Bear)- Ursa Major, Lynx; Cactus Gallery w/sm.red Mammoth- Auriga; Frieze of Red Rhinoceros- Andromeda; Hand Gallery- Cassiopeia; Candle Gallery- Cepheus; Draco- N Ecliptic Pole; Owl- Lacerate; Chamber of the skull- Vega, Lyra; Hillaire Chamber Panel of Horses- Cervids, Cygnus; Megaceros Gallery- Triangles, Aquila; Panel of Felines- Sagittarius; End Chamber, 3 Rhinos- Scorpio; Bison- Lupus; Neolithic: star stones- Orion; Milky Way- Canis Major-Sagittarius; Rhone Alps; cliff above Ardeche r.; Vallon-Pont-d’Arc; Ardeche)
· Church of Saint Eusebe (7th c.CE; 13th c.CE: nave rebuilt; Romanesque tower; Auxerre, Burgundy, Yonne)
· Church of Saint Honoratus (Roman necropolis: Alyscamps; Medieval; Arles)
· Church of Saint Maclou (1432 CE: Gothic; Rouen, Normandy)
· Church of Saint Ouen (12-15th c.CE: Gothic; Benedictine; Rouen, Normandy)
· Church of Saint Trophime (11-15th c.CE: Romanesque; Last Judgment portal; Arles)
· Clermont-Ferrand [MA](Neolithic: Grande Borne menhir- Gemini, Procyon, Canis Minor; Gallic-Averni: Nemessos- sacred forest situated on a mound; 1st CE: Roman: Augustonemetum; Norman-Viking plunders; 1095 CE: starting point of First Crusade; Puy-de-Dome, Auvergne)
· Clermont-Ferrand Cathedral/Saint Nazarius and Celsus (5th c.CE: predecessor church dedicated to Saint Vitalis and Agricola; 760 CE d.by Pepin the Short; 764-8 CE: reconstruction of 2nd cathedral; d. by Normans in 915 CE; 946 CE; 3rd cathedral; 1248 CE: Gothic; Clermont-Ferrand, Puy-de-Dome)
· Clermont-L’Herault [MA](Neolithic; near Dolmen Pouget, Gallardet; star stones- Lupus, Columba; Languedoc; near Montpellier)
· Combe Grenal (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Commana [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus-theta; Commana, Britanny)
· Congy [MA](Neolithic: Menhir de l’Etang de Chenevry-Cepheus and Cassiopeia; Menhir de Haute Borne- Lacerta; star stones- Cepheus, Cassiopeia; Champagne-Ardenne; near Avize, Marne)
· Correze (Dol-de-Bretagne menhir [MA](3000 BCE; Brittany)
· Cosquer cave (20000 BP: cave paintings; Marseille)
· Couches [MA](Neolithic: Menhirs Epoigny; Saint Pantaleon; Solutre Vergisson; earthworks near Cluny; star stones- Perseus, Pleiades; Saone-et-Loire; near Dijon; Burgundy)
· Counozouls [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Canis Major-Sirius; Roussillon; near Perpignan)
· Coutances (Gallic-Unelli; Roman: Constantia; 933 CE: Norman; Manche)
· Coutances Cathedral (5th c.CE: predecessor church d. by Normans in 9th c.CE; 1056 CE: Romanesque-Norman; fire; 1210 CE: Gothic; Coutances, Normandy)
· Creteil (Paleolithic; Neolithic: polishing machine; Merovingian: Vicus Cristolium; Val-de-Marne)
· Crozon [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Scorpio-epsilon/Chin.: Wei; Brest, Britanny)
· Dax (Roman: Civitas Aquensium; Landes)
· Dax Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; collapsed 1646; 1694 CE: present cathedral; Dax, Landes)
· Digne-les-Bains (Neolithic; Roman; Alpes-de-Haute-Provence)
· Dijon (Roman: Divio; 11-15th c.CE: Dukes of Burgundy; Cote-d’Or)
· Dijon Cathedral/Saint Benignus (511-535 CE: predecessor basilliaca over a crypt; 1002 CE: Romanesque; 1137 CE: d.fire; 1280-1325 CE: Gothic; Dijon, Burgundy, Cote-d’Or)
· Dol de Bretagne [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus; St. Malo, Britanny)
· Douarnenez [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-sigma, Antares; Quimper, Britanny)
· Draguignan [MA](Neolithic: Dolmen Pierre de la fee/fruit rock; star stones- Eridanus; French Riviera; near Var, Saint Tropez)
· Eglise Notre-Dame-la-Grande (10th c.CE: Romanesque; oldest Romanesque church in Europe; Poitiers, Vienne)
· Eglise Saint-Bonaventure (1325-7 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Franciscan; Lyon, Rhone)
· Eglise Saint-Etienne (Romanesque; d.Anglo-American bombing rainds in 1944; Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Eglise Saint-Guillaume (1301 CE: Gothic; Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Eglise Saint-Hilaire-le-Grande (11th c.CE; Poitiers, Vienne)
· Eglise Saint-Jean (Gothic; Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Eglise Saint-Nizier (Roman temple of Attis; 5th c.CE: basilica by Eucherius; 6th c.CE: bishops buried-Saint Nicetius; 8th c>CE: ravaged by Saracens; rebuilt in 9th c.; fire in 1253; 14-16th c.CE: rebuilt Gothic; Lyon, Rhone)
· Eglise Saint-Paul (12-16th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Franciscan; Lyon, Rhone)
· Eglise Saint-Thomas (8-9th c.CE: est.Adelochus; burned in 1007/1144; 1196 CE: Roman; 1521 CE: Gothic; Lutheran; organs- played by Mozart, tombs- sarcophagus of Adelochus, frescos; Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Elne (Neolithic: Iberian oppidum; Pyrenees-Orientales)
· Embrun [Greek: Ebrodunum; Roman; Mansio; Hautes-Alpes)
· Embrun Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (5th c.CE: relics of Saint Nazarius; 1170-1220 CE: Romanesque; built over foundations of 9th c.; Hautes-Alpes)
· Evreux (4th c.CE: Gallic-Eburovice: Aulerci; Roman: Mediolanum Aulercorum: Gisacum: theatre, palace, baths, aqueduct, Jupiter Stator; Eure)
· Evreux Cathedral (11th c.CE: Gothic; Evreux, Normandy)
· Frejus (49 BCE: Roman: Forum Julii; 7-9th c.CE: Muslim invasions; Var)
· Frejus Cathedral/Saint Leontius (5-13th c.CE: medieval religious bldgs.; Frejus, Provence, Var)
· Gap (Gaul; 14 BCE: Roman: Vapincum; Hautes-Alpes)
· Gap Cathedral (5th c.CE: predecessor cathedral over a Roman temple of Apollo; Gap, Hautes-Alpes)
· Gavrinis [Breton: “goat” (gavr) “island” (enez)] [MA](4500/3117 BCE: Neolithic: tumulus, dolmen, standing stones, cairn; passage of 23/29 orthostat slabs decorated w/carved symbols and patterns-zigzags, lozenges, snake-like lines; star alignments; star stones- Hydra; Gulf of Morbihan; near Carnac; Larmor-Baden, Britanny)
· Glandeves [Gaulish: “a habitation on the riverbank”](6th c.BCE: Ligurian-Oxybii; 3rd c.BCE: Celto-Ligurian; 125 BCE: Roman; 406 BCE: Burgundian pillage)
· Glozel (Neolithic: 3000 artifacts, clay tablets, sculpture, vases; Vichy)
· Gourin [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus; Quimper, Britanny)
· Grand Menhir, Broken Menhir of Er Grah [MA](4700 BCE; Locmariaquer, Brittany)
· Grenoble (Gallic-Allobroges: Cularo; 286 BCE: Roman: Gratianopolis; wall; 11th c.CE: Counts of Albon; Isere)
· Guernsey [MA](Neolithic: Le Dehus Dolmen contains dolmen deity, Le Gardien du Tombeau; sculpted menhirs; star stones- Sagittarius; Channel Islands, UK; Sark)
· Harrespil [Basque: “stone circle”; “garden/necropolis” (baratz)][MA](1200 BCE: Bronze/Iron; stone circle; tumuli)
· Huelgoat [MA](Neolithic: Le Chaos de Rochers-hundreds of large boulders, Devil’s Grotto, La Roche Tremblante-137 ton boulder, Le Champignon, La Mare aux Fees, La Mare aux Sangliers, Le Camp d’Artus-Gaulish oppidum, La Grotte d’Artus; star stones- Ophiuchus-eta/Sabik; Britanny)
· Janze [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Caput-beta, Bootes; Rennes, Ille-et-Vilaine, Britanny)
· Kerguntuil [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens, Autumn Equinox; near Lannion; Britanny)
· Kerzerho [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; Carnac, Erdeven, Morbihan, Brittany)
· La Bretelliere [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Bootes, Corona Borealis; Western Loire; E Nantes)
· La Chaise (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal; Troyes)
· La Chapelle-aux-Saints (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; Brive-la-Gaillarde)
· La Ferrassie (250-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· La Quina (75-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· La Rochelle (Gallic-Santone; Roman: Saint Eloi and Les Minimes; salt evaporating ponds; Charente-Maritime)
· La Rochelle Cathedral/Saint Louis (1152 CE: predecessor church of Saint Bartholomew w/bell tower; some d.by fire by Huguenots in 1568; 1648-1784 CE; Neo-Classical; La Rochelle, Charente-Maritime)
· La Trinité-sur-Mer [MA](4500/3117 BCE: Neolithic; tumulus, dolmen, standing stones; star alignments; star stones- Leo; near Carnac; Morbihan, Britanny)
· Langres (Celtic-Lingone: Gallo-Roman: Andematunnum; crossroads of 12 roads; triumphal gate; defense walls; Haute-Marne)
· Langres Cathedral/Saint Mammes (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Langres, Haute-Marne)
· Lannion [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Cauda-eta/Alava <= Lannion>; Cotes-d’Armor, Britanny)
· Lanvenael [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-beta; Quimper, Britanny)
· Laon (Gallic-Roman: Alaudanum/Lugdunum Vlavatum; Aisne)
· Laon Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (800 CE: predecessor Carolingian cathedral; 10th c.CE: 2nd cathedral torched 1112 CE; 12-13th c.CE: Gothic; Laon, Aisne, Picardy)
· Lascaux (16000 BP: Paleolithic: cave paintings-2000 figures: animals, humans, abstract symbols; Neolithic; star stones- Leo; Aquitaine; Montignac; near Dordogne)
· Le Mans (Aedui-Aulerci; Roman: Vindinium/Civitas Cenomanorum; amphitheatre, thermae, wall; 11th c.CE: struggles between counts of Anjou and dukes of Normandy; Sarthe)
· Le Mans Cathedral/Saint Julian (1217-54 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Le Mans, Sarthe)
· Le Moustier (250-45k BP: Neanderthal site: 2 rock shelters; Brive-la-Gaillarde)
· Le Puy Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (8th c.CE: place of pilgrimage; 12th c.CE: Romanesque; near [MA] megalithic dolmen crowning Mons Anicius; Le Puy-en-Velay, Auvergne)
· Lectoure (prehistoric oppidum)
· Lesconil [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-alpha, Antares; Quimper, Britanny)
· Les Rochers-de-Villeneuve (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Lezardrieux [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Cauda-theta/Alyr <=Ardrieux>; St. Brieuc, Cotes-d’Armor, Britanny)
· Limoges (Gallic-Lemovice; 10 BCE: Roman: Augustoritum; amphiteatre, forum, baths; temple to Venus, Diana, Minerva, and Jupiter; Haute-Vienne)
· Limoges Cathedral/Saint Stephen (1273-1888 CE: Gothic; Limoges, Haute-Vienne)
· Locmariaquer [MA](Neolithic: 5000 BCE: Er-Grah tumulus passage; dolmen-Table des Marchand-large carvings; 4700 BCE-d.4000 BCE: standing stones-Broken Menhir of Er Grah-280 tons, largest menhir in the world, broken into 4 pieces; Les Pierres Plates/the flat stones; mounds of Mane Retual; dolmens: Kercadoret, Kerveresse, Mane Lud; star alignments; star stones- Hydra; near Carnac; Locmariaquer, Britanny)
· Lodeve [MA](Celtic-Volque-Lutevani; Roman: Luteva; dolmen near Prior of Saint Michel de Grandmont; Herault)
· Lodeve Cathedral/Saint Fulcran; Saint Genesius of Arles (4th c.CE: 1st cathedral and crypt; 10th c.CE: rebuilt; 13-15th c.CE: Gothic; Herault)
· Lugdunum [lugh = Auriga] [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Gemini; Auvergne; Lyon)
· Lyon (Gallic: Lugdunon; hill fort; 43 BCE: Roman: Lugdunum; Ancient Theatre of Fourviere, Ogdeon of Lyon, Amphitheatre of the Three Gauls; Rhone)
· Lyon Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (6th c.CE: predecessor church; 12-15th c.CE: basilica; Lyon, Rhone)
· Macon (1st c.BCE: Celtic-Aedui: Matisco; oppidum; Saone-et-Loire)
· Maguelone (Gallo-Roman: 1/7 cities of Septimania; 462 CE: Visigoth; Villeneuve-les-Maguelone, Herault)
· Maguelone Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Villeneuve-les-Maguelone, Herault)
· Maillezais Cathedral/Saint Peter (f.989 CE; Benedictine abbey; d.in 1562; Maillezais, Vendee)
· Marseille (30000 BP: Paleolithic cave paintings; underwater Cosquer cave; 6000 BCE: Neolithic: brick habitations; 600 BCE: Greek-Phocaea; oldest city in France; 49 BCE: Roman: Massilia; Visigoth; 6th c.CE: Frankish k.; Bouches-du-Rhone)
· Meaux (Gallic-Meldi; Seine-et-Marne)
· Meaux Cathedral/Saint Stephen (12-16th c.CE: Gothic; Meaux, Seine-et-Marne)
· Metz Cathedral/Saint Stephen (5th c.CE: predecessor church; 13-16th c.CE: Gothic; Metz)
· Montpellier Cathedral/Saint Pierre (14-17th c.CE; Montpellier)
· Moula-Guercy (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Moulins Cathedral/Saint Stephen (15th c.CE: Flamboyant; Moulins, Allier)
· Mount Bego [MA](Neolithic; red megalith; star stones- Taurus-Aldebran; French Riviera; near Menton, Nice)
· Moutiers (Celtic-Ceutrone: Darantasia; Roman; Savoie)
· Mur-de-Bretagne [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus-delta; near Saint Gilles-Vieux-Marche; Britanny)
· Nancy (800 BCE; 1050 CE: Nanciacum; Gerard, Duke of Lorraine; Meurthe r.; Meurthe-et-Moselle)
· Nanterre [Celtic: “shrine;””sacred place” (nemeto) “door”(duros)] (Gallo-Roman: Nemetodorum; Mt.Valerien; Hauts-de-Seine; Paris)
· Nantes (Gallo-Roman; 285 CE: Saxon; 500 CE: Frank; 6-7th c.CE: Briton; 843 CE: Norman; Loire-Atlantique)
· Nantes Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (1434-1891 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Nantes, Brittany)
· Narbonne (118 BCE: Gallo-Roman: Colonia Narbo Maritus; horreum, cryptoporticus, Via Domitia; Visigoth: capital of Septimania; Aude)
· Narbonne Cathedral/Saint Justus and Pastor (1272 CE: Gothic; Narbonne, Aude)
· Neaufles-Auvergny [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hercules; near Rouen; Eure, Upper Normandy)
· Nevers (Aedui; 52 BCE: Roman: Noviodunum; Nievre)
· Nevers Cathedral/Saint Cyricus and Saint Julitta (14-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Nevers, Nievre)
· Nice (400000 BP: Lower Paleolithic: Acheulean: flint tools; Terra Amata; 230000 BP: use of fire; construction of houses; 350 BCE: Greeks of Masillia/Marseille: Nikaia [“Nike”]; Roman; 7th c.CE: Genoese League; 859-80 CE: burned by Saracens; Nice)
· Nimes (4-2000 BCE: Neolithic: Bronze Age: Serre Paradis; 2500 BCE: menhir of Courbessac or La Poudriere [MA]; 1800-600 BCE: village; 600-49 BCE: Celtic: Nemausus; hill fort at Mt.Cavalier; 49 BCE: Roman: Colonia Nemausus; aqueduct- Pont du Gard; Tour Magne; 19 BCE: temple of Agrippa- Maison Carree/”Square House”; 2nd c.CE: amphitheatre, thermae, forum; 473 CE: Visigoth; Vistrenque r.; Gard)
· Nimes Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (believed to be on former temple of Augustus; Romanesque-Gothic; Nimes, Gard)
· Notre Dame of Paris Cathedral (1163-1345 CE: Gothic; Paris)
· Notre-Dame-en-Vaux (1157-1217 CE: Gothic; cloister; Chalons-sur-Saone)
· Noyon (Gallo-Roman: Noviomagus/Veromanduorum; 768 CE: where Charlemagne crowned 1st Holy Roman Emperor; Oise)
· Noyon Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1131 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; built over church that burned; Noyon, Oise)
· Oloron Cathedral/Saint Mary (12th c.CE; Oloron-Sainte-Marie, Pyrenees-Atlantiques)
· Orange (Celtic-Cimbri-Teutone: hill fort; 35 BCE: Roman: theatre, triumphal arch; 412 CE: Visigoth; Vaucluse)
· Orleans (Gallic-Carnute: Cenabum; stronghold where the Druids held their annual assembly; 52 BCE: Roman: Aurelianum;
· Orleans Cathedral/Saint Croix (1278-1329 CE: Gothic; Orleans)
· Pech de l’Aze (250-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· Perigueux [Latinized Celtic: “the four tribes” (Petrocorii)](Gallic-Roman: amphitheatre, villa, temple/dormus of Vesunna; Dordogne)
· Perigueux Cathedral/Saint Front (1120 CE; Perigueux, Dordogne)
· Perpignan (Roman; Pyrenees-Orientales)
· Perpignan Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (1324 CE; Perpignan, Pyrenees-Orientales)
· Peyre Quillade stones [MA](menhir; Ariege)
· Pierre-Qui-Vire [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Virgo; near Les Sables d’Olonne, Avrille, Vendee r.; W Loire)
· Plouarzel [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-kappa/Girtab, Autumn Equinox; Pointe de Corsen, Brest, Britanny)
· Ploudalmezeau [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-nu/Lesath; 1978: Amoco Cadiz oil spill; Britanny)
· Plouescat [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Cauda-omicron; Britanny)
· Plouguerneau [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; Britanny)
· Plouhinec [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-tau, Antares; Quimper, Britanny)
· Pointe de la Torche [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-pi; Quimper, Britanny)
· Poiters (Celtic-Pictone: oppidum Lemonum; [MA] Pierre Levee dolmen; Roman: amphitheatre, baths, 3+ aqueducts; Visigoth; Vienne)
· Poiters Cathedral/Saint Pierre (1162 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Poitiers, Vienne)
· Pontigny Abbey/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1114 CE: Cistercian; burials; viticulture; Serein r.; Pontigny, Yonne)
· Pontoise (Roman: Pontisara; Paris, Val-d’Oise)
· Pontoise Cathedral/Saint Maclou (12-16th c.CE: Gothic; Pontoise, Paris)
· Portsall [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-lambda/Shaula = sall; Ploudalmezeau, Britanny)
· Le Pouget [MA](Neolithic: dolmen; star stones- Lupus, Columba, Southern Stars; Gallardet; near Montpellier)
· Quimper (Celtic: capital of La Cornouaille; Roman; Finistere)
· Quimper Cathedral/Saint Corentin (Gothic; Quimper, Finistere, Brittany)
· Regourdou (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Reims (80 BCE: Gallic-Remi: Durocorteron “round fortress”; Roman: Durocortorum; Porte de Mars; triumphal arch, 4 gates, walls; 406 CE: Vandal; 451 CE: Attila the Hun fires/pillage; Marne)
· Reims Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (400 CE: predecessor church of Saint Nicaise; 12th c.CE: Gothic; Reims, Marne)
· Rennes [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Caput; Celtic-Armorican: Condate “confluent”; Roman: wall; Ille-et-Vilaine; Britanny)
· Rennes Cathedral/Saint Pierre (6th c.CE: predecessor church; 12-15th c.CE: Gothic-Neoclassical; Rennes, Ille-et-Vilaine)
· Rieux Cathedral/Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1317 CE; Rieux-Volvestre, Haute-Garonne)
· Riez (Celtic-Ligurian: hill-fort; Roman: Alebaece Reiorum Appolinares: temple of Apollo; Alpes-de-Haute-Provence)
· Riom [MA](Neolithic; Menhir du stade de la Varenne- Gemini-Pollux, Castor; star stones- Gemini; Auvergne; near Clermont-Ferrand)
· Rodez (5th c.BCE: Celtic oppidum; Roman: Segodunum/Civitas Rutenorum; Visigoth; Frank; 725 CE: ravaged by Arabs; Aveyron)
· Rodez Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (516 CE: predecessor church; 1000 CE: rebuilt; 13-15th c.CE: Gothic; Rodez, Aveyron)
· Rostrenen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus-zeta; Britanny)
· Rouen (Gallic-Veliocasses: Ratumacos; Roman: Rotomagus; 2nd city of Gallia Lugdunensis; thermae, amphitheatre; capital of Merovingian Neustria; 841 CE: overrun by Vikings; 10th c.: capital of Duchy of Normandy; Seine-Maritime)
· Rouen Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (4th c.CE: predecessor church perished during Viking raid in 9th c.CE; 1202-1880 CE: Gothic; Rouen, Normandy)
· Roussayrrolles [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Middle/Hole of the Milky Way; Midi Pyrenees; near Toulouse, Tarn)
· Saint Alpin (1170 CE: Romanesque; Chalons-sur-Saone)
· Saint Amans (12th c.CE; 1758-61 CE: rebuilt Baroque interior; 6th c.tapestries representing the miracles of Saint Amand; Rodez, Aveyron)
· Saint Andre en Bas (Benedictine monastery; 1152 CE: rebuilt Romanesque; Vienne, Isere)
· Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges (72 BCE: Roman: Lugdunum Convenarum; 408 CE: Vandal; Haute-Gaudens)
· Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 16th c.CE: Renaissance; Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges, Haute-Gaudens)
· Saint-Brieuc Cathedral/Saint Stephen (6th c.CE: predecessor church f.Saint Brieuc; 14-15th c.CE; Saint-Brieuc, Normandy)
· Saint Cesaire (45-28k BP: Neanderthal-human)
· Saint-Claude Cathedral/Saint Pierre, Saint Paul, Saint Andre (5th c.CE: predecessor Condat Abbey; 4th abbot, Saint Eugendus; 12th abbot, Saint Claudius; 15th c.CE: abbey church; Saint-Claude)
· Saint Denis Cathedral (7th c.CE: burial place of Saint Denis; abbey f.Dagobert I; pilgrimage and burial place for French kings from 10-18th c.CE; 12-13th c.CE: Rayonnant-Gothic; Paris)
· Saint Emilion [MA](Neolithic; Menhir de Pyrefitte, Saint Sulpice de Faleyrens; Gironde, Dordogne River; star stones- Hydra; Aquitaine; near Bordeaux)
· Saint-Etienne (12-16th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; built over Roman fortifications; portal sculpture “Wheel of Life”; Beauvais, Oise)
· Saint-Etienne (9th c.CE: Romanesque; Nevers, Nievre)
· Saint-Flour (Bronze Age: [MA] dolmens; Roman: villas; Cantal)
· Saint-Flour Cathedral/Saint Peter; Saint Florus (1398-1466 CE: Gothic; Saint-Flour, Cantal, Auvergne)
· Saint Gilles-Vieux-Marche [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus-epsilon; near Mur-de-Bretagne; Britanny)
· Saint Guenole [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-delta; Quimper, Britanny)
· Saint-Lizier (72 BCE: Gallo-Roman; Saint Girons, Ariege)
· Saint-Lizier Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Lycerius (Romanesque; Saint-Lizier, Saint Girons, Ariege)
· Saint-Malo Cathedral (1108 CE: monastery; Saint-Malo, Brittany)
· Saint Martin (12th c.CE; abbey; Templar chapel; Laon, Aisne, Picardy)
· Saint Mathieu [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-theta/Sargas <Sumerian/Akk.: maasu = Mathieu>; Britanny)
· Saint Odile, Mont [MA](1000 BCE: Neolithic; Pagan’s Wall-ancient border betwn.France and Germany; Adalric’s castle- Aquarius-Sadal Melik; end of wall- Ecliptic; Quarry-Ancha- Aquarius; Castle of Hail- Piscium; Dreistein “Three Stone Castle”- Aquarius; Odilia’s Source- Winter Solstice, 3117 BCE; Menel Stone/Menelstein; Druid’s Grotto; earthworks; star stones- Aquarius/Al Dalw <Arab.>, Edeleu/Dul/Delle/Daulo/Dolium-The Bucket; near Hohenburg Abbey; Vosges m.; Altitona, Strasbourg, Alsace)
· Saint-Omer Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (Gothic; Saint Omer, Pas-de-Calais)
· Saint-Papoul Cathedral/Saint Papulus (8th c.CE: Abbey of Saint Papoul; 1317 CE: cathedral; Saint Papoul, Carcassonne, Aud)
· Saint-Paul-Trois-Chateaux Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (4-6th c.CE; Saint-Paul-Trois-Chateaux, Drome)
· Saint Peter (ancient Benedictine; 9th c.CE: rebuilt Romanesque basilica; Vienne, Isere)
· Saint-Pierre-en-Vallee (17-18th c.CE: Gothic; over 6th c.abbey; Auxerre, Burgundy, Yonne)
· Saint-Pol-de-Leon Cathedral/Saint Paul Aurelian (6th c.CE: bishopric; 13th c.CE: Gothic; Saint-Pol-de-Leon, Morlaix, Finistere)
· Saint-Pons-de-Thomieres Cathedral/Saint Pontius (936 CE: Romanesque abbey church; Saint-Pons-de-Thomieres, Herault)
· Saint Samson-sur-Rance, La Templais [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus; Britanny)
· Saint-Sulprice-de-Faleyrens [MA](menhir Peyrefitte; Gironde)
· Saint-Urbaine Basilica (1261 CE: Gothic; Troyes, Aube, Champagne)
· Saintes (Roman: amphitheatre, triumphal arch-Arch of Germanicus, thermae, aqueduct; Charente Maritime)
· Saintes Cathedral/Saint Peter (12th c.CE: original; 13-20th c.CE: Romanesque-Flamboyant; Saintes, Charente Maritime)
· Saumur [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Major; btwn. Loire and Thouet r.; near Poitiers, Pays de la Loire, Maine-et-Loire)
· Sarlat Cathedral/Saint Sacerdos (Carolingian Benedictine; 9th c.CE: belfry; 1317 CE: diocese; rebuilt 1680; Sarlat-la-Caneda, Dordogne, Aquitaine)
· Sees Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (13-14th c.CE: Gothic; Sees, Normandy)
· Senez Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (1176-1246 CE: Romanesque; 1673 CE: sundial; Senez, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence)
· Senlis (Roman: Augustomagus/Civitas Silvanectium; amphitheatre; 3rd CE: walls; Oise)
· Senlis Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1153-91 CE: Gothic; 1530-56 CE: trancepts rebuilt after fire; Senlis, Oise)
· Sens (Senone: Agedincum/oppidum Senonas; Yonne)
· Sens Cathedral/Saint Stephen (12-16th c.CE: Gothic; Sens, Bourgogne)
· Simandre-sur-Suran [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pleiades; near Mt.Blanc; near Bourg St.Maurice)
· Sisteron (2000 BCE; Roman; Saracen; Alpes-de-Haute-Provence)
· Sisteron Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Thyrsus (1160-1220 CE: Romanesque; Sisteron, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence)
· Soissons (Celtic-Suessione: Noviodunum; Roman; Aisne)
· Soissons Cathedral/Saint Gervais and Saint Protais (1177-1211 CE: Gothic; Soissons, Aisne)
· Sospel Cathedral/Saint Michael (11/13th c.CE: belltower; 1642-1762 CE: Renaissance; Sospel,
· Strasbourg (600000 BP; Neolithic: Bronze Age; Iron Age; 1300 BCE: propo-Celtic: Argentorate; 12 BCE: Roman: Argentoratum; Alemanni; Hun; Frank; Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Strasbourg Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1015-1439 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; astronomical clock; Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, Alsace)
· Terra Amata (400000 BP: Lower Paleolithic: Acheulean: flint tools; 230000 BP: use of fire; construction of houses; Nice)
· Toul (Gallic-Leuci: capital; Roman: Tullum Leucorum; Meurthe-et-Moselle, Lorraine)
· Toul Cathedral/Saint Stephen (365 CE: diocese; Meurthe-et-Moselle, Lorraine)
· Toulon (Paleolithic: Cosquer Cave; 7th c.BCE: Greek; 4th c.BCE: Ligurian; Visigoth; Saracen attacks; Var)
· Toulon Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (5th c.CE; 11-18th c.CE: Romanesque; Toulon, Var)
· Toulouse (8th c.BCE: Aquitanian-Basque: Tolosa; Iberian; 3rd c.BCE: Celtic Gallic-Volcae Tectosages; 118 BCE: Roman: narbo Martius; Vandal; Visigoth; Merovingian Frank; Haute-Garonne)
· Toulouse Cathedral/Saint Stephen (8-9th c.CE: 1st church; 13-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Flamboyant; Toulouse, Haute-Garonne)
· Tours (Gallic: Turones; 1st c.CE: Roman: Caesarodunum; heart of Carolingian rebirth; Indre-et-Loire)
· Tours Cathedral/Saint Gatien (337-71 CE: 1st cathedral of Saint Maurice burned in 561; rededicated 590; 1166 CE: burned again in conglict between Louis VII and Henry II; 12-16th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Tours, Indre-et-Loire)
· Tregon [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus; St. Malo, Britanny)
· Troyes (Senone; Roman: Augustobona Tricassium; aqueduct; Aube)
· Troyes Cathedral/Saint Pierre and Saint Paul (4th c.CE: original religious bldgs.; oratory; 9th c.CE: cathedral d.by Normans; 940 CE: Romanesque; 1128-9 CE: Council of Troyes; Order of the Knights Templar; burned 1188; 1200-17th c.CE: Gothic; Seine r.; Troyes, Aube, Champagne)
· Tulle Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1317 CE; Tulle)
· Uzes (Gallo-Roman: Ucetia; aqueduct- Pont du Gard; Nimes, Gard)
· Uzes Cathedral/Saint Theodoritus (original cathedral d.during Albigensian Crusade in 12th c.CE; 17-19th c.CE: Neo-classical; Uzes, Nimes, Gard)
· Vaison (Bronze Age: Ligure; 4th c.BCE: Celtic-Vocontii/Voconce; 125 BCE: Roman: villa ruins; Burgundian; Ostrogoth; Frank; Carpentras, Vaucluse)
· Vaison Cathedral/Our Lady of Nazareth (apse and apsidal chapels from Merovingian period; 11th c.CE; Vaison-la-Romaine, Carpentras, Vaucluse)
· Valence (Segalauni: capital; Roman: Valentia Julia; Alan; 413 CE: Goth; Drome)
· Valence Cathedral/Saint Apollinaris (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Valence, Drome)
· Vannes (1st c.BCE: Roman: Darioitum; Morbihan)
· Vannes Cathedral/Saint Pierre (13-19th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Vannes, Morbihan, Brittany)
· Verdun (Celtic-Gallo-Roman: Verodunum; oppidum; Treaty of Verdun split Charlemagne k.into 3 parts; Meuse, Lorraine)
· Verdun Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (330 CE: church f.Saint Sanctinus dedicated to Saint Peter and Paul; 457 CE: Saint Pulchronius built cathedral inside Roman bldg.; 10-18th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Flamboyant-Baroque-Rococo; Verdun, Meuse, Lorraine)
· Vienne (Allobroge: oppidum; 47 BCE: Roman: Vindobona: theatre, aqueducts, roads, ramparts, Temple d/Auguste et de Livie, pyramid; Isere)
· Vienne Cathedral/Saint Maurice (1052-1533 CE: Gothic; Council of Vienne: Pope Clement abolished the order of the Knights Templar; Vienne, Isere)
· Viviers (Gallic-Helvii; Roman; Privas, Ardeche)
· Viviers Cathedral/Saint Vincent (11-12th c.CE; vaulted ceiling d.in 16th c.; Viviers, Privas, Ardeche)
CORSICA: (France); [MA] Dolmen
· Filitosa [MA](3300 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: menhirs; star stones- Draco, North Ecliptic Pole; Bronze Age; Propriano)
· Lucciana (93 BCE: Roman: Mariana)
· Paddaghju [MA](Neolithic; Sartene)
· Tremeca [MA](Neolithic: dolmen; Casaglione, Ajaccio)
· Vescovato Cathedral/Saint Martin (1380 CE; enlarged in 1436; Vescovato)
GERMANY: [megaliths; cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Aachen (Neolithic: Celtic; Roman: Aquis-Granum; Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Aachen Cathedral/Imperial Cathedral/Royal Church of Saint Mary (792 CE: Palatine Chapel by Charlemagne; 814 CE: Sarcophagus of Charlemagne; 936-1531 CE: church of coronation for 30 German kings; oldest cathedral of northern Europe; Aachen, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Abbey of Saint Gall (719 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; collegiate church; Stuttgart, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Altes Lager Menzlin [Ger.: “Old Camp”](900 CE: stone ship; 1.5km S Menslin; Anklam, W Pomerania)
· Andernach [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Leo; Rhine r.; Mayen-Koblenz, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Andreaskirche/Saint Andrew (13-16th c.CE: Gothic cathedral and monastery; Brunswick, Braunschweig)
· Andreaskirche/Saint Andrew (12th c.CE: Ottonian; Evangelical; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Augsburg (15 BCE: Roman: Augusta Vindelicorum; Bavaria)
· Augsburg Cathedral (6th c.CE; Augsburg, Bavaria)
· Bamberg Cathedral/Saint Peter and Saint George (1004-1012 CE: Romanesque; d.by fire in 1081; 13th c.CE: rebuilt; Bamberg, Bavaria)
· Berlin Cathedral (1454 CE: 1st bldg.; Renaissance-Brick Gothic-Baroque-Neoclassical; Berlin)
· Bilzingsleben (370000 BP: Palaeolithic; homo erectus; Thuringia)
· Blankensee [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scutum; Elbe r.; Lubeck; Hamburg)
· Boitin [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cygnus; Schwerin)
· Bonn (Ulbii; 11 BCE: Roman: fort; Cologne, North Rhine-Westpahalia)
· Bonn Minster (11-13th c.CE: collegiate church of Ss. Cassius and Florentius; Cologne, North Rhine-Westpahalia)
· Bremen (Chauci; 150 CE: Roman: Fabiranum; Saxon)
· Bremen Cathedral/Saint Peter (789 CE: 1st church by Saint Willehad; sacked by Saxons in 792; 805 CE: 2nd church; sacked by Danes in 845; 1035-43 CE: rebuilt; destroyed by fire in 1042; 1043-72 CE: Romanesque; 1219-58 CE: Gothic remodel; 1497-1511 CE: High Gothic; crypts/mummies: 90 graves- Willehad of Bremen, Emma of Lesum, Unni; Bremen)
· Brunswick Cathedral (1173-95 CE: Gothic; royal burials: Caroline of Brunswick, George IV of UK, Frederick Duke of Brunswick; Braunschweig)
· CAROLINGIAN Monasteries/Abbeys (around 800 CE): Bavarian Congregation of the Benedictine Confederation
o Altaripa
o Altmunster
o Altomunster (750 CE; Dachau, Bavaria)
o Amorbach (734 CE: Benedictine; Miltenberg, Ascaffenburg, Franconia, Bavaria)
o Andernach
o Annegray
o Benedictbeuren/Saint James; Benedict (740 CE: Benedictine; 955 CE: d.Hungarians; Rococo; Bavarian Congregation; Bavaria)
o Blois
o Chelles (658 CE; Merovingian palace- villa Calae ded. Saint George; Paris)
o Chiemsee
o Corbie (660 CE: Merovingian-Benedictine; Adam and Eve capital; near Amiens; Picardy, France)
o Dol (6th c.CE)
o Echternach (7th c.CE; Luxembourg)
o Faremoutiers (620 CE; Meaux, Seine-et-Marne, France)
o Fecamp (658 CE: Merovingian-Benedictine; 842 CE: d.Vikings; 851 CE: rebuilt; Normandy, France)
o Ferrieres (630 CE: Benedictine; Montargis, Loiret, France)
o Flavigny (717 CE: Benedictine;9th c.CE: Viking raids; 11th c.CE: Carolingian-Romanesque basilica; Dominican; Flavigny-sur-Ozerain, Montbard, Cote-d’Or, France)
o Fleury (640 CE: Benedictine; Saint-Benoit-sur-Loire, Orleans, Loiret, France)
o Fontaine
o Fritzlar (732 CE)
o Fulda (744 CE: Benedictine; Hesse)
o Gorze (749 CE: Benedictine; Metz-Campagne, Lorraine, France)
o Hautvillers
o Hersfeld (736/69 CE: Benedictine; 12th c.CE: Romanesque; Bad Hersfeld, Hesse)
o Holzkirchen
o Honau
o Hornbach
o Jumieges (634 CE: Merovingian-Benedictine; Rouen, Seine-Maritime, Normandy, France)
o Kaiserwerth
o Kempten/Allgau (50 BCE: Celtic Estione: Kambodunon; 15 BCE: Roman; 233 CE: d.by Suebic-Alemanni; 683 CE: d.Franks; 747 CE: f.Irish monks from Abbey of Saint Gall in Switzerland; Bavaria)
o Kitzingen
o Kochel
o Landevennec (485 CE; 8th c.CE: Benedictine; 913 CE: burned by Vikings; Finistere, Brittany, France)
o Lerins (410 CE: Cisternian; fortified monastery; near Cannes, Saint Honorat, Lerins Islands, France)
o Lobbes (650 CE: Benedictine; Lobbes, Hainaut, Belgium)
o Loches
o Lorch
o Lorsch (764 CE: pre-Romanesque; 1170’s CE: Codex Aureus of Lorsch; near Worms; Hesse)
o Luxeuil (Gallo-Roman: Luxovium; thermae; 451 CE: ravaged by Attila, Huns; 585-90 CE: f.Irish Saint Columbanus; 731 CE: Moor raids; 9th c.CE: d.Normans, Magyars, Muslims; Luxeuil-les-Bains, Haute-Saone, Burgundy, France)
o Mazerolles
o Mettlach
o Mondsee (748 CE: Benedictine; former Bavaria; Austria)
o Mont-Saint-Michael (708 CE; 11th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic church; underground crypts and chapels; Normandy, France)
o Montier-en-Der (Gallo-Roman: Puteolus; villa; 670 CE: Benedictine-Cluniac; Voire r.; Haute-Marne, France)
o Murbach (727 CE: Benedictine; Romanesque; Guebwiller, Haut-Rhin, Alsace, France)
o Nantua (660 CE)
o Niederalteich (731 CE: Benedictine; Danube r.; Deggendorf, Bavaria)
o Nivelles (640 CE)
o Noirmoutier
o Nouaille (7th c.CE)
o Novalese/Saint Peter; Andrew (726 CE: Benedictine; Val di Susa, Piedmont, Turin, Italy)
o Ochsenfurt
o Ohrdrut
o Orbais
o Ottobeuren (764 CE: Benedictine; Bavarian Allgau)
o Peronne
o Prum (720 CE: Benedictine; 882-92 CE: plundered by Normans; Rhineland-Palatinate)
o Rebais
o Reichenau (724 CE: Benedictine; Lake Constance; Rhine r.; Konstanz, Baden-Wurttemberg)
o Remiremont (620 CE: Benedictine; Vosges, France)
o Sarlat (9th c.CE; cathedral; Sarlat-la-Caneda, Dordogne, Aquitaine, France)
o Schaftlarn (726 CE: Benedictine; Roccoco; Munich, Bavaria)
o Saint Denis (7th c.CE: Benedictine; f.Dagobert I; 1137 CE: rebuilt Romanesque-Gothic basilica by Abbot Suger; 1231 CE: Rayonnant Gothic; rose window, clerestory, chevet of 9 radiating chapels; royal necropolis of France: all but 3 monarchs of Fr.; Paris, France)
o Saint Gall (719 CE: Benedictine; 924-33 CE: Magyar threats; 937 CE: d.fire; Saint Gallen, Switzerland)
o Saint Hubert
o Saint Maixent
o Saint Maurice d’Agaune (1st c.BCE: Roman: shrine to Mercury; 285 CE: martyrdom of the Theban Legion; 4-5th c.: baptistery; 5-11th c.CE: 4 Carolingian churches built-overs; basilica; 4-8th c.CE: crypts; 11th c.CE: tower; 17th c.CE: current church; Saint Maurice, Switzerland)
o Saint Mesmin
o Saint Mihiel
o Saint Nazaire
o Saint Omer
o Saint Peter
o Saint Quentin
o Saint Riquier
o Saint Trond (7th c.CE; 1129 CE: built up; Sint-Truiden, Limburg, Belgium)
o Saint Wandrille (648 CE: Benedictine; 852 CE: Viking raids; Rouen, Seine-Maritime, Normandy, France)
o Staffelsee
o Stavelot-Malmedy (650 CE: Benedictine; 881 CE: burned by Normans; Walloon, Liege, Belgium)
o Tauberbischofsheim
o Tegernsee (746 CE: Benedictine; Miesbach, Bavaria)
o Tonnerre (800 CE)
o Weissenburg (7th c.CE: Benedictine; Bas-Rhin, Alsace, France)
o Wessobrun (753 CE: Benedictine; Baroque; near Weilheim, Bavaria)
· Cathedral of Constance/Virgin Mary (615 CE: Romanesque cathedral; collapsed in 1052; 1051-69 CE: reconstruction; Constance)
· Church of Our Lady (1425 CE: Gothic; Ingolstadt, Bavaria)
· Church of Saint Andrew (13th c.CE; Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Church of Saint Martin (13th c.CE; Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Church of Saint Paul (13th c.CE; Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Cologne (38 BCE: Ubii: Oppidum Ubiorum; 50 CE: Roman: Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium; North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Cologne Cathedral (predeceding Roman temple by Mercurius Augustus; 4-9th c.CE: 3 predecessor cathedrals; 1248-1880 CE: Gothic; 13th c.CE: Shrine of the Three Kings/Magi, believed to hold the remains of the Three Wise Men; Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Dar Lange Stein [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Leo; near Trittenheim, Bernkastel-Wittlich, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Degernau [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Puppis, Canis Major; near Swiss border; Wutoschingen, Waldshut, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Denghoog [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; Sylt i., North Frisian Islands; near Wenningstedt-Braderup)
· Dessau [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cassiopeia; junc. Mulde and Elbe r.; near Mogdeburg, Saxony-Anhalt)
· Doppelkirche (1151 CE: cathedral; Bonn, Cologne, North Rhine-Westpahalia)
· Drachenfels m. [Dragon’s Rock”] [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Bootes; near Bonn)
· Dresden (7500 BCE: Neolithic: Linear Pottery; Saxony)
· Ehringsdorf (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Erfurt (100000 BCE: Paleolithic; Neolithic; 480 CE: Thuringii; Thuringia)
· Erfurt Cathedral (800 CE: predecessor Romanesque basilica; 14-15th c.CE: Gothic; Wise and Foolish Virgins statues; 1507 CE: Martin Luther ordination; Erfurt, Thuringia)
· Essen (280000 BCE: Vogelheimer Klinge; Mesolithic; 3000 BCE: Megalithic tomb; Chatti-Bructeri-Marsi; 2nd c.BCE: Alteburg castle; North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Essen Cathedral (845 CE: former collegiate church by Altfrid; 1275 CE: Gothic; Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Externsteine [MA](-10000 BCE: Paleolithic-Mesolithic: stone tools; 1100 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- North Celestial Pole; near Bielefeld; Ostwestfalen-Lippe; near Detmold)
· Felsenmeer [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cancer; near Darmstadt-Stromberg; Odenwald m.)
· Frankfurt (Roman; 794 CE: Alemanni-Frank; Holy Roman Empire- Charlemagne imperial assembly; Hesse)
· Frankfurt Cathedral/Saint Bartholomew (5th c.CE: predecessor Merovingian church; 14-15th c.CE: Gothic; Frankfurt, Hesse)
· Frauenkirche/Church of Our Lady (1205 CE; 1450 CE: rebuilt Gothic after fire; Meissen, Dresden, Saxony)
· Freiberg Cathedral/Saint Mary (1180 CE: basilica; collegiate church; 1225 CE: crucifixion group; golden gate; 1484 CE: fire; 1505 CE: rebuilt; Freiberg, Saxony)
· Freiberg Minster (1120 CE: predecessor church; 1200-30 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Freiberg, Saxony)
· Freising (Bronze Age; 8th c.CE: Frigisinga; Bavaria)
· Freising Cathedral/Saint Mary/Corbinian Cathedral (1159-1250 CE: original church d.fire; tomb of Saint Corbinian; 1724 CE: Rococo; Freising, Bavaria)
· Gielow [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; stone cist; near Gielow, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Gnadenthal monastery (Gothic; Ingolstadt, Bavaria)
· Godehardikirche/Saint Godehard (1133-72 c.CE: Romanesque basilica; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Gollenstein [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hydra; 20km E Saarbrucken; Blieskastel)
· Goseck circle (4900 BCE: Neolithic: Bronze Age)
· Goslar (Neolithic: Saxon; Holy Roman Empire; Lower Saxony)
· Great Saint Martin Church (960 CE: Romanesque; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Grob Zastrow dolmen [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Halle/Saale [pre-Germanic: “salt”] (2500-2000 BCE: Bronze Age: Bischofs Wiese: 35 graves; Saxony-Anhalt)
· Halle Cathedral (1271 CE: original Dominican monastery; Saxony-Anhalt)
· Helmsdorf (1940 BCE: Bronze Age: Unetice culture; 14 kurgans; Thuringia)
· Hirsau Abbey (830 CE: Benedictine; Hirsau, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Hildesheim Cathedral/Saint Mary (1010-20 CE: Ottonic Romanesque; bronze doors; bronze column; sarcophagus of Saint Godehard; 11-14th c.CE: renovations; 12th c.CE: shrine of Saint Epiphanius; Hildesheim, Saxony)
· Hirschlanden (600 BCE: warrior sculpture; Hallstatt culture)
· Hospital of the Holy Spirit (1260 CE: Lubeck, Schleswig-Holstein)
· Ingolstadt (806 CE: mentioned by Charlemagne; f.Bavarian Illuminati; Bavaria)
· Konigsaue (80000 BP: flints, hand axes; Saxony-Anhalt)
· Konstanz (Stone Age; Alemanni; 50 CE: Roman: Constantia; Freiburg, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Kreuzkirche/Church of the Holy Cross (1079 CE; d.1945; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Kruckow dolmen [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; Demmin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Kunzing [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Orion; Deggendorf, Bavaria)
· Kyffhauser Nebra [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cepheus; near Andisleben, Erfurt, Thuringia, Saxony-Anhalt)
· Kyhna [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; near Leipzig)
· Lancken-Granitz dolmens [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; 7 dolmens, 3 are encircled by solitary rocks forming either a stone circle or rectangles, one has a solitary “Guardian stone”; Rugen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Lehmsiek Dolmen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Sagittarius; Eckernforde)
· Liebfrauenkirche/Church of Our Lady (Gothic; Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Liebfrauenkirche/Church of Our Lady (15th c.CE; Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Liepen [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; passage grave w/hunenbett; near Liepen, Anklam, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Limburg Cathedral (910 CE: 1st church; 1190 CE: Romanesque; 1827 CE: former monastery raised to become current cathedral; Limburg, Hesse)
· Locknitzer See [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; megalith w/cup mark; near Krakower See and Plauer See, along Recknitz r.; Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Lubeck ([MA]Neolithic dolmens; Slavic; Charlemagne Christianization-Polabian Slavs opposed by Saxons, who moved out; Obotrite confederation; burned by Rani; Schleswig-Holstein)
· Lubeck Cathedral/Saint George (1173-1230 CE: Romanesque; 1266-1335 CE: Gothic conversion; partially d.in bombing raid 1942; Lubeck, Schleswig-Holstein)
· Lubecker Jakobikirche/Church of Saint Lawrence (1334 CE; Lubeck, Schleswig-Holstein)
· Magdeburg (f.Charlemagne)
· Magdeburg Cathedral/Saint Maurice (937 CE: original abbey; shrine of Saint Maurice; burned in 1207 on Good Friday; 1209-1520 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 5 Foolish Virgins statues; 1631 CE: Thirty Years War- 4000 citizens took sanctuary in the church to survive the Sack of Magdeburg; partially d.by firebombing, 1945; Magdeburg, Saxony-Anhalt)
· Magdalenenkirche/Saint Magdelena’s Church (1224 CE: Romanesque; 1456 CE: Gothic; 1720-5 CE: Baroque garden; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Magnikirche (13th c.CE: cathedral; Magniviertel; Brunswick, Braunschweig)
· Mainz (Celtic: Mogons <Gallic god: Mogons, “great one”>; 13 BCE: Roman: castrum Moguntiacum; Frank; Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Mainz Cathedral (911 CE: Romanesque; Saint John’s church; Saint Salvator church; 1279 CE: Gothic; Mainz, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Markt Kirche/Marien Church (1529-54 CE: combination of 2 older churches: 11-12th c.CE: Gertruden Church + Marien Church; Saxony-Anhalt)
· Martinkirche (13-15th c.CE: Gothic; Altstadtmarkt; Brunswick, Braunschweig)
· Mauritiuskirche/Saint Maurice (11th c.CE: Romanic; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Mecklenburg-Vorpommern [MA](3500-3200 BCE: Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; dolmens-5000 tombs, 1000 preserved; barrow/tumuli; stone circles; various Neolithic sites: Rerik; Lancken-Granitz; Grob Zastrow; Kruckow; Nobbin; Locknitzer See; Liepen; Gielow; etc.)
· Meissen Cathedral (13th c.CE: Gothic; Meissen, Dresden, Saxony)
· Merseburg Cathedral (1015-1517 CE: Gothic-Renaissance; Merseburg, Saxony-Anhalt)
· Michaeliskirche (1154 CE: Romanesque basilica; 1517 CE: Martin Luther’s 95 Theses; Zeitz)
· Michaelsberg Abbey (12th c.CE; 1/7 hills; Bamberg)
· Mauritiuskirche/Saint Maurice (11th c.CE: Romanic; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Mittelbrunn [MA](menhir; Rhineland-Palz)
· Munich Frauenkirche (12-16th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Renaissance; crypt of royal tombs of Wittelsbach d. and Archbishops of Munich and Freising; Munich, Bavaria)
· Naumburg Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (1029 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Naumburg, Saxony)
· Neumunster (Romanesque-Baroque church; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Nickern [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pleiades; near Dresden)
· Nuremberg Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (1445 CE: Gothic; badly damaged during WWII; Nuremberg, Bavaria)
· Neanderthal Valley (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; Dusseldorf; Erkath)
· Nibelungen [Old Norse: (Niflung); Norse myth.: royal family of Burgundian lineage who settled at Worms; dwarf (nybling)] [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cancer; near Stromberg and Worms)
· Nogenschwiel [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Puppis, Canis Major; near Swiss border)
· Obermunster (1010 CE: Romanesque basillica; Regensburg, Bavaria)
· Oldenburg [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ophiuchus; Oldenburg)
· Osnabruck [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Serpens Caput; near Osnabruck)
· Osnabruck Cathedral/Saint Peter (11th c.CE; Osnabruck)
· Paderborn Cathedral/Saint Mary, Saint Kilian, Saint Liborius (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; relics of Saint Liborius; crypt; royal tombs; window of three hares; Paderborn, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Passau (Boii; 2nd c.BCE: Roman: Boiodurum/Batavis; Bavaria)
· Passau Cathedral/Saint Stephen (1688 CE: Baroque; largest pipe organ in world; Passau, Bavaria)
· Peterskirche/Saint Peter’s Church (8th c.CE: pre-Merovingian abbey church: Petersbergl; 1158 CE: Bavarian Romanesque; 1327 CE: expanded Gothic after fire; 17th c.CE: Renaissance steeple; Baroque choir; Munich, Bavaria)
· Pfahlbau Museum Unteruhldingen (Neolithic: stilt houses)
· Pulheim [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Bootes; near Cologne; Rhein-Erft-Kreis, N Rhine-Westphalia)
· Ratzeburg Cathedral (1154 CE: Romanesque; Ratzeburg)
· Regensburg (Stone Age; Celtic: Radasbona; 90 CE: Roman: fort, walls-Porta Praetoria; 179 CE: Castra Regina; Bavaria)
· Regensburg Cathedral/Saint Peter (700 CE: original church; 11-17th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Regensburg, Bavaria)
· Hunenbett on Reisenberg [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; Hunenbett/standing stones in rectangular shape; Nobbin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Rerik dolmen [MA](Neolithic: Funnelbeaker culture; dolmen; near Rerik, SE Rugen, Bad Doberan, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
· Rugen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Capricorn, Aquila)
· Saint Andreas (974 CE; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Apostle (9th c.CE; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Catherine Church (14th c.CE: Brick Gothic; Franciscan; Lubeck, Schleswig-Holstein)
· Saint Cecilia (9th c.CE; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Emmeram abbey/Schloss Thurn und Taxis (13th c.CE: Romanesque basillica; Regensburg, Bavaria)
· Saint Georg (11th c.CE; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Gereon Basilica (350 CE; 1067 CE: Romanesque; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Kunibert (1247 CE; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Lambert’s Church (1375 CE; 1535 CE: Munster Rebellion; 3 cages; Munster)
· Saint Maria im Kapitol (690 CE; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Maria Lyskirchen (948 CE; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Mary’s Cathedral (1015 CE: Romanesque; Bernward’s door- bronze; 1000 year old rose bush; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Saint Mary’s Cathedral/Virgin Mary (1272 CE: diocese; Furstenwalde)
· Saint Matthias Abbey (10-12th c.CE: Romanesque basilica; crypt; Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Saint Michael (Baroque church; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Saint Michael’s Church (1010-22 CE: Ottonian; Hildesheim, Lower Saxony)
· Saint Maurice (1235 CE: Gothic; Ingolstadt, Bavaria)
· Saint Pantaleon (10th c.CE: Romanesque; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Peter’s Cathedral (1213 CE: Gothic; Bautzen)
· Saint Paul’s Cathedral (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1540 CE: astronomical clock; Munster)
· Saint Pauline Church (4th c.CE: 1st church; 1148 CE: 2nd church; 1734-53 CE: Baroque; 3rd church; Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Saint Peter (Baroque church; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Saint Sebaldus Church (8th c.CE: original church; 13-17th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Nuremberg)
· Saint Severin (4th c.CE; Altstadt-Sud, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Stephen (Baroque church; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Saint Stephen’s Church (730 CE: many churches; 1668 CE: Baroque; Danube r.; Passau)
· Saint Ulrich (13th c.CE: Transition style; Regensburg, Bavaria)
· Saint Ursula (5th c.CE: built over Roman cemetery where supposedly 11,000 virgins assoc. w/Saint Ursula were buried; Altstadt-Nord, Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia)
· Saint Wenceslas Church (Gothic; Naumburg, Saxony)
· Salzgitter-Lebenstedt (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Schalenstein [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-Antares; Bunsoh Albersdorf)
· Schleswig Cathedral (850 CE: original missionary church; 1134-1200 CE: Romanesque basilica; 1180 CE: Petri Portal; collapse of towers in 1275; 12-16th c.CE: Gothic; royal burials; Schleswig, Schleswig-Holstein)
· Schottenkirche/Church of Saint James (12th c.CE: Romanesque basillica; Regensburg, Bavaria)
· Schwerin Cathedral/Virgin Mary and Saint John (1172-1248 CE; Schwerin)
· Schworstadt [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Argo, Canis Major; near Swiss border; Lorrach, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Siebensteinhauser [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Draco, North Ecliptic Pole; near Bremen)
· Spellenstein [MA](menhir; St.Ingbert)
· Speyer (2500 BCE: Bronze Age; Neolithic; Hallstatt-La Tene cultures; 2nd m.BCE: Celtic-Mediomatrici; 1500 BCE: Golden Hat of Schifferstadt; 50 BCE: Roman-Nemete)
· Speyer Cathedral (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; burial site for Salian, Staufer and Habsburg emperors and kings; Speyer, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Stendal Cathedral (12th c.CE; Stendal)
· Stift Haug (1670-91 CE: Baroque church; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Stiftskirche (10-12th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; collegiate church; Stuttgart, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Stuttgart (1st c.CE: Roman: fort; Alamanni; Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Suntelstein [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Corona Borealis; near Osnabruck)
· Tiengen/Waldshut-Tiengen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Argo, Canis Major; near Freiburg; near Swiss border)
· Trier (2000 BCE: Assyrian; 1st c.BCE: Roman: walls-Porta Nigra, baths, amphitheatre, bridge; Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Trier Cathedral/Saint Peter and Blessed Virgin Mary (4th c.CE: original basilicas; ruined by Franks; rebuilt and d.by Normans in 882; 12-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; royal tombs; Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Ulm (5000 BCE: Neolithic: Eggingen, Lehr; Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Ulm Minster (1377-1890 CE: Gothic; tallest church in world; Ulm)
· Unser Lieben Frauen Monastery/Our Beloved Lady (11th c.CE; Magdeburg, Saxony-Anhalt)
· Wasserburg (Bavaria)
· Wetzlar (5000 BCE: Neolithic: Linear Pottery culture; Bandkeramiker; Roman; Hess)
· Wetzlar Cathedral (897 CE: Salvatore church replaced older one; 10th c.CE: collegiate church devoted to Saint Mary; 1170- CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Hess)
· Wiblingen Abbey (f.1093 CE: Romanesque; 1701 CE: Baroque renewal; Ulm, Baden-Wurttemberg)
· Wildhusen[MA](Neolithic; star stones- Sagittarius; Lubeck)
· Worms [Celtic: “watery area”](Celtic: Borbetomagus; 14 BCE: Roman: temples of Jupiter, Juno, Minerva; Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Worms Cathedral (1110 CE: original building; 12-14th c.CE: Romanesque; Rhine r.; Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate)
· Wurzburg (1000 BCE: Celtic fortification where Fortress Marienberg; Bavaria)
· Wurzburg Cathedral (787-855 CE: 2 original churches d.by fire; 1040-75 CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque basilica; Wurzburg, Bavaria)
· Xanten (2000 BCE: Germanic tribes; 15 BCE: Roman: amphitheatre; Frank; Rhine-Westphalia)
· Xanten Cathedral (1263-1544 CE: Gothic; Rhine r.; Xanten, North Rhine-Westphalia)
GREECE: (Neolithic Bronze; Minoan/Mycanean)[Greek temples]<Cretan-Atlantis>
[NOTE 94] Crete is on the Mediterranean fault line; many Cretan-Minoan (ie. Atlantean) sites were destroyed by a cataclysmic earthquake and tsunami caused by a volcanic eruption on on Thira/Santorini (a major center of Atlantis) volcanic eruption (possible Atlantis site; Nibiru crossing)(c.1500 BCE; 1450 BCE: circa the emergence of Mosaic Hebrew alphabet- Exodus of Moses from Egypt; heiroglyp-phonetic shift)
[NOTE 95: According to Plato: Atlantis was destroyed in a single day and night, the land was swallowed by the sea; end of Atlantis description- new Atlantean center, Thira/Santorini, was destroyed by a volcano and tsunami, which lead to the destruction of Cretan-Atlantis (Cretan-Egyptian link: after destruction perhaps Crete petitioned trading partner Egypt <source of Atlantis myth> for aid); Atlantis had hot and cold water, plumbing;
[NOTE 96: 590 BCE: Greek statesman, Solon was shown inscriptions from 1450 BCE, describing an ancient civilization of great power, ruling all the lands W of Egypt; Atlantis story becomes Greek folklore, until in; 370 BCE: Plato’s version of the Egyptian tale of Atlantis; Solon must have invented the name ‘Atlantis’ because the Egyptians called the people from this ancient world by another name, ‘Keptchu,’ [Egypt.: ‘people of Crete’]; then Greece conquers Crete
· Abdera (700 BCE; Thrace)
· Aegina (2000 BCE: Temple of Aphaea, Temple of Zeus, Temple of Apollo)
· Aigeira/Hyperesia (3000 BCE: theatre)
· Aigosthena (300 BCE: fortified city)
· Akraefnion (Boeotia)
· Akrotiri (2000 BCE: Minoan eruption buried city; Santorini)
· Alifeira (370 BCE; Elis)
· Amfilochia (Aitolia-Acarnania)
· Amphiareion/Limnea of Kalamos (500 BCE; Oropos)
· Amphipolis (437 BCE: Edoni people; Serres)
· Amykles (800 BCE; Laconia)
· Anafi (Cyclades)
· Anemospilia (Minoan: Heraklion, Crete)
· Anthidona (Boeotia)
· Antissa (Lesbos)
· Apollonia (Milos)
· Apollonia (Sifnos)
· Apollonia (Eleutherna, Rethymno, Crete)
· Apsalos (Pella)
· Aptera (1400 BCE; Chania, Crete)
· Archanes (Minoan: Heraklion)
· Argos (Argolis)
· Arisbe (Lesbos)
· Armeni (Rethymno, Crete)
· Arta (300 BCE; Ambracia)
· Asclepion (300 BCE; Kos)
· Asea (Arcadia)
· Asini (Argolis)
· Athens [Odeon of Herodes Atticus (161 CE), Acropolis, Kerameikos (3000 BCE), Pnyx (507 BCE), Colonus, Areopagus, Kallimarmaro Stadium (329 BCE), Temple of Olympian Zeus (600 BCE), Temple of Hephaestus (449 BCE), Ancient Agora of Athens (600 BCE), Roman Forum, Theatre of Dionysus]
· Treasury of Atreus [MA](1250 BCE: Argos; Mycenae);
· Avlida (Boeotia)
· Bassae (500 BCE: Temple of Apollo; Arcadia)
· Brauron (2000 BCE; East Attica)
· Calydon (Aetolia)
· Cassiope (Corfu)
· Cathrea (Kea, Cyclades)
· Chaeronea (600 BCE; Boeotia)
· Chalcis (Euboea)
· Chios (2000 BCE: Temple of Apollo)
· Cleonae (Argolis; Corinth)
· Corfu
· Corinth (6000 BCE)
· Cynosura (Salamis, Piraeus)
· Delium (West Attica)
· Delphi (Oracle; Phocis)
· Delos (3000 BCE: Cyclades)
· Dimini (5000 BCE: Volos, Magnesia)
· Dion (Pieria)
· Dispelion (Kastoria)
· Dodona (2000 BCE: Gaia oracle; Ioannina)
· Dorio (Messenia)
· Dreros (750 BCE; Lassithi, Crete)
· Dystos (Euboea)
· Eadion (Salamis, Piraeus)
· Eani (Kozani)
· Eleftherae (West Attica)
· Eleusina (1700 BCE; West Attica)
· Elis (800 BCE; Ilia)
· Elyros (500 BCE; Rodovani, Crete)
· Epitalion (Ilia)
· Eresos (Lesbos)
· Eretria (600 BCE; Euboea)
· Ephyra/Kichyro (1400 BCE: Necromanteion; Preveza)
· Epidaurus (600 BCE; healing center of Asclepios; theatres; Argolis)
· Tunnel of Eupalinos (600 BCE: aqueduct; Samos)
· Evropos (Kilkis)
· Figaleia (Ilia)
· Fthiotides Thivae (Magnesia)
· Gioura (Neolithic; Alonnisos, Magnesia)
· Gomfoi (Lygaria, Trikala)
· Goniae (Heraklion, Crete)
· Gortyn (7000 BCE; Heraklion, Crete)
· Gournia (Lasithi, Crete)
· Gynaecokastron (Kilkis)
· Gytheio (Laconia)
· Hellenikon (2720 BCE: pyramid; Argolis)
· Hephaestia (Lesbos)
· Hagia Triada (Minoan; Heraklion, Crete)
· Heraion of Argos (Mycenaean; Argolis)
· Heraion of Samos (800 BCE)
· Ialysos/Trianta (Rhodes)
· Ierapetra and Vasiliki (Lasithi, Crete)
· Isthmia (700 BCE: Temple of Poseidon; Corinth)
· Ios (3000 BCE: Cycladic; Cyclades)
· Itanos (Lasithi, Crete)
· Ithica (4000 BCE: Homeric; Kefalonia)
· Ithomi (Messenia)
· Kalymnos (Dodecanese)
· Kameiros (600 BCE: acropolis; Rhodes)
· Kallithea (Temple of Ammon Zeus; Chalkidiki)
· Kastron (Boeotia)
· Kechries (600 BCE; Corinth)
· Kionia (Tinos, Cyclades)
· Kleitor (Arcadia)
· Knossos (1700 BCE; acropolis great hill palace of 1300 chambers; large crystalline gypsum foundation stone; central court yard, Eastern royal quarter, 4-story spiral staircase in the core; timber framing made walls earthquake resistant; terra cotta water pipes; pier and door partitioning, ancient Atlantean site?; Minataur myth; Heraklion, Crete; archeologist- Arthur Evans)
· Kolchis (Kilkis)
· Kos (Carian; Dodecanese; birthplace of Hippocrates)
· Kydonia (Chania, Crete)
· Kyparissia (Messenia)
· Lakeria (Paleolithic; Larissa)
· Lato (500 BCE: Dorian; Lasithi, Crete)
· Lefkadia (Imathia)
· Lefkopetra (Imathia)
· Lentas (3000 BCE; Heraklion, Crete)
· Lepreum (Neolithic; Ilia)
· Lerna (5000 BCE; Argolis)
· Lindos (1000 BCE: Dorian acropolis; Rhodes)
· Linos (Rhodope)
· Lissos (Chania, Crete)
· Loukous (Arcadia)
· Roman Aqueduct of Louros (Preveza)
· Lycaeon (Arcadia; Mount Lykaion: human sacrificial rite feast sacred to Zeus; origin of lyconthropy and Olympic games-Lykaia)
· Lyctus/Lyttos (Heraklion, Crete)
· Lycosura (Arcadia)
· Magasa (Neolithic; Lasithi, Crete)
· Malia (1500 BCE: destroyed by tsunami wave; Heraklion, Crete)
· Mantineia (Arcadia)
· Maroneia (600 BCE; Rhodope)
· Matala (Neolithic caves; Heraklion, Crete)
· Megalopolis (371 BCE; Arcadia)
· Megara (667 BCE; West Attica)
· Menelaeon (Laconia)
· Mesemvria (Evros)
· Midea (Argolis)
· Milos (13000 BP: obsidian; Cyclades)
· Minia (Kefalonia)
· Minoa (Amorgos, Cyclades)
· Mochlos (Lasithi, Crete)
· Mount Athos
· Mount Juktas (Heraklion, Crete)
· Fortress of Mycenae [MA](1600 BCE: Argos)
· Marina (Lemnos)
· Mycenae (3500 BCE: Neolithic; 2nd millenium BCE: Greek; Argos)
· Myrtos Pyrgos (Lasithi, Crete)
· Mystras (Laconia)
· Mytilene (Lesbos)
· Naousa (Imathia)
· Nape (Temple of Apollo; Lesbos)
· Naupactus (Aetolia-Arcanania)
· Naxos (Cyclades)
· Nemea (Corinth)
· Palace of Nestor (Messenia)
· Nicomedia (Macedonian tombs; Imathia)
· Nymphasia (Arcadia)
· Oiniades (Aetolia-Arcanania)
· Olous (Lasithi, Crete)
· Olympia [MA](1000 BCE: Temple of Zeus; Ilia)
· Olynthus (Neolithic; Chalkidiki)
· Orchomenus/Boeotia [SM](2800 BCE; Mt. Olympus; Kalpaki)
· Orchomenus (Arcadia)
· Pegasae (Volos, Magnesia)
· Paleopolis (Andros, Cyclades)
· Panormos (Mykonos, Cyclades)
· Paros (Cyclades)
· Patras (Arcaea)
· Pella (413 BCE: Macedonian capital)
· Perachora (Heraion; Corinth)
· Perrevia (Mt. Olympus; Leivadi, Larissa)
· Petrae (Florina)
· Phalasarna (335 BCE; Crete)
· Phaistos (4000 BCE; Heraklion, Crete)
· Phanarion (Rhodope)
· Phanariion (Icaria, Samos)
· Pharsala (Larissa)
· Pheneos (Mt.Cyllene: myth. birthplace of Hermes; Corinth)
· Philippi (356 BCE; Kavala)
· Phourni (1400 BCE; Heraklion, Crete)
· Piraeus (2600 BCE)
· Plevrona (Aetolia-Arcanania)
· Polyrrinia (Chania, Crete)
· Poseidi (Temple of Poseidon; Chalkidiki)
· Poliochne (Lesbos)
· Poikilassos (Chania, Crete)
· Plataies (Boeotia)
· Poseidonia (700 BCE; Syros, Cyclades)
· Potidaea (600 BCE; Chalkidiki)
· Praessus (Lasithi, Crete)
· Pydna (Pieria)
· Pylos (Messenia)
· Pyrassos/Nea Anchialos (6000 BCE; Magnesia)
· Pyrgos (Boeotia)
· Pythagoreion (600 BCE: Tunnel of Eupalinos; Heraion of Samos)
· Rhamnus (Temple of Nemesis; East Attica)
· Rhodes (Neolithic: walled cities; Dodecanese)
· Samothrace (600 BCE: temple complex; Sanctuary of the Great Gods; Evros)
· Serres (500 BCE)
· Sesklo (Magnesia)
· Sikinos (Cyclades)
· Skillounta (Ilia)
· Sounion (East Attica)
· Sparta (650 BCE; Laconia)
· Spilia (Achaea)
· Stratos (ampitheatre, acropolis, temple of Zeus; Aetolia-Acarnania)
· Stymphalia (Corinth)
· Syia (Chania, Crete)
· Sykyon (Corinth)
· Tanagra/Poimandria (Boeotia)
· Tarra (Agia Roumeli, Crete)
· Tegea (Stadio, Arcadia)
· Tegyra [SM](oracle of Apollo; Boeotia; Mt. Delos)
· Thasos (15000 BP: mining; Kavala)
· Thebes (Boeotia)
· Thermopylae (Fthiotis)
· Thermos (1500 BCE (Aetolia-Acarnania)
· Thespiae (Boeotia)
· Thessaloniki/Salonica
· Thira (4000 BCE: Minoan; 1966: archeo- James Maver Jr. uncovered ancient town of multi-story buildings at Akrothiri, beneath volcanic ash c. 1500 BCE; still being uncovered; terra cotta plumbing connected to lavatories on upper levels of buildings- toilets; possible central site of Atlantis; Santorini, Cyclades)
· Thisbe (Boeotia)
· Tiryns (7000 BP; Argolis; Nauplion)
· Thermae of Traianopolis (Evros)
· Toroni (800 BCE; Chalkidiki)
· Tower of the Winds (53 BCE: Andronikos; octagonal astronomical structure; Athens acropolis)
· Trikke (Trikala)
· Troezen (Piraeus)
· Trophoniou Oracle (Livadeia, Boeotia)
· Tylissos (Heraklion, Crete)
· Vapheion (Laconia)
· Vanaena (Arcadia)
· Vergina (650 BCE: Macedonian tombs; Imathia)
· Vistonis (Xanthi)
· Vrissa (Lesbos)
· Yrtakina (Chania, Crete)
· Zakros (1900 BCE; Lasithi, Crete)
HUNGARY: (ancient Greek colony; cathedrals)
· Aquincum (41 CE: Roman Empire; Budapest)
· Mosque of Pasha Jacowali Hassan (Islamic; Pecs)
· Old Mosque in Pecs (Islamic; Pecs)
· Ullo (3d-4th c.CE: Budapest)
ICELAND: [MA] [megaliths
IRELAND: [MA] [dolmen; megalithic standing stones (star stone markings/petroglyphs); cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
[NOTE 55: Megalithic standing stones are not arbitrary shaped, carved, positioned, or oriented, and may serve a specific purpose (geodetic planisphere of heaven/astronomical system); many may have been shaped to give a living identity (ie.animal forms); many may represent a particular star or constellation; quartz stones markings appear to glow in the dark; many stone markings depicts stars and constellations that are represented by the stone’s location. (Andis Kaulins)]
[NOTE 73] 15th c. maps show a small circular island, called Hibrazil, off the southwest coast of Ireland (island is now submerged, but would have existed during the last ice age, c.10000 BCE) (Graham Hancock)
· Achill Island [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Achill i., Erris, Mayo)
· Aghade [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Pleiades; Carlow)
· Aill Na Mireann [Gaelic: “stone of the division; sim.Latv.: “measure” (merien); sim. Old Irish: “number” (numir); Latv.: “to measure out”(nuomer); German: “count”(nummer); root of English: (number); Pharaonic: “plumbline” (merkhet)] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Cassiopeia, Camelopardalis, North Ecliptic Pole; markings: capstone markings- Draco, Ursa Major and Minor, North Ecliptic Pole, Cassiopeia, Perseus; central stone/front side markings- Bootes, Centaurus, Hercules, Libra, Virgo, Lupus, Leo, Hydra, Crater; Catstone/back side- Vega Lyra, Cygnus, Serpens Caput, Aquila, CoronaScorpio, Sagittarius, Triangulum; West Meath)
· Ardagh/Saint Mel (10th c.CE: former cathedral)
· Ardfert Cathedral (6th c.CE: original monastery f.Saint Brendan; 12-17th c.CE: ruins; Ardfert, Kerry, Dublin)
· Ardgroom [Irish: “two drumlins” (dha dhroim)]/Canfea [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; Beara pen.; Ardgroom, Cork)
· Ardmore [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio, Ophiuchus, Libra; Waterford, Munster)
· Ardmore Cathedral (13th c.CE: ruined; Ardmore)
· Ardristan [Ardri; sim.Pharaonic: Athyr; Arabic: Al Thurayya; for Pleiades][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Pleiades; Carlow)
· Aughnacliffe [Gaelic: “axe” (aughna); Scottish Gaelic: “file” (eigh); Irish: “axe” (oighe); Gothic: “axe” (aqizi)] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Minor; Longford)
· Ballybane [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- False Cross, Carina, Vela, the Sail; Roscommon)
· Ballyboher [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic;star stones- Cetus; Loch Garman; Wexford)
· Ballyedmonduff [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze; construction based on Creevykeel in Sligo; wedge tomb on SE slope of Two Rock Mountain surrounded by U-shaped double walled kerb filled w/stones; “the giant’s grave”; star stone markings- Andromeda, planisphere; Glencullen, Dublin)
· Ballyhaunis [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Ballyhaunis, Erris, Mayo)
· Ballykeel [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Aquila; Armagh)
· Ballylowra [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Taurus; Kilkenny)
· Ballynacloghy [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Leo, Hydra; Galway)
· Ballyvatheen [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Taurus; Kilkenny)
· Baltynanima [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Aries, Triangulum; Wicklow)
· Beenalaght [Irish: “the six” (an seisear)] [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: alignments of 6 menhirs; .5km W Bweeng, Cork)
· Boheh/Cathair na Mart [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; rock art- St. Patrick’s Chair; star stones markings- Hydra, Centaurus, Crux, line of solstices, Milky Way; Westport, Mayo)
· Bohonagh [MA](Bronze: recumbent stone circle-13/17 stones 30ft dia.; 2 portal stones on E-W axis, aligned w/sunset on the equinoxes; quartz inclusions; dolmen w/large 20 ton capstone w/7+ cup-marks on upper surface; 2.4km E Rosscarbery, Cork)
· Brownshill/Portal Tomb [MA](4000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; 3km E Carlow, Carlow)
· Bru na Boinne [“mansion on the Boyne”]/Bend of the Boyne [MA](3500-3200 BCE: Neolithic: complex of dolmens, menhirs, henges, and enclosures; 480 passage graves; Bend of Boyne river sites: Newgrange, Knowth, and Dowth, Cloghalea Henge, Townleyhall passage grave, Monknewtown henge and ritual pond, Newgrange cursus; Bronze/Iron/Roman/Medieval artefacts; Meath)
· The Burren [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: Poulnabrone dolmen; star stones- Bootes, Draco, Aquila, Cygnus, Lyra, Ophiuchus, Hercules, Corona Borealis, Serpens Caput, Coma Berenices, Virgo; Clare, Munster)
· Carrigagulla [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-18 stones; Ballinagree, Cork)
· Carrowkeel [MA](3000/2430 BCE: Neolithic: Cairn G Portal Stone; star stone markings- Virgo, Cygnus- Deneb, Bootes, Lacerta, Cepheus, Ursa Minor, Major, Big Dipper, North Celestial Pole; Summer Solstice Eclipse Position: June 25, 2430 BCE; Sligo; near Boyle, Roscommon)
· Carrowmore [MA](5400 BCE: Neolithic: 30 dolmens; dolmen circles-small dolmens encircled by ring of 30-40 boulders 12-15m dia.; <burial place of Queen Maeve?, ancestor of Celts; Anglo-Saxon: Maiden; Latin: Minerva>; star stones markings- Virgo; Sligo)
· Cashel Cathedral (ruined; Cashel)
· Castlestrange stone [MA](500 BCE-100 CE: Iron Age: granite boulder decorated w/flowing spiral carvings in La Tene style; Castlestrange House; Athleague, Roscommon)
· Ceide [Gaelic: “first of summer” (ceitein); sim. Latvian: “a place to sit” (sede); sim.Scott.Gaelic: “the hollow of a bird’s nest” (cuach)] Fields [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; oldest agriculture of humanity?; earthworks; star stones- Hydra, Corvus, Crater, Centaurus, Crux; near Ballina at Belderrig, Ballycastle, Mayo)
· Christ Church Cathedral (1030 CE: Roman Catholic; Diocese; Dublin, Dublin)
· Cloghstuckagh [Gaelic: “stone” (clog); “sheep horn” (stoc); “hind” (agh)][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Camelopardalis as big horn sheep, North Ecliptic Pole; markings- serpent, Cassiopeia; West Meath)
· Clonard/Saint John (1206 CE: destroyed by fire)
· Clonkeen [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Gemini; Offaly <’Barbarian’ Alioc: “Auriga” (laois); Gaelic: “Gemini” (uabh failghe); sim.Latv.: “two/both” (abi); Anglo-Normon: “Gemini” (frère); Gaelic: “brothers” (vraar); Ovid: “Gemini” (oebalii)>)
· Clonmacnoise [Irish: “meadow of the sons of Nos”] (545 CE: original monastery f.Saint Ciaran; 800 CE: North Cross; 909 CE: Cathedral; 11th c.CE: Temple Dowling; 1124 CE: Round Tower; 12th c.CE: Temple Finghin- Romanesque; 1200 CE: Temple Melaghlin; 17th c.CE: Temple Hurpan; 18th c.CE: Temple Connor; Offaly, Dublin)
· Clonfert Cathedral (563 CE: original monastery, Saint Brendan; 1180-16th c.CE: Hiberno-Romanesque-Gothic; Clonfert, Dublin)
· Cloyne Cathedral/Saint Coleman (1250 CE: church built on older buildings, Saint Brendan; Cloyne, Dublin)
· Cobh [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Canopus; Cork)
· Cork Cathedral (7th c.CE: original church; 1865-79 CE: Gothic Revival; Cork, Dublin)
· Coumaraglin [Gaelic: “river, channel” (mara = amar, amyrr); “river head” (glin = geill); Indo-European/Lav.: “end/tip” (galina)][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Eridanus, Caelum; Waterford)
· Creevykeel [“court tomb”; “court circle planisphere”][MA](8000 BCE: Mesolithic; 3000 BCE: Neolithic; one of oldest sites in Ireland; star stones markings- Virgo, Ophiuchus, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Bootes, Serpens Caput, Aquila, Cygnus, Pegasus, Andromeda, Corvus; 2500 BCE: Bronze; 500 BCE: Iron; Sligo)
· Cruachan Skregg [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Major; Roscommon)
· Derrynablaha [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones markings- Break/Ends of Milky Way, Vela, False Cross, Carina, Puppis; Kenmare, Kerry <Gaelic: “boat” (curach)>]
· Dowth [MA](2500-2000 BCE: Neolithic: passage tomb, tumulus; winter solstice alignment; Bru na Boinne, Newgrange, Meath)
· Drombeg stone circle/The Druid’s Altar (945-830 BCE: recumbent stone circle-13/17 stones; Portal Stones; W of Rosscarbery; Glandore, Cork)
· Drumnart [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle; star stones markings- Cygnus; Monaghan)
· Eightercua [MA](1700 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: menhir; stone row dolmen; 1.5km SE Waterville, Kerry)
· Faulagh [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Faulagh, Erris, Mayo)
· Fenagh Beg [Lietrim: “bootes” (fenagh); Arabic: (nakkar); sim.Gaelic: “nail” (ionga); Latv.: “nail” (nag); “at the nail” (pienaga)] Beg [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; dolmen; star capstone markings- Bootes; 5km from Carrick-on-Shannon; Leitrim)
· Ferns Cathedral/of Saint Edan (1230 CE: original; Gothic; Diocese; 1800 CE: r.; Dublin, Dublin)
· Glantane East [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; dolmen; btwn. Macroom and Millstreet; Cork)
· Glencullen [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: menhir; Ballyedmonduff cairn/dolmen; star stones markings- front- Andromeda, Cassiopeia; back- Bootes, Ophiuchus; Dublin)
· Glendalough [“Glen of Two Lakes”] Cathedral/Saint Peter and Saint Paul (6-13th c.CE: ruined monastery f.Saint Kevin; Glendalough, Dublin)
· Glengad Stone Circle [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Kilcommon, Erris, Mayo)
· Gleninsheen [Gaelic: “web” (sneeuane); “loom” (shaol); sim.Latv.: “sewn” (shujina)][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; dolmen; 31 cm gold collar found 1932; star stone markings- Cancer <spinning wheel>, Leo, Gemini; Clare)
· Grianan of Aileach (800 BCE; Donegal)
· Hill of Tara (3400 BCE; Meath; Leinster)
· Innisfallen Is. (700 CE; Lough Leane)
· Kilclooney (Ardara)
· Kilcommon [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Kilcommon, Erris, Mayo)
· Kilcrea Friary (600 CE; Cork City)
· Kildare [“Church of the Oak”] Cathedral/of Saint Brigid (1223 CE: original Norman church; over Pagan temple of Brigid?; Diocese; Kildare, Dublin)
· Kilfenora [“Church of the Fertile Hillside/White Brow”] Cathedral (1200 CE: partly ruined; Kilfernora, Dublin)
· Kilkenny Cathedral/Saint Canice (6th c.CE: original church; 9th c.CE: Round Tower; 13th c.CE: Gothic; Diocese; Kilkenny, Dublin)
· Killala [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; Killala, Erris, Mayo)
· Killaloe Cathedral (12th c.CE: Gothic; Diocese; 2001 CE: r.; Killaloe, Dublin)
· Kilmore Cathedral (6th c.CE: predecessor church by Saint Feithlimidh; 1454 CE: Roman Catholic Diocese; Kilmore)
· Knockeen Dolmen [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; dolmen; star stones- Eridanus, Columba, Caelum, Horologium, Large Magellan Cloud; Waterford)
· Knocknakilla (1500 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle; radial cairn and 2 pointed portal stones; dolmen; located btwn. Macroom and Millstreet, Cork)
· Knowth [MA](2500-2000 BCE: Neolithic: tumulus/mounds- Draco; largest passage graves at Bru na Boinne w/17 smaller satellite tumuli; large mound contains 2 passages, cruciform chamber, and is encircled by 127/130 kerbstones; megalithic art- spirals, lozenges, serpentiform; star stone markings- North Ecliptic Pole, North Celestial Pole, Pole Star; Equinox alignment; Milankovitch cycles/precession/Earth’s tilt cycle alignments; Bronze-Celtic: 35 cist graves; Iron Age: hill fort w/encircling ditches; Norman: Mellifont monks; Bru na Boinne, Newgrange, Meath)
· Labbacallee wedge tomb [Irish: “hag’s bed” (leaba chailli)] [MA](Neolithic: 3 large capstones, largest-10 tons; 8km NW Fermoy, 2km SE Glanworth, Cork)
· Liagans at Kilmihil [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Cancer, Leo, Hydra; Clare <in N are “wedge tombs”- narrowing stone chamber covered w/mound of earth>; Kilmihil, Clare)
· Limerick Cathedral/Saint Mary (1168 CE: built on Viking meeting place, thingmote; Diocese; Limerick, Dublin)
· Lisbunny [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Orion, Taurus; Tipperary <Gaelic: “the well of Ara” (tiobraid arainn); ara = Orion>; Tyrone-Londonderry)
· Lismore Cathedral/Saint Carthage (17th c.CE: medieval cathedral destroyed by fire; 1663 CE: r.; Diocese; Lismore, Dublin)
· Lisseyviggeen/Seven Sisters [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; near Killarney; Kerry)
· Loughcrew/Sliabh na Cailli [Irish: “mountain of the hag”] [MA](3500-3300 BCE: Neolithic: cairns/passage tomb; petroglyphs-lozenges, leaf shapes, circles, radiating lines; alignments: Cairn L-equinox sunrise; Cairn T-winter solstice sunrise; star stone markings- Cassiopeia, North Ecliptic Pole, North Celestial Pole, Pole Star; near summit of Sliabh na Cailli; Oldcastle, Meath)
· Lough Gur [Gaelic: “lake” (logh); “to hatch, lie on eggs” (gur/guir); Latv.: “to lie down” (gul; “to heat” (kur); lake/nest of the cosmic egg] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: Grange stone circle-113 menhirs, 45m dia., largest in Ireland, 300m W Lough Gur; alignment- summer solstice sunrise at center of circle; largest menhir-Ronnach Croim Duibh/The Black Stone, 13’h, 40 tons; dolmen; crannogs; house outlines-‘The Spectacles’; ring forts, hill fort; findings: 2 hearths, human and cattle bones, bronze, pottery; second smaller stone circle-large menhirs, N large leaning menhir; star stone markings- hole in the Milky Way/cosmic egg,; Grange Lios, Limerick <”meadow” (leim); “heap” (rick); heap in a meadow/hole in Milky Way>)
· Meehambee dolmen [MA](3500 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen- 24 ton capstone; Athlone, Roscommon)
· Monasterboice (521 CE; Drogheda)
· Mullagharoy Cupmarked Stone [MA](3300 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Cupmarked stone- Dracp, Cassiopeia, North Ecliptic Pole, North Celestial Pole, Pole Star, Cepheus; Meath)
· Newgrange/Si An Bhru [Gaelic: “eternal/perpetual” (si); “log/beam” (bhru) = North Ecliptic Pole] [MA](3300 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- 1 BCE: North Ecliptic Pole, North Celestial Pole, Pole Star, Ursa Minor, Draco; Drogheda, Meath <Latv.: “central post” of heaven (miet); Gaelic: “become weak” (meath); “balance” (meidh)>; dome shape- magnetic bowl emitter?)
· Poulnabrone [Gaelic: “hole of the quern” (poll na bron); Irish: “hole of sorrows”][MA](4200-2900/3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen-portal stones; cairn; findings: 16-22 adults, 6 children, polished stone axe, bone pendant, quartz crystals, weapons, pottery; star stone markings- Cancer; 8km S Ballyvaughan; The Burren, Clare)
· Punchestown [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Perseus, Pleiades; Kildare <Gaelic: “oak tree” (darree, darach)>)
· Raphoe Cathedral/of Saint Eunan (6th c.CE: predecessor monastery; 9th c.CE: Diocese; Raphoe)
· Rath Cruathan [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic/Iron Age: rath/ringfort; star stones- Ursa Major; Roscommon)
· Rathiddy [MA](Legend: Cuchulain’s Stone- Cuchulain, who killed the dog Culann, was mortally wounded, tied to this stone, raven lands on his shoulder; 3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Lacerta, Cygnus; Louth)
· Reask (7th c.CE: Christian monastic ruin w/Ogham standing stone; Ballyferriter, Kerry)
· Saint Mary’s Cathedral (6th c.CE: predecessor church; 12th c.-1839 CE: Romanesque; Diocese; Tuam)
· Saint Patrick’s Cathedral (445 CE: predecessor church and monastery by Saint Patrick; destroyed and rebuilt 17x; 1834-40 CE: Diocese; Armagh)
· Saint Patrick’s Cathedral (1191 CE: Gothic; Diocese; Dublin, Dublin)
· Scattery Island Cathedral and Monastery (510-2 CE: original church f.Saint Senan; 535-1189 CE: Diocese; Shannon estuary, near Kilrush, Dublin)
· Seefin Athgreany [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle; star stones- Aries; Wicklow)
· Skregg [Irish Gaelic: “fern/screech owl” (screeaghag oie)][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Ursa Major; Roscommon)
· Temair Hill of Tara [ancient settlement in Meath was called Tara; Ger.: “weight,” fulcrum of the balance of heaven (tara); Eng. (tare)] [MA](3300/1000 BCE: Neolithic; Lia Fail/Stone of Destiny- marks Pole Star 1000 BCE; star stone markings- North Ecliptic Pole, North Celestial Pole, Pole Star, Draco, Ursa Minor, Vega, Lyra, Cepheus, path of precession <Slighe Cualann>; Meath)
· Templebryan Stone Circle/The Druid’s Temple [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-9.5m dia., 300m NW menhir w/Ogham inscriptions; souterrain/underground structure, bullaun/stone bowl; btwn. Bandon and Millstreet; Clonakilty, Cork)
· Three Friars [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Taurus; Kilkenny)
· Timoney [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Orion; Tipperary)
· Togher [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Aries; Wicklow)
· Trim Castle (c.1174 CE; Meath)
· Trim Cathedral/Saint Patrick (medieval tower remnant; 1955 CE: Diocese; Trim, Dublin)
· Tullow [“the mound”] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Pleiades; Carlow)
· Turoe stone [MA](Celtic: granite stone decorated in Celtic La Tene style of carved flowing spirals; star stones- Leo, Hydra; Turoe house; Bullaun, Galway)
· Uragh/Argo [Gaelic: “boat” (curach)] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle- 8’ dia.; petroglyph; star stone markings- Ends of Milky Way, Vela, Carina, the Sail, False Cross, Large Magellan Cloud; near Gleninchaquin Park; near Kenmare; Tuosist, Kerry)
· Waterford Cathedral/Holy Trinity (11th c.CE: first church; 1210 CE: Gothic; 1773-9 CE: medieval vestments discovered; Georgian; Diocese; Waterford, Dublin)
· Wedge tomb Glantane East Poulnabrone (Burren)
ITALY: (Magna-Graecia)[Roman temples; cathedrals]
Notes per Christianization:
[NOTE 0] It is common for cathedral towns to have castles or fortresses. Most cathedrals are built over older cathedrals or Greek/Roman pagan temples, which echo Canaanite-Egyptian prototypes (ie.cross, tau plans), ultimately rooted in ante-diluvian Sumeria.
[NOTE 1] shifting rivalry for the purpose of indigenous policy unification: Egyptian-Hittite; Greece (Delian League; Peloponesian War; Magna Graecia)-Persia; Rome-Saracens; Christian-Muslim; NATO-terror
[NOTE 2] shifting religion for the purpose of maintaining the metaphysical structures; anthropocosmic encoding within mythos-parable: 12 dieties of pantheon = 12 disciples of Jesus
[NOTE 3] there is an ongoing progressive deceptive-belligerent agenda to centralize global political power, perpetually imposed by the pantheistic-monotheistic religions of “civilization” over the nature practice of indigenous people
[NOTE 4] cathedrals are usually located either/and/or in the heart of an early town, apex of a hill, placing it as the tallest edifice conduit
[NOTE 5] there is much earthquake/volcano damage in Italy throughout Italy; many cathedrals were damaged
[NOTE 6] the Florentine Renaissance indicated increased annunaki traffic
[NOTE 7] most Roman Catholic Cathedrals (diocese) emerged within pre-existing Roman settlements; furthermore building up Greco-Roman temples
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Abbazia del Patire (11-12th c.CE: Arab-Norman; mosaics; Rossano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Acerenza Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Canius (5th c.CE: Diocese; 1080 CE: Romanesque; Acerenza, Potenza)
· Acerra Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (ancient Temple of Hercules; 11th c.CE: Diocese; rebuilt many times; Acerra, Naples, Campania)
· Acquaviva Cathedral/Saint Eustace (18-20th c.BCE: ruined Messapian shrine; 1158 CE: Romanesque; 1529 CE: Renaissance; Acquaviva delle Fonti, Apulia)
· Acqui Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (4th c.CE: Diocese; 989-1018 CE: Romanesque-Baroque; Acqui Terme, Alessandria)
· Agrigento (582 BCE: Magna Graeca: Akragas: Doric; Valley of the Temples; d.by earthquakes; Temples of Juno Lacinia and Concordia- converted into Christian church in 597 CE; 480 BCE: Temple of Olympian Zeus; temples of Hephaestus, Hercules, Asclepius; sactuary of Demeter and Persephone/Temple of Castor and Pollux; 406 BCE: Carthaginian fire d.; near necropoleis; Sicily)
· Alatri (2000 BCE: megalithic acropolis; Porta Maggiore w/tetrahedral and polygonal blocks; 5th c.CE: Temple of Venus; under 1137 CE: Romanesque- Collegiata of Santa Maria Maggiore; 6th c.CE: Badia de San Sebastiano; 930 CE: Cathedral of San Paolo; 13th c.CE: Gothic- Church of San Francesco; 1000 CE: Church of San Stefano; 10-11th c.CE: Church of San Silvestro; 13th c.CE: Gottifredo Palace; 15th c.CE: Church of the twelve Marys; Alatri)
· Albano Laziale (1st millenium BCE: capital of Alba Longa; taken by Romans 700 BCE; ancient Roman baths of Cellomaio; Rome)
· Albano Cathedral/Saint Pancras, Saint John the Baptist (1721 CE: Diocese; built on older Roman basilica; Albano Laziale, Rome)
· Albenga (Celtic orgins; 13 BCE: Roman coast roads; Albenga, Savona, Liguria)
o Necropolis on the Via lulia Augusta
o Roman baths
o Roman amphitheatre (2-3rd c.CE)
· Albenga Cathedral/Saint Michael (4th c.CE: predecessor church; 1100 CE; Albenga, Savona, Liguria)
· Alife (Samnite; Roman; amphitheatre; cryptoporticum; Alife, Caserta, Campania)
· Alife Cathedral/Saint Michael (1132 CE: predecessor church; destroyed by earthquakes in 1456 and 1688; 1692 CE: Baroque; Alife, Caserta, Campania)
· Altamura/Altilia [Lat.: Alter Ilium “the other Troy”] (Bronze Age; 50 tumuli/mounds; 6th-3rd c.BCE: megalithic walls; cave-tombs; dinasaur footprints; Altamura, Bari, Apulia)
· Altamura Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1232 CE; Altamura, Bari, Apulia)
· Amalfi Cathedral (11th c.CE: Baroque; Bernini sculptures; Amalfi, Salerno, Campania)
· Amelia Cathedral/Saint Firmina (5th c.CE: Diocese; 872; 1050 CE: campanile; 1629 CE: Baroque; Amelia, Terni, Umbria)
· Anagni (700,000 BP: human settlement; 7th c.BCE: Hernici; Magna Graecia; Roman)
· Anagni Cathedral/Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1071-1105 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Anagni)
· Annunziata (13th c.CE; frescoes; Sant’Agata de Goti, Benevento, Campania)
· Annunziata dei Catalani (12-13th c.CE: Norman-Arab; Messina, Sicily)
· Ancona Cathedral/Saint Ciriaco (1128-1189 CE: Romanesque; Ancona)
· Andria Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (7-8th c.CE: Norman cathedral; 12th c.CE: diocese; 14th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; Andria, Apulia)
· Aosta Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (4th c.CE: original Roman Catholic church; 11th c.CE: Romanesque; 1846-8 CE: neoclassical; Aosta)
· Aquileia Basilica (5th c.CE: baptistry; 1031 CE: basilica on earlier church; 1379 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Aquileia)
· Aquino Cathedral (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Aquino)
· Arch of Augustus (1st c.BCE-1st c.CE; Spello, Perugia, Umbria)
· Archiepiscopal Chapel (500 CE: early Christian; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Arezzo (5th c.BCE: Etruscan necropolis; Chimera of Arezzo; 311 BCE: Roman amphitheatre; Tuscany)
· Arian Baptistry (500 CE: early Christian; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Ariano (7000 BCE: Neolithic; 900 BCE: Hirpini; Ariano Irpino, Avellino, Campania)
· Ariano Cathedral (10th c.CE: Romanesque; Ariano Irpino, Avellino, Campania)
· Assisi (1000 BCE: Umbrian; 450 BCE: Etruscan; 295 BCE: Roman)
· Assisi Cathedral/San Rufino (3rd c.CE: Umbrian Romanesque 3rd church; contains remains of bishop Rufinus; 1140 CE: Romanesque; baptismal for Saint Francis, 1182, Saint Clare, 1193, and disciples; Mt.Subasio; Assisi, Perugia, Unmbria)
· Asti (Neolithic; 174 BCE)
· Atri (11th c.BCE: Illyrian?; 4th c.BCE: Magna Graecia; 282 BCE: Roman)
· Atri Cathedral/Saint Mary (13th c.CE: Romanesque; Atri, Teramo, Abruzzo)
· Auditorium San Francesco (1229-34 CE: church; Chiavari, Genoa, Liguria)
· Avellino/Abellinum (Samnite Hirpini center; Roman)
· Avellino Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Romanesque crypt; over Roman villa built in 129 BCE; Vesuvius eruption and assoc.earthquakes in 346; Avellino, Campania)
· Aversa Cathedral/Saint Paul (1053 CE: bishopric; Romanesque; sculpture of Saint George and the Dragon; Aversa, Caserta, Campania)
· Badia/ancient Cathedral of Saint Romulus-martyr (1028 CE; became a Benedictine abbey with a valuable library which was dispersed; Fiesole, Florence, Tuscany)
· Badia di SS.Flora e Lucilla (12th c.CE: Benedictine; Vasari; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Badia Fiorentina (f.978 CE: Benedictine abbey; 1071 CE: f.hospital; 1284-1310 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1627-31 CE: Baroque; artwork- Lippi, Ferretti, Angelico, Rossellino; Florence, Tuscany)
· Baptistry of Biella (10th c.CE: Lombard Romanesque; Biella, Piedmont)
· Baptistry of San Giovanni (dodecagon isles forming Greek cross; Canosa di Pulglia, Apulia)
· Baptistry of Neon (4-5th c.CE: early Christian; octagonal plan; basilica d.in 1734; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Bari (3rd c.BCE: Roman)
· Bari Cathedral/Saint Sabinus (9th c.CE: diocese; 12-13th c.CE: Apulian Romanesque; Bari, Apulia)
· Barletta (4th c.BCE: Apulian; Norman-Lombard stronghold; Crusader staging post- Teutonic Knights, Templars, Knights of Saint John)
· Barletta Cathedral/Saint Mary Major (former Temple of Poseidon; 3rd c.BCE: grotticella tombs; 6th c.CE: paleochristian basilica; 12th c.CE: Romanesque; 1267 CE: Gothic; Barletta, Apulia)
· Basilica of the Holy Sepulchre (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Baroque; Barletta, Apulia)
· Basilica of Our Lady of Humility (1509 CE: commissioned by Cosimo I de’Medici; arch.Giorgio Vasari; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· Basilica dell’Osservanza (1490 CE: Renaissance; Siena, Tuscany)
· Basilica of the Queen of Peace/Saint Mary (1112-1683 CE; Campagna, Campania)
· Basilica of Saint Clare (13th c.CE: contains remains of Saint Clare; Assisi, Umbria)
· Basilica of Saint Nicholas (1087 CE: relics; Bari, Apulia)
· Basilica of San Domenico (13-14th c.CE; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Domenico (1228-1240 CE: Renaissance-Baroque; works by Pisano and Michelagnolo; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of San Domenico (1394-1458 CE; Perugia, Umbria)
· Basilica of San Domenico (1226-65 CE: Gothic; 14th c.CE: enlarged; earthquake in 1798; Siena, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Francesco (13-14th c.CE: Tuscan-Gothic; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Francesco (1228-53 CE; Assisi, Umbria)
· Basilica of San Francesco (1228-55 CE: Romanesque; 14th c.CE: enlarged Gothic; earthquake in 1798; Siena, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Frediano (6th c.CE: original church; 1112-47 CE: Romanesque; Lucca, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Lorenzo (1419-1490 CE: Renaissance; built over 11th c.Romanesque bldg.; burial place of principal Medici family members; Old Sacristy by Brunelleschi; Laurentian Library by Micheagnolo; Medici Chapels by Matteo Nigetti- Sagrestia Nuova, Cappella dei Principi; art- Cimabue, Donatello, Vasari, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Basilica of San Lorenzo in Doliolo (13th c.CE: originally over 2nd c.CE temple of Feronia; 6th c.CE: crypt; San Severino, Marche)
· Basilica of San Lorenzo (1177 CE: Romanesque; over paleo-Christian; Verona, Veneto)
· Basilica of San Leucio (Magna Graecia pre-Christian: temple of Minerva; 4-5th c.CE: Roman basilica; Canosa di Pulglia, Apulia)
· Basilica of San Pietro in Ciel d’Oro (6th c.CE: burial of Saint Augustine and other Lombard kings; current constr.in 1132; Pavia, Lombardy)
· Basilica de San Prospero (10th c.CE; 16th c.CE: reconstructed; Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of San Tommaso (3rd c.CE; renovated; 9-11th c.CE: frescoes; Nola, Naples, Campania)
· Basilica of San Vitale (548 CE: early Christian; octagon plan; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of San Zeno Maggiore (1123-35 CE: Romanesque; over 2 paleo-Christian- 4th c.shrine of Saint Zeno; Verona, Veneto)
· Basilica of Sant’Andrea (Mantua, Lombardy)
· Basilica of Sant’Andrea (1219 CE: Romanesque; Vercelli, Piedmont)
· Basilica of Sant’Antonio da Padova (1230 CE; Donatello’s equestrian; Padua, Veneto)
· Basilica of Sant’Apollinare in Classe (549 CE: early Christian; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of Sant’Apollinare Nuovo (500 CE: early Christian; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of Santa Croce/Temple of the Italian Glories (1294-1442 CE: neo-Gothic; Franciscan; burial place- Michelangelo, Galileo, Machiavelli, Rossini, Marconi; art- Cimabue, Donatello, Vasari, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Basilica of Santa Lucia extra Moenia (Byzantine; location of martyrdom of Saint Lucius; 15-16th c.CE; Syracuse, Sicily)
· Basilica of Santa Maria dei Servi (1234 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; art; Siena, Tuscany)
· Basilica di Santa Maria dei Servi (1346 CE: Gothic; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· Basilica of Santa Maria Novella (1246-1360 CE: Gothic-Renaissance; Dominican; built on a 9th c.oratory of Santa Maria delle Vigne; pulpit- Brunelleschi; façade- Leon Battista Alberti; art- Lorenzo Ghiberti, Filippino Lippi, Giorgio Vasari, Masaccio, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Basilica of SS. Apostoli (95 CE; rebuilt in 1190; 1740 CE: Baroque; Nola, Naples, Campania)
· Basilica Santa Restituta (6th c.CE: original paleo-Christian; 13th c.CE: rebuilt; Naples, Campania)
· Belley (Roman; 5th c.CE: dio; Ain)
· Bellocchi/Saint Sebastian Cathedral (16th c.CE; ancient cathedral parts were used; Fano, Pesaro e Urbano, Marche)
· Belluno (f.220 BCE: Roman; wall- Porta Dojona and Porta Rugo; Belluno, Veneto)
· Belluno Cathedral/Saint Martin (15th c.CE; Belluno, Veneto)
· Benedictine Monastery of Conversano (6th c.CE; 1266 CE: expelled by Cistercian; decorations of Paolo Finoglio; Conversano, Bari, Apulia)
· Benedictine Monastery of San Paolo (11th c.CE; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· Benevento (Samnium; 274 BCE: Roman; Benevento, Campania)
o Arch of Trajan (114 CE; Egyptian sculptures)
o Arco del Sacramento
o Bue Apis (Egyptian: basement in shape of the ox; predecessor: Temple of Isis)
o Ponte Leproso
o Roman amphitheatre
o Ruins of Santi Quaranta: Roman cryptoporticus, emporium
o Roman Thermae
· Benevento Cathedral/Saint Mary (1279 CE: campanile; Pisan Gothic; near Roman amphitheatre; Benevento, Campania)
· Bergamo (Celtic-Cenomani; 49 BCE: Roman)
· Bergamo Cathedral/Saint Alexander (9th c.CE: basilica of Saint Alexander; demolished in 1561; refubished 1689; Bergamo, Lombardy)
· Bessa [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cygnus; near Mont Blanc; near Turin and Milan)
· Bevagna (Etruscan-Oscan; 90 BCE: Roman)
· Bevagna Cathedral/Saint Michael (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque; Bevagna, Umbria)
· Biella (Ligurian-Celtic)
· Bisceglie/Vigiliae [Lat.”Sentinel”] [MA](4 dolmens; Chianca Dolmen; Neolithic; star stones- Canis Major; Roman; Norman; near Bari)
· Bisceglie Cathedral/Saint Peter (13th c.CE; Bisceglie, Bari, Apulia)
· Bisignano Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Gothic; d.earthquake; Bisignano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Bitonto (Peucetii; 5-4th c.BCE: 1st city walls; Bitonto, Bari, Apulia)
· Bitonto Cathedral/Saint Valentine; Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (paleochristian church; 11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; Bitonto, Bari, Apulia)
· Bobbio/Bobium/Ebovium (Neolithic; 14th c.BCE: Liguri, Celtic-Boii; Roman: Ponte Vecchio; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Bobbio Abbey (10th c.CE: 700 codices; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Bobbio Cathedral (1075 CE: Gothic; near Ponte Vecchio; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Bojano/Bovianum (7th c.BCE: Pentri; cyclopian wall; Bojano, Campobasso, Molise)
· Bojano Cathedral/Saint Bartholomeew (11th c.CE: Norman; d.earthquakes; Bojano, Campobasso, Molise)
· Bologna (4th c.BCE: Celtic-Boii; 189 BCE: Roman; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· Bologna Cathedral/Saint Peter (1028 CE: pre-Romanesque campanile; destroyed by fire in 1141; reconstructed in 1184; portico added in 1396/1467; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· Bolzano (Raetian Eisack; 15 BCE: Roman)
· Bolzano Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1184-1382 CE: Gothic; Bolzano, Trentino-Alto)
· Bova (Neolithic; Ausones; Greek; Roman; Calabria)
· Brescia/Brixia (7th c.BCE: Gaul-Celt; 225 BCE: Roman; Capitolium, 2 domus; Brescia, Lombardy)
· Brescia Cathedral (Old) (11th c.CE: Romanesque on earlier basilica; Brescia, Lombardy)
· Brindisi [Gk.: “deer’s head” (Brentesion); Lat.: (Brundisium)](Magna Graecia)
· Brindisi Cathedral/Visitation of the Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint John the Baptist (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Brixen (8th m.BCE: Upper Paleolithic settlements; 15 BCE: Roman; 5909 CE: Bavarian)
· Brixen Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Cassian (10th c.CE; 13th c.CE: rebuilt; 1745-54 CE: Baroque; Brixen, Trentrino Alto Adige)
· Ca’ Belvedere (800,000 BP: Paleolithic; thousands of chipped flints; Forli, Emilia Romagna)
· Cagli Cathedral/Saint Francis (1234-1348 CE; Cagli, Marche)
· Calabria (6th c.BCE: Magna-Graecia; Reggio; Sybaris; Croton; Locri)
· Camerino (Etruscan; 310 BCE: Roman; Camerino, Macerata, Marche)
· Campagna Cathedral/Queen of Peace (1112-1683 CE; Campagna, Salerno, Campania)
· Campania (550 BCE: Temple of Hera; Paestum)
· Canosa (7th m.BCE: Dauni: acropolis, hypogeum, pagan catacombs, necropoleis; 11-10th c.BCE: Bronze Age; Illyrian- Magna Graecia; 318 BCE: Roman; 4th c.BCE: Ori Tomb, Ipogei Monterisi-Rossignoli, Varrese Tomb, Hypogeum of Cerberus, Ipogeo Scocchera A-B, Ipogei Casieri, Hypogeum Vessel Dario; 3rd c.BCE: Tomb of Largo Constantinople; 2nd c.BCE: Ipogei Lagrasta, Ipogeo dell’Oplita, Ipogeo Matarrese, Ipogeo Reimers; 2nd-4th c.CE: Necropolis of Santa Sofia; Temple of Jupiter Taurus; Canosa di Pulglia, Apulia)
· Canosa Cathedral/San Sabino (7-8th c.CE: basilica over earlier Christian sites; Canosa di Pulglia, Apulia)
· Cappella Sansevero (1590 CE: Baroque art; Masonic symbols; Naples, Campania)
· Capua (600 BCE: Etruscan: tombs, teracotta tablets; 338 BCE: Roman; amphitheatre; Capua, Caserta, Campania)
· Casale Cathedral/Saint Evasius and Saint Lawrence (742 CE: Lombard Romanesque; 1106 CE: rebuilt; Casale Monferrato, Alessandria, Piedmont)
· Castellaneta (3rd-2nd m.BCE: Bronze Age settlements; Sicels, Messapii, Lapyges; Magna Graecia; Saracen; Roman; 1064 CE: Norman; Castellaneta, Taranto, Apulia)
· Castellaneta Cathedral/Saint Nicholas (1220 CE: Baroque; Castellaneta, Taranto, Apulia)
· Catania [Siculian: “flaying knife; skinning place”(katane)](Sicel; Chalcidian-Magna Graecia; Roman; Vandal; Ostrogoth; Norman; Catania, Sicily)
· Catania Cathedral (1078-93 CE: Baroque; destroyed by earthquake and fire in 1169; near Etna volcano- eruptions caused earthquakes; Catania, Sicily)
· Catanzaro Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1121 CE: Norman; built over; 16th c.CE: Renaissance; Catanzaro, Calabria)
· Cathedral of Assunta e Sant’Erasmo (1106 CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque: Moorish arches; bell tower; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· Cathedral of Saint Emidio (Ascoli Piceno, Marche)
· Cathedral of Saint John the Baptist (12th c.CE; Ascoli Satriano, Foggia, Apulia)
· Cathedral of Saint Mary Assumtion (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Tanaro r.; Asti, Piedmont)
· Cathedral of San Corrado (12-13th c.CE: Apulian Romanesque; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· Cathedral of Santa Maria Assunta (1375 CE: Tuscan-Gothic over Etruscan-Roman temple; Orbetello, Tuscany)
· Caulonia (8th c.BCE)
· Cefalu Cathedral/Transfiguration (6th c.CE: mosaic; 1131 CE: Norman; 1215 CE: sarcophagi transfer to Palermo cathedral; 1240-67 CE: new cathedral; 1472 CE: portico; Cefalu, Sicily)
· Cerignola Cathedral/Saint Peter (Cerignola, Apulia, Foggia)
· Cesena Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (1500 CE: Gothic completed; Cesena, Forli, Emilia Romagna)
· Chiavari (8th c.BCE: pre-Roman necropolis; Chiavari, Genoa, Liguria)
· Chiesa del Morti (Middle Ages-Renaissance: mummies; Urbania, Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Chiesa del Santissimo Crocifisso (10th c.CE; crypt; Salerno, Campania)
· Chiesa della Misericordia (13th c.CE: crucifix; Piombino, Livorno, Tuscany)
· Chiesa della SS.Annunziata (14th c.CE; Salerno, Campania)
· Chiesa di San Benedetto (7-9th c.CE; Salerno, Campania)
· Chiesa di San Gregorio (10th c.CE; Salerno, Campania)
· Chiesa Madre of Saint Francis of Assisi (11-12th c.CE; Cerignola, Apulia, Foggia)
· Chieti Cathedral/Saint Thomas and Saint Justin (1069 CE: Gothic; Romanesque crypt; 14th c.CE: campanile enlarged; earthquake damage; 17-18th c.CE: rebuilt Baroque; Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Chioggia Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1110 CE; Chioggia, Venice, Ceneto)
· Chiusi Cathedral/Saint Secundianus (1st c.BCE: Roman swimming pool under bell tower; 560 CE: Romanesque; over pre-existing basilica; 13th c.CE: renovated; Chiusi, Siena, Tuscany)
· Church of Annunziata (1320 CE; 17th c.CE: rebuilt; Gaeta, Latino, Lazio)
· Church of Annunziata (1300 CE; damaged by Turks in 1552; French-Polish in 1799; fire in 1888; restoration in 1930; Minturno, Latino, Lazio)
· Church of Annunziata (13th c.CE; Sant’Agata de Goti, Benevento, Campania)
· Church of Araceli (1244 CE; Guarini; Vicenza, Veneto)
· Church of Badia Nuova (Baroque; Trapani, Sicily)
· Church of Beata Vergine del Monte Carmelo (16th c.CE; Cerignola, Apulia, Foggia)
· Church of Beata Vergine Incoronata (Renaissance; Lodi, Lombardy)
· Church of Carmini (1372 CE; Vicenza, Veneto)
· Church of the Eremitani (1276 CE; contains tombs of Jacopo; Padua, Veneto)
· Church of the Holy Cross (1353-1695 CE; Lecce, Apulia)
· Church of the Immacolata Concezione (1213; Rovigo, Veneto)
· Church of Madonna del Soccorso/La Rotunda (1594-1606: Renaissance; Rovigo, Veneto)
· Church of Magione (1191 CE: Norman; Palermo, Sicily)
· Church of Maria SS. Dell’Intria (Sicilian Baroque; Trapani, Sicily)
· Church of the Ognissanti (Romanesque chapel of Knights Templar; Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia)
· Church of S.Maria Infra Portas (11th c.CE; Foligno, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of S.Maria Infra Portas (1133-1201 CE: Romanesque; Foligno, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of S.Salvatore (12-14th c.CE; Foligno, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of SS.Annunziata (13th c.CE; Campagna, Campania)
· Church of SS.Pietro e Paolo (1st c.CE: over extensive Roman substructures- large reservoirs and amphitheatre; Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Church of SS.Salvatore e Sant’Antonino (11th c.CE; Campagna, Campania)
· Church of Saint Augustine (1257 CE; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Church of Saint Augustine (14th c.CE; Massa Marittima, Grosseto, Tuscany)
· Church of Saint Catherine (1292 CE; Vicenza, Veneto)
· Church of Saint Francis (1244 CE: Gothic; Modena, Emilia-Romagna)
· Church of Saint Francis (1520: Romanesque-Gothic; Rovigo, Veneto)
· Church of Saint Francis (13th c.CE: Baroque; Gerace, Reggio Calabria, Calabria)
· Church of Saint Francis (13th c.CE; Gualdo Tadino, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Saint Francis (former castle of Frederick II; 12th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; 16th c.CE: rebuilt; Irsina, Matera, Basilicata)
· Church of Saint Francis (1320 CE; Minturno, Latino, Lazio)
· Church of Saint Francis (1276 CE: art; Pisa, Tuscany)
· Church of Saint Francis (1327 CE: paintings; Subiaco, Rome, Lazio)
· Church of Saint Francis of Assisi (14th c.CE; Teggiano; Salerno, Campania)
· Church of Saint Martin of Tours (1163 CE; Piazza Armerina, Enna, Sicily)
· Church of Saint Mary (13th c.CE; Bevagna, Laurenzia, Umbria)
· Church of Saint Peter (1476 CE: over temple of Jupiter Capitulinus; Modena, Emilia-Romagna)
· Church of San Bernadino da Siena (1451 CE: Renaissance; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· Church of San Domenico (1475 CE; d.earthquake in 1887; Bisignano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Church of San Domenico (16-18th CE: Baroque caryatids; Nardo, Lecce, Apulia)
· Church of San Domenico (13th c.CE; 14thc.CE: frescoe- Stories of Saint Catherine; San Severino, Marche)
· Church of San Francesco (12th c.CE: Romanesque over pre-exist.Roman fortification; Bitonto, Bari, Apulia)
· Church of San Francesco (1234 CE; 1289 CE: rebuilt; Cagli, Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Church of San Francesco (Middle Ages; Grosetto, Tuscany)
· Church of San Francesco (13th c.CE; Gubbio, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of San Francesco (1280-1307; Lodi, Lombardy)
· Church of San Francesco (1274 CE: Byzantine; Potenza, Basilicata)
· Church of San Francesco al Corso (1239 CE; Baroque; Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Church of San Frediano (1061 CE: basilica; art; Pisa, Tuscany)
· Church of San Giacomo (11th c.CE; 1751 CE: restored after earthquake; Barletta, Apulia)
· Church of San Giacomo (1402 CE: Gothic; Foligno, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of San Giorgio (12th c.CE; Lucca, Tuscany)
· Church of San Giovanni (12th c.CE; Grosetto, Tuscany)
· Church of San Giovanni a Mare (10th c.CE: Byzantine basilica; Gaeta, Latino, Lazio)
· Church of San Giovanni al Sepolcro (12th c.CE; circular plan; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Church of San Lorenzo (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol)
· Church of San Mamiliano (5th c.CE: 500 gold coin treasure; Sovana, Tuscany)
· Church of San Michele Arcangelo (10th c.CE: Romanesque; over pagan temple; Ventimiglia, Imperia, Liguria)
· Church of San Nicola (1097 CE; art; Pisa, Tuscany)
· Church of San Nicolo (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Trevis, Veneto)
· Church of San Rocco (15th c.CE; Massa Marittima, Grosseto, Tuscany)
· Church of San Sepulcro (1275 CE: over pre-existing religious edifice; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· Church of Sant’Agnese (14th c.CE: Gothic; 1520 CE: Grazianni Poluptych by Alberto Piazza; Lodi, Lombardy)
· Church of Sant’Angelo (5-6th c.CE: Paleo-Christian; 16 columns; Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Sant’Ercolano (14th c.CE; Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Sant’Omobono (11th c.CE; Catanzaro, Calabria)
· Church of Santa Chiara (13th c.CE; Gualdo Tadino, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Santa Croce (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· Church of Santa Giuliana (13th c.CE: frescoes; Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Santa Lucia (10-11th c.CE: Byzantine-Romanesque-Apulian; Rapolla, Potenza, Basilicata)
· Church of Santa Margherita (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Apulian; near grottoes and dolmens; Bisceglie, Apulia)
· Church of Santa Maria del Casale (1300 CE: Gothic-Romanesque; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Church of Santa Maria della Misericordia (1537 CE; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Church of Santa Maria di Castello (1121-1208 CE: Lombard-Cosmatesque; Tarquinia, Viterbo, Cerveteri, Lazio, Rome)
· Church of Santa Maria Maddalena (1162 CE: Romanesque; remade Baroque in 18th c.; Lodi, Lombardy)
· Church of Santa Maria Nuova (13th c.CE; Gubbio, Perugia, Umbria)
· Church of Santa Menna (10th c.CE; Sant’Agata de Goti, Benevento, Campania)
· Church of Santissma Trinita (1348 CE; 1723-48 CE: ren.Baroque; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Church of Santissma Trinita (14th c.CE; 12th c.crypt; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Church of Santissimo Rosario (15-16th c.CE: Renaissance; Catanzaro, Calabria)
· Church of Santo Stefano (1286; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· Civitavecchia Cathedral/Saint Francis of Assisi (1610 CE: Baroque; Civitavecchia, Rome, Lazio)
· Colle di Val d’Elsa (4th m.BCE; Siena, Tuscany)
· Como (Bronze Age: Celtic-Orobii; Como, Lombardy)
· Como Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1396 CE: Gothic on previous Romanesque Santa Maria Maggiore; Como, Lombardy)
· Concordia Sagittaria (42 BCE: Roman; 1st c.CE: Roman bridge; 350 CE: Trichora Martyrium; Concordia Sagittaria, Venice, Veneto)
· Concordia Cathedral/Saint Stephen (1466 CE; Concordia Sagittaria, Venice, Veneto)
· Convent of San Francesco (1211 CE: founded by Saint Franceis of Assisi?; San Miniato, Pisa, Tuscany)
· Conversano [MA](Iron Age; 6th c.BCE: Magna Graecia necropolis; megalithic walls; 268 BCE: Roman; Pelasgi; Conversano, Bari, Apulia)
· Conversano Cathedral/Saint Stephen (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Conversano, Bari, Apulia)
· Conza della Campania (Hirpini; Avellino, Campania)
· Cosenza Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (11th c.CE: Romanesque-Renaissance; destroyed by earthquake 1184; rebuilt in 1222; Cosenza, Calabria)
· Crema Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1160-1385 CE: Gothic; first cathedral destroyed in 1160; Crema, Cremona, Lombardy)
· Cremona (400 BCE: Gallic-Celtic; 218 BCE: Roman; Lombardy)
· Cremona Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1107-1196 CE: Romanesque; damaged by earthquake during construction in 1117; 13-15th c.CE: Gothic-Renaissance-Baroque additions; painting: Crucifixion; Cremona, Lombardy)
· Crotone (588 BCE: Magna-Graecia; Olympians of the Panhellenic Games; Calabria)
· Crotone Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (9-11th c.CE; rebuilt Baroque; Crotone, Calabria)
· Erice (Eryx; Sicily)
· Fabriano Cathedral/Saint Venantius (14th c.CE; 1607-17 CE: rebuilt Baroque; Fabriano, Ancona, Marche)
· Faenza Cathedral/Saint Peter (Faenza, Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Fano Cathedral (1st c.BCE: over Vitruvian built temple/ of Fortuna; 12th c.CE: erected over pre-existing cathedral destroyed by fire in 1111; 1607-17 CE: rebuilt Baroque; Fano, Pesaro e Urbano, Marche)
· Fano Cathedral/Saint Mary Major (1521 CE; ancient portal; works by Raphael and Perugino; Fano, Pesaro e Urbano, Marche)
· Fanum Voltumnae [Etruscan: “shrine of Voltumna”](Etruscan temple; league of 12 peoples; Montefiascone, Viterbo, Lazio)
· Feltre Cathedral/Saint Peter and Saint Prosdocimus (Roman city; 14-17th c.CE: Renaissance rebuilt; Feltre, Belluno, Veneto)
· Ferentino Cathedral/Saints John, Peter, and Paul (ancient acropolis; 1099-1118 CE: reconstructed on older church; Ferentino, Frosinone, Lazio)
· Fermo (Myc.: cyclopean walls; 264 BCE: Roman; theatre; reservoir- under Dominican Order monastery; Fermo, Marche)
· Fermo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1227-1366 CE; Fermo, Marche)
· Ferrara Cathedral/Saint George (1135 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Po r.; Ferrara, Emilia Romagna)
· Fidenza Cathedral/Saint Domninus (1227-1366 CE: Romanesque; Fidenza, Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· Fiesole (9-8th c.CE: Etruscan; 283 BCE: Roman theatre, still used; Fiesole, Florence, Tuscany)
· Fiesole Cathedral/Saint Romulus-martyr (Romanesque; Roman columns; polyptych; Fiesole, Florence, Tuscany)
· Florence Baptistry/Battistero di San Giovanni (1059 CE: doors- Andrea Pisano, Lorenzo Ghiberti; Florence, Tuscany)
· Florence Cathedral/Saint Mary/Santa Maria del Fiore Cathedral (5th c.CE: Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore dedicated to Santa Raparata; 1296-1436 CE: Gothic-Renaissance; dome-Brunelleschi; Florence, Tuscany)
· Florence Charterhouse (1341 CE: Carthusian monastery; Florence, Tuscany)
· Foligno Cathedral/Saint Felician (1133-1201 CE: Romanesque; Foligno, Perugia, Umbria)
· Fondi (1000 BCE: Aurunci, Volsci; legend: f.by Hercules)
· Fondi Cathedral/Saint Peter (14th c.CE: over Roman temple of Jupiter; Fondi, Latina, Lazio)
· Forli- Monte Poggiolo (800000 BP: Paleolithic)
· Formia (1st c.BCE: Cicero’s mausoleum, Roman cistern; Formia, Latina, Lazio)
· Formia Cathedral/Saint Erasmus (Renaissance; Formia, Latina, Lazio)
· Forte Michelangelo (1535 CE: Renaissance; built over Roman constructions; Bramante, Michelagnolo; Civitavecchia, Rome, Lazio)
· Fortuna Primigenia (8th c.CE: Phoenician necropolis; 2nd c.BCE: temple of Poseidon; Palestrina, Rome, Lazio)
· Fossano Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Juvenal (13th c.CE; reconstructed in 18th c.CE; Fossano, Cuneo, Piedmont)
· Fossombrone Cathedral/Saints Aldebrand and Augustine (14th c.CE; enlargeed in 18th c.CE; Fossombrone, Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Frascati Cathedral/Saint Peter (1598 c.CE; reconstructed in 18th c.CE; Frascati, Rome, Lazio)
· Gaeta Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (1320 CE; 17th c.CE: rebuilt in Baroque; Golden Grotto; Gothic-Renaissance art; 19 panels by Giovan Filippo Criscuolo; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· Gallipoli Cathedral/Saint Agatha (17th c.CE: Baroque; Gallipoli, Lecce, Apulia)
· Genoa (6-5th c.BCE: Ligure: cemetery; Greek-Etruscan; Phoenician; Roman)
· Genoa Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (5-6th c.CE: dedicated to Saint Sirus; pre-Christian sarcophagi may suggest Roman cemetery; church devoted to 12 Apostles; Romanesque: dedicated to Saint Lawrence; Genoa, Liguria)
· Gerace [Gk.: “sparrowhawk” (lerax)](Neolithic; Sicel; Magna Graecia; Roman)
· Gerace Cathedral (1045 CE: Norman; prison of the Five Martyrs of Gerace; Gerace, Reggio Calabria, Calabria)
· Giovinazzo Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (12-13th c.CE: Apulian Romanesque; Giovinazzo, Bari, Apulia)
· Giardini Naxos (734 BCE; Sicily)
· Gravina Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (11-12th c.CE: Norman Romanesque; reliquary; Gravina in Puglia, Baria, Apulia)
· Grosetto Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (13th c.CE: Romanesque; Grosetto, Tuscany)
· Grottaferrata Cathedral/Abbey of Saint Mary (1024 CE: Romanesque; Grottaferrata, Rome, Lazio)
· Guattari (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal)
· Guastalla (7th c.BCE: Etruscan)
· Guastalla Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (16th c.CE; Guastalla, Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· Gubbio (Bronze Age: Umbrian; 1st c.BCE: Roman: theatre, mausoleum)
· Gubbio Cathedral/Saint Marianus and James (12th c.CE; 4 Evangelist symbols- sphinx; Gubbio, Perugia, Umbria)
· Herculaneum (6th c.BCE)
· Hercules Curinus sanctuary (Roman: Ovid’s villa; near amphitheatre ruins; near hermitage of Pope Celestine V f.in 1241; Sulmona, L’Aquila, Abruzzo)
· Hermitage of Monte Giove (1585 CE: Camaldolese; Naples, Campania)
· Il Pulo (Neolithic: grottoes, ruins; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· Imola Cathedral/Saint Cassian (1187-1271 CE; 1765-81 CE: renovated; Imola, Bologna)
· Innichen Abbey (f.769 CE: Romanesque; Benedictine; 12-13th c.: rebuilt; crypt; dome frescoe- History of Creation; near Tyrol, Austria; San Candido, Bolzano)
· Irsina Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (13th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; 1777 CE: renovated; Irsina, Matera, Basilicata)
· Ischia (Bronze Age: Mycenaean acropolis at Monte Vico; 8th c.BCE: Etruscan-Greek-Phoenician; 322 BCE: Roman)
· Ischia Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (1737 CE; built of chapel of Saint Francis; near Aragonese castle built in 474 BCE; Ischia, Naples)
· Isernia (700000 BP; use of fire; 295 BCE: Roman)
· Ivrea (1st c.CE: Roman: theatre, bridge)
· Ivrea Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (4th c.CE: over Pagan temple; 1000 CE: rebuilt Romanesque; 1785 CE: Baroque facade; Ivrea, Turin, Piedmont)
· Jesi (4th c.BCE: Umbri; 247 BCE: Roman)
· Jesi Cathedral/Saint Septimius (13-15th c.CE; Jesi, Ancona, Marche)
· Labyrinth of Porsenna (6-5th c.BCE: Etruscan-Roman rain water drainage system?; Chiusi, Siena, Tuscany)
· Lanciano/Anxanum (5th m.BCE; 1181 BCE: Frentani; Roman)
· Lanciano Cathedral/Blessed Virgin Mary (1619 CE: basilica; 8th c.: Byzantine Madonna statue; Lanciano, Chieti, Abruzzo)
· L’Aquila Cathedral/Saint Maximus and George (1266 CE: damaged in 1703 earthquake; L’Aquila, Abruzzo)
· Larino amphitheatre (1st c.CE: Roman; Larino)
· Larino Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Pardus (10-11th c.CE: Gothic; Larino, Campobasso, Molise)
· La Spezia [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cassiopeia; Liguria)
· La Trinita della Cava (1011 CE: Benedictine abbey; Gothic cloisters; Cava de Tirreni, Salerno, Campania)
· Lazio (Latium)
· Lecce/Sybar (13th c.BCE: Messapii; 2nd c.CE: Roman amphitheatre; Lecce, Apulia)
· Lecce Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1144 CE; rebuilt in 1230; octagonal loggia; Lecce, Apulia)
· Lipari (5000 BCE: neolithic; necropolis; 9th c.CE: Ausonian settlement burned; Lipari)
· Locri (680 BCE: Locrians; 5th c.BCE: Temple of Marasa; necropoleis; 4th c.BCE: amphitheatre; Locri)
· Lodi Cathedral/Saint Bassianus (1158 CE: refounded after destruction by Milanese forces in 1111; Lodi, Lombardy)
· Lucca Cathedral/Saint Martin (1063 CE; 14th c.CE: Gothic; Lucca, Tuscany)
· Lucca (Etruscan-Ligurian; 180 BCE: Roman amphitheatre; Lucca, Tuscany)
· Lucera (Bronze Age: Etruscan; 320 BCE: Roman amphitheatre; Lucera, Foggia, Apulia)
· Lucera Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1300 CE: built over last mosque in Italy d.in 1300; Lucera, Foggia, Apulia)
· Lugnacco [MA](menhir; NW Italy)
· Luni (1st c.CE: Roman: Luna amphitheatre and temple; Luni, La Spezia, Liguria)
· Maria Santissima Annunziata (1351-32 CE; statue- Pisano; Trapani, Sicily)
· Manfredonia Cathedral/Saint Lawrence of Siponto (1270-4 CE: destroyed by Turks in 1620; rebuilt 1700; Manfredonia, Foggia, Apulia)
· Mantua (f.2000 BCE; 6th c.BCE: Etruscan; Cenomani-Gallic; Roman)
· Mantua Cathedral/Saint Peter (Paleo-Christian 1st structure followed by 2nd church d.by fire in 894; 1395-1401 CE: rebuilt Gothic-Renaissance; Mantua, Lombardy)
· Marienberg Abbey (est.Charlemagne; 780-6-d.880 CE: Benedictine; f.1149 CE: Romanesque; 1271-98: sacked twice by nobles under Abbot Konrad III; Black Death; 1418: burned-rebuilt; 1656: burned; d.1807: by Bavarian gov.; 1816: restored; Austrian; Malles Venosta, Bolzano)
· Massa Marittima Cathedral/Saint Cerbonius (4th c.CE: Roman sarcophagus; 12-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Pisane; Massa Marittima, Grosseto, Tuscany)
· Matera (Paleolithic; 3rd c.BCE: Roman)
· Matera Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Eustace (1203-70 CE: Apulian Romanesque; Matera, Basilicata)
· Mausoleum of Galla Placidia (430 CE: early Christian; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Mausoleum of Theodoric (520 CE: early Christian; mosaics; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Mazara del Vallo/Mazara (9th c.BCE: Phoenician; Greek; Carthaginian; Roman; Vandals; Ostrogoths; Byzantine; Arab)
· Melfi Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Norman-Baroque; 13th c.CE: frescoe: Madonna with Child and Angels; Melfi, Potenza, Basilicata)
· Messina (8th c.BCE: Greek; 397 BCE: Carthaginian; Mamertine; Roman; Goth; Byzantine; Arab)
· Messina Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (12th c.CE: Norman-Gothic; containing remains of king Conrad; astronomical clock; Messina, Sicily)
· Metapontum [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hole in the Milky Way; Gulf of Taranto; Metapontum)
· Milan (400 BCE: Celtic Insubres; 222 BCE: Roman)
· Milan Cathedral/Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (600 BCE: Celtic; then central site of Roman Mediolanum; 5th c.CE: basilica of Saint Ambrose; 836 CE: adjoining basilica; fire damage in 1075; 1386-1965 CE: Late Gothic; Milan, Lombardy)
· Minturno (314 BCE: Roman amphitheatre; Minturno, Latino, Lazio)
· Minturno Cathedral/Saint Peter (9-12th c.CE; Minturno, Latino, Lazio)
· Modena (Iron Age: Villanovan; Ligurian; Etruscan; Gaulish Boii; Roman)
· Modena Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (5th c.CE: 2 previous churches; 1099-1184 CE: Romanesque; Modena, Emilia-Romagna)
· Molfetta [MA](Neolithic: Pulo; star stones- Canis Major; near Bari)
· Molfetta Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1610 CE; Jesuit; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· Monopoli/Gnatia (Peucetian; Greek)
· Monreale Cathedral/Saint Mary (1174-1200 CE; Arab-Norman; Monreale, Sicily)
· Montalcino Cathedral/Holy Savior (14th c.CE; Montalcino, Siena, Tuscany)
· Monte Cassino Abbey/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Benedict (543 CE: accd. to Life of Saint Benedict of Nursia: prior temple of Apollo dedicated to Saint Martin; re-established in 718; Saracens burned it down in 883; rebuilt in 1071; earthquake damage in 1349; almost completely destroyed in 1944; rebuilt; Cassino, Frosinone, Lazio)
· Monte Circeo (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal; San Felice Circeo; Anzio)
· Montefiascone Cathedral/Saint Margaret of Antioch (15-16th c.CE; Montfiascone, Viterbo, Lazio)
· Monte Oliveto Maggiore/Saint Mary (1313 CE; Asciano, Siena, Tuscany)
· Montepulciano (4th-3rd c.BCE: Etruscan; Roman)
· Montepulciano Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1594-1680 CE; Montepulciano, Siena, Tuscany)
· Montevergine/Saint Mary (1124 CE; near ruined temple of Cybele; rebuilt 1961; Montevergine, Mercogliano, Avellino, Campania)
· Monza (Bronze Age: funerary urns, pile dwellings; 3rd c.BCE: Roman; Milan, Lombardy)
· Monza Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (595 CE: oraculum/chapel in Greek cross; 13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Milan, Lombardy)
· Morgantina (1000 BCE; Sicily)
· Mozia (Motia/Motya) (8th c.BCE: Phoenician)
· Muri Abbey/Saint Martin of Tours (f.Habsburgs; 1027 CE: Benedictine; Habsburg burials; former Austria; Muri-Gries, Bolzano)
· Naples (9-8th c.BCE: Magna Graecia; Roman)
· Naples Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (13-14th c.CE: built over 2 paleo-Christian basilicas; Naples, Campania)
· Nardo (Paleolithic; 1000 BCE: Messapi; 269 BCE: Roman)
· Nardo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1000 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Nardo, Lecce, Apulia)
· Narni/Nequinum (Paleolithic-Neolithic; 600 BCE: Osco-Umbrian; 4th c.BCE: Roman)
· Necropolis of the Banditaccia (9th c.BCE: Villanovan-Etruscan; tombs, mounds; Cerveteri, Lazio)
· Necropolis of Monte (10-8th c.BCE; Patti, Messina, Sicily)
· Necropolis of San Cosimo (30-9th c.BCE; Patti, Messina, Sicily)
· Nepi (Bronze Age; 8th c.BCE; 383 BCE: Roman)
· Nepi Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Anastasia (12th c.CE: over ancient pagan temple crypt/altar; rebuilt in 1831; Nepi, Viterbo, Lazio)
· Nicastro Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (paleo-Christian; destroyed by Saracens; rebuilt in 1100; Nicastro, Catanzaro, Calabria)
· Nicosia Cathedral/Saint Nicholas of Bari (14th c.CE: built over pre-existing Norman; Nicosia, Enna, Sicily)
· Nocera Umbra (7th c.BCE: Umbrian; 3rd c.BCE: Roman; Umbria)
· Nola/Nuvlana (1700-1600 BCE: Bronze Age settlement d.by eruption of Mt. Vesuvius; 560 BCE: Ausones; 311 BCE: Roman; Naples, Compania)
· Nola Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Gothic; restored in 1866; d.by fire in 1870; Nola, Naples, Campania)
· Nonantola Abbey/Saint Sylvester (752 CE; d. By Hungarians in 889; 1058 CE: Romanesque; Nonantola, Modena, Emilia Romagna)
· Norcia (Neolithic; 5th c.BCE: Sabines; 205 BCE: Roman; Perugia, Umbria)
· Norcia Abbey/Saint Mary (Renaissance; Norcia, Perugia, Umbria)
· Noto Cathedral/Saint Nicholas (1776 CE; Noto, Siracusa, Sicily)
· Novara Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (11th c.CE; 19th c.CE: demolished and rebuilt; Novara, Piedmont)
· Ognissanti (1250 CE: Umiliati; 1627 CE: early Baroque-Nigetti; art- Ghirlandaio, Botticelli; Florence, Tuscany)
· Oppido Mamertina/Mamerto (3rd c.BCE; Calabria)
· Orbetello (5th c.BCE: Etruscan walls; 280 BCE: Roman city of Cosa; Tuscany)
· Orbetello Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (built over Etruscan-Roman temple; 1375 CE: Tuscan-Gothic; Orbetello, Grosseto, Tuscany)
· Oria/Hyria/Uria (Messapi-Cretan; Roman; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Oria Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1750 CE; built over pre-exist.bldg.damged.by earthquake; Oria, Brindisi, Apulia)
· Orsanmichele [“Kitchen Garden of Saint Michael”](1337 CE: originally, grain market; 1380-1404 CE: Renaissance; 14 external niches- Banco, Donatello, Verrocchio, Lamberti, Ghiberti, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Orte/Hurta (6th c.BCE: Etruscan; necropolis; 300 BCE: Roman; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Ortona (Bronze Age: Frentani; Roman; Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Orvieto (Etruscan: necropolis; 3rd c.BCE: Roman; underground labyrinth city; Terni, Umbria)
· Orvieto Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (13-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Italian Gothic; art: Judgment Day; Orvieto, Terni, Umbria)
· Osimo/Vetus Auximum (Greek-Ancona Greeks; Gaul-Piceni; 174 BCE: Roman; Ancona, Marche)
· Osimo Cathedral/Saint Leopardus (5th c.CE: built by Saint Leopardus over earlier pagan Roman structure; 7th c.CE: reconstructed by Saint Vitalian; stone tablet in crypt; 12-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Osimo, Ancona, Marche)
· Ostia Antica (7th c.BCE)
· Ostuni (Stone Age; Messapii; Roman; Brindisi, Apulai)
· Ostuni Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1088 CE; 1166 CE: Old Testament mosaics; 1481 CE: rose window; Ostuni, Brindisi, Apulia)
· Otranto/Hydrus/Hydruntum (Greek; Roman; Lecce, Apulia)
· Otranto Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Otranto, Lecce, Apulia)
· Padua/Patavium (1183 BCE: Trojan; Roman; Veneto)
· Padua Cathedral/Saint Mary (313 CE: 1st edifice; destroyed by earthquake in 1117; rebuilt Romanesque; 1551 CE: Renaissance-Micheagnolo; Padua, Veneto)
· Paestum (Poseidonia) [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Hole in the Milky Way; 7th c.BCE; Temple of Hera; Athena; Apollo; Jason and the Argonauts; Capaccio, Salerno, Campania)
· Palazzo dei Capitani del Popolo (13th c.CE; Piazza del Popolo; Ascoli Piceno)
· Palermo/Panormus (8000 BCE: Sicani cave art; 1700 BCE; 734 BCE: Phoenician; Greek; Roman; Byzantine; Arab; Sicily)
· Palermo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1185 CE: Anglo-Norman over Byzantine basilica; 9th c.CE: turned into mosque after Saracen conquest; 14-15th c.CE: Renaissance; present Neo-classical; Palermo, Sicily)
· Palestrina/Praeneste (8-7th c.BCE: Phoenician-Etruscan necropolis; bronzes and ivory items; head of Latin League; 499 BCE: Rome; Rome, Lazio)
· Parma (1500-800 BCE: Bronze Age necropoleis; Etruscan; 183 BCE: Roman; Emilia Romagna)
· Parma Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (3-4th c.CE: over pagan temple; 1106 CE: Romanesque; 1196 CE: Baptistry; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark (828 CE: Doge’s Palace; relics of Mark the Evangelist from Alexandria; 832 CE: replacement church; 976 CE: burned in rebellion; 978 CE: rebuilt; 1063 CE: current basilica; Venice)
· Patti Cathedral/Saint Bartholomew (10th c.CE; Patti, Messina, Sicily)
· Pavia Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Stephen (1488 CE: Renaissance over 2 pre-existing Romanesque; Pavia, Lombardy)
· Penne Cathedral/Saint Maximus (8th c.CE: crypt; Penne, Pescara, Abruzzo)
· Perugia Cathedral/Saints Lawrence, Andrew, and Lucy (936-1060 CE: over pre-existing; Perugia, Umbria)
· Pesaro Cathedral (5th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic over pre-existing Roman edifice dedicated to Saint Terence; Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Piacenza (Etruscan bronzes; 218 BCE: Roman; Emilia Romagna)
· Piacenza Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Justina (1122-1233 CE: Romanesque over pre-existing paleo-Christian edifice of 546; Piacenza, Emilia Romagna)
· Piazza Armerina Cathedral/Saint Mary (15th c.CE: foundations; 17-18th c.CE: Baroque; Piazza Armerina, Enna, Sicily)
· Pienza Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (Renaissance; Pienza, Siena, Tuscany)
· Pietrasanta Cathedral/Saint Martin (1223 CE; 1330 CE: enlarged; Lucca, Tuscany)
· Pieve di San Paolo (5th c.CE: paleo-Christian baptismal church; trancept, columns; 8-9th c.CE: rebuilt; 13th c.: Romanesque; 14-15th c.: bell tower; earthquake in 1796; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Pieve di Sant’Eugenia al Bagnoro (1012 CE; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Pieve di San Donnino a Maiano (6-9th c.CE: paleo-Christian original; 14th c.CE: rebuilt; 15th c.CE: frescoes; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Pinerolo Cathedral/Saint Donatus (9th c.CE; Pinerolo, Turin, Piedmont)
· Piemonte (Piedmont) (218 BCE)
· Piombino Cathedral/Saint Anthimus (1377 CE: Pisane-Gothic; Piombino, Livorno, Tuscany)
· Pisa (5th c.BCE: Etruscan necropolis; Arena Garibaldi; 180 BCE: Roman; Tuscany)
· Pisa Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (1064 CE: Byzantine-Romanesque; 1180 CE: Leaning Tower; massive bronze doors added after fire in 1595; Pisa, Tuscany)
· Pistoia (6th c.BCE: Gallic-Ligurian-Etruscan; Tuscany)
· Pistoia Cathedral/Saint Zeno (923 CE: Palaeo-Christian; damaged by fire in 1108; rebuilt in 12th c.; fire in 1202; crypt houses relics of Saint James; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· Pitigliano Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (11th c.CE; Pitigliano, Grosseto, Tuscany)
· Policastro/Pixunte/Pixous (471 BCE: Magna Graecia; Salerno, Campania)
· Pompeii (Vesuvius- 79 CE)
· Pontremoli Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (17th c.CE; Pontremoli, Massa-Carrara, Tuscany)
· Pordenone Cathedral/Saint Mark (1363 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Pordenone, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Veneto)
· Portico of the Templars (13th c.CE; Brindisi, Apulia)
· Potenza Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Gerard (12th c.CE: original; 18th c.CE; Potenza, Basilicata)
· Pozzuoli/Dicaearchia (Greek colony; 194 BCE: Roman; Apostle Paul’s landing place; Serapium; Naples, Campania)
· Prato (Paleolithic; 5th c.BCE: Etruscan; Roman; Tuscany)
· Prato Cathedral/Saint Stephen (10th c.CE: several Romanesque stages; Donatello pulpit; Prato, Tuscany)
· Primerana church (966 CE; expanded into Gothic; 16th c.CE: Renaissance façade; Fiesole, Florence, Tuscany)
· Priverno/Privernum (Volscian; 4th c.BCE: Roman; Latina, Lazio)
· Priverno Cathedral/Saint Mary (1183 CE; houses Saint Thomas’s skull; Priverno, Latina, Lazio)
· Pyrgi (600 BCE; Caere; Rome)
· Ragusa (2nd m.BCE: Sicels; Carthaginian; Roman; Arab; Norman; Sicily)
· Ragusa Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (prehistoric and Roman findings; over medieval castle; earthquake in 1693; 1718-78; Ragusa, Sicily)
· Rapolla Cathedral/Saint Michael (13th c.CE: Lombard-Gothic; Rapolla, Potenza, Basilicata)
· Ravello Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Pantaleon (1272 CE; Ravello, Salerno, Campania)
· Ravenna (Thessalian-Etruscan-Umbrian; 89 BCE: Roman; Emilia Romagna)
· Ravenna Cathedral/Resurrection of Our Lord (5th c.CE: early Christian; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Reggio Calabria/Rhegion (720 BCE: Magna Graecia: walls; Roman: baths; Byzantine; Calabria)
· Reggio Emilia Cathedral/Assumption of Blessed Virgin Mary (9-12th c.CE; 16th c.CE: reconstructed; Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· Riforma Convent (1222 CE; Bisignano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Rieti (Sabine; 3rd c.BCE: Roman: gate, thermae, Lazio)
· Rieti Cathedral/Saint Mary; Saint Gregory (1109 CE: Romanesque; 1639 CE: rebuilt; Bernini statue; Rieti, Lazio)
· Rimini/Ariminus (Etruscan-Umbrian-Greek-Gaul; 2nd c.CE: Roman: Arch of Augustus; amphitheatre)
· Rimini Cathedral/Tempio Malatestiano/Saint Francis of Assisi (13th c.CE: Gothic; Alberti designs; Rimini, Emilia Romagna)
· Ripatranso Cathedral/Saint Gregory (1597 CE: Gothic; Alberti designs; Ripatranso, Ascoli Piceno, Marche)
· Rome (pre-Etruscan settlement; 100 BCE)
· Rossano Cathedral/Saint Mary (11th c.CE; 580 CE: Madonna acheropita; Rossano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Rovigo Cathedral/Saint Stephen (-11th c.CE: original; rebuilt in 1461/1696; art by Palma theh Younger; Rovigo, Veneto)
· Ruvo di Puglia (9th c.BCE: Magna Graecia; Roman; Byzantine; Saracen; Norman; Bari, Apulia)
· Ruvo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Apulian Romanesque; Ruvo di Puglia, Bari, Apulia)
· S.Alo (11th c.CE: Romanesque church; Terni, Umbria)
· S.Maria of the Servites (1319 CE; miracles of Saint Philip Benizi de Damiani; Vicenza, Veneto)
· S.Martino (Lombard; Trevi, Umbria)
· S.Paride ad fontem (4th c.CE: paleo-Christian church built over Roman cistern; 11-12th c.CE; Teano, Caserta, Campania)
· SS.Felice and Fortunato (8th c.CE; Vicenza, Veneto)
· SS.Filippo and Giacomo (12th c.CE; Vicenza, Veneto)
· SS.Trinita (1059 CE: Benedictine abbey; Knights of Saint John; Venosa, Potenza, Basilicata)
· Saben [Lat.: “holy mountain”] Abbey (hill settled in Stone Age; Roman settlement; 6th c.-960: bishopric; 14-15th c.: Saben Castle; est.1687 CE: Benedictine nunnery; settled by nuns from Nonnberg Abbey, Salzburg; looted during Napoleonic wars; former Austria; Klausen, Bolzano)
· Saccopastore (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Saint Agatha (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Asciano, Siena, Tuscany)
· Saint Anthony (1427 c.CE: Franciscan convent; Teano, Caserta, Campania)
· Saint Antuono (11th c.CE; Teggiano, Salerno, Campania)
· Saint Augustine church (originally Saint Apollinaris; rededicated in 1268 CE; Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· Saint Augustinus Cathedral (14-15th c.CE; Ascoli Piceno)
· Saint Benedict (9th c.CE: over temple of Ceres; Teano, Caserta, Campania)
· Saint Benedict basilica (13th c.CE; Norcia, Perugia, Umbria)
· Saint Catherine Cathedral (12th c.CE; Conversano, Bari, Apulia)
· Saint Columbanus Basilica (12th c.CE: mosaic crypt; 1456-1522 CE: Gothic; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Saint Francis (1245 CE; Rieti, Lazio)
· Saint Francis basilica (10-11th c.CE: early Christian; funeral of Dante; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Saint Francis Church and Monastery (13th c.CE; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Saint Francis Cathedral (1289 CE; Conversano, Bari, Apulia)
· Saint Francis Church (1222 CE: Gothic-Italian; accord.to legend built by Saint Francis; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· Saint Francis Church and Monastery (13th c.CE; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Saint Francis of Assisi church (1255-77 CE: Gothic-Renaissance; renovated after earthquake and bombings; Palermo, Sicily)
· Saint John the Baptiste Church (1377 CE: Baroque; Alba)
· Saint John the Baptiste (12th c.CE; Tarquinia, Viterbo, Lazio, Rome)
· Saint John the Evangelist church (5th c.CE: early Christian; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Saint Lawrence Church (12th c.CE; Bobbio, Piacenza, Emily-Romagna)
· Saint Maria Maggiore (525-32 CE: early Christian; rebuilt in 1671; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Saint Mark Oratory (10th c.CE: Byzantine; frescoes; Rossano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Saint Peter in Aquariis (14th c.CE: over paleo-Christian edifice, over Roman bath; Byzantine frescoes; Teano, Caserta, Campania)
· Saint Peter Martyr Cathedral (13th c.CE: Holy Thorn; Ascoli Picenso)
· Saint Silvestro (1195 CE: Romanesque; Bevagna, Umbria)
· Saint Stephen (11th c.CE: Templar church; Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· Saint Victor and Corona sanctuary (12-15th c.CE: Byzantine-Renaissance; Giottesque frescoes; Feltre, Belluno, Veneto)
· Salerno/Irna (9th c.BCE: Oscan-Etruscan: necropolis; 5th c.BCE: Samnite; 194 BCE: Roman; Campania)
· Salerno Cathedral/Saint Matthew (1080 CE: Byzantine-Romanesque over pre-existing church and Roman temple; Roman sarcophagi; Salerno, Campania)
· Saluzzo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1491-1501 CE: Lombard Gothic-Baroque; Saluzzo, Cuneo, Piedmont)
· San Adoeno abbey (11th c.CE; Bisceglie, Bari, Apulia)
· San Andrea Apostolo (14th c.CE; Atri, Teramo, Abruzzo)
· San Augostino (14th c.CE; Atri, Teramo, Abruzzo)
· San Bartolomeo Church (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Campobasso, Molise)
· San Bartolomeo in Pantano (12th c.CE; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· San Benedetto (7th c.CE; 13-15th c.CE: frescoes; Priverno, Latina, Lazio)
· San Benedetto Battista al Tempio (14th c.CE; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· San Bernadino (1428-62: late-Gothic; Rossano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· San Biagio (Romanesque church; Belluno, Veneto)
· San Carpoforo (11-12th c.CE: apse-crypt; built on prior Temple of Mercury housing remains of Saint Carpophorus, and other local martyrs; Como, Lombardy)
· San Cataldo (Norman; Palermo, Sicily)
· San Claudio (11th c.CE: Romanesque built over paleo-Christian cemetery; 14th c.CE: frescoes; Spello, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Domenico (13-14th c.CE: Gothic cathedral; Alba)
· San Domenico (13th c.CE: Gothic; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Domenico (13th c.CE; Terracina, Latina, Lazio)
· San Esuperanzio Cathedral (Gothic; Cingoli, Macerata, Marche)
· San Fedele Cathedral (1120 CE: Romanesque; Como, Lombardy)
· San Fortunato (7th c.CE: palaeo-Christian: 2 lion sculptures on entrance portal remain; 1292 CE: Gothic Franciscan; Todi, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Francesco (1236 CE: Romanesque; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· San Francesco (1258 CE: Gothic; Ascoli Piceno)
· San Francesco (1258 CE: built over pre-exist.7th c.CE; Eucharistic Miracle relics; Lanciano, Chieti, Abruzzo)
· San Francesco (1289 CE; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· San Francesco (1222 CE: Gothic Cistercian; Terracina, Latina, Lazio)
· San Francesco (Romanesque; Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia)
· San Francesco (Gothic church; Trevi, Umbria)
· San Francesco (1231-70 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Trevis, Veneto)
· San Francesco (14th c.CE: Gothic-Romanesque; Urbino, Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· San Francesco (Gothic built over pre-exist.Lombard fortress; Viterbo, Lazio)
· San Francesco Cathedral (1240 CE; using old Roman ampitheatre brickwork?; Fermo, Marche)
· San Francesco d’Assisi (1471 CE; Castellaneta, Taranto, Apulia)
· San Francesco del Prato (13th c.CE: Gothic; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· San Gaetano (1604-48 CE: Baroque- Nigetti, Silvani; built over Romanesque church; Florence, Tuscany)
· San Gennaro extra Moenia (2nd c.CE: Catacombs of San Gennaro; 4th c.CE: basilica; 11/15th c.: expanded; became hospital in 1648; Naples, Campania)
· San Getulio (Romanesque built in middle ages over Roman temple; 1155 CE: d.by Normans; Teramo, Abruzzo)
· San Giacomo (Romanesque; Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia)
· San Giovannello (10th c.CE; Gerace, Reggio Calabria, Calabria)
· San Giovanni (1330-1504 CE: Gothic; Saluzzo, Cuneo, Piedmont)
· San Giovanni Battista (Romanesque; Matera, Basilicata)
· San Giovanni Battista (1683 CE: Baroque; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· San Giovanni Battista (12th c.CE; Rimini, Emilia Romagna)
· San Giovanni Battista e Lorenzo church (841 CE; mostly destroyed in WWII; Formia, Latina, Lazio)
· San Giovanni Battista al Tempio (11th c.CE: Templar-Hospitaller; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· San Giovanni a Carbonara (1343 CE: Augustinian; Naples, Campania)
· San Giovanni a Mare Church (10th c.CE: Byzantine basilica; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· San Giovanni degli Eremiti (12th c.CE: Gothic-Arab reconstruction; Palermo, Sicily)
· San Giovanni del Toro (1000 CE; Ravello, Salerno, Campania)
· San Giovanni Evangelista (10th c.CE; rebuilt 1498/1510 after fire; Parma, Emilia Romagna)
· San Giovanni Evangelista (14th c.CE; Piazza Armerina, Enna, Sicily)
· San Giovanni Evangelista (9th c.CE; 13 c.CE: rebuilt; 14th c.CE: frescoes-stories of Saint Katherine; Priverno, Latina, Lazio)
· San Giovanni Fuoricivitas (12-14th c.CE: Romanesque; Baroque-Roccoco painting; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· San Giovanni in Zoccoli (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Viterbo, Lazio)
· San Giovannino (1200 CE; Baroque paintings; Reggio Emilia, Emilia Romagna)
· San Gregorio Armeno (10th c.CE: over Roman temple of Ceres; Naples, Campania)
· San Gregorio Maggiore (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Leonardo (14th c.CE: Gothic-Romanesque; Campobasso, Molise)
· San Lorenzo (12th c.CE: Romanesque cathedral; Alba)
· San Lorenzo (10th c.CE: paleo-Christian original; 13th c.CE: rebuilt Romanesque; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· San Lorenzo (12th c.CE; Spello, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Lorenzo of the Friars Minor (1280 CE: Gothic; tombs; Vicenza, Veneto)
· San Lorenzo Maggiore (13th c.CE: over Greco-Roman city; Naples, Campania)
· San Luca church (15th c.CE; crypt: Episodes of the New Testament, Madonna del Latte; Formia, Latina, Lazio)
· San Marco (1443 CE: neo-Classical-Renaissance; over 12th c.Vallombrosan monastery; Florence, Tuscany)
· San Martino (12th c.CE; Tarquinia, Viterbo, Lazio, Rome)
· San Martino church (12th c.CE; 16th c.CE: enlarged; art- Guido Reni; Siena, Tuscany)
· San Michele (Romanesque-Gothic; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· San Michele (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; Potenza, Basilicata)
· San Michele Arcangelo (944 BCE; 11-12th c.paintings; Capua, Caserta, Campania)
· San Michele in Foro (795 CE: built over Roman forum; rebuilt 1070; 13th c.CE: facade; Lucca, Tuscany)
· San Michele Maggiore (11th c.CE: Romanesque over pre-existing Lombard church; Pavia, Lombardy)
· San Michele in Borgo (990 CE; 12th c.CE: enlarged into Romanesque; Pisa, Tuscany)
· San Miniato/Quarto (Paleolithic; Etruscan; Roman; Pisa, Tuscany)
· San Miniato al Monte (1013 CE: Romanesque; Florence, Tuscany)
· San Miniato Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Genesius (Romanesque-Gothic-Renaissance; San Miniato, Pisa, Tuscany)
· San Nicola (13th c.CE; Priverno, Latina, Lazio)
· San Nicolo (1304 CE: Augustinian convent; Gothic; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Nicolo and Cataldo church (1180 CE; rebuilt facade in 1716; Lecce, Apulia)
· San Nicolo Regale church (1124 CE: Norman; Mazara del Vallo, Trapani, Sicily)
· San Pancrazio (Gothic-Romanesque; Tarquinia, Viterbo, Lazio, Rome)
· San Paolo a Ripa d’Amo (9th c.CE; 12th c.CE: enlarged into Romanesque; Pisa, Tuscany)
· San Paolo inter vineas (10th c.CE: Spoletine Romanesque; rose window; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Paragorio church (11th c.CE: Romanesque basilica; Noli, Savona, Liguria)
· San Pietro (1326 CE: Gothic-Baroque; paintings; Belluno, Veneto)
· San Pietro church (Byzantine: frescoes; Otranto, Lecce, Apulia)
· San Pietro (medieval monastery; Bovara, Trevi, Umbria)
· San Pietro Apostolo (12th c.CE; Molfetta, Bari, Apulia)
· San Pietro di Castello (16th c.CE; Venice)
· San Pietro extra Moenia (f.419 CE: housing Peter’s relics over ancient necropolis; 12-15th c.CE: Romanesque; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Pietro a Majella (14th c.CE; Naples, Campania)
· San Pietro Martire (1294-1343 CE; Naples, Campania)
· San Petronio Basilica (1393-1479 CE: Gothic; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· San Ponziano (12th c.CE: Romanesque; with crypt w/Roman spolia columns; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Salvatore basilica (4-5th c.CE: incorporates Roman temple cella; 8th c.CE: reconstructed by Lombards; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· San Severino Marche (Paleolithic; 7-5th c.BCE: Piceni: necropolis; temple of Feronia-catacombs; 3rd c.BCE: Roman: Septempeda- baths, walls; Marche)
· San Sisto (9th c.CE: Romanesque; Viterbo, Lazio)
· San Sylvestro church (Romanesque: bell tower; Orte, Viterbo, Lazio)
· San Teodoro (1117 c.CE; Pavia, Lombardy)
· San Tommaso (1069 CE: Romanesque; Ascoli Piceno)
· San Tommaso d’Aquino (13th c.CE; Priverno, Latina, Lazio)
· San Vittore (996 CE: Romanesque; Ascoli Piceno)
· San Vincenzo (12th c.CE; Bevagna, Umbria)
· Sanctuary of Anglona (11-12th CE: Romanesque over church from 6-7th c.; Tursi, Matera, Basilicata)
· Sanctuary of SS.Trinita (11th c.CE; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· Sanctuary of Santa Caterina (12th c.CE; houses miraculous crucifix; Siena, Tuscany)
· Sant’Abbondio Basilica (1095 CE: Romanesque; frescoes; Como, Lombardy)
· Sant’Agata de Goti Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (10th c.CE: Romanesque; Sant’Agata de Goti, Benevento, Campania)
· Sant Agostino (1270 CE: Baroque restoration; Lanciano, Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Sant Agostino (13th c.CE: Romanesque; Rieti, Lazio)
· Sant Agostino Cathedral (14th c.CE: Cistercian; 15-17th c.CE: Baroque; Como, Lombardy)
· Sant Agostino (14th c.CE: Gothic; Norcia, Perugia, Umbria)
· Sant’Agostino (14th c.CE; Trapani, Sicily)
· Sant’Agostino (13th c.CE: Gothic-Romanesque; choir from 6th c.; Urbino, Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Sant’Anastasia (1290-1481 CE: Dominican; Verona, Veneto)
· Sant’Andrea (1025 CE; 14th c.CE: frescoes; Perugia, Umbria)
· Sant’Andrea (Byzantine domes; Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia)
· Sant’Angelo dei Lombardi Cathedral/Saint Michael (11th c.CE; rebuilt in 16th c.; Sant’Angelo dei Lombardi, Avellino, Campania)
· Sant’Anna dei Lombardi (1411 CE; Naples, Campania)
· Sant’Ansano (18th c.CE; over 1st c.Roman temple and Saint Isaac’s crypt; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· Sant’Eligio Maggiore (1270 CE; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Caterina a Formiello (1510-93 CE: Dominican; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Caterina a Magnanapoli (1575 CE: Baroque; Rome, Lazio)
· Santa Chiara (13th c.CE; Atri, Teramo, Abruzzo)
· Santa Chiara (1313-1340 CE: Provencal-Gothic; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Corona (1260 CE: Dominican; Palladio, Bellini; Vicenza, Veneto)
· Santa Croce (1179 CE; Vicenza, Veneto)
· Santa Donna Regina Nuova (14th c.CE; 1616-27 CE: new edifice; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Eufemia (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· Santa Felicita (4th c.CE: original church; 11th c.CE: new; 1736-9 CE: current; Vasari corridor; 1419-23 CE: Barbadori/Capponi chapel-Brunelleschi; Florence, Tuscany)
· Santa Lucia church (13-14th c.CE: Romanesque: former Saint Maria in Pensulis; 1456 CE: Renaissance; 1648 CE: Baroque; Gaeta, Latina, Lazio)
· Santa Maria a Gradi (1043 CE: monastery; 1591 CE: Baroque; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria a Gradillo (11th c.CE; Ravello, Salerno, Campania)
· Santa Maria Assunta (13th c.CE: abbey church; art; La Spezia, Liguria)
· Santa Maria degli Alemanni (13th c.CE: Gothic; Teutonic Knight chapel; Messina, Sicily)
· Santa Maria del Carmine (1268 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1328/1464 CE: enlarged; 16-17th c.CE: Baroque; d.fire in 1771; 1782 CE: Rococo; 1425 CE: Brancacci Chapel; frescoes- Masaccio, Masolino da Panicale, Lippi; 1675 CE: Corsini Chapel; Florence, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria del Carmine (13th c.CE: Provencal-Gothic; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Maria della Consolazione (1508-1607 CE: Renaissance Bramante; Todi, Perugia, Umbria)
· Santa Maria del Mastro (1083 CE; Gerace, Reggio Calabria, Calabria)
· Santa Maria della Luce (13th c.CE: Angevine-Gothic; ship deck plan, frescoes; Castellaneta, Taranto, Apulia)
· Santa Maria della Pomposa (1135 CE: 2 previous churches; 1099-1184 CE: Romanesque; Modena, Emilia-Romagna)
· Santa Maria della Purita (1550s CE; Palladio; Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia)
· Santa Maria della Salute (Gothic; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Santa Maria delle Grazie (15th c.CE: Late Gothic-Renaissance; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria delle Grazie Church (Senigallia, Ancona, Marche)
· Santa Maria delle Grazie al Calciinaio Church (1484-1515 CE: Renaissance; Francesco di Giorgio Martini; Cortona, Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria di Gesu (15-16th c.CE; Trapani, Sicily)
· Santa Maria Donna Regina Vecchia (780 CE: Basilian; earthquake in 1293; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Maria in Colleromano (12th c.CE; Penne, Pescara, Abruzzo)
· Santa Maria in Gradi (11-12th c.CE; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria in Porto (16th c.CE: Baroque; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Santa Maria La Nova (1279 CE; Naples, Campania)
· Santa Maria Maddalena (1561 CE; over 14th c.structure; Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria Maggiore/Saint Mary the Greater (earliest church of Assisi)
· Santa Maria Maggiore (1227 CE: Bourgogne-Cistercian; 1540: updated Baroque; Lanciano, Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Santa Maria Maggiore/Saint Mary the Greater (13-14th c.CE: Gothic; Ferentino, Frosinone, Lazio)
· Santa Maria Maggiore (6th c.CE: dome, 40 ancient columns; 14th c.CE: frescoes; Nocera Inferiore, Salerno, Campania)
· Santa Maria Maggiore (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque; ciborium; Sovana, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria Maggiore (10-11th CE; rebuilt Baroque in 15th c.; Tursi, Matera, Basilicata)
· Santa Maria Nuova Church (1554 CE: Renaissance; Giorgio Vesari; Cortona, Arezzo, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria Nuovo (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Santa Maria in Ripalta (11th c.CE; Pistoia, Tuscany)
· Santa Maria in Vescovio (8th c.CE; 12th c.CE: Romanesque; Rieti, Lazio)
· Santa Maria Panaghia (Byzantine; frescoes; Rossano, Cosenza, Calabria)
· Santa Sofia (760 CE: Lombard; Benevento, Campania)
· Santa Sofia (10-12th c.CE: crypt; Byzantine-Romanesque-Gothic basilica; Padua, Veneto)
· Santi Giovanni e Paolo (Romanesque; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· Santa Trinita (f.1092 CE: pre-existing Vallumbrosan church; 1258-80 CE; 20 chapels- Sassetti Chapel; 15th c.CE: Renaissance art- Silvani, Nigetti, Aretino, Ghirlandaio, Signoria, Cigoli, Roselli, Banco, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Santissima Annunziata (f.1250 CE: original Servite church; 1469-81 CE: Renaissance-Alberti; art- Fiorentino, Sarto, Rosselli; Florence, Tuscany)
· Santissima Annunziata (1320 CE: church-orphanage; 16-17th c.CE: remade into hospital-church; Naples, Campania)
· Santo Spirito (12-18th c.CE; Atri, Teramo, Abruzzo)
· Santo Spirito (1428 CE: Renaissance; over 13th c.Augustinian convent; Brunelleschi; frescoes- Botticini, Roselli, Lippi, Michelangelo, etc.; Florence, Tuscany)
· Santo Spirito church (1498-1504 CE: Renaissance reconstruction; Siena, Tuscany)
· Santo Stefano (5th c.CE: original built by Saint Petronius over temple of Isis; church of the Holy Sepulchre; 8th c.CE: church of Saint John the Baptiste; 13th c.CE: church of Holy Trinity; Bologna, Emilia Romagna)
· Sarsina (Umbrian; 271 BCE: Roman: public baths, temples, fortifications, urns, bronzes; Emilia Romagna)
· Sarsina Cathedral/Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Vicinius (1000-8 CE; Sarsina, Forli-Cesena, Emilia Romagna)
· Sarzana Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1204-1474 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; over former San Basilio; Sarzana, Forli-Cesena, Emilia Romagna)
· Savona Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1480-3 CE; near Sistine Chapel; Savona, Liguria)
· Scala Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (13th c.CE; Scala, Salerno, Campania)
· Segesta (5th c.BCE; Sicily)
· Segni (495 BCE: Roman: acropolis- temple of Juno; 10th c.CE: Saint Peter church; Segni, Rome, Lazio)
· Segni Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (17th c.CE: built over former Saint Bruno temple; 11th c.CE: bell tower; Segni, Rome, Lazio)
· Selinunte (650 BCE)
· Senigallia (4th c.BCE: Gallic-Senones; 280 BCE: Roman; Marche)
· Septempeda (Roman baths, gates and walls; San Severino, Marche)
· Sessa Aurunca/Aurunci (Magna Graecia: ancient ruins; cyclopean walls; Roman amphitheatre and portico beneath San Benedetto church and San Giovanni monastery; Sessa Aurunca, Caserta, Campania)
· Sessa Aurunca Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (1103 CE: Romanesque Sessa Aurunca, Caserta, Campania)
· Sezze/Setia (legend: f.by Hercules; 5th c.BCE: Volscan- Latin League member; polygonal block walls; 382 BCE: Roman: villas; Latina)
· Sezze Cathedral/Saint Mary (13th c.CE: Gothic over ancient remains; Sezze, Latina, Lazio)
· Sicani cave (8000 BCE: cave art; Palermo, Sicily)
· Siena/Saena Julia (900-400 BCE: Etruscan; Gallic-Saenone; Roman; Tuscany)
· Siena Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1215-63 CE: Romanesque-Tuscan Gothic over 9th c. church; art works by Bernini, Michelagnolo, Donatello, etc.; octagonal pulpit by Pisano; Siena, Tuscany)
· Siponto [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Canis Major; f.by Diomedes; 335 BCE: Magna Graecia; 189 BCE: Roman; 663 CE: Salvic; 9th c.CE: Saracen; 1042 CE: Norman; 13th c.CE: earthquakes caused abandoning of town; Apulia)
· Sora (Volscian; 345/14/5 BCE: Roman; Apulia)
· Sora Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1155 CE; d.earthquake in 1634; Sora, Frosinone, Apulia)
· Sorrento/Surrentum (600 BCE: Oscan ruins; Magna Graecia; 90 BCE: Roman; Campania)
· Sovana Cathedral/Saint Peter (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque over 8th c.crypt; Sovana, Tuscany)
· Spello/Hispellum (Umbrian; 1st c.BCE: Roman: Porta di Venere/Gate of Venus; Porta Consolare; amphitheatre; Arch of Augustus; Perugia, Umbria)
· Spello Cathedral/Saint Mary Major (1159 CE: Romanesque built over temple of Juno and Vesta; Perugia, Umbria)
· Spina [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pegasus; 6th c.BCE: Etruscan port city; N Comacchio, Bologna)
· Spirito Santo (originally Arian temple; 5th c.CE: early Christian; Ravenna, Emilia Romagna)
· Spoleto (5th c.BCE: Umbrian walls; 2nd c.CE: Roman; amphitheatre; 2 theatres- 1) former Saint Agatha church, 2) became fortress of Totila/church of San Gregorio; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· Spoleto Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (12th c.CE: Romanesque over 1st cathedral dedicated to San Primiano and d.by emperor; Spoleto, Perugia, Umbria)
· Squillace/Scylletium (Magna Graecia)
· Strongoli/Petelia (Magna Graecia)
· Suasa (3rd c.BCE)
· Subiaco (Aequi; 304 BCE: Roman; Rome, Lazio)
· Subiaco Abbey (f.6th c.CE: Benedictine; 9th c.CE: d2x by Saracens; 10th c.CE: rebuilt; Subiaco, Rome, Lazio)
· Sulmona Cathedral/Saint Pamphilus (Romanesque over Roman temple; Sulmona, L’Aquila, Abruzzo)
· Susa (Gallic; 1st c.BCE: Roman: amphitheatre, Arch of Augustus; Piedmont)
· Susa Cathedral/Saint Justus (f.1029 CE: Benedictine abbey of Saint Justus; 1100 CE: Romanesque; joined to a Roman gate, Porta Savoia of 4th c.; Susa, Turin, Piedmont)
· Sutri (Etruscan-Roman: amphitheatre; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Sutri Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1207 CE: Romanesque; crypt; 20 columns of different origin; near the rock-cut-church of Madonna del Parto, one of many Etruscan tombs; Sutri, Viterbo, Lazio)
· Sybaris (6th c.BCE)
· Syracuse (734 BCE: Magna Graecia)
o Roman amphitheatre
o Temple of Apollo (adapted to Byzantine church; and Arab mosque)
o Temple of Olympian Zeus (6th c.BCE)
o Theatre (Greek: large; near latomie, stone quarries; used as ancient prison; Orecchio di Dionisio)
o Tomb of Archimede (Grotticelli Necropolis)
· Syracuse Cathedral/Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (7th c.CE: built over incorporated Temple of Athens of 5th c.BCE; Syracuse, Sicily)
· Taormina/Taurmina/Naxos (Siculi; 832 BCE: Greek; Messina, Sicily)
o Greek Theatre (adapted to Byzantine church; and Arab mosque)
· Taormina Cathedral/Saint Nicolas of Bari (13th c.CE; Taormina, Sicily)
· Taranto (6th c.BCE: Magna Graeca: temple ruins; Taranto, Apulia)
· Tarquinia (9th c.BCE: Villanovan Banditaccia necropolis; 3rd c.CE: Etruscan necropolis: Tomba dei Rilievi; mounds and dice types of tombs; Cerveteri, Lazio, Rome)
· Teano/Teanum Sidicinum (Oscan: fortress beneath 15th c.castle; 334 BCE: Roman: theatre, amphitheatre; Campania)
· Teano Cathedral/Saint Clement (1050-1116 CE: basilica using Corinthian columns from ruins of ancient town; 2 sphinxes; crypt housing Roman sarcophagus; Teano, Caserta, Campania)
· Tega Chapel (14th c.CE; frescoes; Spello, Perugia, Umbria)
· Teggiano/Tegianum (Oscan-Sabellian; 4th c.BCE: Lucanian; ruins; Roman; Salerno, Campania)
· Telese Terme/Telesia (Samnite; 207 BCE: Roman: baths, amphitheatre, aqueduct; Campania)
· Teramo (7-5th c.BCE: Etruscan-Phoenician; Praetutii; 290 BCE: Roman: theatre, amphitheatre; Goth; Byzantine; Abruzzo)
· Teramo Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Berardo (1158-76 CE; material taken from theatre and amphitheatre; Teramo, Abruzzo)
· Terlizzo Cathedral/Saint Michael (13th c.CE: Romanesque; 18-19th c.CE: neo-Classical; Terlizzo, Bari, Apulia)
· Termoli (prehistoric: necropolis; Roman: villae; Norman; Campobasso, Molise)
· Termoli Cathedral/Saint Bassus and Timothy (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque; earthquake d. in 1456; Turk sack d.in 1566; Campobasso, Molise)
· Terni (7th c.BCE: Sabini; 3rd c.BCE: Roman: amphitheatre; gate of Porta Sant’Angelo- ¼ entrances to city; Umbria)
· Terni Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (17th c.CE: Baroque; over paleo-Christian edifice; organ by Bernini; Terni, Umbria)
· Terracina/Anxur [Volscian: “Jupiter” (luppiter Anxur/ Anxurus)](Volscian; 509 BCE: Roman; 1st c.BCE: Jupiter Anxur: inscriptions to Venus; oracle hole; Capitolium dedicated to the Capitoline Triad- Jupiter, Juno, Minerva; Latina, Lazio)
· Terracina Cathedral/Saint Caesarius (1074 CE: Gothic-Romanesque ensconced within temple of Rome and Augustus; 12/18th c.CE: renov.; Terracina, Latina, Lazio)
· Tindari (396 BCE: Greek-Lacedaemonian; temple of Mercury; ruins; Patti, Sicily)
· Todi/Eclis/Tutere [Italic: “border;” border of Etruscan dominions] (myth.: 1330 BCE: f.by Hercules, who killed Cacus here; 8-7th c.BCE: Umbri; 217 BCE: Roman: Nicchioni; Perugia, Umbria)
· Todi Cathedral/Annunciation of the Virgin Mary (11th c.CE: Gothic; Lombard plan; erected over Roman temple of Apollo; bronze statue of Mars, later brought to Vatican; 1190 CE: rebuilt; 1513 CE: great rose window; Todi, Perugia, Umbria)
· Tolentino/Tolentinum (Paleolithic; 8-4th c.BCE: Piceni: tombs; Roman; Marche)
· Torcello Cathedral/of Santa Maria Assunta (639 CE; 864/1008 CE: renovations; Venice)
· Torre Pinta (catacombs; Otranto, Lecce, Apulia)
· Trani Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1143 CE: Romanesque-Arab; 1230-9 CE: crypt; Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia)
· Trapani/Drepanon [Gk.: “sickle”]/Eryx (myth.origins: 1- Demeter’s sickle, Persephone, Hades, 2- Saturn, Cronus, sickle; 1000 BCE: Elymians; 260 BCE: Carthaginian; 241 BCE: Roman; Vandal, Byzantine; Arab; Norman; Sicily)
· Trapani Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (1421 CE; Sicily)
· Treia (380 BCE: Sabine; 109 BCE: Roman; Egyptian religious statues; Macerata, Marche)
· Treia Cathedral/Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Medieval; Macerata, Marche)
· Trento (Rhaetian?; 4th c.BCE: Gaul-Celtic; Roman: underground remains; Ostrogoth; Byzantine; Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol)
· Trento Cathedral/Saint Vigilius (12-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; built over late-Roman basilica and crypt; Fountain of Neptune; Trentino-Alto Adige, South Tyrol)
· Trevi Cathedral/Saint Emilianus (Romanesque; Trevi, Umbria)
· Treviso/Tarvisium (Celtic; 89 BCE: Roman; Veneto)
· Treviso Cathedral/Saint Peter (orig. late-Roman church; 1520 CE: crypt and Chapels of Santissimo and Malchiostro; Veneto)
· Tricarico (6th-3rd c.BCE: Cerra del Carto; 500 BCE: Roman: Civita: fortified center, mosaic pavements; Matera, Basilicata)
· Tricarico Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1383 CE; Matera, Basilicata)
· Triest (3rd m.BCE: Carni; Illyrian-Histri; 2000 BCE: Illyrian-Veneti; 177 BCE: Roman: Arch of Riccardo; temples- Athena, Zeus on S.Giusto hill; amphitheatre; long duration under Hapsburg monarchy; Friuli-Venezia Giulia)
· Triest Cathedral/Saint Justus (Romanesque-Gothic over 6th c.Roman propylaea-Capitoline Temple: Capitoline Triad-Jupiter, Juno, Minerva; pyramidal altar; 9-11th c.CE: 2 basilicas erected; 14th c.CE: basilicas joined by nave; Friuli-Venezia Giulia)
· Troia/Aecae (Greek; 214 BCE: Roman; Foggia, Puglia)
· Turin Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (1491-8 CE; Chapel-Shroud of Turin; Piedmont)
· Tursi Cathedral/Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary (15-16th CE; Tursi, Matera, Basilicata)
· Tuscania (Neolithic; legends: f.by Ascanius or Hercules and Araxes; 7th c.BCE: Etruscan: acropolis; necropleis-Tomb of the Queen and Pian di Mola; 4th c.BCE: Greek; 280 BCE: Roman; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Tuscania Cathedral/Saint Mary Major (Romanesque; pair of free standing columns-replica Boaz and Jachin; Viterbo, Lazio)
· Tusculum (8th c.BCE)
· Udine (Neolithic; Greco-Roman; Friuli-Venezia Giulia)
· Ugento/Uxentum (Uxen; Greco-Roman; Lecce, Apulia)
· Umbriatico (Oenotrians; Greco-Roman; Crotone, Calabria)
· Umbriatico Cathedral/Saint Donatus (Middle ages; Crotone, Calabria)
· Urbino Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1021 CE: over 6th c. religious edifice; earthquake d.in 1789; Pesaro e Urbino, Marche)
· Vasto (1300 BCE: Greek; f.by Diomedes; Chieti, Abruzzo)
· Villa Romana del Casale (4th c.CE; Piaza Armerina)
· Valeia (102 BCE), Piacenza (218 BCE)
· Velletri (Volsci; 365 BCE: Roman: amphitheatre; Rome, Lazio)
· Velletri Cathedral/Saint Clement (4th c.CE: over ruins of ancient temple; 1659-62 CE: rebuilt; Rome, Lazio)
· Venafro (4th c.BCE: Samnite: walls; polygonal structure; Roman: amphitheatre, aqueduct; Isernia, Molise)
· Venafro Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (5th c.CE: built over ancient pagan temple; Gothic-Baroque restoration; Isernia, Molise)
· Venosa/Venusia (600000 BP: Paleolithic: Notarchirico; Greek-f.Diomedes; 291 BCE: Roman: walls, amphitheatre; 4-5th c.CE: Hebrew catacombs; Potenza, Basilicata)
· Venosa Cathedral/Saint Andrew (incorporates Roman works; Potenza, Basilicata)
· Ventimiglia/Albium Intemelium (paleolithic Cro-Magnon: caves of Balzi Rossi; Ligurian; 115 BCE: Roman: theatre, walls, mosaics; Imperia, Liguria)
· Ventimiglia Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (11th c.CE: Romanesque; baptistry built on ruins of earlier Lombard church, over Roman temple; Imperia, Liguria)
· Vercelli/Vercellae (600 BCE: Libici-Ligurian; 101 BCE: Roman; Piedmont)
· Vercelli Cathedral/Saint Eusebius (9th c.CE; Piedmont)
· Veroli Cathedral/Saint Andrew (Gothic; Frosinone, Lazio)
· Verona (Euganei; 550 BCE: Cenomani; 300 BCE: Roman: amphitheatre, arena, Porta Bosari, Arco dei Gavi, Porta Leoni; Veneto)
· Verona Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (2 paleo-Christian churches; d.earthquake in 1117; 1187 CE: Romanesque; Veneto)
· Vicenza (Euganei; 3rd-2nd c.BCE: paleo-Veneti; 157 BCE: Roman; Palladio works; Veneto)
· Vicenza Cathedral/Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary (11th c.CE; 13/16/19th c.: restored; Veneto)
· Vieste Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (Romanesque; 18th c.CE: Baroque; Foggia, Apulia)
· Vigevano Cathedral/Saint Ambrose (963-7 CE: init.; 1530-1606 CE; Pavia, Lombardy)
· Viterbo Cathedral/Saint Lawrence (legend: built over Etruscan temple of Hercules; 12th c.CE: Romanesque; Lazio)
· Vittori Veneto (Celt; Veneti; 1st c.BCE: Roman; Treviso, Veneto)
· Voltera/Velathri (Neolithic; 3rd-2nd BCE: Etruscan: walls-Porta dell’Arco, Porta Diana; 1st c.BCE: Roman: theatre; Pisa, Tuscany)
· Voltera Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (13th c.CE: Romanesque; enlarged after earthquake; Etruscan; 1st c.BCE: Roman: theatre; Pisa, Tuscany)
Sardinia: (Italy) [MA] [dolmen; star stones- Pole Star; 4th m.BCE: 2400 hypogeum/chamber/rock-cut-tombs, domus de janas (Sard.: “House of the Fairies”); nuraghe (Bronze Age; 18-15th c.BCE: 8000 megalithic edifices; only a few have been excavated); cathedrals]
· Abbey of Alghero (Chalcolithic-Bronze; 4000 BCE: Ozieri; Anghelu Ruju- necropolis, 36 tombs carved with bulls’ heads; 1500 BCE: Nuraghe; Phoenician edifices)
· Aiodda (giant’s tomb; near Nurallao)
· Basilica of San Gavino (11th c.CE: Romanesque; crypt hold several Roman sarcophagi; Porto Torres)
· Basilica of Sant’Antioco di Bisarcio (Romanesque; Ozieri, Sassari)
· Bosa [MA](prehistoric: Ozieri-Beaker; domus de janas and nuraghe; Phoenician; Roman)
· Bosa Cathedral/Immaculate Conception (12-15th c.CE; Bosa, Sassari)
· Cagliari (prehistoric: Necropolis of Tuvixeddu; 7th c.BCE: Phoenician colony; 283 BCE: Roman; amphitheatre)
· Caiazzo (Cyclopean wall remains; 306 BCE: Roman cistern; Caiazzo, Caserta, Campania)
· Caltagirone [Arab.: “hill of vases” (Qal’at-al-ghiran)](2nd m.BCE: 2 necropoleis; Sicels; Arab; Caltagirone, Sicily)
· Caltanissetta (406 BCE: Carthaginian; Roman; 829 CE: Saracen; Caltanissetta, Sicily)
· Caltanissetta Cathedral/Saint Mary (1539-1622 CE: late Renaissance- Baroque; Caltanissetta, Sicily)
· Castelsardo [MA](pre-Nuragic: megalithic walls; Nuragic: nuraghe Paddaju; Roman; Castelsardo, Sassari)
· Cathedral of Saint Nicolas of Bari (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Sassari)
· Church of Saint Francis of Assisi (1200 CE; Oristano)
· Church of Saint Peter (12th c.CE; Sassari)
· Church of San Francesco (15th c.CE: Gothic; Iglesias)
· Dolianova (Nuraghe sa dom’e S’Orcu, Sant’Uanni, fortresses covered by trees; [AS] Mitza salamu e Sadom e s’ossu; Giant’s tombs in Su Tiriaxiu; Roman Baths- Sa Cora; Dolianova)
· Church of San Pietro in Vincoli (13th c.CE: Ittiri, Sassari)
· Church of Santa Maria di Betlam (13-19th c.CE: Lombard-Romanesque; Sassari)
· Coddu Vecchju (Giant’s tomb; Arzachena)
· Dolianova Cathedral/ of San Pantaleo (1160-1289 CE: Romanesque-Pisane; Dolianova)
· Ena e Thomes (Bronze age: nuraghe; Dorgali)
· Goni [MA](menhir; Goni, Cagliari)
· Goronna
· Grotte di San Michele (3500-2700 BCE; Ozieri)
· Iglesias Cathedral/Saint Clare (1288-1325 CE; Iglesias)
· Imbertighe (Bronze age: tomb; Borore)
· Ispinigoli caves (12km series of caves; Bronze age: tombs; Dorgali)
· Ittiri [MA](Neolithic: Domus de Janas, nuraghe, necropolis; Sassari)
· Lanusei [MA](18th c.BCE: tombs; Bronze age)
· Li Lioni (Neolithic necropolis; Porto Torres)
· Lolghi (Bronze age: nuraghe; Arzachena)
· Losa [MA](nuraghe)
· Los Millares [MA](3025 BCE: Beaker; 70 tholos “beehive” tombs; sim.Sumerian structures)
· Lotzorai [MA](Neolithic: Domus de Janas)
· Madau (Bronze age: giant tomb; Fonni)
· Menhirs Valley [MA](menhir; Ozieri)
· Monte d’Accoddi [MA](4th m.BCE: Neolithic; pre-nuragic; ziggurat; Sassari)
· Muraguada (Bronze age: giant tomb; Bauladu)
· Muravera [MA](Nuraghe)
· Nora (nuraghe; Phoenician)
· Nuoro/Nugoro (3500 BCE: Ozieri; center of Nuragic civ.)
· Nuraghe Arrubiu [MA](6000 BCE: Orroli)
· Nuraghe of la Camusina [MA](Neolithic: nuraghe; Porto Torres)
· Nuraghe of Li Pedriazzi [MA](Neolithic: nuraghe; Porto Torres)
· Nuraghe Losa [MA]
· Nuraghe Maiori [MA](Tempio Pausania)
· Nuraghe of Margone [MA](Neolithic: nuraghe; Porto Torres)
· Nuraghe of Minciaredda [MA](Neolithic: nuraghe; Porto Torres)
· Nuraghe Paddaju [MA](Castelsardo)
· Nuraghe Polcu [MA](Tempio Pausania)
· Nuraghe la Prisciona [MA](giant’s grave; Arzachena)
· Nuraghe sa dom’e S’Orcu (Dolianova; Punta Bruncu Salamu)
· Nuraghe Sant’Antine [MA](Torralba, Sassari)
· Nuraghe Sant’Uanni (Dolianova)
· Olbia [MA](nuraghe)
· Oristano Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1130 CE: Gothic; 17th c.CE: Baroque; Oristano)
· Orroli [MA](nuraghe; Cagliari)
· Osono (Bronze age: nuraghe-giant tomb; Triei)
· Ozieri Cathedral/Immaculate Conception (15th c.CE: Ozieri, Sassari)
· Pescaredda
· Pimentel [MA](Neolithic: Domus de Janas)
· Porto Torres [MA](3000 BCE: ziggurat; Domus de Janas; Sassari)
· Dolmen Sa Coveccada (Mores)
· Sa Dom’e s’Orcu [MA](Bronze age; Quartucciu, Siddi)
· Sa Ena’s Thomes Giant’s grave (Bronze age: nuraghe; Dorgali)
· Sa Perda Pinta Boeli Marroiada [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pole Star; near Nuoro)
· San Simplicio cathedral (11-12th c.CE: Romanesque; Olbia)
· Sant’Andrea Priu [MA](Domus de Janas- 18 chambers; Roman-Byzantine: trans.cave church; Bonorva)
· Santa Chiara (1428 CE: Franciscan church; Oristano)
· Santa Giusta (Phoenician: 50 amphorae, chamber tombs)
· Santa Giusta/Saint Justa (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Santa Giusta, Oristano, Sardinia)
· Santu Bainzu
· Sarroch [MA](nuraghe)
· Sassari (Neolithic; Nuragic: nuraghes and domus de Janas; Monte d’Accoddi; Phoenician; Roman)
· Sedini [MA](Neolithic: Domus de Janas)
· Serra Orrios [MA](nuraghe)
· Sorres Cathedral/Saint Peter/Abbey of San Pietro di Sorres (Borutta, Sassari)
· Sortali
· Su Crocifissu Mannu (Neolithic necropolis; Porto Torres)
· Su Mont’e s’Abe [MA](Bronze age; Olbia)
· Su Nuraxi di Barumini [MA](16th c.BCE: nuraghe; Barumini)
· Tempio Pausania (Nuragic; Phoenician)
· Tempio Cathedral/Saint Peter (Tempio Pausania)
· Tharros (800 BCE: Phoenician)
· Tiscali Macomer [MA](richest region of nuraghi; cave; Dorgali)
· Tomb of San Cosimo (Bronze age: nuraghe; Gonnosfanadiga)
· Villanovaforru [MA](nuraghe; Medio Campidano)
· Villaperuccio [MA](Neolithic: Domus de Janas; Carbonia-Iglesias)
LATVIA: [megaliths; cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Davini [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; Davinu Upurakmens; star stones- Aquila, Deneb, Lyra, Cygnus, Summer Solstice Line w/Riga and Pokainu Mezs; near Riga)
· Dzelzamura Medibu Pils [Latv.: “steelhammer castle”] [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Minor)
· Kolkas Rags [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Winter Solstice Line, Rasalhague)
· Muldakmens [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Cepheus, on Winter Solstice Line)
· Pokainu Mezs [“Owl Forest”] [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Major-Mizar, Summer Solstice Line)
· Riga [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Center of Heaven, North Ecliptic Pole)
· Riga Cathedral (1211 CE: Protestant-Lutheran; Daugava r.; Riga)
· Saint James Cathedral (1225 CE: Gothic-Baroque; Protestant-Lutheran; Daugava r.; Riga)
· Skierskani [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Taurus-Aldebaran, Winter Solstice Line)
· Zilaiskalns [“blue hill”] [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- planisphere)
LITHUANIA:
· Kaunas Cathedral Basilica/Saint Peter and Paul (1413 CE: Late/Brick Gothic-Renaissance; Roman-Catholic; Kaunas)
· Vilnius Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (pre-Christian Baltic pagan god Parkunas worship location; 1251 CE; 1263: converted back to pagan worship; 1387: Gothic; burned in 1419; renovated in 1522; fire in 1530; rebuilt in 1534-57; 1623-36: Baroque; 1769: collapse of southern tower killed 6 people; Vilnius Old Town)
LUXEMBOURG: [megaliths; cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Ferschweiler [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Corvus; near Luxembourg City)
· Luxembourg City (Roman cross roads)
· Notre Dame Cathedral/Saint Peter and Paul (1613 CE: Gothic-Renaissance; Jesuit; Roman-Catholic; Luxembourg City)
MACEDONIA:
· Aladja Mosque (1438 CE: Islamic; Skopje)
· Astibo (early Roman: Stip)
· Bara Tumba (Neolithic; Bitola)
· Bargala (4th c.CE: fortified town; Stip)
· Bylazora/Vylazora (4th c.BCE: Veles)
· Church of Saint George (1071 CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; reconstructed in 1313/1318; Kumanovo, Staro Nagoricane)
· Church of Saint John at Kaneo (1447 CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; Ohrid)
· Church of Saint Panteleimon (1164 CE: Byzantine; frescoes; Gorno Nerezi, Karpos, near Skopje)
· Church of Saint Sophia (9-10th c.CE: Bulgarian-Byzantine; Ottoman mosque; 11-13th c.: frescoes; Macedonian Orthodox; Ohrid)
· Church of Saint Vraci (14th c.CE: frescoes; Ohrid)
· Church of Saint Zaum/Saint Bogorodica Zahumska (Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; Ohrid)
· Colored Mosque in Tetovo (1495 CE: Islamic; Tetovo)
· Estipeon (3rd c.CE: Byzantine; Stip)
· Heraclea Lyncestis (4th c.BCE: Bitola)
· Isak Bey Mosque (Islamic; Skopje)
· Karpino Monastery (1100 CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; 16-17th c.CE: monastery; frescoes; Kumanovo)
· Kokino [MA] (1800 BCE: Bronze Age; megalithic observatory; Kumanovo)
· Lesok Monastery (1326 CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; Totovo)
· Monastery of Saint Naum (905 CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; Ohrid)
· Mustapha Pasha Mosque (1492 CE: Islamic; Skopje)
· Ohrid (4th c.BCE: Lacus Lychnitis: Bryge-Enchelean/Greek; theatre; 2nd c.BCE: Roman; 867 CE: Bulgarian)
· Osogovo Monastery/Saints Joachim, Mary (12th c.CE: Macedonian Orthodox; Kriva Palanka)
· Saint Erasmus (6th c.CE: necropolis; Ohrid)
· Saint Jovan Bigorski Monastery/Saint John the Baptist (1020 CE: Macedonian Orthodox; 16th c.: d.Ottomans; restored in 1743; Mavrovo)
· Saint Panteleimon (9-10th c.CE: Byzantine; liturgical bldg.-Cyrillic alphabet; crypt of Saint Clement; 15th c.: Ottoman-Turk: mosque; 16th c.: converted back into church; 17th c.CE: mosque; Ohrid)
· Scupi/Tumba (81 CE: Roman colony; Skopje)
· Stobi (4th c.BCE: Paeonian; Gladsko)
· Tetovo (6100 BCE: Stone Age/Neolithic; Iron Age: Bryge; 3rd c.BCE: Macedonian-Paionian-Agrianian; 29 BCE: Roman; 14th c.: Ottoman)
· Trebenista (7th c.BCE: Iron Age; Illyrian acropolis; Ohrid)
· Treskavec Monastery (12th c.CE: Byzantine; Macedonian Orthodox; rebuilt in 14th c.; m.Zlatoriv; Prilep)
· Utrecht (2200 BCE: Stone Age; Bronze Age; 50 CE: Roman fortification: Traiectum)
· Vardarski Rid (early antiquity: acropolis; Gevgelija)
· Veluska Tumba (Neolithic; Bitola)
· Vinicko Kale (Vinica)
NETHERLANDS: [megaliths; cathedrals]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
· Assen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Libra; near Drenthe)
· Borger [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Libra; near Drenthe)
· Emmen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Libra; near Drenthe)
· Groningen (3950-3720 BCE: [AS]; 3rd c.CE: settlement)
· Meppel [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Libra; near Drenthe)
· Northsea shore (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Roermond (Celtic; Roman; 1180-1543: Guelders; Hanseatic League; Minster church; Saint Christopher Cathedral; 1543-1702 CE: Spanish Netherlands; 1702-16: Dutch; 1716-94: Hapsburg monarchy; 1792-1814: French; 1814-: Netherlands)
· Saint Bavo’s Cathedral (695 CE: 1st church f.Saint Willibrord; 1559 CE: Roman Catholic; Haarlem)
· Saint Catherine’s (1456 CE: Carmelite friary; 1529 CE: Knight’s Hospitaller; Utrecht)
· Saint John’s (1220-1340 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1559 CE: diocese; s-Hertogenbosch)
· Saint Martin (600 CE: Merovingian 1st chapel; d. by Normans in 9th c.; 1023 CE: rebuilt Romanesque; partially d.fire in 1253; 1254 CE: Gothic; 1580 CE: Protestant church; Utrecht)
· Terneuzen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Virgo; the Scheldt <Fr./Latv.: “divide“ (skelte)>, original dividing line between French and Germanic tribes)
· T-shaped Hunebed D27 [MA](Borger-Odoorn)
NORWAY: [megaliths; rune stones/picture stones; stone burial ships (400-900 CE); cathedrals]
· Bergen Cathedral (1181 c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1248/1270/1463/1623/1640: burned; Rococo interior; Bergen)
· Borg (Viking longhouse)
· Borre (5th c.CE: Merovingian; mound cemetery)
· Gokstad ship burial (9th c.CE: Viking: ship found beneath burial mound; Sandar, Sandefjord, Vestfold)
· Nidaros Cathedral (1079-1300 c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1152-1537: archdiocese; 1537: Lutheran; 1327/1531: fire dmg.; 1708: burned; 1719: struck by lightning- fire; Trondheim)
· Oseberg ship burial (834 CE; Tonsberg, Vestfold)
· Oslo Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1632-9: new construction; burned in 1689; reconstructed; Oslo)
· Stavanger Cathedral (1100-1125 c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1272: fire-rebuilt; Stavanger)
· Troms (Ice Age: Sami culture; Norse-Viking)
· Troms Cathedral (13th c.CE: first church; 1861: current church; Troms)
· Tromsdalstinden [SM](Troms)
· Tune (900 CE: ship burial; Ostfold)
POLAND: [mounds (kurgan/kopiec), stone circles and stelae, cathedrals, abbeys]
[NOTE 14] The Teutonic Knight Order (f.Acre, Israel in 1190, after the Knights Templar, and Knights of Malta/Hospitaller; originally an order which provided hospitals to pilgrims, later became a military order), holding allegiance to the Holy Roman Empire and the Roman Catholic Pope, invaded Baltic states (eg.Prussia, Pomerelia, Samogitia, Courland, Livonia, Estonia, Gotland, Dago, Osel, and Neumark; 1260-1410 CE), in a effort to subdue Baltic pagans and establish a monastic state. The monastic state went into decline after the Protestant reformation (c.1577 CE). In the 19th c.CE, the Teutonic Order, though in a state of suppression, was headed by the Hapsburg dynasty; revealing the connection, and possible farce-conflict between one of the illuminati banking families and the Roman Catholic Church. Why was Hitler shaking the Pope’s hand during WWII?
[NOTE 15] Neolithic Bronze Age cultures (utilizing mounds, and stone circles and stelae, animal sacrifice/Ashvamedha) were linked with Indian cultures through Scythia (bronze age chariot culture.
[NOTE 16] Major cathedrals located on ley line intersections, serving as royal necropolies, may have functioned as spiritual portals to a particular after-life inter-dimensional destination.
· Belchatow (pagan temple on kurgan)
· Bernadine church and monastery (1468-1507 CE; Radom)
· Biskupin (720 BCE: Iron Age; Lusatian; Znin)
· Brachnowko [MA](megaliths; 7km S Chelmza; Gmina Chelmza, Torun)
· Cathedral Basilica of the Assumption of Mary (1340 CE; Wloclawek)
· Cathedral Basilica of Saint James the Apostle (1187-14th c.CE: Romanesque; modeled after Saint Mary’s in Lubeck; 1677: d.Scanian War; 1690-3: rebuilt Baroque; collapse of spire during WWII; Szczecin)
· Cathedral Basilica of Saint John the Baptist and Saint John the Evangelist (13th c.CE: first church; Brick Gothic; rebuilt until 15th c.; Torun)
· Cathedral Basilica of Saint Peter and Saint Paul (10th c.CE: Romanesque; 1034-8 CE: d.pagans; rebuilt; 14-15th c.CE: Gothic; 1622: fire- rebuilt Baroque; 1772: fire- rebuilt Neo-Classical; 1945: fires- Gothic; Poznan)
· Cathedral of the Holy Trinity (Sarnok)
· Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception of the Blessed Virgin Mary (14th c.CE: Roman Cath.; Koszalin)
· Cathedral of Saint Hedwig (1294 CE; Zielona Gora)
· Cathedral of Saint Stanislaus and Saint Wenceslaus (14th c.CE: Gothic; Swidnica)
· Cathedral of the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (15th c.CE; 1711: ren.Baroque; Zywiec)
· Chelmska hill/Gollenberg (Prehistory: pagan holy site; 1991 CE: “sanctuary of the covenant”; Koszalin)
· Chelmza (10000 BCE: reindeer hunter settlements; 4500 BCE: 1st agricultural settlements)
· Church of the Holy Cross (14th c.CE; Opole)
· Church of the Holy Cross (14th c.CE; 1679/1690: expanded; Zywiec)
· Church of Saint Adalbert (10th c.CE; Opole)
· Church of Saint James/Sanctuary of Blessed Sadok and 48 Dominican martyrs/Sanctuary of Our Lady of Rosary (12-13th c.CE: Romano-Gothic; Dominican monastery; 1260: Mongol invasions; Sandomierz)
· Church of Saint John the Baptist (1065 CE: early church; 1538 CE; Wloclawek)
· Czestochowa (1300-500 BCE: Bronze-Iron Age: Trzciniec-Lusatian culture)
· Drohiczyn (Neolithic: La Tene culture)
· Frombork Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Andrew (13th c.CE; Copernicus; Frombork)
· Gdansk/Danzig (Oksywie culture; 1st c.CE: Wielbark-Goth culture)
· Giecz (10th c.CE)
· Gniezno (Paleolithic; early Slavonic settlements: Lech and Maiden Hills)
· Gniezno Cathedral/Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Adalbert (1175 CE: Gothic; 2-winged bronze doors depicting scenes of martyrdom of Saint Wojciech; his silver relic coffin; 1025-1340 CE: royal coronations)
· Grzybnica [MA](megaliths; 15km SE Manowo, 23km SE Koszalin)
· Guciow (1500 BCE: Trzciniec culture: kurgan burial site)
· Jasna Gora Monastery (1382 CE: Pauline monastery; Black Madonna; Czestochowa)
· Jawczyce (Neolithic- Bronze age: kurgan-mound tombs)
· Kalisz (2nd c.CE: Roman; Roman Catholic diocese)
· Kielce (5th c.BCE-6-7th c.CE: Celt; Vistulan; mid-13th c.CE: d.Mongols)
· Kopiec Esterki (14th c.CE: by Casimir III for his wife)
· Kopiec Tatarski (triangular mound pointing E; bones, ancient coins, ceramics; 1534 CE: Templum S.Leonardi built on mound; d.WWII; Przemysl)
· Kopiec Wladyslaw III (1444 CE; Varna)
· Kopiec Wyzwolenia (1937 CE)
· Kosciuszko Mound (1823 CE; Krakow)
· Krakus Mound (2nd-1st c.BCE: Celtic?; legend: burial place of Polish prince Krakus c.1190; kurgan burial site; near Krakow)
· Krasnik (Neolithic: Stone Age: Unetice culture: kurgans)
· Krzemionki Opatowskie (Neolithic)
· Legnica (Celtic and East Germanic trade route intersection; Ptolemaic: Lugii; 1241 CE: Mongol invasions; 1676: Hapsburg)
· Leki Male (2000-1800 BCE: Bronze Age: Unetice culture; 14 kurgans; Gmina Luttow, Wieruszow, Lodz)
· Leubingen (1940 BCE: Bronze Age: Unetice culture; 14 kurgans)
· Lubna-Jakusy (1500 BCE: Trzciniec culture: kurgan burial site; Sieradz)
· Odry (Iron Age: stone circle; Odry, Gmina Czersk)
· Oliwa Cathedral/Holy Trinity, Blessed Virgin Mary, Saint Bernard (1186 CE: Cistercian Monastery; 1224: Romanesque oratory burned during pagan Prussian crusade; rebuilt in 1234; destroyed again by Prussian crusade; 1350: destroyed by fire; 1577: burned by mercenary army in rebellion of Gdansk; rebuilt in 1578-83; 1594: consecrated; Baroque-Rococo interior; crypt: Pomeranian Dukes; 1831: Prussian authorities closed monastery; 1925: diocese Gdansk)
· Ostrow Lednicki (Middle Ages: castle; Gniezno-Poznan)
· Pelplin Abbey/Cathedral Basilica of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1258-1823 CE: Brick-Gothic; Cistercian; Pelplin)
· Pilakno (kurgan-mound; 1348 CE: Teutonic Knight fortress; Mragowo)
· Pilsudski’s Mound (for Jozef Pilsudski; Krakow)
· Plesnik (kurgan-tombs)
· Plock Cathedral/ (1075 CE: Romanesque; fire; 1136-44 CE: rebuilt; Plock)
· Prezemysl (f.8th c.CE: monastic settlement)
· Saint Jacob’s Cathedral (Olsztyn)
· Saint Jacob’s Church (14th c.CE: Gothic; Torun)
· Saint James Cathedral (Olsztyn)
· Saint John the Baptist church (1360-70 CE: Gothic; Radom)
· Saint John’s Cathedral (1390 CE: Masovian Brick Gothic; coronation and burial site for many Masovian Dukes; 17th c.CE: Early Baroque interiors; Warsaw)
· Saint Mary’s Basilica (1260s CE: Brick Gothic; turned into nun’s abbey; Kolobrzeg)
· Saint Mary’s Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque-Brick Gothic; 1537: Protestantism; Gorzow Wielkopolski)
· Saint Mary’s Church (1243 CE: early wooden church; 1343-1502 CE: Brick Gothic; 1577: Lutheran; Baroque Royal Chapel; Gdansk/Danzig)
· Saint Mary’s Church (14th c.CE: Franciscan; Torun)
· Saint Mary’s Church (1411 CE; Warsaw)
· Saint Nicholas Cathedral (1443-7 CE: rebuilt 20th c.; Bielsko-Biala)
· Saint Nicholas Cathedral (13th c.CE: Gothic; fire dmg.in 18th c.; d.in WWII; rebuilt in 1992; Elblag)
· Saint Peter and Saint Paul (1128 CE; Szczecin)
· Saint Waenceslaus church (13th c.CE: Gothic; Radom)
· Saint Witalis Church (1330 CE; Wloclawek)
· Sanok (pre Roman: Celt-Anarti; Goth; Vandal; Roman; 9th c.CE: Hungarian-Slav Lendian: fortified town; Great Moravian Empire)
· Sandomierz [Old Polish: “judge peace”](Neolithic; 1241/1259/1287: Tatar raids)
· Sandomierz Cathedral/Cathedral Basilica of the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary (1360 CE: Gothic; 18th c.CE: Baroque; Sandomierz)
· Sieradz (1500 BCE: Trzciniec culture: kurgan-tomb with man and woman; Warta r.; Lodz)
· Skalbmierz (4000 BCE: kurgans)
· Torun (1100 BCE: Lusatian culture; 1230: Teutonic Knight castle)
· Trawiasta Buczyna (1200-1000 BCE: hundreds of stone kurgans)
· Trzcianka hill fort (Early Middle Ages)
· Union of Lublin Mound (1869-90 CE; Lviv)
· Wanda Mound (legend: burial place of Polish princess Wanda, daughter of Krakus; kurgan burial site; Krakow)
· Wawel Cathedral/Cathedral Basilica of Saint Stanislaus and Wenceslaus (1000 CE: Gothic; 14th c.CE: Saint Leonard’s crypt: burial chamber for Polish monarchs and national heroes; Krakow)
· Wesiory [MA](Neolithic: stone circles; Wesiory, Gmina Suleczyno, Kartuzy)
· Wroclaw Cathedral/Saint John the Baptist (10th c.CE: 1st church- Bohemian; 1039: d.Bohemian troops; rebuilt Romanesque; after Mongol invasions- rebuilt Brick Gothic; 1540: fire- Renaissance; 1759:” burnt towers- neo-Gothic; Wroclaw)
· Zambrow (kurgans)
· Zamosc Cathedral/Holy Ascension and Saint Thomas the Apostle (Renaissance-Baroque; Zamosc)
PORTUGAL: [MA] [dolmen, cathedrals]
· Abrigo do Lagar Velho (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Leiria)
· Alcalar, Megalithic Monuments of [MA](Neolithic; Mexilhoeira Grande, Portimao, Algarve, Faro)
· Alcobaca Monastery (f.King Afonso Henriques as gift to Bernard of Clairvaux to commemorate his victory over the Moors at Santarem in 1147; 1153 CE: Cistercian; 1178-1252: Gothic; large library- mostly now in Lisbon; royal tombs: King Pedro I: decorated reliefs: scenes- Saint Bartholomew’s life, Christ, Crucifixion, Last Judgment; Chapel of Saint Bernard: sculpture depicting “Death of Saint Bernard”; Royal Pantheon- 12 apostles, 4 evangelists, mandorla christ; Sacristy; Room of the Kings; Cloister of Silence: Renaissance; Alcobaca, Leiria)
· Almendres Cromlech [MA](5000 BCE: cromlech- archeoastronomical; Guadelupe, Evora)
· Anta Grande da Comenda da Igreja [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora do Bispo, Montemoro-Novo, Evora)
· Anta Grande do Paco [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora do Bispo, Montemoro-Novo, Evora)
· Anta Grande do Zambujeiro [MA](4000 BCE: dolmen; Nossa Senhora da Tourega, Evora)
· Belem/Santa Maria de Belem parish (1497: Vasco da Gama departure place; tower; Lisbon)
· Braga (Iron Age: Bracari: castrum/fortified village; 136-20 BCE: Roman: Bracara Augustus; 410 CE: Sueves; 584: Visigoth; 8th c.CE: Arab-Moor; 1070: bishopric restored)
· Braga Cathedral/Se Catedral de Santa Maria de Braga (d.3rd c.CE; 1071 CE: bishopric; 1107: archbishopirc; Burgundian Romanesque Cluny monastic; 1486-1501: Gothic-Baroque modifications; Braga)
· Cachao da Rapa, Prehistoric Rock Art (Neolithic: dolmens; findings: lithic flakes of quartz, schist implements, rounded pebbles, machetes; lithic remnants: archs, circles, semi-circles; Chalcolithic/Iron Age settlements; Ribalonga, Carrazeda de Ansiaes)
· Casainhos, Megalithic Monuments [MA](Neolithic; Fanhoes, Loures, Lisbon)
· Castro of Aldeia Nova (Neolithic; Miranda do Douro)
· Castro of Alvarelhos (Neolithic; Alvarelhos, Trofa, Porto)
· Castro of Arades (Neolithic; Aplendurada Matos, Marco de Canaveses, Porto)
· Castro of Azere (Neolithic; Azere, Arcos de Valdevez, Galacia)
· Castro of Bom Successo (Neolithic; Mangualde, Mangualde)
· Castro of Briteiros (Neolithic; Salvador de Briteiros, Guimaraes, Braga)
· Castro of Castelo Velho [MA](Neolithic; Terena, Alandroal)
· Castro of Cola [MA](Neolithic; Ourique)
· Castro of Melgaco (Neolithic; Paderne, Melgaco)
· Castro of Monte Padrao (Neolithic; Monte Cordova, Santo Tirso, Porto)
· Castro of Monte Redondo (Neolithic; Guisande, Braga)
· Castro of Nossa Senhora da Guia (Neolithic; Baioes, Sao Pedro do Sul)
· Castro of Rocha Forte (Neolithic; Lamas, Cadaval, Lisbon)
· Castro of Sabroso (Neolithic; Sao Martinho de Sande, Guimaraes, Braga)
· Castro of Sacoias (Paleolithic; Neolithic: tumulus of Donai; 1000-700 BCE: Bronze Age: Terra Fria; Bacal, Braganca)
· Castro of Santa Maria dos Galegos [MA](Neolithic; Santa Maria dos Galegos, Barcelos)
· Castro of Sao Caetano (Neolithic; Longos Vales, Moncao)
· Castro of Sao Miguel de Amendoa (Neolithic; Amendoa, Macao, Santarem)
· Castro of Zambujal (Neolithic; Santa Maria do Castelo e Sao Miguel, Torres Vedra)
· Cathedral of Evora/Virgin Mary (1184-1204 CE: 1st bldg.; 1280-1340: enlarged Gothic- cloisters; Renaissance: pipe organ, choir stalls; 16th c.: Manueline chapel; 18th c.: Baroque main chapel; Evora)
· Cave of Ermigeira (Paleolithic; Maxial, Sintra)
· Cave of Nossa Senhora da Luz [MA](Paleolithic; Rio Maior)
· Church of Saint James (12th c.CE: Coimbra)
· Cividade de Terroso (800 BCE; Povoa de Varzim)[MA]
· Coa Valley (22-10k BP: Peleolithic: classic-Neanderthal; Chalcolithic/Bronze Age; Coa r.; Vila Nova de Foz Coa)
· Coimbra (Roman: Aeminium; 5th c.CE: dioc.; 465-8: plundered by Germanic tribes; hill by Mondego r.; 586-640: Visigoth: Eminio; 711: Moor: Qulumriyah; link between N-Christian and S-Muslim; 12th c.: reconquered by Christians- bishopric)
· Conimbriga (9th c.BCE: Celtic; Roman; Coimbra)
· Conjuto Megalitico do Monte dos Amantes [MA](9 menhirs; Vila do Bispo)
· Cromeleque da Portela de Mogos [MA](46 menhirs; Vila do Bispo)
· Dolmen da Aboboreira [MA](Neolithic; Ovil, Baiao, Porto)
· Dolmen of Adrenunes [MA](Neolithic; Colares, Sintra, Lisbon)
· Dolmen of Agualva [MA](Neolithic; Sao Martinho, Sintra, Lisbon)
· Dolmen of Aldeia da Mata [MA](Neolithic; Aldeia da Mata, Crato)
· Dolmen da Aliviado [MA](Neolithic; Escariz, Arouca, Porto)
· Dolmen of Alto de Miraflores [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Arca [MA](Neolithic; Arca, Oliveira de Frades)
· Dolmen of Arraiolos [MA](Neolithic; Arraiolos, Evora)
· Dolmen of Barrocal [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora da Tourega, Evora)
· Dolmen of Barrossa [MA](Neolithic; Vila Praia de Ancora, Caminha)
· Dolmen of Belas [MA](Neolithic; Agualva-Cacem, Lisbon)
· Dolmen of Cabeca Gordo [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Capela de Nossa Senhora do Monte [MA](Neolithic; Penela da Beira, Pendono)
· Dolmen of Carapito I [MA](Neolithic; Carapito, Aguiar da Beira, Guarda)
· Dolmen of Casal-Mau [MA](Neolithic; Santa Eulalia, Arouca)
· Dolmen of Cas-Freires [MA](Neolithic; Ferreira de Aves, Satao, Visieu)
· Dolmen of Casa dos Galhardos [MA](Neolithic; Santa Maria da Devessa, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Coureleiros II [MA](Neolithic; Santiago Maior, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Coutada de Alcogulo [MA](Neolithic; Santa Maria da Devessa, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Coutada de Barbacena [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Crato [MA](Neolithic; Crato e Martires, Crato)
· Dolmen of Cunha Baixa [MA](Neolithic; Cunha Baixa, Mangualde)
· Dolmen of D.Miguel [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Fonte Coberta [MA](Neolithic; Vila Cha, Alijo)
· Dolmen of Fonte de Mouratao [MA](Neolithic; Sao Joao Baptista, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Herdade da Candeira [MA](Neolithic; Redondo, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade das Comendas [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora do Bispo, Montemoro-Novo)
· Dolmen of Herdade das Dessouras [MA](Neolithic; Redondo, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade de Freixo [MA](Neolithic; Monte do Trigo, Portel, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade de Galvoeira [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora de Machede, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade de Montinho [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora de Machede, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade da Murteira [MA](Neolithic; Torre de Coelheiros, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade da Ordem [MA](Neolithic; Maranhao, Avis)
· Dolmen of Herdade da Serranheira [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora do Bispo, Montemor-o-Novo)
· Dolmen of Herdade do Silval [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora da Graca do Divor, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade da Tisnada [MA](Neolithic; Torre de Coelheiros, Evora)
· Dolmen of Herdade de Tourais [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora de Vila, Montemor-o-Novo)
· Dolmen of Herdade de Zambujal [MA](Neolithic; Sao Bento do Mato, Evora)
· Dolmen of Mamaltar do Vale de Fachas [MA](Neolithic; Rio de Loba, Viseu)
· Dolmen of Melrica [MA](Neolithic; Santiago Maior, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Nave do Grou [MA](Neolithic; Sao Joao Baptista, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Olival de Monte Velho [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Orca [MA](Neolithic; Oliviera do Conde, Carregal do Sal)
· Dolmen of Paco das Vinhas [MA](Neolithic; Canaviais, Evora)
· Dolmen of Paiva [MA](Neolithic; Paiva, Mora)
· Dolmen of Paranhos [MA](Neolithic; Paranhos, Seia, Guarda)
· Dolmen of Paredes [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora da Graca do Divor, Evora)
· Dolmen of Pedras Negras (Neolithic; Canecas, Odivelas, Lisbon)
· Dolmen of Penalva [MA](Neolithic; Antas, Penalva do Castelo, Viseu)
· Dolmen of Pinheiro do Campo [MA](Neolithic; Sao Sebastiao de Giesteira, Evora)
· Dolmen of Porto de Cima de D.Miguel [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Pero d’Alva [MA](Neolithic; Santiago Maria da Devessa, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Pombais [MA](Neolithic; Santiago Maria da Devessa, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Queiriga [MA](Neolithic; Queiriga, Vila Nova de Paiva)
· Dolmen of Santa Maria [MA](Neolithic; Santa Maria, Penafiel, Porto)
· Dolmen of Sao Brissos [MA](Neolithic; Santiago do Escoural, Montemoro-Novo)
· Dolmen of Serra de Soajo [MA](Neolithic; Soajo, Arcos de Valdevez)
· Dolmens of Serra do Alvao [MA](Neolithic; Lixa do Alvao, Vila Pouca de Aguiar)
· Dolmen of Silval [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora da Graca do Divor, Evora)
· Dolmen of Tintinolho [MA](Neolithic; Faia, Guarda)
· Dolmen of Torna de Paco Pereira [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Torrao [MA](Neolithic; Barbacena, Elvas)
· Dolmen of Vale da Rua [MA](Neolithic; Sobrado, Castelo de Paiva)
· Dolmen of Varzea dos Mouroes [MA](Neolithic; Santiago Maior, Castelo de Vide)
· Dolmen of Velada [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora do Bispo, Montemoro-Novo)
· Dolmen of Venda do Duque [MA](Neolithic; Vimieiro, Arraiolos)
· Dolmen of Vidigueira [MA](Neolithic; Redondo, Redondo, Evora)
· Dolmen of Vila de Nisa [MA](Neolithic; Espirito Santo, Nisa)
· Dolmen of Vila Nova de Sao Pedro [MA](Neolithic; Vila Nova de Sao Pedro, Azambuja)
· Dolmen of Vilarinho [MA](Neolithic; Vilarinho da Castanheira, Carrazeda de Ansiaes)
· Dolmen of Varas do Fojo [MA](Neolithic; Santo Agostinho, Moura)
· Escoural, Prehistoric Rock Art (50000 BP: Paleolithic; Santiago do Escoural, Montemoro-Novo)
· Evora (Lusitanian; 57 BCE: Roman: Corinthian Diana Temple- ded.cult of Emp.Augustus; 584: Visigoth; 715: Moor)
· Figueira Brava (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Arrabida mts.)
· Fonte do Milho
· Guarda Cathedral (1199 CE: bishopric; Romanesque; 13th c.CE: 2nd cathedral; 1390-16th c.CE: Gothic-Manueline; Guarda)
· Lajes das Fogacas [MA](Neolithic; Lanhelas, Caminha)
· Lapa do Fumo (Neolithic; Castelo, Sesimbra, Lisbon)
· Lisbon [MA](Neolithic: dolmens, menhirs; 1st m.BCE: Indo-European Celt invaded; intermarried w/Pre-Indo-European- Cempsi; 1200 BCE: Phoenician: Allis Ubbo [“safe harbor”]; Rome: Felicitas Julia; theatre; Cassian Baths beneath Rua da Prata; temples to: Jupiter, Diana, Cybele, Tethys, and Idae Phrygiae; necroplis beneath Praca da Figueira; forum; insulae)
· Loios Convent and Church (15th c.CE: Gothic; tombs, cloister; Evora)
· Lisbon Cathedral/Santa Maria Maior de Lisboa (Phoenician remains; 4th c.CE: bishopric; 1147 CE: Late Romanesque-Gothic; 14-16th c.: earthquakes and reconstructions; tombs; Lisbon)
· Menhir of Abelhoa [MA](Neolithic; Monsaraz, Reguengos de Monsaraz)
· Menhir of Courela da Casa Nova [MA](Neolithic; Silveiras, Montemor-o-Novo)
· Menhir of Outeiro [MA](Neolithic; Monsaraz, Reguengos de Monsaraz)
· Menir da Cabeca do Rochedo [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Concelho de Lagos)
· Menir de Aspradantes [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Vila do Bispo)
· Menir de Padrao [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Vila do Bispo)
· Menir dos Almendres [MA](Neolithic: menhir; 1.3km N Cromleque dos Almendres; Evora)
· Menir de Mac Abraao [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Vila de Frades, Vidigueira, Beja)
· Menir de Sao Paio de Antas [MA](Neolithic: menhir; S Viana do Castelo)
· Menires de Lavajo I [MA](Paleolithic; Neolithic: 3 menhirs; Alcoutim, Algarve)
· Monastery of Santa Clara-a-Velha (f.1280s CE: Order of the Poor Clares; d.1311; 1314: rf.by Queen/Saint Elizabeth of Portugal; 14th c.CE: Gothic; ruined; 1612: floods- elev.pavement; 1647-77: nuns left for Monastery of Santa Clara-a-Nova on hill nearby; Gothic tomb of Elizabeth trans.there; Mondego r.; Coimbra)
· New Cathedral of Coimbra (1541 CE: Jesuit College of Coimbra; 1759: Jesuit Order banned from Portugal; 1772: bishporic seat trans.to Old Cathedral of Coimbra; influential facade in Brazil; statues of 4 Jesuit Saints; facade: upper-Baroque, lower-Mannerist; Coimbra)
· Old Cathedral of Coimbra (1139 CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Arabic-Renaissance; 1772: bishporic seat trans.to Old Cathedral of Coimbra; Coimbra)
· Painted Dolmen of Antelas [MA](Neolithic; Pinheiro de Lafoes, Oliveira de Frades)
· Pedra de Ouro (Neolithic; Cadafais, Alenquer, Lisbon)
· Porto (Proto-Celtic/Celtic; 4th c.CE: Roman; Suevi; 5-6th c.CE: bishopric; 711: Moor)
· Porto Cathedral (1110-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; sarcophagi; 1333: Gothic funerary chapel added- Joao Gordo Knight Hospitaller tomb: relief of Apostles; Gothic cloister: azulejos- depictions of Virgin Mary, Ovid’s Metamorphoses; Porto)
· Praia das Macas, Megalithic Monuments [MA](Neolithic; Colares, Sintra, Lisbon)
· Prehistoric Rock Art Site of Vale de Junco [MA](Neolithic; Esperanca, Arronches)
· Quinta da Nora, Megalithic Monuments of [MA](Neolithic; Vila Nova de Cacela, Vila Real de Santo Antonio)
· Quinta de Rouxinol (Neolithic; Corroios, Seixal, Lisbon)
· Roca do Casal do Meio, Megalithic Monuments [MA](Neolithic; Castelo, Sesimbra, Lisbon)
· Saint Bras Chapel (1480 CE: Mudejar-Gothic; Evora)
· Saint Francis Church (1226 CE: Romanesque; 1475-1550 CE: Gothic; Evora)
· Santa Cruz Monastery (f.1131 CE: Romanesque; Augustinian; tombs of King Alfonso Henriques and Sancho I; Coimbra)
· Santarem (Lusitani; Phoenician; Greek; Roman: Scalabis; Visigoth; Moor; Christian)
· Sao Joao de Valinhas (10th c.BCE)
· Senhor dos Martires [MA](Neolithic; Santa Maria do Castelo, Alcacer do Sal)
· Serra da Brenha, Megalithic Monuments [MA](Neolithic; Alhadas, Figueira da Foz, Coimbra)
· Tholos do Barro, Funerary Monument [MA](Neolithic; Sao Pedro e Santiago, Torres Vedras)
· Vale de Coa, Prehistoric Rock Art (Neolithic; Vila Nova de Foz Coa, Guarda)
· Vale do Rodrigo [MA](Neolithic; Nossa Senhora da Tourega, Evora)
ROMANIA: [Greek colony; cathedrals]
· Armenian Church (1395 CE; Iasi)
· Barboi Church (1843 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Barnova Monastery (1628 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Barnovschi Monastery (1627 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Biserica Neagra/Black Church (1383-1444 CE: Gothic; Roman Catholic-Lutheran; Golden Gate; octagonal columns; 1689: fire set by Hapsburg forces during Great Turkish War- ka.”Black Church”; rebuilt Baroque; Anatolian carpets; Bohemian Gothic art: sculptures, murals; Brasov, Transylvania)
· Biserica Saint Nicholas (14th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; frescoes by Misu Popp; Brasov, Transylvania)
· Brasov (9500 BCE: Neolithic Bronze Age settlements: Dacian citadels: Valea Cetatii, Pietrele lui Solomon, Sprenghi, Tampa, Dealul Melcilor, Noua; Transylvanian Saxons-German colonists)
· Bucium Monastery (1853 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Callatis (6th c.BCE: Greek colony; Mangalia)
· Cetatuia Monastery (1669-72 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Coasta lui Damian (Neolithic: Tiszapolgar; Salaj)
· Curtea de Arges Cathedral/Saint Nicholas (1512-21 CE; monastery; tambours, window slits; Curtea de Arges)
· Frumoasa Monastery (1726 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Giurtelecu Simleului (Middle Ages: Maeriste; Zalau)
· Galata Monastery (1582-4 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Golia Monastery (1564 CE: Romanian Orthodox; 1650: rebuilt late Renaissance; Byzantine frescoes; Iasi)
· Hlincea Monastery (1587 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Histria/Istros [Thracian river god, Danube] [MA](Neolithic: menhir; 650 BCE: Greek colony; Roman; Sinoe l.)
· Iasi Neolithic: Cucuteni-Trypillian culture)
· Iasi Metropolitan Cathedral/Saint Paraschiva, Presentation of Jesus, Saint George (15th c.CE: White Church; 17th c.CE: Presentatioin Church; 1833-87: late Renaissance-Baroque; Gheorghe Tattarescu paintings; Iasi)
· Mangalia Mosque [SR](1575 CE: Islamic; Mangalia)
· Pestera cu Oase (45-28k BP: Neanderthal-human)
· Saint Sava (1583 CE; Iasi)
· Saint Spiridon (1747 CE: Moldavian; Romanian Orthodox; Iasi)
· Sarmisegetusa (101 CE: Dacian)
· Trophaeum Traiani (109 CE: Roman monument; Adamclisi)
· Tomis (600 BCE: Greek colony; Constanta)
RUSSIA: [megaliths (found in Caucasus m., White Sea, Barents Sea, Vera i.); kurgan-mounds; cathedrals]
(see also Russia in Asia)
· Annunciation Church (1179 CE; Myachino; Novgorod)
· Antoniev Monastery (f.St.Anthony of Rome; 1117 CE: Romanesque; Russian Orthodox; frescoes; Volkhov r.; Novgorod)
· Assumption Cathedral (1101 CE: Monomakh Cathedral; 1611: explosion-collapse; 1772: new Baroque cathedral; Smolensk)
· Assumption Church (1180s CE; Volotovo Field; Novgorod)
· Cathedral of Annunciation/of the Theotokos (1484-9 CE: Renaissance; Moscow Kremlin)
· Cathedral of the Mother of God of the Sign church (1688 CE; Novgorod)
· Cathedral of Saint Sophia/Holy Wisdom of God (10th c.CE: original oaken cathedral; 1045-50 CE: Romanesque; 11th c.: frescoe; Plock Cathedral gates; 1862: bronze monument: Millennium of Russia; Veliky Novgorod)
· Christ’s Nativity church (1387 CE; cemetery; Novgorod)
· Dolmens of the Caucasus [MA](4000 BCE: Gelendzhik; Zhane r.; Mamed canyon)
· Dormition Cathedral (1326-7 CE: Theotokos cathedral; 1472: new construction- collapse; 1475-9 CE: Renaissance; coronations of Russian Tsars; Cathedral Square; Moscow Kremlin)
· Dormition Cathedral (1158-60 CE: Theotokos cathedral; 6 pillared, 5 domes; expanded in 1185-9; Vladimir)
· Ipatovo (4th m.BCE: Proto-Indo-European: Maykop culture: kurgan; 3rd c. BCE: Sarmatian grave ontop of mound; Hellenistic coins; 18th c.: Turkic Nogai burials; Stavropol Krai)
· Khutyn Monastery of Saviour’s Trasfiguration and Saint Varlaam (f.1192 CE; Novgorod)
· Konigsberg Cathedral (1333-1525 CE: Brick Gothic; Roman Catholic; Lutheran; Kaliningrad)
· Kutuluk (2400 BCE: kurgan: skeleton with copper vajra-like object on left eyebrow; Samara/Kuybyshev)
· Ladoga (900 CE: Viking; Norse Sagas; Leningrad)
· Maikop kurgan (3rd m.BCE: golden bull figurine; Early Bronze Age; Maikop)
· Maykop culture (3500 BCE; Taman peninsula)
· Moscow (2nd c.BCE: Vyatich fortified structure on Borovitsky Hill; Neglinnaya r. into Moskva r.)
· Mound of Immortality (mounds: Polotsk, Orsha, Bryansk, Smolensk, Yefremov; 1898 CE: for Adam Mickiewicz; Novogrudok, Belarus)
· Myrrh-bearing Women church (1510 CE; Novgorod)
· Novgorod (Viking trade route; Volhov r.; Lake Ilmen)
· Peryn Monastery (1230s CE; Novgorod)
· Qolsharif Mosque (16th c.CE: Islamic; confluence of Volga and Kazanka r.; Kazan)
· Cathedral of Saint Nicholas (1113-23 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Basil’s Cathedral/Cathedral of Intercession of Theotokos on the Moat/Trinity Church (14th c.CE: Trinity church- 8 outer churches around a central 9th, Intercession; geometric center of Moscow; 1555-61 CE: 10th church erected over grave of Fool Vasily/Basil; earthly symbol of Heavenly City/Jerusalem; Russian Orthodox; Red Square; Moscow Kremlin)
· Saint Boris and Gleb church (1586 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Demetrius church (1467 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Demetrius Cathedral (1194-7 CE: Vladimir)
· Saint John’s the Apostle church (1384 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Nicholas Cathedral of Vyaschizhy Monastery (1685 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Nicholas church (1292 CE; 14th c.: frescoes; Lipnya Islet; Novgorod)
· Saint Paraskeva-Piantnitsa Church (1207 CE; Yaroslav’s Court; Novgorod)
· Saint Peter and Pavel church (1185-92 CE; Swallow’s Hill; Novgorod)
· Saint Peter and Paul church (1367 CE; Slavna; Novgorod)
· Saint Peter and Paul church (1406 CE; Kozhevniki; Novgorod)
· Saint Simeon church (1462 CE; Novgorod)
· Saint Theodor’s church (1360-1 CE; 1380s: frescoes; Novgorod)
· Sarkel (833 CE: Khazars; Rostov)
· Savior Church (1198 CE; Nereditsa; Novgorod)
· Savior Church (1374 CE; Ilyina st.; Novgorod)
· Savior Church (1345 CE; Serbian frescoes; Kovalevo; Novgorod)
· Tanais (450 BCE: Ancient Greek Colony; Necropolis, 300+ burial mounds)
· Tmutarakan (500 BCE: Ancient Greek Colony; Hermonassa)
· Trinity Cathedral (12th c.CE: over rock temple; 16th c.CE: 1st church; 18th c.CE; Desna r.; Trubchevsk, Bryansk)
· Twelve Apostles church (1455 CE; Novgorod)
· Vladimir (25000 BP)
· Yuriev Monastery/Saint George (f.Prince Vsevolod Mstislavich and Pskov; 1030 CE: monastery; 1119 CE: 3-domed cathedral; 1928: 5/6 churches d.; 1991: Russian Orthodox; Novgorod)
SERBIA: (Celt-Greek-Roman)
· Bajrakli Mosque (1575 CE: Islamic; Belgrade)
· Bovan/Balwan [MA](Neolithic: graves of the “Latins” and the “Jidovs”; Bovan; N Alexinati)
· Curug (50 BCE: Celt/Roman)
· Contra Margum (Kovin)
· Ergeta (Brza Palanka)
· Gamzigrad-Felix Romuliana (289 CE: Roman complex by Galerius; Zajecar)
· Horreum Margi (Cuprija)
· Justiniana Prima (530 CE; Skopje; Mala Kopasnica)
· Kalemegdan (50 BCE: Celt; 368: Roman; Belgrade)
· Lepenski Vir (7000 BCE: Mesolithic; Donji Milanovac)
· Mediana (306 CE: Roman; Nis)
· Naissus (5000 BCE: Neolithic; Roman; Nis)
· Petrovaradin Fortress (19000 BCE: Paleolithic; 3000 BCE: Bronze Age; 1692: fortress by Prince Croy; Novi Sad)
· Plocnik (5500 BCE: Neolithic Vinca; Prokuplje)
· Remesiana (202 CE: Septimus Severus; Bela Palanka)
· Risovacka Cave (Paleolithic; Arandelovac)
· Rudna Glava (5000 BCE: copper mining, metallurgy- Vinca; Stara Zagora)
· Singidunum (Paleolithic; Neolithic-Vinca; 600 BCE: Celt; Roman; Belgrade)
· Sirmium (3rd c.BCE: Celt; Roman; Sremska Mitrovica)
· Starcevo (6000 BCE)
· Taliata (Donji Milanovac)
· Taurunum (Neolithic; Celts; Zemun)
· Tasmajdan Park (Roman; Belgrade)
· Trajan’s Bridge (2d c.CE)
· Timacum Minus (Knjazevac)
· Viminacium (1.5 mil.BP: mammoth skeleton; Kostolac)
· Ulpiana (1st c. BCE: Roman; Kosovo)
SLOVAKIA: (Celt-Greek-Roman)[cathedrals]
· Banska Bystrica (2000-1700 BCE: Spania Dolina; prehistoric copper miners; Lusatian culture; 3rd c.BCE: Celtic-Cotini; Puchov culture; Germanic-Quadi; 9th c.: Slavic; 1536: Hapsburg monarchy)
· Bardejov (Stone Age)
· Blatnica (8-9th c.CE; 12th c.CE: castle: sword; near Turiec)
· Bratislava (5000 BCE: Neolithic: Linear Pottery culture; 200 BCE: Celtic Boii; 1st-4th c.CE: Rome; grape farming and wine making; 5-6th c.CE: Slavs)
· Cataj (5000 BCE; Senec)
· Cathedral of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary (13th c.CE: Gothic; Renaissance painting; Roznava)
· Celemantia (2nd c.CE: Roman castellum; Iza; Komarno)
· Cierne Klacany (1209; Moravce; Nitra)
· Devin Castle (8th c.CE; Neolithic settlement; Celt; Roman; Bratislava)
· Drazovce church (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Nitra)
· Ducove (Neolithic; Celt; Roman; 9th c. CE: castle; Piestany; Moravany)
· Ganovce (proto-Neanderthal; 1317; Poprad)
· Gerulata (2nd c.CE: Roman; Bratislava)
· Havranok (300 BCE: Puchov/Celt shrines; Bobrovnik)
· Kosice (Paleolithic)
· Levoca (Stone Age)
· Moravany nad Vahom (1348; Piestany)
· Nitra (6000 BP; 4th c.BCE: Celtic; 396 CE: Germanic-Quadi; 5th c.CE: Slav)
· Niza Mysla (1270; Kosice)
· Ochoz (250-45k BP: transition-Neanderthal)
· Presov (Paleolithic)
· Pusty hrad (Celt/Roman; Medieval castle; Zvolen)
· Saint Aegidius (1240 CE: Gothic; Bardejov)
· Saint Catherine’s Church (13-15th c.CE; Kremnica)
· Saint Egidius (13th c.CE: Gothic; Poprad)
· Saint Emmeram’s Cathedral (11-12th c.CE: rotunda; 1333-55: Gothic- upper church; 1621-42: Baroque- lower church; Nitra)
· Saint Elisabeth Cathedral (14th c.CE: Gothic; Kosice)
· Saint Helen’s Church (MA: Gothic; Trnava)
· Saint John the Baptist Cathedral (1629-37 CE: Baroque; Trnava)
· Saint Martin’s Cathedral (1221 CE: Romanesque; Holy Savior; 1311-1452: Gothic; earthquake dmg in 1869; coronation of Ferdinand I of Hapsburg; catacombs and sepulchers; Bratislava)
· Saint Michael Chapel (14th c.CE: Gothic; Kosice)
· Saint Nicholas’s Church (MA: Gothic; Trnava)
· Saint Nicholas Concathedral (14th c.CE: Gothic; Presov)
· Saint Stephen church (9th c.CE: fundamentum; 11-12th c.CE; Nitra)
· Sala (250-45k BP: transition-Neanderthal)
· Trnava (Neolithic)
· Vrable (6000 BCE: Neolithic; Nitra)
SLOVENIA:
· Divje Babe (43k-700 BP: classic-Neanderthal; bone flute; Cerkno)
· Ljubljiana (2000 BCE: Veneti-Celt-Illyrian; 3rd c.: Celtic-Taurisci; 50 BCE: roman: Emona; 6th c.: Slovene; 9th c.: Frankish; 1278: Habsburg)
· Saint Nicholas’s Cathedral (1262 CE: Romanesque; 1361: fire- Gothic; 1701-6: Baroque; frescoes; Ljubljiana)
SPAIN: [MA] [dolmen; talaiot; Phoenician necropoleis]
[NOTE 81] Last ice age seems to have ended around 1500 BCE (coinciding w/Hebrew Exodus) when the sea level was rising (N. Atlantic) due to the melting of Ice Age glaciers, while the Nile, Euphrates, and Indus were drying out, causing mass migrations of peoples (including the Sea Peoples, or displaced Atlanteans, while their coastal megalithic civilization was being destroyed <submerged>; hydrology: waters cooled, decreasing evaporation and cloud density, hence the Ice Age ended and sea levels rose; warm ocean waters increase cloud density for an Ice Age (James Nienhuis)
[NOTE 83] the megalithic structures (discovered under water beyond modern coastlines) were not built underwater, but rather had to have been constructed before the oceanic level changes; (Childress)
[NOTE 82] Destruction of Atlantis: Plato describes that the Atlanteans had a divine essence within them that was being diminished over time; ‘Zeus sends his wrath from the center of the universe’; if the center of universe meant center of milky way galaxy, this may refer to active galactic nucleus phase (photonic belt), which could cause an Earth cataclysm (William Henry)
[NOTE 65] Submerged sites (in 100-200’ water) off the coast of Spain: W Gibraltar; Tarifa; Cadiz (Gades); Rota; Chipiona; Plato referred to as the ‘Pillars of Hercules’, gateway to Atlantis beyond the Mediterranean in the Atlantic Ocean; Atlantean? There are 200+ sunken cities (using megalithic Cyclopian construction; sim. Giza in Egypt, Stonehenge in Britain, Baalbek in Lebanon, and the <hermazo> dolmens of Spain) in the Mediteranean Sea, which is indicative of a cataclysmic flood (Childress), consequential of the polar ice sheets melting (Hancock; James Nienhuis).
[NOTE 66] Dolmens of S.Spain (Andalusia; Basque peoples) became the foundations for Roman construction near Rhonda, located near the source of the Guadiaro r., in the Sierra Morena mts., the most richest mining area in the ancient world w/depostis of gold, copper, silver, tin, lead, and mercury; source of wealth for Atlanteans? (accd. Plato) to trade with Minoans, Greeks, Canaanites, and Egyptians; Atlanteans would bring mineral deposits down the river to Seville; copper and tin are used to make bronze (ie. used for circum-navigating boat rivets in the ancient world); the Atlanteans were the dominant shipping and military power in the western Mediterranean and eastern Atlantic, ranging from Gibraltar to Cornwall, England, where there are tin mines and submerged sites (Avalon), and Scandanavia, and southward to France, Spain, and Portugal, Canary Is., Malta, Sardinia, eastward in the Mediterranean to Italy and Libya, and to the Americas, the Carribean, and New Foundland; these Sea Peoples followed trade wind routes around the basin of the Atlantic Ocean
[NOTE 77] Plato’s detailed description of Atlantis reflected in the Bible: Southern Spain and North Africa are also referred to as the Hesperides (supposedly mythological) [daughters of Atlas (man of maps- precession measurer), grand-daughters (nymphs) of Poseidon (means: ‘father Sidon’; Sidon was a son of Canaan, indicating that the Atlanteans originally came from the eastern Mediterranean, from the port city of Sidon, in the land of Canaan; Cadiz/Gades was also named after another son of Poseidon; Atlas’s father)]; Atlantean-Phoenician (Hesperide) base at Seville [Gk.: Tartessos; Biblical: Tarshish]; under penalty of death, the Phoenicians had to keep the trade routes (esp. Atlantic routes; Spain, France, Cornwall, Britain) a secret, where tin and copper trade was flourishing (David Childress);
[NOTE 17] The Knights Templar, emerged out of the Kingdom of Aragon; hence, with the founding fathers of the USA, being free mason- templars, the USA is the evolution of the Kingdom of Aragon.
[NOTE 18] The Renaissance is the consequence of the Christian crusading kingdoms via knight orders obtaining-understanding the mathematics of the Muslim-Arab-Moor-Seracen.
[NOTE 19] The revelation of Moses, the first phoenetic script-alphabet, seemed to have been best preserved-disseminated by the Ishkur-Baal-Dionysis worshiping, Canaanite-Phoenicians; which mirrored into Greek, and evolved into Latin, and branching into its derivatives (eg.English, Spanish, French). Language is a method of genetically programming thought. The alphabet-gematria encodes chromosomal data. Tone causes transmutation of DNA.
[NOTE 20] Where the martyr lies, the cathedral dies, with a crypt beneath over necropolei. The Roman Empire transformed into the Holy Roman Empire, after making saints out of their Christian martyrs. Christianity became the extension of Egyptian Theosophy (ie.afterlife, resurrection, trinity, etc.); the cathedrals (like pyramids) became the new sound technologies of the earth grid (ie. with: acoustical naves for hymn vibrations, steeple lightning rods, twin bell tower tuning forks, stained glass colored light revealing encoded information).
[NOTE 21] The crusades was like the modern space race to the moon, with the prize being the relics of Solomon’s Temple in Jerusalem (Anunnaki mission control of the post-diluvial earth).
· Abbey of Santa Maria la Real de Las Huelgas (f.Alfonso VIII of Castile; 1187 CE; 1199: Cistercian; 1212: Alfonso VIII burial; King’s Hospital; Burgos, Castile-Leon)
· Alcala de Henares (Calcothic-Celtiberian: Iplacea; 1st c.BCE: Roman: Complutum; Visigothic; 711: Moors: al-qala “citadel”; 1118: Castile; Madrid)
· Alcala de Henares Cathedral (414 CE: chapel at site of Justus and Pastor’s martyrdom; 5-7th c.: cathedral; 1122: rebuilt; 1495-1517: rebuilt Isabelline Gothic; Madrid)
· Alicante (5000 BCE: hunter-gatherer settlements near Mt.Benacantil; 1000 BCE: Phoenician-Greek; 6th c.BCE: Carthaginian-Roman: Akra Leuka “white mountain/point”/Lucentum; necropolis; 5th c.CE: Visigothic; 8th c.CE: Arab; 1246: Castilian; 1298: Aragon; Valencia)
· Almeria Cathedral (orig.Muslim mosque; converted to Christian church; d.earthquake in 1522; 16th c.CE: rebuilt Renaissance; Almeria, Andalusia)
· Almorabitin (10th c.CE: mosque; Granada, Andalusia)
· Altamira [Celt.: “rock, stone;” “people who live in the rocks”; highlanders](16500 BP: cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· Andre Mariaren Basilica (San Sebastian, Basque country)
· L’Arbreda (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal)
· Astorga Cathedral/Santa Maria (11-13th c.CE: Romanesque pred.; 1471-18th c.: Gothic-Baroque-neo-Classical; Astorga, Castile-Leon)
· Astorga (Celtic settlement; Roman: Asturica/Urbs magnifica: military camp, sewers, 2 baths, forum, mosaics, walls; 850-866 CE: campaigns of Alfonso I of Asturias; “Desert of the Duero;” Castile-Leon)
· Atapuerca [AS] (prehistoric fossils of earliest hominids in Europe; Burgos, Castile and Leon)
· Avila (5th c.BCE: Vettones: Obila “High Mountain”; Greek: Abula; Roman: Abila; Visigoths; Arabs; 11th c.CE: Christian)
· Avila Cathedral (12-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Avila, Castile-Leon)
· Axeitos dolmen [MA](3000 BCE; Ferrol, Galicia)
· Axlor (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Dima)
· Baelo Claudia (Phoenician-Carthaginian; Roman forum: Baetica)
· Badajoz Cathedral/Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint John the Baptist of Badajoz (Visigothic early Christian Mozarabic church Campo de San Juan; former mosque; 1270: Gothic; Badajoz, Extremadura)
· Banyoles (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Catalonia)
· Barbastro (Roman: Barbatius; Visigoth; Huesca)
· Barcelona (Phoenician: Barkeno; Greek: Barkinon; mythical f.Hercules; 3rd c.BCE: Carthaginian: Barcino; f.Hamilcar Barca- father of Hannibal; 15 BCE: Roman: Barcilonum- castrum; 5th c.: Visigoths; 8th c.: Arab; 801 CE: Carolingian; 1137: Aragon)
· Barcelona Cathedral/Holy Cross and Saint Eulalia/La Seu (faced Roman forum; f.343 CE?; over former Visigothic crypt dedicated to Saint James; 13-15th c.CE: Gothic; gargoyles; Barcelona, Catalonia)
· Basilica de la Encina (1573 CE: Renaissance; Ponferrada, Castile and Leon)
· Basilica of Begona (16th c.CE; Bilbao, Biscay, Basque country)
· Basilica of Our Lady of the Pillar/Mary (1st-2nd c.CE: RC; dawn of Christianity in Spain; apparition of Mary to Saint James the Great, the apostle- brought Christianity to Iberia; Romanesque-Baroque; Ebro r.; Zaragosa, Aragon)
· Basilica of San Isidoro (ancient Roman Mercury temple; 10th c.CE: monastery of Saint John the Baptist: Benedictine nuns; 938-1002: Muslim invasions; d.by Al-Mansur Ibn Abi Aamir; 1063: Romanesque-Gothic-Renaissance; reded.- tomb and relics of Saint Isidore of Seville; Puerta del Cordero- tympanum depicting sacrifice of Abraham; 12th c.CE: Royal Pantheon- funeral chapel of kings of Leon; Romanesque art, Visigothic capitals, murals; Leon, Castile-Leon)
· Basilica of San Julian de los Prados (9th c.CE: pre-Romanesque; Oveido, Asturias)
· Basilica de San Vicente (12-14th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; crypt; Avila, Castile-Leon)
· Basilica of Santa Maria (over mosque; 14-16th c.CE: Gothic; Alicante, Valencia)
· Basilica de la Virgen de los Desamparados (Gothic; Valencia)
· Baza (4th c.BCE: Iberian: Basti; Roman; Visigoth; Moor; Baza, Granada, Andalusia)
· Bilbao (4000 BCE: burial sites on Avril and Artxand m.; 3rd-2nd c.BCE: Roman: Amanun Portus)
· Burgo de Osma (Celto-Roman: Uxama; Castile-Leon)
· Burgos (800,000 BP: early humans; Celtiberian: city; Hispania Citerior; Visigoth; 8th c.: Arabs; 9th c.: Leon)
· Burgos Cathedral/Virgin Mary (earlier Romanesque cathedral; 1221-1230 CE: French Gothic; 15-16th c.: modifications- principle facade, Chapel of the Constable, cimborio of trancept; octagonal spires; 18th c.: transformed statuary of doors of principle facade; Renaissance-Baroque interiors; Burgos, Castile-Leon)
· Caceres (25000 BCE: Paleolithic: Maltravieso Cave- painting; 25 BCE: Roman; Visigothic; Arab; Extremadura)
· Cadiz (1104 BCE: Phoenician; Greek: Gadira; 500 BCE: Carthage; 206 BCE: Roman; 410 CE: Visigoth; 550: Byzantine; 572: Visigoth; 711-1262: Moorish)
· Cadiz Cathedral (1260 CE: older cathedral; burned in 1596; 1722-1838: Baroque-Rococo-Neoclassical; Cadiz, Andalusia)
· Calhorra (Paleolithic-Iron Age; 187 BCE: Roman: Calagurris; 9-10th c.: Moor; 1045: Christian; La Rioja)
· Calhorra Cathedral/Saint Emeterius and Celedonius (Calhorra, La Rioja)
· Canary Islands [Egy: Anubis cult?; Gk: knew of “dog-headed ones” in far W; Ln: “the ones who worship dogs; the ones with dogs” (canaari) “Island of the Dogs” (Insula Canaria); ](prehistoric animals: giant lizards or giant rats, {Ln: “sea dogs”- monk seals?} Neolithic: indigenous Guanches-Berber; Phoenician; Greek; Carthaginian- Hanno navigator; Roman; Arab-Muslim- Ibn Farrukh navigator; mega-tsunami catalyst possibility from La Palma to Chesapeak Bay)
· Capocorb Vell (Llucmajor)
· Carihuela (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Andalucia)
· Cartegena (Mastia; 228 BCE: Carthaginian: Carthago Nova; 209 BCE: Roman; 409-25 CE: Vandal; 425-551/624-714: Visigoth; 551-624: Byzantine; 8-13th c.: Moor; 1245: Aragon; Murcia)
· Casa de los Botines (1892-3 CE: neo-Gothic; Antonio Gaudi; Leon, Castile-Leon)
· Castillo de los Templarios (1178 CE: Knights Templar Castle; Ponferrada granted to Templars by Ferdinand II of Leon; Ponferrada, Castile and Leon)
· Castro of Barona (Porto do Son, A Coruna)[MA]
· Cathedral of Burgo de Osma (1232-1784 CE: Gothic-Baroque-Neoclassic; Burgo de Osmo, Castile-Leon)
· Cathedral of Juan de Albacete (Mujedar temple; 1515 CE: Gothic; 17th c.: Renaissance-Baroque; Albacete, Castile-La Mancha)
· Cathedral of La Seu Vella/Saint Mary (previous paleo-Christian/Visigothic church; 832: rebuilt into mosque; 1149: Augustinian; reconsecrated as Santa Maria Antiqua; 1203-1431 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Lleida, Catalonia)
· Cathedral of San Salvador/Holy Savior (King Fruela I; f.781; 802: enlarged; 12th c.: restored; 14-16th c.: Gothic-Flamboyant-Classic; 9th c.: Camara Santa/Holy Chamber: Agatha Box, <from Jerusalem-Africa-Oviedo>; burials: royalty- Fruela I, saints- Eulogius of Cordoba, martyr; Oviedo, Asturias)
· Cathedral of Santa Maria del Romeral/Saint Mary of the Rosemary Field (12-13th c.CE; Monzon)
· Cathedral of Santa Maria (14th c.CE: Gothic; Vitoria, Basque country)
· Cathedral of Santa Maria d’Urgell (1035: Church of Sant Miguel; 1116 CE: Catalan Romanesque; la Seu d’Urgell, Catalonia)
· Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela/Saint James the Great (legend: James apostle brought Christianity to Celts; beheaded in Jerusalem in 44 CE, remains brought back to Galicia; 3rd c.CE: tomb of St.James; rediscovered in 814; 829/899 CE: pre-Romanesque; 1075-1211 CE; 1128 CE: Romanesque-Baroque; facades; Portico da Gloria; crypt: relics of Saint James and 2 disciples; Botafumeiro-thurible, largest censer in world; Santiago de Compostela, Galicia)
· Cathedral of Santo Domingo de la Calzada/Saint Dominic (12th c.CE; 1537-40: Renaissance sculpted altar; Santo Domingo de la Calzada, La Rioja)
· Chapel of Saint Francis (1538 CE: Renaissance; Baeza, Andalusia)
· Church of Magdalena (13th c.: Romanesque; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of Magdalene (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Tudela, Navarre)
· Church of La Merced (Mudejar-Baroque; Turuel, Aragon)
· Church of S.Maria (1140 CE; Vic, Catalonia)
· Church of San Anton (ancient walls below; 11th c.CE; Bilbao, Basque country)
· Church of San Claudio de Olivares (12th c.: Romanesque; presbytery; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of San Gines (Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha)
· Church of San Isidoro (12th c.: Romanesque; archivolts; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of San Juan de Peurta Nueva (12th c.: Romanesque; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of San Martin (17th c.CE; Turuel, Aragon)
· Church of San Miguel (12th c.CE; 17th c.: Baroque; Turuel, Aragon)
· Church of San Nicolas (12th c.CE; Tudela, Navarre)
· Church and convent of San Pablo (15th c.CE; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Church of San Pedro y San Ildefonso (over Visigothic temple; 11th c.; 12-13th c.: Romanesque; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of San Salvador (17th c.CE: Mudejar; 14th c.: wooden sculpture of Christ; Turuel, Aragon)
· Church of San Salvador de Palat del Rey/Holy Savior of the King’s Palace (10th c.CE: pre-Romanesque; oldest church in Leon; Leon, Castile-Leon)
· Church of Sant Llorenc (12-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Lleida, Catalonia)
· Church of Santa Maria la Nueva (12th c.; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church Santa Maria (13th c.CE: Gothic; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Church of Santiago (Caceres, Extremadura)
· Church of Santiago (16-18th c.CE: Baroque; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Church of Santiago de los Caballeros (11th c.; El Cid created knight here; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Church of Santiago El Burgo (12th c.: Romanesque; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Ciudad Rodrigo (Neolithic Celtic: Mirobriga; Roman: Augustobriga; Leon: walls; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Ciudad Rodrigo Cathedral (12-14th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Leon: walls; Ciudad Rodrigo, Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Collegiate Church of Sant Feliu (14th c.CE: Gothic; Girona, Catalonia)
· Concatedral de San Pedro (12-13th c.CE; rebuilt in 16th c.; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· Concaterdal de Santa Maria (13th c.CE: Gothic; Castellon de la Plana, Valencia)
· Concaterdal de Santa Maria de Guadalajara (13-14th c.CE: Mudejar; Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha)
· Convent of Annunciation (16th c.CE; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Convent of Saint Stephen (16th c.CE: Dominican; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Convent Church of Santo Domingo (16th c.CE; 1934: burnt- reconstructed after Civil War; Oveido, Asturias)
· Convent of the Madre de Dios (13th c.CE; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Convent of Saint Francis (18th c.CE; art; Lugo, Galicia)
· Convent of San Marcos (Renaissance; now luxury hotel; Leon, Castile-Leon)
· Convent of Santa Clara (f.1283 CE; Tortosa, Catalonia)
· Convento de las Duena (15th c.CE; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Cordoba (32000 BCE: Neanderthal; 8th c.BCE: Tartessos; Carthaginian; 206 BCE: Roman: temple; Theatre of Marcellus; mausoleum; Cercadilla; bridge; 552-72: Byzantine; 6th c.: Visigoth; 711: Muslim; Andalusia)
· Coria (3rd-4th c.CE: Roman: walls; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Coria Cathedral/Santa Maria de la Asuncion (Gothic; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Cova d’en Daina (Romanya de la Selva, Catalunya)[MA](2700-2200 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; 10m dia. tumulus; alignments: summer-winter solstice; Romanya de la Selva, Santa Cristina d’Aro)
· Cuenca (Roman: Segobriga, Ercavica, Gran Valeria; 714 CE: Muslim; 12th c.CE: Christian Aragon)
· Cuenca Cathedral/Our Lady of Grace (1182-1270 CE: Gothic; 1st in Spain; 15th c.: Renaissance- apse isle; Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha)
· Cueva de Menga [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: barrows-dolmen, constructed w/32 megaliths-lg.180 tons; findings: several hundred skeletons; near Dolmen de Viera; 4km from subterranean structure known as Tholos de El Romeral; Antequera)
· Cueva Negra (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal; Murcia)
· Del Valle cave (prehistoric: cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· Dolmen de Viera [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen covered by tumulus-50m dia., 180 tons; corridor consists of 16 megalithic slabs on ea.side, now 14L/15R remain; alignments: SE-96°=summer solstice-sunrise illuminates dolmen, like most Iberian tombs; near Dolmen de Menga; Dolmenes de Tomillos, Alcala del Valle; 4km from Tholos de El Romeral; Antequera, Malaga, Andalusia)
· El Pendo (prehistoric: cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· El Roser (13th c.CE: Dominican convent; reformed into parador; Lleida, Catalonia)
· El Soplao (prehistoric: cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· El Sidron (250-45k BP: Neanderthal)
· Episcopal Palace (19th c.CE: Neo-Gothic; Antonio Gaudi; Astorga, Castile-Leon)
· Ferrol (prehistoric human settlements: burial chambers [MA], petroglyphs; Phoenician; Greek; 1st c.BCE: Roman; Vandal raids; 411 CE: Suebi; 584: Visigoth; 711-39: Arab; Visigoth; Lugo, Galicia)
· Getafe (100000 BCE: Lower Paleolithic; stone tools, pots, bracelets; Manzanares r.; 2nd c.BCE: Roman: villa- La Torecilla; Suebi-Vandal-Visigoth-Alan invasions; 8th c.: Moor; 1085: Christian; Madrid)
· Gibraltar (250-45k BP: Neanderthal; Gorham’s Cave; 950 BCE: Phoenician; Carthagianian-Roman; Vandal; Visigoth; 711 CE: Islamic)
· Girona (Ausetani: Gerunda; Roman: citadel, wall; Visigoth; Moor; 785: Charlemagne; 11th c.: Aragon; Catalonia)
· Girona Cathedral/Saint Mary (early Christian church; 717: Muslim conquest- mosque; 785: reconquered by Frank, Charlemagne; reconsec.in 908; 11th c.CE: Romanesque; 13th c.CE: Gothic; 1606: Baroque; Girona, Catalonia)
· Granada (Ibero-Celtic; 5th c.BCE: Greek: Elibyrge; Roman: Illiberis; 711: Moorish)
· Granada/Annunciation/Incarnation Cathedral (1492-1667 CE: Renaissance-Baroque; Granada, Andalusia)
· Guadalajara (Carpetani?: Arriaca [Iberian: ”stony river”]; Roman: Henares bridge; 8th c.CE: Moors: Wadi-al-Hajara [Arabic: “valley of stones”]; 1085: Christian)
· Hermitage de la Paz (Caceres, Extremadura)
· Hermitage of San Antonio (Caceres, Extremadura)
· Huesca (pre-Roman Ilergete: Bolskan; 30 BCE: Roman: Osca; Arab: Wasqah; 1096: Christian)
· Huesca Cathedral/Transfiguration (previous mosque; 1273-15th c.CE: Gothic; 1300-1313 CE: apostles door; Huesca, Aragon)
· Huelva (3000 BCE: Tartessus; Phoenician: Onoba; Greek; Roman: Onuba; Arab: Walbah; 1755: Lisbon earthquake)
· Iglesia de la Concepcion (1511 CE: San Cristobal de La Laguna, Canary Is.)
· Iglesia del Espino (16th c.CE; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· Iglesia de San Francisco (18th c.CE: Baroque; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Iglesia de San Juan (13-15th c.CE; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Iglesia de San Mateo (former mosque; 15th c.CE; Caceres, Extremadura)
· Iglesia de San Miguel/Saint Michael (13-18th c.CE; Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha)
· Iglesia de San Pedro (14-15th c.CE: Gothic; Ciudad Real, Castile-La Mancha)
· Iglesia de San Pedro (1100 CE; Avila, Castile-Leon)
· Iglesia de Santiago (13th c.CE: Gothic; Ciudad Real, Castile-La Mancha)
· Iglesia de Santo Domingo (Caceres, Extremadura)
· Iglesia de los Santos Justo y Pastor (16th c.CE; Getafe, Madrid)
· Jaca Cathedral (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Jaca, Huesca, Aragon)
· Jaen/Assumption of the Virgin Cathedral (ancient mosque; 1249 CE; 1570-1802: Spanish Renaissance; Jaen, Andalusia)
· Jerez de la Frontera/Xeres (3rd m.BCE: Tartessian; Neolithic-Copper; Phoenician: Xera; Roman: Asta Regia; Muslim: Xerez; Vandal; Visigoth; 711: Arab; Habsburg; Cadiz, Andalusia)
· Jerez de la Frontera Cathedral (17th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· Jerez de la Frontera Mezquita de Bab al-Mardum/Mosque of Cristo de la Luz (999 CE: Islamic; Toledo)
· La Castillo cave (prehistoric: cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· La Magdalena church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· La Pasiega cave (prehistoric: paleolithic cave paintings; Monte Castillo, Puente Viesgo, Cantabria)[MA]
· La Rabida Monastery (Saturn’s Rock; Phoenician altar to Melqart/Baal/Hercules; Roman: shrine of Proserpina; sanctuary of Moors: training monastery for mounted monk-warrior order; and Knights Templar; f.1261 CE: Franciscan; rocky bluff; Tinto and Odiel r.confluence; Christopher Columbus visit to consult Franciscan monks on New World voyage; Huelva, Andalusia)
· La Seo/San Salvador Cathedral/Savior (Roman forum: Caesaraugusta; 9th c.CE; 1029-1095 CE: Mosque: Saraqusta al Baida Zaragoza la Blanca; 1140 CE: Romanesque<exterior, lower apse>-Gothic<upper apse>-Mudjedar[ext.wall>; 1403: old dome collapsed- Renaissance<tomb of the arch bishop>-Baroque<tower, gate>; Ebro r.; Saragossa/Zaragosa, Aragon)
· Las Medulas (25 BCE: most important Roman gold mine; rock cut aqueduct; Ponferrada, El Bierzo, Castile and Leon)
· Las Monedas cave (prehistoric: paleolithic cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· Leon (1st c.BCE: Roman: Legio; walls; 586: Visigoth; Muslim; 856/910: Leon)
· Leon Cathedral/House of Light/Santa Maria de la Regla (13-16th c.CE: Rayonnant Gothic; Renaissance- choir; Leon, Castile-Leon)
· Lleida/Lerida (Ilergete: Iltrida/Ilerda; Roman; Visigoth; Moor; Aragon)
· Logrono (Roman: Vareia; bridge; Celt; 10th c.: Navarre-Castile possession disputes- Castile; 1609-10: Inquisition-Basque witch trials; La Rioja)
· Lucentum (Phoenicia-Greek; Roman necropolis; Alicante)
· Lugo (Celt: cult of Lugh, bearer of the Grail and God of Light; Roman: Lucus Augusti; walls, bridge; Galicia)
· Lugo Cathedral/Saint Froilan (755 CE: first church; 1273: Romanesque-Gothic-Renaissance-Baroque-Neoclassical; 1755: earthquake dmg.; Lugo, Galicia)
· Madrid (1470 BCE: Lower Paleolithic; bell shaped vases; Roman; Visigothic; Muslim: fortress of Mayrit/Madrid in 860-80; 1083: Castile)
· Malaga (770 BCE: Phoenician: Malaka; 6th c.BCE: Carthaginian; 218 BCE: Roman: Malaca: theatre, amphitheatre, walls; Arab; Christian)
· Malaga/Incarnation Cathedral (1528-1782 CE: Renaissance; Malaga, Andalusia)
· Merida (25 BCE: Roman; 6th c.: Visigoth; 713: Muslim; 1230: Christian; Guadiana r.; Badajoz, Extremadura)
· Merida Cathedral/Saint Mary Major (1239-1579 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Guadiana r.; Badajoz, Extremadura)
· Mezquita de Cordoba/Great Mosque of Cordoba/Assumption of Our Lady Cathedral (orig.pagan temple; 600 CE: Christian Visigothic church of Saint Vincent; 784 CE: Islamic mosque; 1236: re-converted into cathedral; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· Mezquita de las Tornerias (11th c.CE: Islamic; Toledo)
· Monasterio de San Juan de los Reyes/Saint John the Evangelist (1477-1504 CE: Elizabethan Gothic; Toledo, Castile-La Mancha)
· Monastery of Poblet (f.1151 CE; Tarragona, Catalonia)
· Monastery of San Pedro Viejo (1100-1241 CE: Romanesque; 1140: cloister; 17th c.CE: rebuilt; Huesca, Aragon)
· Monastery of San Salvador of Leyre (842 CE: Romanesque; Porto Speciosa; 11th c.: crypt; Navarre)
· Monastery of San Vicente (8th c.CE: Benedictine; pre-Romanesque; 11-12th c.: reworked; Oveido, Asturias)
· Monastery of Sant Daniel (11th c.CE: Romanesque; Girona, Catalonia)
· Monastery of Santa Faz (15th c.CE: Baroque; Alicante, Valencia)
· Monastery of Valvanera (11th c.CE; 15th c.CE: Gothic; Najera, La Rioja)
· Mondonedo Cathedral (1230 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 18th c.CE: Baroque towers; Mondonedo, Lugo, Galicia)
· Monzon (Knights Templar: castle; Parliament of Aragon)
· Morin cave (prehistoric: paleolithic cave paintings; Cantabria)[MA]
· Murcia Cathedral/Saint Mary (former mosque; 13-18th c.CE: Gothic-Plateresque-Baroque; bell tower
· Najera (Roman: Tritium; Muslim: Naxara “town between the rocks”; Castile-Leon; La Rioja)
· Ourense (Roman: Burgas hot springs; bridge; 5-7th c.CE: Suebi; 716 CE: Moor; Norse and Arab invasions; Galicia)
· Orihuela Cathedral (14-16th c.CE; Orihuela, Valencia)
· Ourense Cathedral (f.572 CE: Suevian basilica; 13th c.: Romanesque-Gothic; Door of Paradise; Capilla del Cristo; Ourense, Galicia)
· Our Lady of the Angels monastery (14th c.CE; Cerro de los Angeles; Getafe, Madrid)
· Palencia (Celtiberian: Pallantia; fortified settlement; 2nd c.BCE: Roman; Castile-Leon)
· Palencia/San Antolin Cathedral/Saint Antoninus of Pamiers (Visigothic crypt: of San Antolin; 1321-1504 CE: Flamboyant Gothic; Palencia, Castile-Leon)
· Pamplona (75 BCE: Roman: Pompaelo; Vascone: Iruna; 4-9th c.: Visigothic; 8th c.: Moor-Frank; 1512: Navarre; Navarre)
· Pamplona Cathedral (14th c.CE: Gothic-Neoclassical; cloister; Pamplona, Navarre)
· Plasencia Cathedral/Saint Mary (1189 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Plasencia, Caceres, Extremadura)
· Pontevedra (Greek traders?; 1st c.BCE: Roman: Pontis Vetera “old bridge”; 5-6th c.CE: Suebi; Way of Saint James; Lerez r.; Galicia)
· Puerta del Sol (14th c.CE: Mudejar; Knights Hospitaller; Toledo, Castille-La Mancha)
· Real Monasterio de Santo Tomas (15th c.CE: Dominican; Avila, Castile-Leon)
· Sacromonte Abbey (catacombs beneath church: site of San Cecilio martyrdom; f.17th c.CE: Mudejar; Granada, Andalusia)
· Sagrada Familia basilica (Antonio Gaudi: 1882-: Gothic-Art Nouveau; gargoyles; Barcelona, Catalonia)
· Salamanca (Celtic-Vacceos; 3rd c.CE: Carthaginian; Roman: Helmantica; bridge; 712 CE: Moor; Castillian; Duero r.; Castile-Leon)
· Salamanca New Cathedral/Saint Mary (16-18th c.CE: Gothic-Renaissance-Baroque-Plateresco; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Salamanca Old Cathedral/Saint Mary (12-14th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Salamanca, Castile-Leon)
· Salvatierra [MA](Neolithic: dolmen; Salvatierra)
· Saint Benedict/San Benito (1500-1515 CE: Gothic; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Saint Francis (1391-1492 CE: Gothic; Turuel, Aragon)
· Saint James/Santiago church (17th c.CE: reredos depicting Adoration of the Magi; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Saint Mary of La Redonda Concathedral (Logrono, La Rioja)
· Saint Nicholas Cathedral (12th c.CE: Romanesque; d.by fire in 1222; 1231: replaced by Gothic-Baroque; Pamplona, Navarre)
· Saint Sebastian monastery (1014 CE: San Sebastian, Basque country)
· Saint Sernin Cathedral (13th c.CE: Gothic; Pamplona, Navarre)
· San Agustin Church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Andres Church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Dionisio Church (1457 CE; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· San Estaban Church (13-14th c.CE: Gothic; Burgos, Castile-Leon)
· San Francisco church (1566 CE; 17th c.: ren.; Plaza de Mina, Cadiz, Andalusia)
· San Francisco church (13th c.CE; Palencia, Castile-Leon)
· San Gil Abad (ancient Roman road; 13-14th c.CE: Romanesque-Mudejar-Baroque; Zaragoza, Aragon)
· San Gines (Soria, Castile-Leon)
· San Ignacio de Loiola church (San Sebastian, Basque country)
· San Juan de Duero (12th c.CE: cloister; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· San Juan de Letran Church (1737 CE: Baroque; façade; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· San Juan de Rabanera (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· San Juan de los Cabelleros Church (1264 CE; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· San Lorenzo Church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Marcos Church (13th c.CE; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· San Mateo Church (Gothic; oldest in city; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· San Maximo (600 CE: Visigoth cathedral; 713-1489: Muslim mosque; Baza, Granada, Andalusia)
· San Miguel Church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Miguel Church (15th c.CE: Gothic-Baroque; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· San Miguel Church (13th c.CE; Palencia; Castile-Leon)
· San Miguel church (16th c.CE: Jesuit; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· San Miguel de Lillo/Saint Mary; Michael (9th c.CE: pre-Romanesque shrine; 12-13th c.: collapsed; Oveido, Asturias)
· San Miguel de los Navarros (13-14th c.CE: Mudejar-Baroque; Zaragoza, Aragon)
· San Nicholas (Soria, Castile-Leon)
· San Nicolas concathedral (1613-62 CE: Doric-Ionic-Baroque; Alicante, Valencia)
· San Pablo (13-14th c.CE: Gothic-Mudejar; Zaragoza, Aragon)
· San Pablo Church (13th c.CE: Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Pablo Church (1270 CE: original Dominican convent; façade; funerary chapel; 1540: Renaissance: star decorated dome; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· San Pedro (16th c.CE: Mudejar; Turuel, Aragon)
· San Pedro/Saint Peter (Romanesque-Baroque; Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha)
· San Pedro Church (4th c.CE: edifice housing remains of Cordoban maryrs: Januarius, Martial, and Faustus; 1236 CE: Gothic-Romanesque; Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· San Polo (monastery: Knights Templar; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· San Salvador Church (former mosque; 16th c.CE: Mudejar; Granada, Andalusia)
· San Zolio monastery/San Francisco church (housed in 18th c.CE: Rococo structure; Benedictine Palencia; Castile-Leon)
· Sant Pau del Camp monastery (f.Wilfred II of Barcelona; 9th c.CE; 985: attacked by Muslims; 14th c.CE: Gothic; gargoyles; Barcelona, Catalonia)
· Sant Pere de Galligants (992 CE: Benedictine monastery; 1117: united w/Abbey of Sainte-Marie de Lagrasse; 1339: restored Romanesque to Aragon; Girona, Catalonia)
· Santa Ana Church (16th c.CE: Mudejar; Granada, Andalusia)
· Santa Cruz church (Romanesque; Baeza, Andalusia)
· Santa Maria Cathedral (former Moorish mosque; 1147 CE: converted Christian; 1529: Gothic; Baeza, Andalusia)
· Santa Maria Magdalena (13-14th c.CE: Gothic-Mudejar; Zaragoza, Aragon)
· Santa Maria del Mar (998; 1329-1383 CE: Gothic; gargoyles; Barcelona, Catalonia)
· Santa Maria del Naranco/Saint Mary (9th c.CE: pre-Romanesque shrine; sim.Roman tetrastyle amphiprostyle temple; Oveido, Asturias)
· Santa Maria del Pi (413 CE: early Christian church; 987: Romanesque; dedicated to Blessed Lady of the Pine Tree; 14th c.CE: Catalan-Gothic; gargoyles; Barcelona, Catalonia)
· Santa Maria del Romeral (9th c.CE; Knights Templar; Monzon, Huesca, Aragon)
· Santa Maria La Antigua/Saint Mary the Ancient (over Roman baths; 1095 CE: original structure f.Count Pedro Ansurez; 12th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; pyramid-shaped tower; Esgueva r.; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Santa Maria la Blanca (1180 CE: Mudejar-Almohad synogogue; oldest synagogue in Europe; owned by Catholic church; Toledo, Castile-La Mancha)
· Santa Maria La Real de las Huelgas monastery (1600 CE: Cistercian; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Santa Maria La Real de Najera monastery (1052 CE; 15-16th c.CE: current; Najera, La Rioja)
· Santa Marina Church (7th c.CE: previous Visigothic church and Mosque existed; 13th c.CE: proto-Gothic-Mudejar-late Romanesque; Fernandine-Alphonsine; Cordoba, Andalusia)
· Santander (Roman: Portus Victoriae luliobrigensium
· Santander Cathedral/Assumption of the Virgin Mary of Santander (8th c.CE: former Santander Abbey/Abbey of the Holy Bodies; ded.Emeterius, Celedonius, martyrs; 12-14th c.: Gothic; Santander, Cantabria)
· Santiago Cathedral/Saint James the Great (12th c.CE: Gothic; Bilbao, Basque country)
· Santiago Church (13th c.CE; Jerez de la Frontera, Andalusia)
· Santiago church (1533 CE: Renaissance; Almeria, Andalusia)
· Santo Domingo Church (1512 CE: Mudejar; Granada, Andalusia)
· Santo Domingo (12th c.CE: Romanesque; Soria, Castile-Leon)
· Santo Toribo de Liebana monastery (prior 6th c.CE: Benedictine; largest surviving piece, L arm, of Lignum Crucis/True Cross brought from the Church of the Holy Sepulcher by Saint Turibius of Astorga; pre-Romanesque church; 1256: Romanesque-Gothic; Franciscan; Liebana, Cantabria)
· Savior/El Salvador Church (1550 CE: Gothic; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Segorbe Cathedral (1534-1795 CE; Segorbe, Valencia)
· Segovia (Celtiberian: Segobriga [“city of victory”]; 75 BCE: Roman: aqueduct; necropolis; Castile-Leon)
· Segovia Cathedral/Virgin Mary (1525 CE: Basque-Castilian Gothic; Castile-Leon)
· Seminary of Saint Phillip Neri (1660 CE; Baeza, Andalusia)
· Seu Nova (Baroque cathedral; Lleida, Catalonia)
· La Seu d’Urgell (Iberian: Arse-d’Urgui; Castellciutat hill)
· Seville (Roman: Hispalis; 5-6th c.CE: Vandal-Visigoth; 712-1248: Moorish; Christian)
· Seville Cathedral/Saint Mary of the See’s (1198 CE: Almohad Mosque; 1248: Christianized; 1376: earthquake d.minaret; 1402-1575: new construction; 1888: main dome and vaults collapse; Seville, Andalusia)
· Siguenza Cathedral (built over earlier Romanesque; Gothic; Renaissance altar; funerary art; Siguenza, Castille-La Mancha)
· Siguenza (Celtiberian Arevaci: Segontia/Villavieja [“dominating over the valley”]; Roman; Visigoth; Moorish; Castilian)
· Sima de la Palomas (250-45k BP: proto-Neanderthal; Murcia)
· Soria (4th c.BCE: Celtiberian [Gk.hero- Orias; Daurias = Duero r.]; Roman; Suebi; Arab; 8th c.CE: Christian; Castile-Leon)
· Tarazona (Roman: Turiaso; 8th c.: Muslim; 1119: Aragon)
· Tarazona Cathedral (12th c.CE: French Gothic-Mudejar; Tarazona, Aragon)
· Tarragona (Iberian: Kesse?; Cyclopean walls; Phoenician: Tarchon; Roman: Tarraco; amphitheatre near Knights Templar el Milagro, ruins; Aqueduct de les Ferreres; walls- Portal de Sant Antoni, Forum, tower of Scipios, arch of Sura/Bara, Aurelian Way)
· Tarragona Cathedral (prev.Roman temple; Visigothic cathedral; Moorish mosque; 1154 CE: Romanesque; 1195: Gothic basilica: +2 aisles and trancept, cross vaults; 1250: tower-dome; 1375: tympanum; Tarragona, Catalonia)
· Tholos de El Romeral [MA](Neolithic: subterranean structure; 4km from Dolmen de Viera and Dolmen of Menga; Antequera, Andalusia)
· Toledo (Bronze Age; Roman: Toletum; Visigoth; Moor; Castillian)
· Toledo Cathedral/Saint Mary (587 CE: early temple of Saint Eugene of Toledo; over mosque; 1226-1493 CE: High Gothic-Mudejar; modeled after Bourges Cathedral; Puerta del Perdon; Puerta del reloj- tympanum depicting life of Christ; Door of Lions; Retable; Sacristy- painted ceiling by Luca Giordano; monstrance; Toledo, Castile-La Mancha)
· Tortosa (Iberian: Hibera?; Roman: Dertosa; Moor; Count Ramon Berenguer IV of Barcelona 2nd crusade)
· Tortosa Cathedral/Assumption of the Mother of God (1347 CE; Tortosa, Catalonia)
· Tudela (lower Paleolithic; Celt-Iberian settlement; Roman; 802: Muslim; Navarre; Navarre)
· Tudela Cathedral (former mosque turned over 1121; 12-13th c.CE: Mudejar-Romanesque-Gothic-Baroque; Puerta del Juicio; Tudela, Navarre)
· Tui (Roman: Tude; Visigothic; Pontevedra, Galicia)
· Tui Cathedral (11-13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Pontevedra, Galicia)
· Turuel Cathedral/Saint Mary of Mediavilla (13th c.CE: Romanesque-Gothic-Mudejar; Turuel, Aragon)
· Valencia (137 BCE: Roman: Valentia “strength/valor”; Visigoth; Moor: Balansiya; Catalan-Aragon)
· Valencia Cathedral (13-15th c.CE: Romanesque; Gothic-Baroque; Valencia)
· Valladolid [Arabic: “City of <Damascan caliph> Walid” (Baladul Walid)](Celtiberian: Vallis Tototum “waters valley”; Roman; Moor; 10th c.: Castilian, Castile-Leon)
· Valladolid Cathedral/Catedral de Nuestra Senora de la Asuncion de Valladolid (16th c.CE: unfinished; Valladolid, Castile-Leon)
· Vic (Roman: Ausa; Visigothic: Ausona; 788: d.Muslims; Catalonia)
· Zafarraya (250-45k BP: classic-Neanderthal; Granada)
· Zamora (Lusitanian; Roman: Occelum Durii/Ocellodurum; Visigothic: Semure; Moor: Semurah/Azemur; Castile-Leon)
· Zamora Cathedral (orig. church: El Salvador; 1151-74 CE: Romanesque; 15th c.: Gothic; Duero r.; Zamora, Castile-Leon)
· Zaragoza (Sedetan-Iberian: Salduie; 25 BCE: Roman: Caesaraugusta; 5th c.: Goth; 714: Berber-Arab; Aragon)
BALEARIC ISLANDS: [MA] (2000 BCE: Talayotic; Bronze age; talayot; Phoenician; Majorca and Minorca)
· Capocorb Vell [MA](5 talayot; Llucmajor)
· Ibiza (654 BCE: Phoenician: Ibossim; Es Culleram cave shrine to the goddess Tanit; Greek; 209 BCE: Carthaginian; Roman; Vandal; Byzantine; Moor; King Sigurd I of Norway; 1235: King James of Aragon)
· Naveta de Tudons [MA](1200-750 BCE: Bronze Age: chambered tomb; 100 men, bronze bracelets, bone and ceramic buttons; btwn.Ciutadella de Minorca and Ferreries)
· Palma (Talaiotic settlement; Phoenecian; Cathaginian; Roman camp: Pollentia; Vandal; Byzantine; 902-1229 CE: Moor: Medina Mayurqa; Aragon; Majorca)
· Palma Cathedral/La Seu/Saint Mary of Calencia Cathedral (f.King James I Aragon; 1229 CE: Gothic; 1901: renovations- Antonio Gaudi abandoned work; Palma, Majorca)
· Santa Eulalia church (Gothic; King James II crowned; Palma, Majorca)
· Ses Paisses [MA](Arta)
· Son Olesa dolmen [MA](Majorca)
· Talati de Dalt [MA](Minorca)
· Trebaluger [MA](Minorca)
· Es Trepuco [MA](Minorca)
· Torre d’en Galmes [MA](Minorca)
SWEDEN: [megaliths; rune stones/picture stones (400-900 CE); cathedrals]
[NOTE 83] Submerged megalithic site found in the Gulf of Botnia, midway between Sundsvall and Kristinestad; soot covered rocks encircling an egg-shaped hole; 60m dia. object (UFO?), 10-13’ high off seabed; 300m flattened out runway, cleared seabed track, leading up to the object
· Adelso (Stone; Iron; Viking; i. Lake Malaren)
· Alby (Stone Age; Oland)
· Ale’s Stones [MA](3500 BCE: remains; 600 CE: stone ship-59 lg. boulders; legend: King Ale is buried there; 10km SE Ystad; Kaseberga, Scania)
· Anund’s Mound
· Birka (Viking; Stockholm)
· Bjorketorp Runestone [MA](Neolithic?: menhirs, stone circles; 6-7th c.CE: proto-Norse: one of world’s largest rune stone; translation: “master of the runes conceal here runes of power. Incessantly maleficence, insidious death he who breaks this; prophesy destruction”; near Ronneby; Bjorketorp, Blekinge)
· Blomsholm (Stromstad)
· Gamla Uppsala (3rd c.CE: mounds; Uppsala)
· Gene fornby (Nordic bronze age; Iron Age; Ornskoldsvik)
· Gettlinge [MA](Mesolithic: bone spears, elk antler harpoons, flint; Neolithic: menhirs; dwellings; Bronze Age: barrows; bronze chains, bone needle case; Viking: stone ship burial ground; fringe of Stora Alvaret, Oland i.)
· Haga [“tall mound”] Kurgan/King Bjorn’s Mound (1000 BCE: Nordic Bronze Age kurgan; constructed of turfs laid over cairn, built over wooden chamber containing hollow oak coffin w/cremated remains; human sacrifice- marrow removed from bones; Bronze Age sword, razor, 2 brooches, guilded buttons, 2 pincers, other bronze objects; mentioned in Hervarar saga- Tolkien inspiration; Uppsala)
· Helgo (200 CE; 6th c.CE: Buddha sculpture and Egyptian scoop found; i.Malaren lake)
· Hulterstad (Mesolithic: village; Viking: stone burial ship; fringe of Stora Alvaret, Oland i.)
· Linkoping Cathedral (11th c.CE: original wooden church; 1120: stone church-basilica; 1230: enlargement; 1251: coronation of Valdemar; 1408-20: Gothic; Lutheran; Linkoping)
· Lund (1st c.BCE: Upparka; oldest city in Sweden; 1020 CE: f.Sweyn I Forkbeard/Cnut the Great of Denmark)
· Lund Cathedral (1085: early cathedral; 1123: crypt; fire in 1234; 1370: Gothic choir; 1424: astronomical clock; 1527: Franciscan monastery shut down by mob; Lund)
· Saint Nicolaus Church (1230 CE; burnt in 1525; ruin; Visby)
· Sigtuna (1000 CE: church ruins; l.Malaren; Stockholm)
· Skara Cathedral (11-13th c.CE; crypt; Skara)
· Stones of Gettlinge (Oland)
· Storkyrkan Cathedral (1279; 1527: Lutheran; Saint George and the Dragon; Stockholm)
· Strangnas Cathedral (pagan ritual spot; 11th c.CE: where missionary Saint Eskil was killed; 12th c.CE: original wood cathedral; 1296: Scandanavian Brick Gothic; burials of Charles IX and Maria of Palatinate-Simmern; Strangnas)
· Tjelvar’s Grave (Oland)
· Uppakra (1st c.CE; Lund)
· Uppsala Cathedral (13th c.CE: Gothic-Dutch Renaissance-Baroque; burials of Swedish kings- Gustav Vasa; Uppsala)
· Uppsala Temple (destroyed in 11th c.CE: Norse-pagan temple; Gamla Uppsala: mounds, postholes beneath church)
· Valsgarde (550 CE: Iron Age/Vendel Age: mounds; Viking Age: ship burials; near Uppsala)
· Vasteras Cathedral (Brick Gothic; Vasteras)
· Vaxjo (Bronze Age: petroglyphs; Stone Age sacrifice stones; Vaxjo)
· Vaxjo Cathedral (1690-1710 CE; Lutheran; Vaxjo)
· Vendel (Iron Age: Ohthere mound; N of Uppsala)
· Visby Cathedral (12th c.CE; Lutheran; Visby)
SWITZERLAND: (megaliths; cathedrals)
· Abbey of Saint Gall/Gallen (612 CE: Irish monk Gallus built hermitage at Steinach r.; f.abbey in 720: abbey of Saint Gallen; 926: Wiborada, woman precognitive of Hungarian invasion- monks escape w/treasure; Wiborada stays behind and killed by raiders; 954: walls protect from Saracens; Baroque; Saint Gallen)
· Basel (Roman: Basilea “kingship”; Augusta Raurica theatre)
· Basel Munster (1st c.BCE: Celtic temple on Munster hill; Roman fort; 7th c.CE: Luxeuil monastery; 1000 CE: Haito Munster; Romanesque; 1019-1500 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; crypt; earthquake in 1356 d.5 towers; 1421-1500: extended; 1528-9: Protestant Reformation- art works destroyed; Basel)
· Basilique de Valere/Notre Dame (12-13th c.CE: fortified church; Sion)
· Bern (2nd c.BCE: Gaulish oppidum; Roman)
· Bern Munster (1191: orig.small chapel; 13th c.CE: enlarged to 3-nave church; 1421 CE: Gothic; tympanum-Last Judgment; 1441-50: stained glass- “Dance of Death”; Renaissance choir; Bern)
· Cathedral of Saint Nicholas (Fribourg)
· Chur (3900-3500 BCE: Pfyn culture; Bronze-Iron Age; Celtic: kora/koria “tribe”; Roman: Curia Raetorum; routes; 4th c.CE: Christian bishopric; 451: Ostrogoths: Theodoricopolis; 6th c.CE: Franks; 925-6 CE: dmg.by Magyars; 940-54: Saracens; 958: Holy Roman Empire; Hapsburg County of Tyrol)
· Concise [MA](Neolithic: menhir)
· Fraumunster abbey (f.853: Benedicitine; Chagall stained glass choir windows; 1045: coin mint; Zurich)
· Fribourg (Neolithic; Roman river crossing; 1277: Habsburg)
· Geneva (Celto-Germanic: Helvetii; 121 BCE: Roman; 4th c.CE: bishopric; 443: Burgundian; 534: Frank; 888: new K.Burgundy; 1033: German; 1154: bishops of Geneva had prince status in Holy Roman Empire; center of Calvinism- Protestant Reformation; center of many international organizations- UN, WTO, etc.)
· Grandson [MA](5000 BCE: Neolithic: menhir in Les Echatelards; near other Neolithic settlements: Les Buttes, Le Repuis, Le stand, Les Tuileries; Bronze Age settlements: Corcelettes-piles for stilt houses, vases; Iron Age: Certosa brooch; Roman; Grandson, Yverdon-les-Bains, Jura-Nord Vaudoise, Vaud)
· Grossmunster (Roman burial ground; 820: original Carolingian church; accd.to legend: commissioned by Charlemagne to be imperial church; 1100-1220 CE: Romanesque; monastery church; crypt; Zwingli- Protestant Reformation; Zurich l.; Zurich)
· La Tene (450 BCE: Iron Age culture; l.Neuchatel)
· Lausanne (Celtic settlement: Vidy-Ouchy; Roman: Lousanna military camp; Dukes of Savoy)
· Lausanne Catehdral/Notre Dame (1170-1240 CE: Gothic-Flamboyant; Lausanne)
· Lugano (Stone Age: Breganzona, Castagnola, Davesco, Gandria; ground/quern stones; Copper-Iron Age; 5th-2nd c.BCE: Etruscan-Celtic monuments, grave, and money- Davesco-Soragno, Pregassona, Viganello; 1st c.BCE: Roman; fighting between Guelphs and Ghibellines; disputes between Como and Milan)
· Maigrauge Abbey (1255; 1262: Cistercian; Fribourg)
· Saint Lawrence Cathedral (9-15th c.CE: Romanesque-Baroque; 818: original cathedral oriented in opposite direction; Lugano)
· Saint Luzius (old church; 1178-1282; Episcopal Seminary built on 6th c.ruins; Chur)
· Saint Maria Himmelfahrt Cathedral/Assumption (Romano-Gothic; crypt- remains of Jorg Jenatsch; paintings by Durer; Chur)
· Saint Mary of Angels Church (16th c.CE: Lugano)
· Saint Maurice (Roman: Agaunum; Valais)
· Saint Maurice abbey (temple of Mercury; martyrs of the Theban Legion led by Saint Maurice; Saint Maurice, Valais)
· Saint Peter Church (former Roman castle; temple of Jupiter; 8-9th c.CE: early church; 1000 CE: Romanesque; 1230: rebuilt; 1460: Gothic; largest church clock face in Europe; Lindenhof hill; Zurich)
· Saint Pierre Cathedral (Roman site; 8-10th c.CE: cathedral- Funerary cult; 12th c.CE: 2 more structures; Geneva)
· Saint Ursus Cathedral (Roman fortress; 1762-73; Solothurn)
· Sion (Neolithic: Celtic-Seduni; 1st c.BCE: Roman)
· Solothurn (Celtic settlement; 14-37 CE: Roman: Salodurum; 1127: dukes of Zahringen; 1295: alliance w/Bern- Swiss Confederation; 1382: Habsburgs attacked; renounced 2 yrs.later)
· Yverdon-les-Bains [MA](5000 BCE: Neolithic: 3000 BCE: stone rows; 2nd c.BCE: Celtic Helvetii; 1st c.BCE: Roman: Ebredunum-castrum; Yverdon-les-Bains, Jura-Nord, Vaud)
· Zurich (Neolithic-Bronze Age; 5000 BCE: Celtic settled; 15 BCE: Roman: Turicum; fortification; Carolingian; center of Protestant Reformation; Linth r.; Walen l.; Zurich l.)
UKRAINE: [kurgan](p.USSR)
· Armenian Catehdral (1363-70; Lviv)
· Berezan Island (7th c.BCE: Greek col.; Runic inscriptions; Borysthenes; Ochakov)
· Boundary Stones [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: 15 pairs of parallel stone monoliths; 20 barrows w/in 1-2 km rad.; “Devil’s Cave”)
· Chersonesos Taurica (6th c.BCE: Greek colony; Sevastopol)
· Dovbush rocks pagan observatory [MA](1700 BCE; Ukraine)
· Kiik-Koba (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Latin Catehdral (1344 CE; burned 1350; 1360: reconstr.; 1761-76: Baroque; Lviv)
· Mezmaiskaya Cave (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Muierii (45-28k BP: Neanderthal-human)
· Olvia/Pontic Olbia (5th c.BCE: Greek colony; temple of Apollo; founded by Milesians; Nikolaev)
· Ryzhanovka kurgan (3rd c.BCE: tomb: Scythian chieftain; 125km S Kiev, Ukraine)
· Saint Sophia Cathedral (1037 CE: Byzantine; 5 naves, 5 apses, 13 cupolas; Kiev)
· Solokha kurgan (4th c.BCE: 2 royal Scythian tombs: central tomb- robbed in antiquity, 2 horses in rich attire; intact lateral tomb- male ruler covered in gold, buried w/weapons bearer, servant, 5 horses, bronze greaves, bronze helmet, sword in gold sheath, silver quiver, 80 bronze arrowheads, golden comb- 3 fighting warriors; confirmed Herodotus- Gerrhos, royal Scythian burial site; Dnepr r.; near Velikaya Znamenka; Zaporizhia Oblast, Ukraine)
· Staroselje (45-28k BP: transitional-Neanderthal)
· Other Cities of the Euxine (Black) Sea; Taurica (Crimea): Greek Colonies
· Gorgippia
· Hermonassa
· Kerkinitis
· Kiev Kiev (ancient Viking crossroads)
· Kimmerikon
· Panticapaeum
· Phanagoria
· Tanais
· Theodosia
· Tyras
UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND:
[MA] [dolmen, cairn, stone circles, standing stones (star stones-megaliths); cathedrals, abbeys]
Notes pertaining to the Roman Empire:
[NOTE 8] As the Sumero-Egypto-Greco-Roman empire expands into Europe (as the Holy Roman Empire and the British Empire, and on to America, the Globe, and beyond… ”to boldly go where no man has gone before,” the Celtic-Phoenician-Viking druidic culture contracts into the “New World.”
[NOTE 78] Submerged cities off the coast of Cornwall (aka. Avalon), a tin mining station for the Atlanteans (c.2000 BCE)
ENGLAND:
· Abbeys/Priories:
[NOTE 11] Abbeys are institutions between church and state; because generally they are either founded by and/or granted to royalty and/or knightships.
[NOTE 12] Many English abbeys/priories/friaries dissolve, consequently due to the Treaty of Toledo (c.1539).
o Beadlow Priory/Saint Mary Magdalen (f.1140/6-1435 CE: Benedicitne; trans.from Milbrook; cell of St.Albans Abbey; abandoned 1435; Bedfordshire)
o Bushmead Priory/Saint Mary (f.1185/95-1536 CE: Augustinian; Bedfordshire)
o Caldwell Priory/Saint John the Baptist (f.1153-1536 CE: Augustinian; Bedfordshire)
o Chicksands Priory/Saint Mary (f.1147-1538 CE: Gilbertine; Crown prop.in 1936; in Military base 1995; Bedfordshire)
o Dunstable Priory/Saint Peter (f.1131-1540 CE: Augustinian; gr.Sir Leonard Chamberleyn; Bedfordshire)
o Dunstable Friary (f.1259-1539 CE: Dominican; Bedfordshire)
o Elstow Abbey/Saint Mary; Helena (f.1078-1539 CE: Benedictine; Bedfordshire)
o Greyfriars Bedford/Saint Francis (f.1238-1539 CE: Franciscan; Bedfordshire)
o Grovebury Priory/Leighton Buzzard Priory (f.1189-1414 CE: Benedictine; cell of Fontevrault; Bedfordshire)
o Hardwick Preceptory (f.1279-1489 CE: Knights Hospitaller; Bedfordshire)
o Harrold Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Peter (f.1138-1536 CE: Augustinian; William Lord Parr; 1608-10 CE: Harold Hall mansion and farmhouse; Bedfordshire)
o Markyate Priory/Holy Trinity (f.1145-1537 CE: Benedictine; gr.George Ferres; Markyate cell; Bedfordshire)
o Melchbourne Preceptory (f.12th c.-1550 CE: Knights Hospitaller; Bedfordshire)
o Millbrook Priory/Saint Michael (f.1097 CE: Benedictine; trans.to Beadlow; Bedfordshire)
o Newnham Priory/Saint Paul (f.1247-1539 CE: Augustinian; Bedfordshire)
o Pulloxhill Grange (Augustinian; grange of Dunstable Priory; Bedfordshire)
o Ruxox Cell (Augustinian; cell for Dunstable; Bedfordshire)
o Warden Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1136 CE: Cistercian; Bedfordshire)
o Woburn Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1136-1538 CE: Cistercian; from Fountains Abbey; Bedfordshire)
o
o Bisham Abbey/Holy Trinity (f.1260-1307 CE: Knights Templar; f.1337-1536 CE: Augustinian; 1537-8 CE: Benedictine; 1554 CE: gr.Sir Edward Hoby; Berkshire)
o Bradfield Abbey (f.1066 CE; Berkshire)
o Bromhall Priory/Saint Margaret (f.1200-1522 CE: Benedictine; daughter house of Chertsey; Saint john’s College Cambridge; some remains in farm buildings; Berkshire)
o Cookham Abbey (f.726 CE; Berkshire)
o Donnington Friary (f.1404-1538 CE: Crouched Friars; Berkshire)
o Greenham Preceptory (f.1199-1540 CE: Knights Hospitaller; Berkshire)
o Hurley Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1065-1536 CE: Benedictine; gr.Sir Leonard Chamberleyn; Berkshire)
o Kintbury Abbey/Saint Mary (f.1147 CE: Benedictine; Berkshire)
o Poughley Priory/Saint Margaret (f.1160-1524 CE: Augustinian; farmhouse; Berkshire)
o Reading Abbey/Our Lady; Saint John the Evangelist (f.1121 CE: Cluniac; 1210-1539 CE: Benedictine; 1550 CE: gr.Duke Edward of Somerset; 1550-1643 CE: quarried and dismantled; ruins; Berkshire)
o Reading Nunnery (f.976-1016 CE; Berkshire)
o Reading Greyfriars/Saint Francis (f.1233-1538 CE: Franciscan; re-used as Town Hall then back to Parish church; Berkshire)
o Sandleford Priory/Saint John the Baptist (f.1193/1202-1478 CE: Augustinian; converted to country house, now Angelican Convent School; Berkshire)
o Shalford Preceptory (Knights Templar/Hospitaller; Berkshire)
o Stratfield Saye Priory/Saint Leonard (f.1169-1399 CE: Benedictine; 17th c.CE: ‘The Priory’ at Beech Hill; Berkshire)
o Templeton Camera (Knights Templar; Berkshire)
o
o Austin Friary (f.Sir Simon and Sir William Montacute; 1313-1538 CE: Augustinian; 1543 CE: Maurice Dennis; Bristol)
o Blackfriars (f.Sir Maurice Gaunt; 1227/8-1538 CE: Dominican; gr.William Chester; became: Friars Quaker meeting house, then Bristol Register Office, now restaurant; Bristol)
o Bristol Preceptory (Knights Templar; Bristol)
o Greyfriars/Saint Francis (f.1234-1538 CE: Franciscan; gr.Mayor and citizens; Bristol)
o Sack Friary (f.1266-86 CE: Friars of the Sack; 1322 CE: church; Bristol)
o Saint Augustine’s Abbey (f.1140 CE: Augustinian; Bristol Cathedral; Bristol)
o Saint James’s Priory (f.1120-1543 CE: Benedictine; Bristol)
o Saint Mary Magdalen Nunnery (f.Eva Fitzharding; 1173-1536 CE: Augustinian; gr.Henry Bayne, John Marsh; Bristol)
o Saint Philip’s Priory/Saint Jacob (f.900 CE; Bristol)
o Westbury Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.716 CE; 963 CE: Benedictine; cell of Worchester Cathedral; Bristol)
o Whitefriars/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1267-1538 CE: Carmelite; occ.: mansion; boy’s school; Colston Hall; Bristol)
o
o Ankerwycke Priory/Saint Mary Magdalene (f.1160-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1538/9 CE: gr.Lord Windsor; 1550-1 CE: gr.Sir Thomas Smith; Ruins in Ankerwycke House; Wraysbury, Buckinghamshire)
o Biddlesden Abbey/Saint Mary (f.1147-1538 CE: Cistercian; 1540/1: gr.Thomas Wriothesley; remains demo.1727; private house-Biddlesden Park; Buckinghamshire)
o Bradwell Priory/Saint Mary (f.Meinfelin Lord of Wolverton; 1155-1526 CE: Benedictine; Christ Church, Oxford; 1542/3: gr. Arthur Longfield; private; Buckinghamshire)
o Bulstrode Preceptory (f.1276 CE: Knights Templar; Buckinghamshire)
o Burnham Abbey/Saint Mary (f.Richard King of Romans; 1265-1539 CE: Augustinian; 1544 CE: Anglican Augustinian Society of the Precious Blood; Buckinghamshire)
o Chetwode Priory/Saint Mary; Nicholas (f.Ralph de Norwich; 1244-1535 CE: Augustinian; 1460: annexed to Notley; Buckinghamshire)
o Hogshaw Nunnery (f.1180 CE: Sisters of Saint John; 15th c.CE: Knights Templar; Buckinghamshire)
o Hogshaw Commandery (f.1180-1470 CE: Knights Hospitaller; 1470: gr.Matilda Lane; 1543-1650: church; ruiuned in 1700; Buckinghamshire)
o Lavendon Abbey/Saint John the Baptist (f.John de Bidun 1154/8-1536 CE: Premonstratensian; 1536: gr.Sir Edmund Peckham; ‘Lavendon Grange,’ once home of Sir Isaac Newton’s relatives; Buckinghamshire)
o Little Marlow Priory (f.Jeffrey Lord Spensar; 1218/44-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1540: gr.John Tiltey, E.Restwold; Buckinghamshire)
o Luffield Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.Robert II, Earl of Leicester; 1123 CE: Benedictine; Buckinghamshire)
o Medmenham Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.Hugh de Bolbec; 1201-1547 CE: Cistercian monks from Woburn Abbey; gr.Robert Mone, etc.; manor house; Buckinghamshire)
o Missenden Abbey/Saint Mary (f.1133-1538 CE: Augustinian-Arroasian; daughter house of St.Mary de Bosco, Ruisseaville, France; gr. Duke of Northumberland; residential college; Buckinghamshire)
o Muresley Priory (f.1135 CE: Benedictine; community evicted; 1537: gr.Sir John Dance; Buckinghamshire)
o Newton Longville Priory (f.1150-1442 CE: Cluniac; gr.New College, Oxford; 1550: manor house; Buckinghamshire)
o Notley Abbey/Saint John the Baptist (f.Walter Giffard, Earl of Buckingham, Lady Ermgard; 1162-1542 CE: Augustinian; gr.Sir William Paget; private; Buckinghamshire)
o Ravenstone Priory (f.Peter de Chaseport, Keeper of Royal Wardrobe; 1255-1544 CE: Augustinian; 1548: gr.Sir Francis Bryan; 19th c.: ‘Abbey Farm’; Buckinghamshire)
o Snelshall Priory/Saint Leonard (f.Sybil de Aungervill; 12th c.-1535 CE: f.Ralph Mortel; Premonstratensian; Nemedictine; gr.Francis Piggot; Buckinghamshire)
o Tickford Priory (f.Fulk Paynell; 1140-1524 CE: Benedictine-Cluniac; cell of Marmoutier; sold by James I to Henry Atkins, MD; Buckinghamshire)
o Widmere Commandery (Knights Hospitaller; Buckinghamshire)
o Wing Priory (f.Empress Matilda; 7th c.CE: Benedictine; daughter of Saint Nicholas monastery; gr.Sir Robert Dormer; Buckinghamshire)
o
o Anglesey Priory/The Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Nicholas (f.Henry I; 1135-1535 CE: Augustinian; 1538: gr.John Hynde; private house-Anglesey Abbey; Cambridgeshire)
o Barham Friary (f.1272-1539 CE: Crutched Friars; Cambridgeshire)
o Barnwell Priory/Saint Giles (f.Norman lord Picot; 1092 CE: Augustinian; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge Austin Friary (f.1092 CE: Augustinian; trns.to Barnwell in 1112; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge Blackfriars (f.1258 CE: Dominican Friars; 1543: gr.Edward Erlington, Humphrey Metcalf; Emmanuel College U.Cambridge; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge Pied Friary (f.1273-9 CE: Pied Friars; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge White Friary (f.13th c.CE: Carmelite Friars; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge Saint Mary’s Friary (f.13th c.CE: Friars of Saint Mary; Cambridgeshire)
o Cambridge Saint Edmund’s Priory (f.1291-1539 CE: Gilbertine; gr.Edward Ebrington, Humphrey Metcalf; Cambridgeshire)
o Chatteris Abbey (f.Alfwen/Ethelstan, Earl of the East angles; 1016-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1551: gr.Edward Lord Clinton; Cambridgeshire)
o Chippenham Preceptory (f.William de Mandevill; 1184 CE: Knights Hospitaller; 1540: gr.Sir Edward North; Cambridgeshire)
o Denny Abbey/Saints James, Leonard, Denny (f.Robert Chamberlain of Conan IV, Duke of Brittany; 1159 CE: Benedictine; cell of Ely; 1169-1308 CE: Knights Templar preceptor; 1308-1536 CE: f.Mary de Saint Pol, Countess of Pembroke; 1540: gr.Edward Erlington; Farmland Museum; Franciscan; Cambridgeshire)
o Duxford Preceptory (f.1273 CE: Knights Templar; Cambridgeshire)
o Ely Cathedral Priory/Saints Peter, Etheldreda (f.673 CE; 9th c.-1540 CE: Benedictine; Cambridgeshire)
o Fordham Priory/Saints Peter, Mary Magdalene (f.Dean of Fordham; 1227 CE: Gilbertine; 1540/1: gr.Philip Parry; private house-‘Forham Abbey’; Cambridgeshire)
o Great Wilbraham Preceptory (13th c.CE: Knights Templar; Cambridgeshire)
o Huntingdon Priory/Saint Mary (f.1086-1538 CE: Benedictine-Augustinian; Cambridgeshire)
o Ickleton Abbey (f.Aubrey de Vere, Earl of Oxford; 1190-1538 CE: Benedictine; gr.Thomas Goodrich; Abbey Farm; Cambridgeshire)
o Isleham Priory/Saint Margaret (f.1086-1414 CE: Benedictine; gr.Pembroke College, Cambridge; Cambridgeshire)
o Marmont Priory (f.Ralph de Hauvill; 12th c.CE: Gilbertine; gr.Percival Bowes, John Mosyer; Cambridgeshire)
o Newnham Whitefriars (f.1249-92 CE: Carmelite Friars; Cambridgeshire)
o Peterborough Abbey/Saints Peter, Paul, Andrew (f.665/966-1539 CE: Benedictine; 1540-: cathedral; Cambridgeshire)
o Ramsey Abbey (f.969-1539 CE: Benedictine; Cambridgeshire)
o Saint Ives Priory (f.1017 CE: Benedictine; house; Cambridgeshire)
o Saint Neots Priory (f.974 CE: Benedictine; cell of Ely; 1113: cell of Bec; Cambridgeshire)
o Sawtry Abbey (f.1147-1536 CE: Cistercian; from Warden Abbey; Cambridgeshire)
o Shingay Preceptory (f.Sibylla de Raynes, daughter of the Earl of Montgomery; 1144-1540 CE: Knights Hospitaller; 1180: Sisters of Saint John nuns cell moves to Buckland Priory; gr.Richard Longe; Cambridgeshire)
o Spinney Abbey/Saint Mary; Holy Cross (f.Hugh de Malebisse; 1216-1228 CE: Augustinian; 1449: Absorbed into Ely; 1544/5: gr.Sir Edward North; house and farm; Cambridgeshire)
o Stonely Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1180-1536 CE: Augustinian; Cambridgeshire)
o Swaffham Bulbeck Priory/Saint Mary (f.Isabel the Bolebec; 12th c.-1538/9 CE: Benedictine; gr.Thomas Goodrich, Bishop of Ely; Cambridgeshire)
o Thorney Abbey/Saints Mary; Botulph (f.1st Abbot of Peterborough; 972-1539 CE: Achorite/hermits-Benedictine; gr.John, Earl of Bedford; church in parochial use; Cambridgeshire)
o Waterbeach Abbey/Saint Clare (f.Denise Munchensey; 1294-1351 CE: moved to Deny due to flooding; Cambridgeshire)
o
o Chester Abbey/Saint Peter, Paul; Werburgh; Christ; Blessed Virgin Mary; (f.875-907 CE: secular; 1092-1540 CE: Benedictine; 1541-: episcopal dio.cathedral; Cheshire)
o Chester Carmelite Friary (f.Thomas Stadham; 1279-1538 CE: Carmelite; gr.John Coke; Cheshire)
o Chester Grey Friary (f.Albert of Pisa; 1237/8-1537 CE: Thomas Stadham; 1279-1538 CE: Carmelite; gr.John Coke; Cheshire)
o Chester Friary of the Sack (f.1274-1300 CE: Friars of the Sack; Cheshire)
o Chester Priory/Saint Mary (f.Randal, Earl of Chester; 12th c.-1537 CE: Benedictine; gr.Urian Brereton; 1964: co.police hq; Cheshire)
o Combermere Abbey/Saint Mary; Michael (f.Hugh de Malbane, Lord of Nantwich; 1133 CE: Savignac; 1147-1538 CE: Cistercian; gr.William Cotton; Cheshire)
o Darnhall Abbey/Saint Mary (f.Edward I of England; 1271/4 CE: Cistercian monks from Abbey Dore; tr.Vale Royal; Cheshire)
o Norton Priory/Saint Mary (1134 CE: tr.from Runcorn by William FitzWilliam, Baron of Halton; 1391-1536 CE: Augustinian; 1545: gr.Richard Brooke; mansion d.in 1928; Norton Priory Museum; Cheshire)
o Poulton Abbey (f.Robert Butler to the Earl of Chester; 1153-1544 CE: Cistercian; 1214 CE: tr.Dielacres Abbey due to Welsh incursions; gr.William Cotton; Cheshire)
o Runcorn Priory/Saint Mary; Saint Bertelin (f.William FitzNigel, 2nd Baron of Halton; 1115 CE: Augustinian; 1134: tr.Norton Priory; All Saints Parish church; Cheshire)
o Stanlow Abbey (f.John FitzRichard, 6th Baron of Halton; 1115 CE: Augustinian; 1296-1442: tr.Whalley Abbey; 1553: gr.Sir Robert Cotton; Cheshire)
o Vale Royal Abbey (f.1277-1545 CE: Cistercian; from Darnhall; never completed project of King Edward I; 1543: gr.Thomas Holcroft; Cheshire)
o
o Bodmin Friary (f.1260-1538 CE: Franciscan; Cornwall)
o Bodmin Priory (f.6th c.CE: Celtic; 936 CE: Benedictine; 1124-1539 CE: Augustinian; secular/industrial use; Cornwall)
o Cardinham Grange (medieval; Cornwall)
o Crantock Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Kea Monastery/Old Kea (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Lammana Priory/Saint Michael (f.6th c/CE: Benedictine; 1114-1549 CE: cell of Glastonbury Cornwall)
o Lannachebran Cell (f.Saint Achebran; Cistercian; 1559 CE: gr.Francis, Earl of Bedford; Cornwall)
o Lanwethinoc/Padstow Monastery/Saint Petroc (f.Bishop Wethinoc; Celtic; Cornwall)
o Madron Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Manaccan Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Minster Priory/Saint Mertherian (f.William de Bottreaux; 1190-1407: Celtic-Benedictine; Cornwall)
o Probus Monastery (f.10th c.-1549 CE: Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Anthony Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Buryan Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Carrok Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint German Priory (1184-1539 CE: Augustinian; Cornwall)
o Saint Goran Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Keverne Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Kew Cell/Saint Daw; Kew (f.961-3 CE: Augustinian; 1283: secular college; 1496/1883: church restored; Cornwall)
o Saint Mawgan Monastery (Celtic-Cluniac; Cornwall)
o Saint Michael’s Mount Priory (f.1135 CE: Benedictine; fortress-monastery-residence; Cornwall)
o Saint Neot’s Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Saint Piran’s Monastery (Celtic; Cornwall)
o Scilly Priory (12th c.CE: Celtic-Benedictine; cell of Tavistock; 1834: Tresco Abbey Gardens by Augustus Smith; Cornwall)
o Temple Templars Preceptory (-1308-12 CE: Knights Templar; Cornwall)
o Tintagel Monastery (f.350 CE: Celtic; Norman castle; Cornwall)
o Tregonan Grange (f.1263-1527 CE: Cistercian; grange of Beaulieu Abbey; Cornwall)
o Tywardreath Priory (f.1088-1536 CE: Benedictine; daughter house of the monastery of Saint Serge at Angers; Cornwall)
o
o Armathwaite Nunnery/Jesus Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1089 CE: Benedictine; Cumbria)
o Calder Abbey (f.1135-7/1143 CE: Savignac monks from Furness; tr.Hood; rf.1143 CE: 1147-1536: Cistercian; private; Cumbria)
o Carlisle Cathedral Priory/Holy Trinity (1092 CE: secular; f.1122-1540 CE: Augustinian; Episcopal dio.cathedral; Cumbria)
o Carlisle Dominican Friary (f.1233-1539 CE: Dominican; Cumbria)
o Carlisle Franciscan Friary (f.1233-1539 CE: Franciscan; Cumbria)
o Cartmel Priory (f.1189-1536 CE: Augustinian; Cumbria)
o Conishead Priory/Virgin Mary (f.1188 CE: Augustinian; 1160: orig.hospital; Buddhist Manjushri Kadampa Meditation Center; Cumbria)
o Furness Abbey (f.1124-1537 CE: Savignac-Cistercian; Cumbria)
o Holmcultram Abbey (f.1150-1538 CE: Cistercian; d.arson in 2006; Cumbria)
o Lanercost Priory (f.1166-1537 CE: Augustinian; private house-‘Dacre Hall;’ Cumbria)
o Penrith Friary (f.1291-1539 CE: Augustinian; 1717: house-‘Friarage;’ Cumbria)
o Saint Bees Priory (900 CE: earlier church; f.1120-1539 CE: Benedictine; Cumbria)
o Seaton Priory (f.13th c.CE: Benedictine; farm house-‘Seaton Hall;’ Cumbria)
o Shap Abbey (f.1199-1540 CE: Premonstratensian; Cumbria)
o Wetheral Priory (f.1106-1542 CE: Benedictine monks from Saint Mary’s Abbey, York; Cumbria)
o
o Barrow Camera (f.14th c.CE: Knights Hospitaller; 16th c.: inc.Arleston House; Derbyshire)
o Beauchief Abbey (f.Robert, Lord Alfreton; 1183-1536/7 CE: Premonstratensian; gr.Sir Nicholas Strelly; Derbyshire)
o Bradbourne Priory/Church of All Saints (f.1328 CE: Augustinian; cell of Dunstable Priory; Derbyshire)
o Breadsall Priory (f.1266-1552 CE: Augustinian; gr.Henry, Duke of Suffolk; mansion; Mariott Breadsall Priory Hotel; Derbyshire)
o Calke Priory (f.Maud, widow of Earl of Chester; 1161-1547 CE: Augustinian; trns.Deepdale; gr.John, Earl of Warwick; mansion-‘Calke Abbey’; Derbyshire)
o Dale Abbey (f.from Newhouse; 1162-1536 CE: Augustinian-Premonstratensian; tr.to Stanley; Derbyshire)
o Darley Priory/Saint Mary (f.Robert de Ferraris, Earl of Derby; 1146-1538 CE: Augustinian; 1540: gr.Sir William West; Derbyshire)
o Derby Augustinian Priory/Saint Helen (f.1137 CE: Augustinian; 1146: most tr.to Darley; 1160: hospital; Derbyshire)
o Derby Cluniac Priory/Saint James (f.1140-1536 CE: Cluniac; gr.cell to Bermondsey Abbey; Derbyshire)
o Derby Black Friary (f.1239-1539 CE: Dominican; 18th c.: ‘Friary Hotel’; Derbyshire)
o Gresley Priory/Saint George (f.William de Greisley; 1135-40-1534/4 CE: Augustinian; gr.Henry Cruche; Derbyshire)
o King’s Mead Priory (f.1160-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1543/4: gr.Francis, Earl of Shrewsbury; Derbyshire)
o Locko Preceptory/Saint Mary Magdalene (f.1297-1375 CE: Saint Lazarus Hospitallers; Leper Hospital; Derbyshire)
o Repton Priory/Holy Trinity (f.660 CE: Augustinian; d.by Danes; 1153-9-1538 CE: rebuilt; Maud, widow of Ranulph, Earl of Chester; 1557: remains inc.Repton School bldgs.; Derbyshire)
o Repton Abbey/Holy Trinity (f.Saint David; 6th c.CE: Anglo-Saxon double monastery; Saint Wystan’s Church; Derbyshire)
o Stydd Preceptory (f.Ralph de Fun and Sir William Meynill; 1136 CE: Knights Hospitaller; d.by Danes; 1543/4: gr.Charles, Lord Montjoy; Church of Saint Saviour; Derbyshire)
o Waingroves Preceptory (Knights Hospitaller; Derbyshire)
o Yeaveley Preceptory (f.1190-1540 CE: Knights Hospitaller; farmhouse; Stydd, Derbyshire)
o
o Axminster Monastery (f.757 CE: Saxon; f.Athelstan; 936-1535 CE; Devon)
o Axmouth Priory (f.Richard de Rivers, Earl of Devonshire; 1387-1414 CE: Benedictine; alien priory; 1552: gr.Walter Erle; Devon)
o Barnstaple Priory/Saint Mary Magdalene (f.Johel of Totness; 1199-1535 CE: Cluniac; alien priory; 1537/8: gr.William, Lord Howard; Devon)
o Bodmiscombe Preceptory (f.13th c.-15th c.CE: Knights Templar; absorbed by Buckley Abbey; Devon)
o Brightley Priory (Cistercian; Devon)
o Buckfast Monastery (f.13th c.-15th c.CE: Knights Templar; absorbed by Buckley Abbey; Devon)
o Buckfast Abbey/Our Lady (f.Ethelwerd; 1136 CE: Savignac; 1148-1539 CE: Cistercian; 1882: merged w/Benedictine; gr.Sir Thomas Dennys; Devon)
o Buckland Abbey (f.Amicia, Countess of Devonshire; 1278-1539 CE: Cistercian from Quarr; 1541/2: gr.Richard Greynfeld; Devon)
o Canonsleigh Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint John the Evangelist (f.William de Clarville, Lord of Burlescombe; 1161 CE: Augustinian; rf.Maude, Countess of Devon; 1285-1539 CE: Augustinian nuns; farm bldgs.; Devon)
o Careswell Cell (Cluniac; 1546/7: gr.John Etherege; Devon)
o Chudleigh Abbey/Saint Bridget of Syon (Bridgittine nuns; Devon)
o Cornworthy Priory (f.Edgecomb; 1205/38-1560 CE: Augustinian nuns; gr.Edward Harris and John Williams; Devon)
o Cowick Priory/Saint Andrew (f.1144-1538 CE: Benedictine; alien cell of Bec; 1451: gr.Eton College; 1464: gr.Tavistock Abbey; Devon)
o Dartmouth Friary (Augustinian; 16th c.: church of Saint Petrox; Devon)
o Dunkeswell Abbey (f.William de Briwere; 1201-1539 CE: Cistercian; 1534/5: gr.John, Lord Russel; 1842: Holy Trinity parish chapel; Devon)
o Exeter Cathedral Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary; Saint Peter (f.690 CE; 932: Benedictine nuns; Devon)
o Exeter Black Friary (f.1232-1538: Dominican; 1773: Bedford House; Devon)
o Exeter Grey Friary (f.1240-1538: Franciscan; moved by Bishop Bytten S of city; 1292-1303: moved behind N and W gates; Devon)
o Exeter Monastery (f.King Etheldred; 868 CE; Devon)
o Exeter Monastery (f.Athelstan; 932 CE; Danish raids; 1019: recalled by Canute; Devon)
o Exeter Polsloe Priory/Saint Katherine (f.1160-1536 CE: Benedictine nuns; demo.; country house; Devon)
o Exeter Nunnery (Augustinian nuns; Devon)
o Exeter Saint James Priory (f.Baldwin de Redverus, Earl of Devon; 1143 CE: Cluniac; daughter house of the Abbey of Saint Martin-in-the-fields, Paris; house-‘The Old Abbey’; Devon)
o Exeter Saint Nicholas Priory (f.William the Conqueror; 1087-1536 CE: Benedictine; 1540/1: gr.Sir Thomas Denys; 1820: private houses-monastic arch.restored; 1913: Exeter Corp.; 1916: museum; closed until 2008; Devon)
o Frithelstock Priory/Saints Mary; Gregory (f.Sir Robert Beauchamp; 1220-1536 CE: Augustinian; 1537/8: gr.Arthur Viscount Lisle; Devon)
o Hartland Abbey (f.Gytha, wife of Earl Godwin; 1161-9-1539 CE: Augustinian; 1545/6: gr.William Abbot; remains in Hartland Abbey house; Devon)
o Ipplepen Priory (f.1143-1414 CE: Augustinian; alien cell-daughter house of Saint Pierre-Rille; 1438: gr.Ottery Saint Mary; house-‘The Priory’; Devon)
o Kerswell Priory (Cluniac; Devon)
o Marsh Barton Priory/Saint Mary (f.1142-1539 CE: Augustinian; cell of Plympton; Devon)
o Modbury Priory/Saint George (f.1140-1430 CE: Benedictine alien priory; gr.Eton College; 1461-7: reverted to Tavistock Abbey; Devon)
o Newenham Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.Reginald de Mohun, Earl of Somerset; 1246/7-1539 CE: Cistercian; daughter house of Beaulieu; l.Duke of Suffolk; Devon)
o Otterton Priory (f.1087-1414 CE: Benedictine; alien priory-cell of Mont Saint Michael, Normandy; gr.Syon Abbey; 1539: gr.Richard Duke; mansion; Devon)
o Pilton Priory (Benedictine; Devon)
o Plymouth Black Friary (f.1431 CE: Dominican; Black friars Distillery; Devon)
o Plymouth Grey Friary (f.1383-1538 CE: Carmelite; 1513: private; Devon)
o Plymouth White Friary (f.1296/7-1538 CE: Carmelite; Devon)
o Plympton Priory/Saints Peter and Paul (f.904-1539 CE: Augustinian; 1121: church; Devon)
o Sidmouth Priory (f.11th c.-1414 CE: Augustinian-Benedictine; alien priory-daughter house of Mont Saint Michel; 1431: Bridgettine grange of Syon Abbey; Marlborough Hotel; Devon)
o Tavistock Abbey (f.Ordgar, Earl of Devonshire; 961/74-1539 CE: Benedictine; gr.John, Lord Russel; mansioin-‘The Bedford Hotel’; Devon)
o Teignmouth Abbey/Saint Scholastica (f.1662 CE: Benedictine nuns; daughter house of Ghent; Devon)
o Torre Abbey (f.William de Briwere; 1196-1539 CE: Premonstratensian; 1543/4: gr.John Saint Leger; country house-Torbay Corp.; Devon)
o Totnes Priory (f.John Aluredi; 1088-1536 CE: Benedictine; alien priory-cell of Saint Serge, Angers; 1543/4: gr.Catherine Champernoun; Devon)
o Totnes Trinitarian Priory (f.1271-1509 CE: Trinitarian; 1515: gr.vicars of Exeter cathedral; seized by Crown; 16th c.-1801: returned to vicars; Devon)
o
o Abbotsbury Abbey/Saint Peter (f.Orcius, steward to Canute; 1026-1539 CE: Benedictine; gr.Sir Giles Strangwaies; private; Dorset)
o Bindon Abbey (f.Robert de Burgo; 1172-1539 CE: Cistercian; from Little Bindon; 1540/1: gr.Sir Richard Poynings; private; Dorset)
o Bridport Friary (f.1261-1365 CE: Carmelite; Dorset)
o Bridport Priory (f.13th c.CE; Dorset)
o Cerne Abbey/Saints Peter, Edwold (f.Engleward; 987-1574/5 CE: Benedictine; gr.John Dudley; private house; Dorset)
o Chilcombe Camera (Knights; Dorset)
o Christchurch Priory (f.1150-1539 CE: Augustinian; earlier church demo.1094; Dorset)
o Cranborne Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Bartholemew (f.Aylward Sneaw; 980-1540 CE: Benedictine; mother/cell house of Tewkesbury Abbey, Gloucestershire; surrendered to Henry VIII; 1559/60: gr.Thomas Francis; Dorset)
o Dorchester Friary (f.1267-1536 CE: Franciscan; gr.Sir Edmund Peckham; Dorset)
o Forde Abbey (f.1136-1539 CE: Cistercian; 1146: tr.Brightley; mansion; Dorset)
o Frampton Priory (f.William the Conqueror; 1077-1571/2 CE: Benedictine; alien priory-daughter house of Caen, Normandy; gr.Sir Christopher Hatton; Dorset)
o Gillingham Friary (f.1267 CE: Dominican; Dorset)
o Holme Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1142-1547 CE: Cluniac; gr.John Hannon; 1746: parish church; mansion; Dorset)
o Horton Priory/Saint Wolfrida (f.Ordgar, Earl of Devonshire; 960-1547 CE: Benedictine; gr.Edward, Duke of Somerset; then to William, Earl of Pembroke; 18th c.: church; Dorset)
o Kingston Camera (Knights; Dorset)
o Little Bindon Abbey (f.William de Glastonia; 1149 CE: Cistercian; 1172: tr.Bindon; Dorset)
o Loders Priory/Saint Mary Magdalene (f.Richard De Redveriis; 12th c.CE: Benedictine; 1399-1414 CE: Cathusian under Saint Anne at Coventry; 1414 CE: Bridgetine nuns under Syon, Isleworth; Dorset)
o Lulworth Abbey/Most Holy Trinity (f.Thomas Weld; 1795 CE: Trappist monks from Val Sainte; 1817: returned to Melleray; Dorset)
o Mayne Preceptory (f.1471-1563/4 CE: Knights Hospitaller; gr.William Pole and Edward Downing; Dorset)
o Melcomb Friary (f.Rogers Esq.of Brianton; Dominican; 1543 CE: gr.Sir John Rogers; Dorset)
o Milton Abbey/Saint Michael and Mary (f.Athelstan; 938/64-1539 CE: Benedictine; gr.Sir John Tregonwall; 1771: mansion; school; Dorset)
o Muckleford Grange (Benedictine; alien cell-Tiron Abbey, Normandy; Dorset)
o Piddletrenthide Priory (d.-1354 CE: Benedictine; Dorset)
o Povington Priory (Benedictine; alien house-Beo-Hellouin, Normandy; Dorset)
o Shaftesbury Abbey (f.888-1539 CE: Benedictine; 1547/8: gr.William, Earl of Southhampton; walled garden; Dorset)
o Sherborne Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.998-1536 CE: Benedictine; gr.Sir John Horsey; public school; Dorset)
o Shapwick Grange (-1414 CE: Carthusian; Dorset)
o Spetisbury Priory (f.Robert, Earl of Mallent and Leicaster; Augustinian; 1543: gr.Charles Blount, Lord Mountjoy; Dorset)
o Spetisbury Priory (Benedictine nuns; alien cell-abbey of Saint Peter of Preaux, Normandy; Dorset)
o Saint Monica;s Priory, Spetisbury (f.1800 CE: Augustinian; 1861: Bridgettine nuns; 1887: Lateran; 1907-1926: Ursuline nuns; Dorset)
o Stour Provost Grange (f.1070-1471 CE: Benedictine; alien grange-Saint Leger Preaux; Dorset)
o Tarrant Abbey (f.1100-1540s CE: Cistercian nuns; Dorset)
o Wareham Nunnery/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.7th c.CE: Benedictine; alien house-daughter of Lira, Normandy; 876/1015: d.by Danes; Dorset)
o Wareham Priory/Lady Saint Mary (f.Robert, Earl of Leicaster; 12th c.-1536 CE: Benedictine; alien priory-cell of Tire Abbey, Normandy; gr.Thomas Reve, George Cotton; Dorset)
o West Lulworth Priory (f.William de Glastonia; 1149 CE: Cistercian from Forde Abbey; 1172: tr.Bindon; Dorset)
o Wimborne Minster/Saint Cuthburga (f.Saint Cuthburga; 705-1547 CE: Benedictine nuns; gr.Edward, Duke of Somerset; Dorset)
o Winterborn Monkton Grange (f.1214-1450 CE: Cluniac; alien grange; Dorset)
o
o Bradbury Cell (f.12th c.CE: Benedictine; Durham)
o Baxterwood Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary (f.1180-1186 CE: Augustinian; Durham)
o Durham Cathedral Priory/Saint Mary; Cuthbert (f.Bishop William of Saint Carileph; 997/1093-1540 c.CE: Benedictine; Durham)
o Egglestone Abbey/Blessed Virgin Mary, Saint John the Baptist (f.1198-1540 c.CE: Premonstratensian; Durham)
o Finchael Priory/Blessed Virgin Mary, Saint John the Baptist (f.Randal, Bishop of Durham; 1115 c.CE: Benedictine; 1534/5: gr.Dean of Durham; Durham)
o Haswell Grange (Benedictine; Durham)
o Jarrow Priory/Saint Paul, Jarrow (f.Saint Benedict and King Egfrid of Northumbria; 681/2 CE: Saxon; 1069: d.William I; 1072: Benedictine; cell of Durham; 1536: gr.William, Lord Eure; 18th c.: demo.; Durham)
o Neasham Priory/Saint Mary (f.1156 CE: Benedictine nuns; 19th c.: house-‘Neasham Abbey’; Durham)
o Wearmouth Abbey/Saint Peter (f.674-1545/6 CE: Benedictine; gr.Thomas Whitehead; Durham)
o
[NOTE 52: pertaining to astronomical sites: earthworks: tumulus (mound) represents a star; barrow represents a large star; cairn; standing stone; megalithic architecture]
[NOTE 53: Norse-Pharaonic Egyptian script similarities]
[NOTE 54: Andis Kaulins’s speculations of standing stones as megalithic geodetic astronomical tools (“star stones”; megalithic star-stone alignments by region and site, and stone markings/carvings matching those pertaining alignments) in conjunction with his linguistic (esp.Gaelic, Latvian, Pharaonic) hypotheses are compiled for study; see http://www.megaliths.net; North Ecliptic Pole at Paris, North Celestial Pole near Orleans at 3117 BCE]
[NOTE 55: There is an archeo-astronomical-geodetic correspondence between the Neolithic Megalith architecture (geomancy) and crop circle (geoglyph/agriglyph) location/formation, receiving the energy from stars and constellations, including sun, moon, and planets, through an intricate electro-magnetic (geo-energy) earth-grid meridian system; Hermetic Philosophy: “…as above, so below…”]
[NOTE 56: Possibile causes of crop circles: 1) Advanced and unknown high-technology of: a) humanity (governments, or private groups; motives: i) stage an alien invasion or contact; b) extra/intra terrestrial advanced tech.; 2) Planetary geophysics; 3) Gaeia communication; geo-electro-magnetic energetic response; 3) Water (aquifer) technology in conjunction with the Neolithic earth grid megalithic star map; Questions: 1) Why Wiltshire? Stonehenge? Avebury?; 2) Avebury-Cydonia, Mars connection: mirrored geomancy; 3) Near Earth Grid Point 11 (Scotland)]
[NOTE 57: Crop Circle/Agriglyphs phenomena in the modern era began in 1890/1972; after launching of first Martian orbiter, Mariner 9, in 1971; now over 10,000 formations found in 29 countries; 1980-99: generally demonstrates genuine crop circle phenomenon; after 2000: crop circles are generally hoaxes; according to Colin Andrews (veteran researcher on the subject), most (80%) crop circles of 2000 were man made (hoaxes), while 5% showed Earth’s magnetic grid altered between 3-5°; first record of crop circles was in 1678]
[NOTE 58: Crop Circle medium: wheat, oilseed rape/canola, corn, barley, rye; sorghum, soybean, rice]
[NOTE 59: World Crop Circles: 1993: Holland, Hungary, Switzerland, USA< Canada, Japan, Australia, Russia, France; 1994: Czech Rep., Krasnoyarsk-Siberia; 2006: hoaxes appeared in France, Hungary, Germany, Belgium, Netherlands, Italy; 2007: Germany-18 hoaxes; Netherlands-12 hoaxes; Poland, Czech Rep., Switzerland hoaxes; Italy-22 hoaxes]
[NOTE 60: Crop circle anomalies: genuine cc appear on Earth meridians/nodes of electro-magnetic energy, as well as over aquiferous ground (commonly in chalk soil)- creating an electro-magnetic field in water; subtle manipulation of local gravity field (anti-gravitational affect); plants bent not broken-folded 90°; blown and elongated nodes, superficial charring; off-center ‘herringbone swirl plant lay; off-center magnetic N by 4°; higher radiation levels; generates dowsing confirmations for electro-magnetic energy; changes in the plants at a cellular level; soil dehydration; bright lights (spheres/orbs) observed- creating crop circles; ufo sightings; animals disturbed (sickness/barking) prior and during; electrical like noises; power outages; genuine cc-MHz range, while microwave generated cc-GHz range; done quickly and usually in the dark; military intervention/monitoring; pilgrims; psychedelic and/or various energetic affects on human psyche/energy]
[NOTE 61: Crop Circles are ‘natural’ manifestations of energy (electro-magnetic/EM/light and sonic wave frequencies conducted through local life/earth) in conjunction with water (aquifers); the primary motion of energy is in a spiral; in conjunction with water (aquifers; southern England has the deepest aquifers in the world); spinning/spiraling electro-magnetic energy (EM) w/in water creates an energy field]
[NOTE 62: Crop Circles appear in certain conditions: the Sun is near solar minimum (22-year magnetic cycle; Sun’s magnetic field reversal point in 2006, affects solar wind and its interaction with the Earth’s magnetic field, which crop circles utilize; hence a decrease in crop circles since 1998)]
[NOTE 63: Crop Circle applications: anti-gravity technology design; resonant healing; advanced mathematics (ie. 5 Euclidean geometry theorems; a 6th based on Pyolemy’s Theorem of Chords; harmonic manipulation of time- sound contributes to the generation of crop circles); enlightenment: awaken humanity through glyph/symbols generated by sonic vibration through the electro-magnetic earth grid (diamagnetic system), to manipulate the local gravitational field (anti-gravity) through spinning the flow of water]
[NOTE 64: Crop Circle hoax signs: 1) construction lines under flattened crop; 2) satellite microwave generated: toxic electricity causing illness, lingering for one day only (differing from genuine crop circle energy resonance which is still felt years after); 3) generated from inside out]
· Adams Grave [MA]<CC: 2000: circle w/grapeshot>(Neolithic: long barrow; CC; Wiltshire)
· All Cannings <CC: 1999: bio-hazard symbol> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Allington Down <CC: 2000: platonic solids; hoax: star tetrahedron> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Alnwick <CC> (nr.Alnwick, Wiltshire)
· Alton Priors <CC>(see White Horse, Alton Barnes below)
· Andrew Lloyd Webber’s farm <CC: 1995: 5-pointed star in motion>
· Arbor Low Henge [MA](Neolithic- Altair in Aquila: 42 star stone egg-shaped henge- constellations/zodiac w/center of heaven; findings: human remains near central cove w/in circle; Youlgreave and Bakewell; Peak District, Derbyshire)
· Arthur’s (King) Cave (Bronze Age: star- Draco; Hereford)
· Arthur’s Stone [MA](3700-2700 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen-capstone 25+ tons; star stones- Bootes; Golden Valley; btwn.Dorstone-Bredwardine; Herfordshire)
· Ashbury <CC> (nr. Wantage, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Ashford <CC: 1994: circle, rings, semi-circles, lines; 5/8 mi. L> (nr. Ashford)
· Avebury [MA] <CC: wheat, oilseed rape, barley; crop circles: epicenter for 90% reported crop circles in the world; 1990-2001: Avebury Trusloe, Waden Hill, Windmill Hill, Molescroft, Berwick Bassett-Winterbourne Monkton, Avebury The Sanctuary, Silbury, Stone Avenue, Avebury Down, Yatesbury, Avebury Manor, Knoll Down; 1994: at stone circle- spider web; 1999: triangular tessellation/rhombic-dodecahedron tilings; HAARP-hoax?; octagonal array of circles- season finally; wheat; generated from outside-in; overlapping and underlapping lay proved that the entire area collapsed simultaneously; symbol for pi; 2001: hoax; 2002: Ridgeway, Devizes rd.; hoaxes; 2003: Green St.; 2005: hoax> (7000-4000 BCE: flints; 4000/2600 BCE: Neolithic: henge/stone circle; star- Perseus; Avebury, Wiltshire)
· Ballowall/Carn Gloose [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: barrow-72’ dia.; cairn; star stones- Circinus; near St.Just; southwest Cornwall)
· Badbury <CC: 2001: grid sphere encircled by ouroborus; sim.Euler’s Hollow Earth>
· Barbury Castle <CC: 1991: large tetrahedron with circles; 1997: ringed circle w/6 arrayed crescents; encodes Ptolemy’s theorem of chords- foundation of trigonometry; contains geometry of crop circle from Stretall, appearing 2wks later; canola; 1999: hexagonal-military tech.-hoax?; 2001: triangle inscribed w/in circle; 3 circles w/centerpoints at triangular vertex point intersections with outer circle; 2006: hoax; 2008: hoax-1991 inspired; pi to base 10; 2010: hoax; ball of light> (500 BCE: Iron Age: hill fort, earthworks/barrows; on Ridgeway route; Roman; near Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Barton Le Cley <CC: 2001: electro-magnetic diagram; hoax>
· Beacon Hill <CC: 1994: circles, rings> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Beardown Man [MA](Neolithic: menhir; near Devil’s Tor; Dartmoor)
· Beckhampton <CC: 1998: pentagrams; hoax; 1999: hexagonal-military tech?; 2000: 11-fold geo.spiral; 2001: 16 circles increasing in size from center w/outer circles partially shaded; hoaxes> (nr.Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Beelsby <CC> (nr. Grimsby)
· Belas Knap [MA](Neolithic: Cotswold-Severn Cairn: chambered long barrow on Cleeve Hill; star- Cepheus; near Cheltenham-Winchcombe, Gloucestershire)
· Berwick Bassett <CC: 2001: log./golden mean spirals; unfolding triangles w/in a circle>(Wiltshire)
· Bevis’s Thumb (Lower Paleolithic: 524000-478000 BP: near remains of “Boxgrove man”/Homo Heidelbergensis; near Chichester; 8000 BCE/ice age aftermath: Mesolithic: nomadic hunters arrive in Sussex from Europe cont.; 4300-3400 BCE: Neolithic: barrow, tumulus; near Ouse r.; Sharpsbridge; star- Aries, Hammal; near The Trundle; 1400-1100 BCE: Bronze: Beaker pottery; Iron: near Cissbury Ring: flint mines; near Compton, West Sussex)
· Bignor (Roman road, villa; Chichester)
· Birkrigg stone circle/Druid’s Temple [MA](1700 BCE: Bronze Age; 2 mi. S Ulverston, Cumbria)
· Birmingham (10400 BP: artifacts; Canterbury)
· Birmingham Cathedral/of Saint Phillip (1710-25 CE: Baroque; 1905 CE: Diocese; Birmingham, Canterbury)
· Bishops Cannings <CC: 1990: 2 celtic crosses w/thin rings, 4th ring intercepts 1st ring of adjacent circle; film: hovering shining object above field, operating slowly, disappearing at phenomenal speeds when approached; wherever balls hovered, small ‘grapeshot’ circles reflected in crop> (Vale of Pewsey; nr.Devizes, Wiltshire)
· Blackburn (Bronze Age: cinerary urn, tumulus; Iron Age: sacred spring; Roman: temple of Serapis; Anglo-Saxon; Lancashire, York)
· Blackburn Cathedral/of Saint Mary the Virgin with Saint Paul (1000+ BP: original Norman; 1820-1967 CE: Gothic Revival; 1926 CE: Diocese; Blackburn, Lancashire, York)
· Boscawen-Un [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle w/leaning pillar w/in; St.Buryan; Penzance, Cornwall)
· Boskednan stone circle/Nine Stones of/Nine Maidens [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle-10/22 stones, 69m peri.; nearby barrow; Boskednan, Penzance, Cornwall)
· Bradford Cathedral/of Saint Peter (r.1066 CE: Saxon original; 1400-1965 CE: Gothic; 1919 CE: Diocese; Bradford, York)
· Brentwood [Middle English “burnt wood”](Bronze Age: Celtic; 44 CE: Roman: road; Essex)
· Bridestones [MA](Neolithic site- chambered cairn; Bridestone Congleton- Birds Head, Aquila, Gardom’s Edge Stone, Devil’s Ring and Finger- Aquila, Hercules, Bird’s Head Gardom’s Edge- Aquilae; near Congleton, Cheshire)
· Brighurst <CC: 2000: iris>(Midlands)
· Bristol (60000 BP: palaeolithic; Iron Age forts at Leigh Woods, Clifton Down, Avon Gorge, and Kingsweston Hill; Roman: Abona/Sea Mills; bath, road, villas, forts; Norman: castles; Canterbury)
· Bristol Cathedral/Cathedral Church of the Holy and Undivided Trinity (1140 CE: original Augustinian Romanesque; 1220-1877 CE: Norman-Gothic; 1543 CE: Diocese; seat of Bishop; Bristol, Canterbury)
· Brown Willy Cairns [MA](2162-1746 BCE: Bronze Age: 9 cairns; from Stannon Stone Circle- autumn equinox rises over Brown Willy North Cairn; assoc. w/Rough Tor; Bodmin Moor, Cornwall)
· Bury of Saint Edmunds (Roman: Villa Faustina; Suffolk)
· Bythorn <CC: 1993: pentagram, circles, rings, 10 petals> (nr.Molesworth, Huntingdonshire, Cambridgeshire)
· Caerwent Magor [MA](Iron Age site: star stones- Ursa Major; Hereford)
· Calderstones Park [MA](Neolithic: 6 dolmen; druidical circle; caves- Ursa Major; Devil’s Ring and Finger; star stone markings- Aquila, Capricorn; Allerton, Liverpool)
· Caldicot [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: Sudbrook, Portskewett, Heston brake; star stones- Ursa Major; Monmouthshire)
· Calleva Atrebatum (Iron Age: Roman town; Silchester)
· Came Wood Chalbury [MA](Neolithic: star- Orion; Wiltshire)
· Canterbury (Paleolithic: axes; Neolithic: Bronze Age pots; Celtic-Cantiaci: main settlement; 1st c.CE: Roman: theatre, temple, forum, public baths; Anglo-Saxon-Jutish; Kent)
· Canterbury Cathedral (597 CE: Diocese; f.602 CE: original Saxon; 740-58 CE: mausoleum; 941-58 CE: lengthening nave; 997 CE: monastery est.; 1011 CE: damaged in Norman raids; 1077 CE: rebuilt after Norman conquest; 1174 CE: fire; 12th c.CE: monastery, choir; 14-16th c.CE: rebuilt nave; Gothic; Canterbury, Kent)
· Carlisle (Celtic-Cumbric: Caer castle Luel/Llewelyn; Roman: Luguvalium [Lat. “the place/wall of Lugus/local deity; Loki?; Welsh: Caerliwelydd; Scots Gaelic: Cathair Luail; York)
· Carlisle Cathedral/of the Holy and Undivided Trinity (1123-1540 CE: Norman-Gothic; 1133 CE: Diocese; Carlisle, York)
· Carn Brae [MA](Neolithic: star stones; measures Summer Solstice 3117 BCE at Hydra; southwest Cornwall)
· Castlerigg/Carles stone circle [MA](3200 BCE: 33m dia. stone circle-38 stones; Autumn Equinox appears over Threlkeld Knott; Keswick, Cumbria)
· Chadlington Hawk Stone [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Wing of Cygnus marks line of Milky Way and Winter Solstice, Ursa Minor, Pole Star, Draco, Deneb; 3m S Chipping Norton, Oxfordshire; South Central England; Neolithic enclosure at Knollbury, NW of Chadlington)
· Chedworth Roman Villa (Gloucestershire)
· Cheesefoot Head <CC: 1981: 52’ circle flanked by 2 smaller circles align. N-S; 1995: designs: magnetic energy, atoms, fertility/duality symbolism> (Winchester, Hampshire)
· Chepstow <CC> (nr. Chepstow, nr.Caldicot)
· Cherhill Down <CC: 1993: broken dumbbell, circles, ring, semi-cirles, lines; 2002: mandala: 75 radial spears divided concentrically into thirds; ea.tip is generated by a series of interlocking vesica piscis> (nr.Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Chester (Celtic-Cornovii; 70 CE: Roman: Deva Victrix; fortress; Cheshire, York)
· Chester Cathedral/of Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary (875 CE: convent; 907 CE: secular canons; 1093-1540 CE: Benedictine abbey; 1272-1530s CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1541 CE: Diocese; Chester, Cheshire, York)
· Chew Stoke (Upper Palaeolithic; Romano-Celtic: double-octagonal temple to Mercury; Bristol)
· Chichester/Noviomagus Reginorum (Romano-British foundations)
· Chichester Cathedral (681 CE: previous Saint Wilfrid cathedral; 1075 CE; 1187 CE: fire; 1199 CE: reconsecrated; Gothic-Norman; Angelican Diocese; Chichester, Sussex)
· Chicklade <CC> (btwn. Salisbury and Warminster, Wiltshire)
· Chilbolton <CC: 1999: computer fractal/Sierpinski Sieve: diamond grouping of circles; 2000: overlapping circles, spheres w/in spheres-molecular structures; hoax?; 2001: 2 crop glyphs-hoaxes: face (on mars?), 1974 Arecebo message, NASA sent into space; > (nr. Chilbolton Observatory; Stockbridge, Hampshire)
· Chilcomb Farm <CC: 1990: first pictogram; dumbbell-set standard for the month, advancing to haloes recognized as Sun God symbols-a universal message?> (Norman church-grave yard; Chilcomb, nr.Winchester, Hampshire)
· Chilton Foliat <CC: 2002: molecular spin; harvested soon after; hoax?>
· Chirton <CC> (nr.Chirton, Devizes, Wiltshire)
· Chiseldon <CC: 1996: vesica piscis/yin-yang; hoax?> (Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Chysauster (100 BCE: Roman village; Cornwall)
· Chun quoit (Penwith, Cornwall)
· Cissbury Ring (Neolithic: barrow, tumuli; star- Cetus, Aquarius; near Trundle and Brevis’s Thumb; Iron Age: hill fort; Worthing, West Sussex)
· Clemsford (early Roman settlement)
· Clemsford Cathedral/of Saint Mary the Virgin, Saint Peter and Saint Cedd (1200-1520 CE: Gothic; 1914 CE: Diocese; Clemsford, Essex)
· Coberly <CC> (nr. Cheltenham, Glouchester)
· Combe Gibbet Barrow (Neolithic/Bronze Age: long barrows; star- Triangulum; Combe; near Newbury)
· Coombe Hill [MA](3200 BCE: Neolithic: causeway enclosure; Object 6362; star stones- near Triangulum; near Jevington, East Sussex; South Downs, Southeast England)
· Corhampton Down <CC: 1980’s: 3 circles equilaterally spaced;> (Bronze Age: bowl barrows; Iron Age: circlular earthworks; Hampshire)
· Corringdon Ball [MA](Neolithic: star stones: curb circle- Pyxis; stone rows- Antila, Vela; Devon)
· Cornwall Apus [Abzu] [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Southern Triangle; southwest Cornwall)
· Coventry (Bronze Age: Corieltauvi; West Midlands)
· Coventry Cathedral/of Saint Michael (1095-1102; 1918 CE: Diocese; 14-15th c.CE: Gothic; 1956-62 CE: Modern; Coventry, West Midlands)
· Craddock Moor Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-16 fallen and overgrown stones; from here Brown Willy marked the midsummer sunset; ½ mi. NW from the Hurlers; Bodmin Moor; Minions, southwest Cornwall)
· Creswell Crags [MA](43000-10000 BCE; Neolithic; cave art; caves- Ursa Major: star stone markings- Aquila, Capricorn; near Creswell, Whitewell, Worksop; Derbyshire-Nottinghamshire border)
· Crickley Hill (Neolithic: star- Draconis; Hereford)
· Danebury Hill <CC: 1998: heptagonal ring; 1999: 9 groupings of circles; illustrating symbolic stages of the Moon covering the Sun during an eclipse-lunar eclipse 1999; 640’L; impressive spiral lay of plants; aligned with hill fort on magnetic-energy line; canola>(6th c.BCE: Iron Age: hill fort; ditch ring; Stockbridge; Winchester)
· Derby (Roman: camp Derventio; Saxon; Viking; Canterbury)
· Derby Cathedral/of All Saints (943 CE: original structure; 1350-1725 CE: Gothic-Neoclassical; 1927 CE: Diocese; Derby, Canterbury)
· Derbyshire Peak [MA](Neolithic star stone sites- Arbor Low Henge- Altair, Bridestones- Aquila, Bull Ring- Dove Holes village, Gardom’s Edge- Chesterfield, Five Wells- Buxton, Backstone Edge- Aquila, Minning Low Cairn, Thor’s Cave- Milky Way “hole”; Derbyshire)
· Devil’s Arrows [MA](Neolithic: menhirs- originally 5 stones; NNW-SSE alignment w/southern most moonrise; Boroughbridge, Harrogate, N Yorkshire)
· Devil’s Den <CC: 1999: hexagonal; 160’w; military tech.?> (Neolithic: cairn)
· Ditchley Earthworks (Neolithic: star- Cepheus, Milky Way; Hereford)
· Doll Tor [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle-6 menhirs; Birchover, Derbyshire)
· Dorchester [MA](Neolithic: star- Orion; Bronze Age: Sinodun hills; 8m SE Oxford; Oxfordshire)
· Dorset Cursus [MA](Neolithic: earthworks spanning 10km; star- Taurus; Dorset)
· Drizzlecombe/Thrushelcombe [MA](2000 BCE: Neolithic: cists/kistvaens; Bronze Age: stone rows, cairns, menhirs; 4 mi. E Yelverton; Dartmoor, Devon)
· Duggleby Howe (Neolithic: round barrow/mound; Great barrows of East Yorkshire)
· Duloe stone circle [MA](Bronze age urn full of bones was found underneath one of the stones, allegedly crumbled into the air; 5 mi. from Looe; Duloe, Cornwall)
· Durham (2000 BCE; York)
· Durham Cathedral/of Christ, the Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Cuthbert (635 CE: original; 875 CE: Viking raids; 997 CE: secular canons; Diocese; 1093-1540 CE: Benedictine priory; 1093-1133 CE: Romanesque; Durham, York)
· East Field (Alton Barnes) <CC: 1994; 1996: 500’ DNA spiral/sin-cos/light wave (enabling 3D objecets to be calculated into 2D) created by golden light beam projected from large red ball of light encircled by smaller yellow spheres; no damage to plants; 1998: heptagonal hoax?; 2001: pyramid w/rising sun; hoax?; hoax: replica of 1995 asteroid belt; 2003: hoax; 2007: hoax> (nr.Alton, Wiltshire)
· East Kennett <CC: 2000: square grid w/in a circle-1600 elements; hoax: heart; 2001: consecutive log.triangles w/in a circular ring; hoax?> (nr.Avebury, Wiltshire)
· Ely Cathedral (630 CE: previous bldgs.: convent; 970-1540 CE: secular canons; Benedictine priory; 1109 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Ely, Cambridgeshire)
· Escrick <CC: 1999: square and circle engraved w/rows of circles revealing the number ‘80’>(Selby, N Yorkshire)
· Etchilhampton Hill <CC: 1996: sanskrit similar to solar plexus chakra symbol in circle; ¾ mi. l.; 2002: hexagonal mandala: circle overlapping; symb.molecular DNA; harvested soon after; hoax?; hoax; 2006: hoax; 2011: cuboctahedron/VE; 2007: simple circle w/herringbone-type lay surrounded by wide ring, on a hill w/ancient well; 2008: hoax-Celtic cross> (nr.Devizes, Wiltshire)
· Exeter (Celtic?; 250 BCE: Hellenistic coins- trade with Mediterranean; 50 CE: Roman: Isca Dumnoniorum; Devon)
· Exeter Cathedral/of Saint Peter (1050-1400 CE: Norman-Gothic; Exeter, Canterbury, Devon)
· Fernacre stone circle [MA](Neolithic/Bronze; alignments w/Rough Tor due N and Brown Willy due E; Bodmin Moor; 2km NE St.Breward, Cornwall)
· Firle Beacon [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Procella, Capricorn; btwn.Eastbourne and Brighton; South Downs, East Sussex, Southeast England)
· Fishbourne (1st c.CE: Roman palace; Chichester)
· Five Kings [MA](Neolithic: menhirs; Upper Coquerdale, Northumberland)
· Flag Fen (10th c.BCE: Bronze Age/Iron Age: round house; Peterborough)
· Froxfield <CC: 1994> (Neolithic/Bronze Age: bowl barrows; Roman villa; Wiltshire)
· Gatcombe [MA](Neolithic: star- Ursa Minor; betwn. Minchinhampton and Avening; Gloucestershire)
· Giants Grave <CC: 1997: Hopi-Wiltshire connection: pentagram-golden mean/triangle-108 (moon), Pythagorean talisman of health; healing benefit> (Easton Hill; nr.Avebury, Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Gloucester (Roman: Colonia Nervia Glevensium/Glevum)
· Gloucester Cathedral/of Saint Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity (681 CE: monastery and convent; 823 CE: secular canons; 1022-1539 CE: Benedictine priory; 1089-1499 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Gloucester, Canterbury)
· Gog Magog Hills <CC: 2001: ‘the angel’; hoax?>(Cambridgeshire)
· Golden Ball Hill <CC: 2000: lotus-5 petals around 6; highest EM frequencies-rendering camera circuit boards obsolete, creating polarizing effect on LCD displays; 2001-2: hoax; 2004: hoax>
· Goodaver stone circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-23/28 menhirs +1 recumbent, 32.3m dia.; Bodmin Moor; near Bolventor; Altarnun, Cornwall)
· Goodworth Clatford <CC: 1996: physics of sound vibration-cymatics; plants are bent (consist.) at 90°, 6” from soil surface rather than 1” typ.; barley>(S Andover; Hampshire)
· Goonhilly Downs [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Lizard Penin.; Cornwall; Satellite Earth Station)
· Gough’s Cave (7150 BCE: oldest complete human skeleton; Cheddar, Somerset)
· Great Witcombe [MA](Neolithic Age site: star- Draconis; Roman villa; Glouchester, Glouchestershire)
· Grey Wethers [OE: “sheep”][MA](Neolithic: 2 stone circles-33m dia. w/N-S alignment to their center points; N circle-20 remaining stones; S circle 29 remaining stones; N Postbridge- 13th c.CE, Dartmoor, S Devon)
· Grimes Graves (3000 BCE: Neolithic: flint mining complex; Brandon)
· Grey Wethers (Postbridge)
· Hackpen [“serpent”] Hill <CC: 1997: 4th fractal-style (sim.Milk Hill tretactys); imperfection-missing circle in variable position; chaos theory: Strange Attractors-systems in dynamic flux; 1999: 9 interlocking crescents; Fibonacci curves; 500’ dia.; high EM freq.; visitors credit cards were demagnetized> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Hadrian’s Wall (122 CE: Roman wall)
· Hannington <CC> (N Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Hambledon Hill (Neolithic: causedway enclosures, earthworks; star- Taurus; Dorset)
· Harrow Hill (Neolithic: star- iota, Cetus; near Trundle and Brevis’s Thumb; West Sussex)
· Hembury [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Procyon; Devon)
· Henwood Down <CC: 1997: Ant>
· Hereford Cathedral/of Saint Mary and Saint Ethelbert (680 CE: Diocese; 1110-1250 CE: Gothic; 13th c.CE: Mappa Mundi; Hereford, Canterbury)
· Herefordshire Beacon (Iron Age: Midsummer Hill; star- Pole Star; Hereford)
· Hinton Parva <CC> (nr. Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Hoar Stones [MA](Neolithic: stone circle- 38 stones; 2 small mounds- remnants of barrows?; star- Cepheus; Corndon Hill; Chirbury, 3 mi. E Montgomery; Shropshire)
· Huneaton <CC: 1993: dumbbell-halo> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Hunter’s Burgh [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Indus-Pavo-Octans; East Sussex; Southeast England)
· The Hurlers [MA](Neolithic: 3 stone circles: southern circle: 35m dia.circ.-9 stones; central inner circle: 42m dia.slightly elliptical-14/28 stones survive; northern circle: 33m dia.circ.-15/30 stones survive; The Pipers-2 stones 100m SW center circle; petrifaction legend; star stones-Centaurus; near Tremar Coombe; .8km W Minions; Bodmin Moor, Cornwall)
· Inkpen <CC> (nr.W.Woodhay, Wiltshire)
· Kent <CC: 2000: 3 cycles of 12 growing circles w/in a colossal ring; Kent’s Cavern (37-40000 BP: oldest radiocarbon dated homosapiens in Europe; could have been occupied by homo neanderthalensis; cave system- hole in Milky Way near Canis Major; area of Mithras worship; Torquay, Devon)
· King’s Somborne <CC> (nr. Winchester, Wiltshire)
· Kingston Russel [MA](Bronze/Iron Age site: stone circle-18 stones; star- Orion; near Abbotsbury; Long Bredy, 7 m W of Dorchester, Dorset)
· Kirkstall Abbey (1152 CE: Cistercian monastery; Leeds)
· Knap Hill <CC: 1999: 9-fold; hoax>(Neolithic mound: star- Perseus; Avebury)
· Knowlton Circles (Neolithic: henge; star- Taurus; ruined Norman church; Dorset)
· Lamorna Cave (Neolithic: star stones- Large Magellanic Cloud; southwest Cornwall)
· Lane End <CC> (nr. Winchester, Wiltshire)
· Lanyon Quoit [MA](Neolithic site: dolmen; star stones- Centaurus; 2m SE Morvah; southwest Cornwall)
· Laughter Tor [MA](Neolithic: menhir; near Two Bridges; Dartmoor, Devon)
· Leaze Stone Circle [MA](1700 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle-16/22 menhirs, 4 fallen, 24m dia.; near Rough Tor, Tolborough Tor, Catshole Tor, Brown Willy, Garrow Tor; Bodmin Moor; St.Breward, Cornwall)
· Leicester (Celtic: Corieltauvi capital; 50 CE: Roman: Ratae Corieltauvorum: baths; Jewry Wall, artefacts; Anglo-Saxon; 9th c.CE: Viking; Canterbury)
· Leicester Cathedral/of Saint Martin (1086-1867 CE: Gothic; 1927 CE: Diocese; Leicester, Canterbury)
· Leper Stone/Newport Stone [MA](menhir-sarsen stone; Newport Essex)
· Lewes [MA](Neolithic: star stones: Aries-Capricorn-South Pole stars; obelisk tunnel- Aquarius; Mount Caburn, Males Burgh, Firle Beacon- Capricorn; Thunder’s Barrow Hill and Thunder Barrow Formalhaut- Piscis Austrinus; Alfriston, Wilmington, Folkington- Indus; Money Burgh- Winter Solstice of 3117 BCE; Saltdean- Grus; 5 Lords- Tuscana; Coombe Hill- Souther Triangle; Bishopstone, White Horse, Seven Sisters- Hydrus; Litlington- Octans; deciphered Tifinag Norse symbol script, [Tifinag: (gno-mai-n meri-n)” the measure of the <change of> the wall, or boat <of heaven>”; sim.Latvian: (ugunu maina meriens) “<heavenly> fire change measure”; sim.Pharaonic Egyptian hieroglyphs (chnum) Capricorn = “the boat”; East Sussex; Southeast England)
· Lichfield <CC: 1995: rings-mathematical theorem breakthrough in geometry> (Staffordshire, Cantebury)
· Lichfield Cathedral/of the Blessed Virgin Mary and Saint Chad (787-1089 CE: Diocese; 1200-1340 CE: Gothic; Lichfield, Staffordshire, Canterbury)
· Liddington Castle/Hill Fort <CC: 2001: 3 crescent rings forming 3 vesica piscis and central triangle; shield emblem of protection> (7th c.BCE: Bronze/Iron Age: hill fort, earthworks; near The Ridgeway; near Swindon; Wiltshire)
· Lincoln (1st c.BCE: Iron Age: Celtic: Lindon [Brythonic: “The Pool”]; round wooden dwellings; Roman: Lindium Colonia/Lindum: Newport Arch; Viking raids; 5 Boroughs; Canterbury)
· Lincoln Cathedral/of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Lincoln (1072 CE: Diocese; 1185 CE: destroyed by earthquake; 1185-1311 CE: Gothic; 1300-1549 CE: tallest bldg.in world; Lincoln, Canterbury)
· Littlebury Green <CC: 1996: egg of life: harmonics and electro-magnetic spectrum geometry> (Bronze/Iron Age: Ring Hill Fort W Audley End; Roman; Littlebury; 15m S Cambridge; near Saffron Walden. NW Essex)
· Little Woodbury (Iron Age: roundhouse; Salisbury)
· Lockeridge <CC: dragon>(Neolithic/Bronze Age; 3 mi. W Marlborough, Wiltshire)
· London (Bronze Age: spear heads; 43 CE: Roman: Londinium: wall, gates- Ludgate, Newgate, Aldersgate, Cripplegate, Bishopgate, Aldgate; Anglo-Saxon)
· Long Meg and Her Daughters/Maughanby Circle [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle-51 stones set in an oval, 100m long axis; petrifaction legend-coven of witches turned to stone by wizard Michael Scot; Penrith, Cumbria)
· Louth <CC> (nr. Louth)
· Lullingstone (Iron Age: hill fort; Roman: villa; castle; Kent)
· Lyneham Grim’s Ditch [MA](Neolithic Age site: star stone: Lyneham Stone- Cepheus, Pharaoh’s Emigrant Son; Hereford)
· Maiden Bower [MA](Neolithic: star stones; near Royston- Line of the Solstices betwn., Silbury Hill-top of Perseus; line of the Equinoxes- 3117 BCE; Bedford)
· Maiden Castle (Neolithic; star stone- Orion; Wiltshire)
· Manchester [der.Celtic: <mamm-> “breast-like <Old English: ceaster> “hill”]; (Celtic; Roman: Mamucium; fort-settlement; York)
· Manchester Cathedral/of Saint Mary, Saint Denys, and Saint George (Celtic stronghold; 1215 CE: predecessor church; 1421-1882 CE: Gothic; 1847 CE: Diocese; Manchester, York)
· Marden [MA](Neolithic: largest henge site for star- Pleiades; betwn. Avebury and Stonehenge; Wiltshire)
· Marlborough Downs <CC: 2004; 2009: canola; 2011> (nr.Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Martin’s Down (Neolithic: star- Orion; Wiltshire)
· Mayburgh Stone [MA](Neolithic: henge; King Arthur’s Round Table earthwork; stone markings: map of Far East, Austrailia, Americas; Canis Major, Carina, Volan, Musca, Dorado, Hydrus; 1m S Penrith; Eamont Bridge, Cumbria, Cumberland)
· Men-an-Tol [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Three stone; betwn. Madron-Morvah; southwest Cornwall)
· Mere <CC> (N Shaftesbury, Wiltshire)
· Merlin’s Barrow/Mound <CC> (2400 BCE: Neolithic: tumulus; legend: burial site of Merlin; at Marlborough College, Wiltshire)
· The Merry Maidens/Dawn’s Men [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-19 stones; petrifaction legend; near St.Buryan, W Penwith)
· Milk Hill <CC: 1991: Hebrew-post-Augustian Latin script: “I oppose acts of craft and cunning” (oppono astos); 1997: 200’L fractal version of Star of Solomon (sim.Silbury Hill but more complex); hexagonal geometry-using tretactys (10 points arranged in a triangle = 3 creative points of light/threefold-trinity invisible causal universe at the apex + 7 creative-manifest intervals of the pure music scale; building modules; wheat; Nick Riley farm; 204 circles-set new record; 1998: 9-fold; hoax; 1999: simple set of rings, circles and a crescent; 2001: 6 rotating arms held 413 circles; microwave energy-disappeared next day; deformed seeds; hoax; 2004: hoax-‘the bee’; caduceus/winged disk; ball of light; hoaxes> (nr.Alton Barnes White Horse; nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Minchinhampton (Iron Age: star stones: the Long Stone- middle of heaven, Ursa Minor, Pole Star <slot shows movement of 1000 years>, Draco, Hercules, The Adze/Axe, the Conger Eel at the Cord of the Fish; Tingle Stone Avening- Cepheus; Hereford)
· Mitchell’s [OE: “big” (micel)] Fold [MA](Bronze Age: stone circle-30 stones, 15 still standing; Corndon Hill; Stapeley Hill; Chirbury w/Brompton, Shropshire)
· Morcott <CC: 2001: hexagonal bow w/in circle>
· Morgans Hill <CC> (nr.Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Mulfra Quoit [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Centaurus, Lupus; southwest Cornwall)
· Nempnett Thrubwell (Neolithic Celtic: oval barrow/chambered cairn; Bath)
· Newcastle (2nd.CE: Roman: Pons Aelius; fort and bridge across the Tyne; Hadrian’s Wall; Anglo-Saxon; Norman; York)
· Newcastle Cathedral/of Saint Nicholas, Saint Denys, and Saint (1080-1500 CE: Gothic; 1216 CE: destroyed by fire; r.1359 CE; 1882 CE: Diocese; near Hadrian’s Wall; Newcastle, York)
· Nine Ladies [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; King Stone; petrifaction legend; summer solstice; btwn.Matlock and Bakewell near villages Birchover and Stanton-in-Peak; Stanton Moor, Derbyshire)
· Nine Stones of Altarnun [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-8 stones w/1 in center, 15m dia.; Bodmin Moor; 3km SE Altarnun; Cornwall)
· Nine Stones and Cerne Giant [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-9 stones; star- Orion; near Winterbourne Abbas; near Dorset; Wiltshire)
· Normanton Down Barrows <CC: 2002: dinergic spirals-hexagonal; 6 ribbons; star tetrahedron/octahedron; surrounded by 11 tumuli; EM in high MHz-tingling sensations, dizziness, disorientation for almost a week>(2600 BCE: Neolithic: long barrow; Bronze Age: round barrows; near Stonehenge; Salisbury)
· Northhampton (Bronze Age; 7-8th c.CE: Mercia; Norman; East Midlands)
· Norwich (near Roman: Venta Icenorum; 450 CE: Anglo-Saxon; 1004 CE: Viking raids; 25 churches; Norman; Norfolk)
· Norwich Cathedral/of Christ (1095 CE: Diocese; Benedictine priory; 1096-1145 CE: Norman-Gothic; Norwich, Norfolk)
· Notgrove [MA](Neolithic: star- Cepheus; Hereford)
· Nympsfield [Celtic/OE: “open land by holy place”; Celtic: “holy place” (nimet); OE: “field” (feld)] [MA](Neolithic: star- Ursa Minor; Hereford)
· Offa’s Dyke (Neolithic/Bronze: massive linear earthwork; star- tip of Scorpio c.2750 BCE; at border btwn. Wales and England; delineation btwn. Anglian and Mercia kingdoms; near Clun; Hereford)
· Ogbourne St.George <CC: 2003: subtle circles and crescents; central spiral motion rotating outwards in 8 movements (ref.octave); former Knights Templar property; wheat; circle dia.relating with diatonic music scale; 20 balls of light caught on film; oriented 19/20° to local sacred site>(3 mi.N Marlborough, Wiltshire)
· Old Winchester Hill <CC: 2001: simple rings-heptagonal proportions w/nested square; Neolithic EM grid line>(Neolithic; Hampshire)
· Oliver’s Castle <CC: 1992: 3 circles in triangle; 1994: interlocking crescents; sim.prior Steven Greer group visualization; 1996: snowflake hoax-Discovery Channel conn.?; first filming of crop circle forming by John Whaley- 16 sec. creation>
· Overton <CC: 1999: 2D unfolded icosahedron-10 hexagons with many smaller circle clusters; 2002: hoax>(Neolithic/Bronze/Iron Age: burrows; E Andover, Hampshire)
· Oxenwood/Shalbourne <CC: 2004: dragon feet glyph; plants bent at 45/51/60° (square/heptagram/hexagram); 200’L energetic discharge- tingling sensation felt in palms, high-pitch whispering in R ear, increased third eye activity; blown and elongated nodes w/superficial charring> (3000 BCE: Neolithic: long barrow; Wiltshire)
· Oxford Cathedral/of the Holy and Undivided Trinity (727 CE: convent; 1004 CE: secular canons; 1122-1524 CE: Augustinian priory; 1160-1200 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1546 CE: Diocese; Oxford, Canterbury)
· Peel Mesolithic: settlement; Neolithic farmers; 550 CE: Celtic monastery on Saint Patrick’s Isle; 800 CE: Noreseman; Neb r.; Isle of Man)
· Peel Cathedral/of Saint German (r.1700s CE: original; 1980 CE: Diocese; Peel, York, Isle of Man)
· Peterborough (Bronze Age; 44-8 CE: Roman: Durobrivae; fort at Longthorpe; Anglian: Medeshamstede; Norman; Canterbury)
· Peterborough Cathedral (655 CE: original Saxon abbey; 870 CE: d.by Vikings; r.1118-1237 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1542 CE: Diocese; Peterborough, Canterbury)
· Pewsey Vale (see ‘White Horse, Pewsey’ below)
· Pimperne [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: star- Taurus; 2m NE Blandford Forum, Dorset)
· The Pipers [MA] (Neolithic: 2 portal menhirs 120m SW center The Hurlers circle; view through portal frames Stowe’s Hill; petrifaction legend; finds: bronze dagger, gold beaker, beads, flint at Rillaton Barrow; near Tremar Coombe; .8km W Minions; Bodmin Moor, Cornwall)
· Portsmouth (pre-Roman; Roman: Portus Adurni: Canterbury)
· Portsmouth Cathedral/of Saint Thomas (1180-1991 CE: Germanic Romanesque; 1927 CE: Diocese; Portsmouth, Hampshire, Canterbury)
· Ridgeway <CC: 2002: hexagonal; tesseract-true crucifix, cathedral floor plan; harvested soon after; hoax?; 2011> (Avebury; nr. Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Ridhadh/Rollright Stones [MA](2500 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle; 1800 BCE: King’s Stone- Deneb; 4000-3500 BCE: Whispering Knights- portal dolmen; star- Cygnus; Long Compton, Great and Little Rollright villages; 2.5m N Chipping Norton)
· Ripon (Brythonic-Brigantes; large circular earthwork; Roman: near North Stainley; 7th c.CE: Anglian Northumbrian; 658 CE: Christian church: Inhrypum; Norman; York)
· Ripon Cathedral (pre-660 CE: monastery; 672 CE: Saxon predecessor church; 10th c.CE: college; secular canons; 1160-1547 CE: Anglo-saxon-Gothic; 1836 CE: Diocese; Ripon, York)
· Rochester (Neolithic: Belgic settlement near Kit’s Coty House; Celtic-Cantiaci: ½ oppidia; 43 CE: Romano-British: Durovernum Cantiacorum; Kentish kings; Norman; Kent, Canterbury)
· Rochester Cathedral (604-1080 CE: secular canons; Diocese; 1179-1238 CE: Norman-Gothic; Rochester, Kent, Canterbury)
· Rollright Stones/The Kings Men Stone Circle [MA]<CC>(3000/1792 BCE: star stones circle: Vega/Lyra, Draco [sim.Pharaonic Egy.: Menit (chain) “counterweight” to sistrum musical instrument, originally made with stones and a turtle shell]; 3800-2300 BCE: Kings Stone (shaped like a swan’s head- Deneb in Cygnus, Aquila, Cepheus, Cassiopeia, Pegasus; surrounded by cardinal megaliths; Virgo stone; triangulation of stones: Broken Megalith- gamma Cygnus; Whispering Knights (5 megaliths)- 5 stars at epsilon Cygnus; near Dragon Hill, White Horse, Uffington Castle, Wayland’s Smithy; Long Compton, Warwickshire)
· Rombalds Moor [MA](Neolithic site- 25mi. dia.; petroglyphs; rock drawings; star stones- Brimham Rocks, Denton Moor, Middleton Moor, Ilkley Otley, Otley Chevin, Harewood, Eller Wood, Harrogate Spofforth, Snowden carr- Pavo the Peacock; Pateley Bridge- Indus; Skipton Moor- Tucana; Rivock Edge, Baildon Moor- Octans; betwn. Ilkley and Keighley; W Yorkshire)
· Ropley <CC: 1995: most complex design to date-98 circles, varying in 1-15’ w; solar system w/central sun, planets, and thin orbital lines; hypothetical archeoastronomy: diatonic ratio of planetary positions relative to Earth (not shown): 11/1903-Wright Brothers and 7/11/1971 Mariner 9- Martian messages? (latest Crop Circle phenomenon begins 1972); time difference from events 67 years-number of asteroids in design; barley> (Hampshire)
· Rough Tor [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Corona Borealis; 3m SE Camelford and 1m NW Brown Willy; Cornwall)
· Roundway Hill <CC: 1996: sanskrit similar to root chakra symbol in circle; 1997: computer chip: ¾ mi.L; square w/in circle w/grid of 28x25 lines; 150’N cc: 6-pointed star; 1999: 3D cube; double heptagram star-12 circles; hexagonal array-19 circles; 2011: cuboctahedron/VE> (nr.Devizes, Wiltshire)
· Royston Therfield Heath [MA](Neolithic: barrows; near Maiden Bower- Lacework Nebula/NGC 6960; Line of the Solstices betwn., Silbury Hill-top of Perseus; line of the Equinoxes- 3117 BCE; near Bedford; Royston Cave; Royston-Therfield, Hertfordshire)
· Rudston Monolith [MA](1600 BCE: menhir-tallest in UK; star stone: Eridanus, Hydrus; 1600 BCE: Rudston, Bridlington, East Yorkshire)
· Saint Albans (Celtic-Catuvellauni settlement at Prae Hill; Roman: Verulamium; Ver r.; Mercian Angles: Verlamchester; 1st draft Magna Carta
· Saint Albans Cathedral (793 CE: Offa’s abbey; 976-1539 CE: Benedictine abbey; 1877 CE: Diocese; 1077-1893 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; Saint Albans, Hertfordshire, Canterbury)
· Saint Edmunds Cathedral/of Saint James (1065 CE: original; 1503-2005 CE: Gothic-Revival; 1914 CE: Diocese; Bury of Saint Edmunds, Canterbury)
· Saint Paul’s/London Cathedral (604 CE: Diocese; original Saxon; 962; 1088-1314; 1677 CE: Baroque; London, Canterbury)
· Saint Paul’s/Dundee Cathedral (604 CE: Diocese; original Saxon; 962; 1088-1314; 1677 CE: Baroque; London, Canterbury)
· Salford (Stone Age; Neolithic: Bronze Age: flint arrow heads and tools; Roman; Manchester)
· Salisbury (Neolithic settlement on hilltop of Old Sarum; became hill fort in Iron Age; Roman: Sorviodunum; Saxon: Searesbyrig; Norman: Seresberi; Wilthire, Canterbury)
· Salisbury Cathedral/of Saint Mary (1220-1320 CE: Early English Gothic; 1220 CE: Diocese; Salisbury, Wiltshire, Canterbury)
· The Sanctuary <CC: 1998: hexagonal/VE: 3 outer rings, 6 inner petals> (Neolithic; near Stonehenge-Avebury, Silbury Hill, West Kennet Long Barrow; 5m W Marlborough, Wiltshire)
· Scorhill/Gidleigh/Steep Hill Stone Circle [MA](8500 BCE: Mesolithic: flint artefacts; Bronze Age: stone circle-23 stones and 11 recumbent, 27m dia.; The Tolmen- stone w/lg. donut-shaped hole; archeoastronomy- sun sets over stone’s tip on midsummer’s eve; Gidleigh, Devon)
· Sheffield (12800 BP: Upper Paleolithic; Iron Age: Pennine-Brigantes; Celtic: k.Elmet; Don and Sheaf r.; York)
· Sheffield Cathedral/of Saint Peter and Saint Paul (9th c.CE: predecessor church; Sheffield cross; 1200-1966 CE: Gothic-Modern; 1914 CE: Diocese; Sheffield, York)
· Silbury Hill/[‘The Hill of the Shining Ones’(Anunnaki)] <CC: 1988: cardinal quintuplet-4 outer circle rotated clockwise, 5th central counter-clockwise; 1990; 1992: Celtic/Buddhist: mandala/dharma wheel; 1997: 250’, 126 circles; wheat; near another cc-canola 600’N; a 2nd cc appeared 12’ from the 1st 3 days later; on St.Michael Line, Lei line; 1998: hoax; 1999: Mayan/Aztec star/cross; 2000: 8-fold geometry-double square w/in 4 rings; rings w/square, pentagon, hexagon w/in, encode Hawkins’ Theorem III, octave ratio; 2001: hoax; 2002: hoax; 2004: hoax: Egypto-Greek winged disc; 2010: single circles on tumulus magnetic node; 40cc>(2750 BCE: Neolithic: Avebury-Stonehenge assoc.site; largest mound/tumulus in Europe- 40m h; star- Perseus; sim.Chinese- Da Ling/Great Mound; Avebury)
· Silent Circle CCIC <CC> (Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Snape boat grave (6th c.CE: barrows, ship burials; Snape Common, Aldeburgh, Suffolk, E Anglia)
· Snowden Carr/Crags [MA](Neolithic: stone circle, cairns, rock carvings; The Skull Stone- Large Magellanic Cloud and Southern Stars; Tree of Life Stone- Tucan, South Pole Star; Askwith Moor; N Yorkshire)
· Sompington <CC: 2002: dinergic spirals>
· Southwark (Prehistoric burial mounds; Roman: road junction- Stane St., Watling St.; Borough High St.; Thames r.; London)
· Southwell (Corieltauvi; Roman; Saxon; London)
· Southwell Minster Cathedral/of the Blessed Virgin Mary (627 CE: predecessor church; 1108-1300 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1884 CE: Diocese; Southwell, York)
· Southwark Cathedral/of Saint Saviour and Saint Mary Overie (1106-1897 CE: Romanesque-Gothic; 1905 CE: Diocese; Southwark, London, Canterbury)
· Stannon Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic/Bronze Age: stone circle-47 menhirs and 30 recumbent, 2 displaced stones, 42.6m dia., 4 outlying jagged stones; findings: pottery, flint tools, whetstone; alignments: Rough Tor; sunrise w/neighboring hills; Dinnever Hill; 2.5 mi. SE Camelford; Bodmin Moor; St.Breward, Cornwall)
· Stanton Drew [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circles-27/30 stones; Great Circle-113m dia.; second largest to Avebury; findings: round bell, bronze serpent ring; flints found ¼ mi. away; Stanton Drew, Bristol, Somerset)
· Stanton St.Bernhard <CC: 2001-2: hoax: mandala; 2011> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Star Carr (8770 BCE: Mesolithic: Maglemosian culture; Scarborough) Sutton Hoo (600 CE: Bronze Age: mounds; Woodbridge)
· Stonehenge [MA]<CC: 1991: epicenter for 90% reported crop circles in the world; L-R insectograms; near neolithic sites of Silsbury Hill, Avebury, Winterbourne Stoke, Nine Stones and Cerne Giant; 1996: Julia Set-149 circles in 45min. during day; 1997: 32 snowflake-6 arrayed kabbalahs-trees of life (30 circles X 6 = 180 circles + center and overall perimeter = 182) in same field as Julia Set>(2500/1750 BCE: Neolithic: lunar-solar calculator: Heel Stone-Summer Solstice in 1749 BCE, Cancer, Hydra, Leo, Ursa major, Orion; Slaughter Stone- Ursa Major/Minor, in line w/North Celestial Pole Star and Summer Solstice point on the ecliptic; outer ring: 56 Aubrey Holes- eclipse prediction based on 18.6 year cycle of eclipses x3; next ring in: 30 “Y” Holes- 30 day “full” months; next ring in: 29 “Z” Holes- 29 day “defective” months; 29/30 megalithic star stones <hypothesized 29/30 standing, (f)allen, (m)issing megaliths; megaliths = 12 zodiac houses, stars, constellations; (S)arsens 1-30 in outer ring of megaliths marked moon stations in stars; S1- Head of Hydra, Cancer; S2-Alphard, Hydra-neck; S3- Ursa Major-f, Cygnus, Aquila-b; S4- Head of Leo; S5-Leo Denebola-Covus; S6- Coma Berenices and Virgo-Spica; S7- Bootes-Arcturus; S8f- Libra; S9f- Autumn Equinox; S10- Corona Borealis; S11- Serpens Caput; S12f- Scorpio; S13m- Sagittarius; S14f- Aquila; S15m- Capricorn; S16- Aquarius; S17m- Cygnus-Deneb; S18m- Aquarius bucket; S19f- Lacerta, Pegasus; S20m- Pisces; S21- Cassiopeia; S22- Andromeda; S23- Aries; S24m- Spring Equinox; S25f- Perseus, Pleiades; S26f- Taurus; S27- Auriga; S28- Orion-f, Corona borealis, Serpens Caput; S29- Canis major-f, Ophiuchus-b; S30- Cancer, Canis Minor; 19 Bluestones- Metonic Cycle, 19 year lunar cycle; 10 (T)rilithons forming an inner horseshoe, oriented NE, the Avenue in line w/Heel and Slaughter Stones, represented 10 constellations along the ecliptic; open end of horse shoe excluding Cancer-Hydra, Leo toward Summer Solstice; T51- Virgo, Coma Berenices; T52- Bootes; T53- Scorpio head-f; T54- Scorpio-b; T55- Sagittarius; T56- Capricorn; T57- Andromeda, Cassiopeia; T58- Triangulum, Aries; T59- Perseus, Pleiades; T60- Taurus>; surrounding barrows (2-2.5m rad): stars- Pole Star in 3000 BCE; Level of the Equinoxes, Ara and Scorpio, Antares, Libra, Lupus, Hercules, Sagittarius, Aquila and Sagitta, Cygnus, Lyra, Cepheus, Andromeda and Aries, Cassiopea, Perseus, Auriga, Draco, Eridanus, Aldebran, Orion, Gemini, Procyon, Ursa Major, Leo, Corvus, Virgo-Spica, Hydra, Corvus, Summer Solstice-3117/1657 BCE; earthworks- Milky Way; marked Pole Star in 1750 BCE; <CC: Earth measure analogy (squaring the circle): relates also w/crop circle geometries; Earth’s diameter- 5040 mi.; Earth’s + Moon’s <relationship by divine numbers> radius- 7920 mi.; :: inner ring- 50.4’; outer ring- 79.2’; common number found in ancient cultures (Plato describes these numbers as the key symbols in the divinely ordered creation; Crooked Soley crop circle on 8/2002 echoes proportion w/inner ring at 504, and outer ring 792; 504+792=1296=6x6x6x6; in an ancient Greek alphabet the numbers correspond w/letters of a name, “goddess of all creation”; perfect rotating DNA spiral): 5040 = 1x2x3x4x5x6x7; 7920 = 8x9x10x11>; 2m W of Amesbury, 8m N Salisbury; Wiltshire)
· Stowe’s Pound [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Virgo; hillfort; Devon)
· Stowell <CC: 1998: heptagon>(N Cirencester; Gloucestershire)
· Stretall <CC: 1997: ringed circle w/partial triple array flower of life juxtapositions-tetrahedral; encodes Ptolemy’s theorem of chords- foundation of trigonometry; geometrical connection w.Barbury Castle> (Essex)
· Stripple Stones [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; menhir/standing stone; star stones- Bootes; Hawk’s Tor; vallum/Roman camp; Bodmin Moor; 10km NE Bodmin; Cornwall)
· Sugar Hill <CC: 1999: 9-fold star in a circle; magnetically aligned w/tumuli>
· Sutton Hoo (Neolithic/Bronze Age: mounds, pits containing flint-tempered earthenware pots, cremations, ship burial; Iron Age/Romano-British; 6-7th c.CE: ship burial; ceremonial helmet; near Woodbridge, Ipswich/Gipeswic, Suffolk)
· Swinside-Black Combe Seahenge/Holme I [MA](2049 BCE: Bronze Age: stone circle in the sea; Lake District/Holme-next-the-Sea, Norfolk, Cumbria)
· Temple Balsall <CC> (nr.Balsall Common, Knowle; SE Birmingham)
· Thornborough Henges/Circles (3500 BCE: star map: calculate position ofg North and South Polar Stars w/celestial meridian 3117 BCE; Hydrus, Tucane, Southern Pole Star, Octans, Apus, Triangulum, Ara, Antares; Masham; Ripon, North Yorkshire)
· Tintagel/Trevena [MA](Neolithic: star stones; castle; legends surrounding King Arthur and the Round Table; Cornwall)
· Tregeseal East/The Dancing Stones (Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle; petrifaction legend; near St.Just, W Penwith)
· Tregiffian [MA](Neolithic: chambered tomb w/entrance lined w/stone slabs; star stones- Southern cross/crux; Lamorna, southwest Cornwall)
· Trethevy Quoit [MA](Neolithic: dolmen; star stones- Hydra, Leo; 9th c.CE: King Doniert’s Stone- commemorates K.Dungarth of Cornwall; Tremar Coombe, N of Liskeard; St. Cleer, Cornwall)
· Trimontium (140 CE: Roman fort; Newstead)
· Trippet Stone Circle [MA](1700 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle-8/26-28 menhirs, 31.9m dia.; alignments- Arcturus over Rough Tor; findings: flint flakes; Bodmin Moor; 9km NE Bodmin, Cornwall)
· The Trundle [OE: “circle”] (Neolithic: barrow, tumuli; Slindor Earthworks; Devil’s Ditch; star- Piscis and ecliptic intersection; Harrow Hill and Brevis’s Thumb; Saint Roche’s Hill; 3m N Chichester; West Sussex)
· Uley [MA](Neolithic: star- Ursa Minor; btwn. Dursley and Stroud; Gloucestershire)
· Verulamium (Roman city; St.Albans)
· Vindolanda (Roman fort; Hadrian’s Wall; Chesterholm)
· Wakefield <CC: 2000: rotating hexagon: 55 large circles, 300’ dia.>(Neolithic-Iron; W Yorkshire)
· Wakefield Cathedral/of All Saints (11th c.CE: predecessor church; 1300-1905 CE: Gothic; 1888 CE: Diocese; Wakefield, York)
· Walmsgate <CC> (btwn. Louth and Alford)
· Wansdyke [root: “Woden’s dyke”] (Neolithic/Iron age sites: earthworks- runs from 250 BCE: Iron Age Celtic: hill fort-Maes Knoll in historic Somerset, at E end of Dundry Hill S of Bristol to Savernake Forest near Marlborough; star- Perseus, Milky Way; Roman boundary?; Wiltshire)
· Warminster <CC: 1972: circle w/smaller circle> (Iron Age: hill forts; Wiltshire)
· Waylands Smithy Long Barrow [MA]<CC>(3700 BCE: ph1- oval barrow; 3400 BCE: ph2- stone chambered long barrow; 3000 BCE?: Neolithic Age sites: Almaak, Mahik; star stones- Andromeda; Hoar Stones <3> of Enstone- the lizard, Lacerta, Draco, Cepheus, Pole Star, Andromeda-Almaak, Cassiopeia, Aries, Pegasus-Scheat, Mahik = Cord of the fish; barrow: marks line from Andromeda to Pegasus; near 1400-600 BCE: Uffington White Horse Hill and Uffington Castle/hill fort; Ashbury, E Swindon; Oxfordshire)
· Wells (Roman; Saxon)
· Wells Cathedral/of Saint Andrew (705 CE: first church; 909 CE: Diocese; 1176-1490 CE: Early English Gothic; Wells, Somerset, Canterbury)
· West Kennet Long Barrow [MA]<CC: 1998: 33-petaled Beltaine Wheel; canola; preceeding power outages; electrical equip.malfunctions w/in design- playback equip. sped up; 1999: Mayan/Aztec cross/compass>(3600 BCE: Neolithic: menhirs-chambers; Severn-Cotswold tombs; artefacts: grooved ware sim.Windmill Hill; local legend: visited on Midsummer Day by a ghostly priest and a large white hound; star stones- Perseus; Silbury Hill, Avebury, Wiltshire)
· West Overton <CC: 2002: dinergic spirals; sim.blood corpuscle axenome microtubule; 2003: series of 6-petaled flowers in harmonic expansion, lightly brushed; expanding rings marking intersection points of petal tips, defined by ratios matching the music scale notes; spirals and music: sound-light mechanism in manifesting process/cc phenomena; petals formed by log.spirals- opposite sides of petal requires twist of 19.47° (sim.planetary physics- star tetrahedron w/in a sphere)>
· West Stowell <CC: 1994> (Wiltshire)
· West Tump (Neolithic: star- Draconis; Hereford)
· Westwoods <CC> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Weyhill <CC: 1998: 1st of year; 2 overlapping circles w/rings; (7) heptagonal geometry-geo.of soul; pure music scale intervals> (nr. Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· White Barrow/White Tor [MA](Neolithic: long barrow; star stones- Hydra’s head; Salisbury Plain; Tilshead, Wiltshire)
· White Hawk [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Grus; East Sussex; Southeast England)
· White Horse, Alton Barnes/Alton Priors (South Field) <CC: 1990: 5 single circles, 2 dumbells, 1 flanked by 2 boxes, claw, 603’,trident symbol of transformation; thousands of giddy pilgrims; Army intervention- led to the Bratton Castle hoax which turned off the phenomenon to the public; 1991: pictogram: keys-1 is 360’ l; 1994: magic eye; 1997: 4D tube torus: 300’; 12 circles arrayed about center-kabbalistic-12 sephira; dowsing: perfect stillpoint of energy at formations energy center, 28’ from physical center; helicopter disruptions to drum circle; 1999: Quetzalcoatl serpent; military ultrasonic experiements w/black helicopters; not interested in Knaphill hoax 100’ away; beneath Adam’s Grave long barrow; 2000: South Field: daisy-8/16-fold geometry; morning dew on wheat undisturbed; pentagonal ratio of concentric EM bands detected w/dowsing and meditation; hoax; 2002: series of knots decreasing by 2/3 (water/life proportion); ‘rope’ effect symbolic of the spiral movement of water; at 19.5°N (sim.latitude of upwelling in planetary physics; wake produced by object in water) of this cc, a geodetic EM line connects w/Adam’s Grave Neolithic Long Barrow; 36 elements; hoax: ‘Signs’; hoaxes; 2003: hoax; 2004: hoax; 2008: hoax> (Alton Barnes; nr.Marlborough, Wiltshire)
· White Horse, Bourton <CC: 5 pointed star> (Bourton>
· White Horse, Cherhill <CC: 1998: 18 circles; 1999: 9-fold triangles and 6 interlocking crescents; aligned w/Neolithic structures and EM line> (effigy matches the constellation Taurus rising; nr.Marlborough, Wiltshire)
· White Horse, Hackpen Hill <CC> (nr.Swindon, Wiltshire)
· White Horse, Pewsey <CC: Pewsey Vale: 2002: shell: cochlea spiral (rep.interplay of light, gravity, and sound); diminishing radius at 2/3 proportion; angles and dimensions ref.sunspot cycles (11.06 years); shell angle 39° (2x19.5°); 29 lines ref.leap lunar month, bones in human skull; 2004: simple 3 circles and ring; blown nodes, elongated nodes, charring on plants; 2009?; 2010: hoax>(nr.Pewsey, Wiltshire)
· White Horse, Roundway <CC> (N Devizes, Wiltshire)
· White Horse, Uffington <CC> (nr.Wantage, Wiltshire)
· Whitesheet Hill (Neolithic: causeway, camp, 1800 BCE- 12 barrows/burial mounds; Iron Age: fort; star- Taurus; Wiltshire)
· Will Butler Farm <CC: 1997: ant; dowsing levels high- on Lei line, oriented 78°E; dowsable square around top circle’s center; arms/antenna oriented towards old trees marking the geodetic line; geodetic line marker; monitoring unmarked military helicopters appeared shortly after event at 4am> (60 mi. E Stonehenge)
· Wilton <CC> (nr. Hungerford, Wiltshire)
· Winchester <CC>(Iron Age: valley fort, Oram’s Arbour; Roman: Venta Belgarum; Anglo-Saxon; Hampshire, Canterbury)
· Winchester Cathedral/of the Holy Trinity, and of Saint Peter and Saint Paul and Saint Swithun (642 CE: original pre-Norman; 650 CE: Diocese; 1079-1912 CE: Norman-Gothic; Winchester, Hampshire, Canterbury)
· Windmill Hill <CC: 1993: dumbbell; 1996: 198-circle, 1000’w triple Julia Set; braided wreaths, nests, catherine wheels, central huts; 1999: 400’; square w/in circle w/230 inner circles accentuating a cross/compass; aligned to various barrows atop the hill; 2000: 3D square grid w/alternating rectangles, like a ball stretching through a net; curvature of light around planets; 4D-quantum physics; camera failures w/in formation; 2000: 2) magnetic grid; splitting chromosomes (crop circle energy disrupts chromosomes in plants); brain hemispheres; 2001-2: hoax; 2003: series of nested pentagrams, formed by crescents, in outward expansion; hoaxes>(Neolithic causeway; star- Perseus; nr. Silbury Hill; Avebury)
· Windmill Tump/Rodmarton Chambered Tomb (Neolithic: stone tumulus/barrow; star- Ursa Minor, Polaris; Rodmarton, betwn. Cherington and Tarlton; Stratford-on-Avon, Gloucestershire)
· Winterbourne Abbas (Neolithic: star- Orion; near The Nine Stones- stone circle; SW Dorset)
· Winterbourne Stoke <CC: 1989: 4-quatered swastika>(Neolithic: star- Pleiades; 5km W Stonehenge; Wiltshire)
· Windmill Hill <CC> (nr.Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Winsford <CC: 1994: scorpion- 13 circles and moon symbols> (nr.Avebury, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Woodborough Hill <CC: 1998: heptagonal; 2000: sunflower-golden mean spiral-22x2 spirals (clockwise and counterclockwise), 14 radual circles; 2001: hoax-yearly homage of German researchers Hans Kyborg and Joachim Koch; referenced and influenced local energy grid; 2004: Kyborg and Koch-hoax> (nr.nr.Devizes, Wiltshire)
· Woodhenge <CC>(Neolithic: timber circle; star- Pleiades; Avebury; Wiltshire)
· Worcester (400 BCE: Neolithic: near Severn r.; Roman: fort; Vertis?; Anglo-Saxon: Weorgoranceaster; Canterbury)
· Worcester Cathedral/of Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary (670 CE: Diocese; 1084-1504 CE: Norman-Gothic; Worcester, Canterbury)
· Worlaby <CC> (btwn. Louth and Alford)
· Wroxeter (Roman city; Shropshire; Shrewsbury)
· Yatesbury <CC: 2001: hoax> (nr.Avebury, Marlborough, Swindon, Wiltshire)
· Yeavering (Bronze Age: burials; Kirknewton)
· York [Celtic-Brythonic: “place of the yew trees” (Eborakon); Welsch: yew = efrog; Irish Gaelic: eabhrac; Scottish Gaelic: eabraig; Anglian: Eoforwic; Germanic root: “boar” eburaz](8-7000 BCE: Mesolithic; Brigante; 71 CE: Roman: Eboracum; 7th c.CE: Anglian; 866 CE: Viking/Danish: Jorvik; Norman: York)
· York Minster Cathedral/of Saint Peter (627 CE: predecessor church; 741 CE: destroyed by fire; r.10th c.CE; 1075 CE; destroyed by Danes; 1080-15th c.CE: Gothic; 314 CE: Diocese; York, York)
· Zennor Quoit [MA](2500-1500 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; star stones- Centaurus, Lupus; Zennor, St. Ives, southwest Cornwall)
ISLE OF MAN: [ma]
· Ballakelly [MA](Neolithic site: horse shoe shaped star stone- Corona Australis)
· Cashtal yn Ard [MA](Neolithic site: large stone curve; star stone- Corona Australis; Maughold)
· King Orry’s Grave [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Corona Australis; Laxey)
· Mull/Meayll Hill (Neolithic site: rep.Corona Australis; Cregneash)
Northern Ireland: [stone circles]
· Annaghmore [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Aquila; near Loughgall; Armagh)
· Aughlish [MA](Bronze Age: 6 stone circles- one w/41 small stones; 2 stone rows-lunar alignments; near Feeny; Londonderry)
· Ballykeel [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Aquila; Armagh)
· Ballynoe Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic/Bronze Age: stone circle-50 menhirs, 2 fallen stones have cup-marks, 6 outlying stones; oval mound w/stone cairn at core in E part of circle; large cists were found in the E and W ends of mound containing cremated bones; 2.5 mi. S Downpatrick, Down)
· Barnmeen [Gaelic: “young kid” (mean); Pharaonic: (min); sim. Assyrian: “goat-fish” (muna); Gaelic: “notch, gap” (barn = born/bearn)] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Capricorn, Aquarius; Down)
· Beaghmore [MA](3000/2000-1200 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: 7 low stone circles, 12 cairns, 10 stone rows, earthworks; alignments: solstice sunrise; 2900-2600 BCE: findings: hearths, flint tools; star stones Ophiuchus, Serpens Caput, Scorpio, Corona Norealis, Ara, Telescopium; 8.5 mi. NW Cookstown, Tyrone)
· Corick [MA](Neolithic: 5 stone circles, 1 has a large menhir in the center; 3 stone rows; Ballynascreen, Magherafelt, Londonderry)
· Crag of Hole Stone [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Sagittarius; Belfast)
· Down/Downpatrick Cathedral/of the Holy and Undivided Trinity (12th -1987 CE: Diocese; reputed burial place of Saint Patrick; Downpatrick)
· Drumskinny [MA](2000 BCE: Neolithic: stone circle; Drumskinny, Fermanagh)
· Giant’s Ring [MA](2000 BCE: Neolithic: circular earthwork-180m dia.; dolmen/passage tomb at center of enclosure faces W; there may be other tombs outside the enclosure; Ballynahatty, Belfast)
· Holestone and crag [MA](Neolithic; star stone markings: Sagittarius, Aquila, Capricorn; Antrim)
· Killadeas [sim.Latv.: “bear” (lacis)][MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; signature of Merlin/Morias Aesculapius?; star stone markings- Hercules, Draco, Vega, Bootes, Ursa Major, Virgo; Killadeas, Fermanagh)
· Legananny [Irish: “Aine’s standing stone” (Liagan Aine)](2500 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; assoc. to Irish goddess Aine; Leitrim, Down)
· Navan Fort/Emain Macha (4000 BCE: Neolithic: surrounding ditch; 95 BCE: mound; Armagh)
· Newry Cathedral/of Saint Patrick and Saint Colman (6th c.CE: predecessor church; 1641 CE: destroyed by fire; 1825-29 CE: Diocese; Newry, Armagh)
· Tireighter [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; star stone markings- Sagittarius; Derry)
· Tirnony [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; star stone markings- Sagittarius, Corona Australis, Indus, Telescopium, Pavo, Ara; Derry)
Scotland:
Mesolithic [MA](11000-4300 BCE); Neolithic [MA] (3900-2460 BCE; 1st c.BCE: broch/stone tower)
[NOTE 9] The Norman Gothic style of architecture (ie.cathedral; remenescent of Solomon’s Temple, and Luxor) enhanced/expanded Rome abroad by sea; and enhanced Romanesque architecture (ie.cathedral) with the vesica pisces (ie.boat peoples: dragon-boat; Biblical: ark).
· Aberdeen (8000 BP: Neolithic sites; array of sites shows path of precession of the solstices and equinoxes, path of the Pole Star over 26,000)
· Achnabreck/Kilmartin Glen [MA](Neolithic/Bronze Age; 350 ancient monuments w/in 6mi. rad.; standing stones, henges, cists, linear cemetery of cairns, cup/ring markings; Gleb Cairn, Nether Largie North/Mid/South Cairn, Ri Cruin Cairn; Ballymeanoch, Temple Wood; star stones- Hydra; Kilmartin Glen; betwn. Oban-Lochgilphead; near Dunadd; Argyll and Bute)
· Achnacree [MA](6000/3116 BCE: Neolithic: menhirs, stone circlestar stones- Summer Solstice; Isle of Mull)
· Alfirk Midmar Kirk [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cepheus; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Al-gol Collace Newbigging Pitcur [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Aviemore Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Ursa Major; Inverness)
· Avinagillan [MA](Bronze Age; standing stone; star stones- Gemini; Kintyre)
· Ballochroy [MA](Bronze Age; standing stones; star stones- Gemini; Kintyre)
· Ballymeanoch [MA](2000 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age; 2 rows of standing stones w/4 and 2 stones ea.; stone circle, henge, cairn, cup and ring markings; star stones- Hydra; Kilmartin Glen)
· Balmalloch [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Lupus; Dumfries, Galloway)
· Balnuaran of Clava [Gaelic: “pole” (bal); “Milky Way” (nuaran); sim. Heb./Arabic: (nahr)]/Clava Cairns [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: standing stones; 3 ring-typed cairns; cupmarked stones: Dragon Head Stone- Cepheus, Cygnus, Vega, Aquila; E Stone at middle cairn- Aquarius, Pegasus; W Stone at SW cairn- Virgo, Spica, Arcturus; stone at inner entrance near SW cairn- Polaris, Ursa Minor; stone rings- Pole Star, solstice line; cairns: middle- line of Equinoxes on ecliptic, solstice line w/stone ring; 5 mi. E of Inverness, 1 mi. SE Culloden Battlefield)
· Balquhain Stone Circle/Chapel of Garioch/Inveramsay [MA](Neolithic/Bronze Age: stone circle-4/12 menhirs, 4 fallen stones, 4 removed; rock art-cup marks; lunar alignments; 3 mi. from Inverurie, Aberdeenshire)
· Ban [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Orion; Arran i.)
· Barpa Langass [MA](Neolithic; chambered cairn; star stones- Scorpio; Lewis; Isle of N Uist, Outer Hebrides)
· Barpa nam Feannag [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; N Uist)
· Bargrennan [MA](Neolithic; White Cairn; star stones- Lupus; Dumfries, Galloway)
· Beacharr [MA](Bronze Age; standing stone; star stones- Gemini; near Tayinloan; Kintyre)
· Belfarg [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Triangulum; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Beorgs of Housetter North Roe [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hydra; Shetland Islands)
· Blackhammer Chambered Cairn [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; Rousay i.; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Blasthill [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Canopus; Kintyre)
· Blue Cairn Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle, several pits; Aberdeenshire)
· Boreland [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Eridanus; Dumfries and Galloway)
· Broch of Mousa (100 BCE: Iron Age; Shetland i.)
· Broomend of Crichie [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cepheus; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Bucharn Bocina [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Minor-Polaris; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Cairn Holy I-II [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Eridanus; Newton Stewart, Dumfries, Galloway)
· Cairn o’Mount [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Andromeda-Galaxy M31; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Callanish/Calanais Stones I-X [Latv.: “end” (Gallanish)][MA](-3000/2900-2600 BCE: Neolithic: stone circles; Callanish I stone circle-13 stones 13m dia.; Callanish II stone circle-5/10 stone ellipse w/11th outlier, 21m major axis, 19m minor axis; 8.5m dia. cairn; Callanish III stone circle-17 stone ellipse; Callanish IV stone circle-6 stones elliptical 13.5m major axis, 9m minor axis; Callanish VIII/Tursachan stone semi-circle-4 stones on edge of cliff Great Bernera; star stones- Scorpio; Fishhook in Polynes.; Hancock: two stones form a window that frames the sunrise during the summer solstice; Lewis i., Outer Hebrides)
· Capo long barrow [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Andromeda; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Carlin [Scots: “male of low birth” (churl); “old woman/hag” (kerlin; kerl); Old Norse: (kerling); Gaelic: “old hag/Goddess of Winter” (cailleach)] Stones/Carlin Stane (assoc. w/old hags, witches; legend: Cailleach; sites: Carlin Skerry, Orkney; Alvah- part of a cromlech, Aberdeenshire; Backhill of Drachlaw- axe-hammer, 3 bronze armlets, flint chips found, Aberdeenshire; Bishop Hill, Perth and Kinross; Dunlop, N Ayrshire; Darvel, Waterside, Knockshinnoch-cairn, East Ayrshire; Carlins Cairn, Castle Douglas, Wigtown, Dunfries and Galloway; Scottish Borders)
· Carnbaan [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra, Argos; Kilmartin Glen)
· Carn Ban [MA](Bronze Age; Marilyn-hill; star- Hydra; Mull i.)
· Carn Liath [“grey cairn”] [MA](Neolithic; star stones- phi-Lupus, Centaurus; Grampian range; 30m NW Dundee)
· Cauldside Burn [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Eridanus; Dumfries, Galloway)
· Clach a’ Charridh/Shandwick Stone (Tain)
· Clach na Tiompan Nembus [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Clach an Trushal/Shaula [Scottish Gaelic: “Stone of Compassion”] [MA](2500 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age: menhir; star stones- Scorpio; site of battle between Macaulays and Morrisons; Steinacleit stone circle is visible to NE; 20 mi. SW to Callanish; Ballantrushal, Lewis)
· Cladh Hallan (1600 BCE: mummies; Outer Hebrides)
· Colmeallie Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: recumbent stone circle and menhirs; much has been blundered for building materials; Glen Esk, Angus)
· Corriechrevie [MA](Bronze Age; cairn; star stones- Gemini; Glasgow; Kintyre)
· Corriedow [MA](Bronze Age; The White Cairn; star stones- Eridanus; Dumfries, Galloway)
· Crarae [MA](2036 BCE: Neolithic; star stones- Leo-Regulus; Kilmartin Glen)
· Croft Moraig Mirzac [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Cuff Hill [MA](Neolithic: rocking stone; star stones- Orion; Ayrshire <Gaelic: (inber-ayr); Sumerian: (nibiru)>; Ayrshire)
· Cullerlie Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; star stones- Cepheus; Grampian m.; near Echt, Aberdeenshire)
· Cuween Hill Cairn [MA](Neolithic Age; cairn: 5 chambers as the Nunki of ancients; star stones- Sagittarius-The Bow; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>; main island of Orkney)
· Doddington [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Cetus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Draffen [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Stewarton, E Ayrshire)
· Druid Temple Farm [MA](Neolithic: star stones- Ursa Major; near Leys Castle; Inverness)
· Drumelzier Haugh/Merlin’s Stone [MA](Neolithic Age; burial place of Merlin?; star stones- Taurus, Orion; Broughton; Peebles)
· Drumtrodden [MA](3117 BCE: Neolithic Age; star stones- Eridanus, Cetus, Fornax, Caelum, Vernal Equinox mark; Dumfries-Galloway)
· Drybridge [MA](menhir at Stane Field near old railway station; cursus henge; twin concentric circle structure; findings: perforated stone axe, flint flakes; North Ayrshire)
· Dun Bharp Barra [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Scorpio-delta/Dschubba, Crux; Uist)
· Dun Carloway (1st c.BCE: broch; Carloway, Isle of Lewis)
· Dundee [Gaelic: “fort”(dun) ”fire”(deagh)](Mesolithic)
· Dun Muirich [MA](Iron Age; star stones- Cancer; Glasgow)
· Dun Rostan [MA](Iron Age; star stones- Cancer; Glasgow)
· Dun Telve (100 BCE: broch; Glenelg)
· Easter Aquhorthies Recumbent Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic; recumbent stone circle; star stones- Cepheus; Grampian m.; Inverurie, Aberdeenshire)
· Easter Broomhouse [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Aries; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Eday Island [Latv.: “leads” (vadi)][MA](Neolithic; star stones- Sagittarius-feathers of arrows; Orkney i.)
· Edinburgh (Bronze Age: Holyrood, Craiglockhart Hill, Pentland Hills; Iron Age: Hallstatt, La Tene Celtic; Votadini; Bernician Angles)
· Eildon Hill (1000 BCE: hill fort Melrose)
· Farka Dain [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Minor; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Fortingall [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Fowlis Wester [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Gallow Hill [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pavo-Feather end of arrow; Shetland Islands)
· Garrabost Girtab [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Scorpio; Lewis i.)
· Garynahine [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; near Callanish; Lewis i.)
· Gigha Island [MA](Neolithic: cairns, menhirs, duns/hill forts; Ogham stone near Kilchattan; Gigha i.; off W Kintyre)
· Gildun Glassel [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Ursa Minor; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Gleck-pabae [MA](Iron Age; star stones- Gemini; Glasgow)
· Glen Lussa [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Canis-Sirius; Kintyre)
· Gourdon long barrow [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Andromeda; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Granny Kempock Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Gourock, Inverclyde)
· Greadal Fhinn [MA](3116/2036 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age; star stones- Crux; Mull i.)
· Gruting School [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pavo-Feather end of arrow; Shetland Islands)
· Herscha Hill (Neolithic: mound; Aberdeenshire)
· Highbanks [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Eridanus; Dumfries, Galloway)
· Hoy Island [Latv.: “stuffed bird” (izbaznis)][MA](Neolithic Age; The Dwarf Stone Head of the Arrow- arrowhead carved into stone; star stones- Sagittarius-arrowhead; Orkney i.)
· Isbister [Latv.: “stuffed bird” (izbaznis)][MA](Neolithic Age; Tomb of the Eagles; star stones- Sagittarius-pointing to Aquila; Orkney i.)
· Islay, Cramond, Rum, Applecross, Colonsay, Skye, Oronsay)
· Inverness (3000 BCE: Neolithic sites- Ursa Major, Bootes, Corona Borealis, Hercules, Ophiuchus, Scutium, Aquila; Pict)
· Jarlshof (3200/2500 BCE: Neolithic; Bronze/Iron; Pictish; Viking; Shetland i.)
· Kelvingrove [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic; stone gave Glasgow its name; Glas Ghu [Mesop./Indo-European: “Taurus” (ghu)] Stone- Taurus-Aldebran, Hyades, Pleiades, Scorpio, Line of Solstices and Equinoxes; Glasgow)
· Kilmichael Glassary [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra-head; Kilmartin Glen)
· Kilpatrick [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Orion; Arran i.)
· Kinnell Park [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Auriga; Kintyre i.)
· Kintraw [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra; Mull i.)
· Lagmore Rakis [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Draconis; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Loanhead of Daviot Recumbent Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: recumbent stone circle-10 stones +1 recumbent stone; star stones- Cepheus; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Loch a’Bharp [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; Uist)
· Lochbuie [Scot.Gaelic: “yellow loch”][MA](Neolithic; star stones- Crux; Mull i.)
· Lochmaben Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Dumfries)
· Longmanhill [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cygnus; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Lordenshaws [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Phoenix; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Loudon Wood [MA](Neolithic; Cairn Catto; star stones- Lacerta; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Lundin Links [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Triangulum; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Macbeth Stone Meigle [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Perseus, Milky Way; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Machrie Moor [MA](Neolithic: 2500 BCE: stone circles; 500 BCE: standing stones; star stones- Orion; Giant’s Graves; Kings Cave- believed to have been used by Robert the Bruce; Machrie, Arran i.)
· Maes Howe [MA](3100 BCE: Neolithic; mound; chambered cairn and passage gravestar stones- Sagittarius-The Bow; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Marionburgh [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Draconis; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Mid Gleniron [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Caelum; Dumfries-Galloway)
· Midhowe Chambered Cairn [MA](Neolithic; Rousay i.; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Millport [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Cumbrae i., Firth of Clyde)
· Mine Howe (3000 BCE: Neolithic: mound; Orkney i.)
· Monamore Glen [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Orion; Arran i.)
· Monzie [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Perseus; waterfall; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Mossyard [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Eridanus; Dumfries-Galloway)
· Muir of Gormack Blairgowrie [MA](Iron Age; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Old Kieg [Latv.: “tree of heaven” (kuok)][MA](Neolithic; largest recumbent stone in Scotland- brightest star near celestial center; star stones- Draconis, Mesopotamian Caga Gilgati E-dul-Kug; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Papa Westray [MA](Neolithic; 3500 BCE: Knap of Howar-farmstead; star stones- Sagittarius, Heavenly Archer-Center of the Galaxy; Orkney i.)
· Pinhouland [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Pavo-Feather end of arrow; Shetland Islands)
· Poltalloch [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hydra; Kilmartin Glen)
· Port Charlotte Procyon [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Canis Minor; Inner Hebrides)
· Pul The Blue Cairn [MA](Neolithic; Blue Cairn; star stones- Ursa Minor; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Punds Water [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Octans; Shetland Islands)
· Quarry Wood/Dilgan Elgin [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Lyra-Vega; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Raedykes [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cassiopeia, Sumerian Eridug-empty part of sky; Roman fort; Aberdeen Grampian)
· Reineval Vanand [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; Uist)
· Ring of Brodgar (2500 BCE: Neolithic; henge/stone circle-27/60 still standing; 104m dia.; Sagittarius-The Bow; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Rinyo [MA](Neolithic; Rousay i.; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Rottenreoch [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Rounds of Tivla [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra, Garden at the South Pole; Shetland Islands)
· Rousay Island [Latv.: “notch” (rievis)][MA](Neolithic; Taversoe Tuick-cairn; Midhowe Chambered Cairn; Blackhammer Chambered Cairn; Yarsow-tomb; star stones- Sagittarius-The Four Fingers, Corona Australis; Bronze Age: burnt mounds; Iron Age: crannogs, brochs; Viking boat burials; medieval church; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Rubh’an Dunain [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Centaurus; Skye i.)
· Saint Ninian’s Cave [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Great Looped Nebula; Dumfries-Galloway)
· Saint Paul’s/Dundee Cathedral (80 CE?: fortifications; castle may have been besieged by William Wallace, Andrew de Moray, Robert the Bruce during Wars of Scottish Independence; 1853 CE: Scottish Episcopal; Diocese of Brechin; Dundee)
· Sanday Island [Latv.: “side” (sani)][MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Sagittarius-The Quiver; Orkney i.)
· Scarista [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio; Harris, S Uist)
· Scord of Brouster [MA](3400/2220 BCE: Neolithic; stone circle; farm site; star stones- Pavo-Feather end of arrow; Shetland Islands)
· Sheldon Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; 32.9m dia.; solar alignments; 200m N Sheldon Farm; SE Oldmeldrum, Aberdeenshire)
· Skara Brae [MA](3180-2500 BCE: Neolithic; “Heart of Neolithic Orkney”; older than Stonehenge; star stones- Sagittarius-The Bow; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Staneydale Temple [MA](Mesolithic-Neolithic/Bronze/Iron; star stones- Pavo-Feather end of arrow; Shetland Islands)
· Steinacleit/Leschat [Lewis = Lesath] [MA](3000-1500 BCE: Bronze Age; chambered cairn; near SW standing stone-Clach an Trushal; stone circle; star stones- Scorpio-stinger; Lewis, Outer Hebrides)
· Standing Stones/Stanes of Stenness [Latv.: “stave/ middle of bow” (stienis/steipis); Akk.: (Sin-nun-tu)] [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: originally a stone circle-12 stones in 32m dia. ellipse; Watch Stone; Odin Stone; pottery links to Skara Brae and Maeshowe; “Heart of Neolithic Orkney”; star stones- Sagittarius-The Bow; S end of Loch of Stenness and Loch of Harray; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Strichen Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; destroyed 2x; Strichen, Aberdeenshire)
· Stocky Muir [MA](Neolithic; Red Rock; star stones- Taurus-Aldebran; Glasgow)
· Strathgroy [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Perseus; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Strauss Strichen [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cygnus, Deneb; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Strichen sc (Strichen, Aberdeenshire)
· Strontroiller Diarmid’s Stone [MA](3116 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra; Mull i.)
· Sun Honey [MA](Bronze Age: clava-type round cairn; star stones- Cepheus, Cygnus; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Swinburne [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Eridanus; Hadrian’s Wall; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Taversoe Tuick [Latv.: “grasp” (tvers)][MA](Neolithic; star stones- Sagittarius-The Four Fingers, Corona Australis; Rousay i.; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Temple Wood/Half Moon Wood [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age; 2 stone circles N-S: S-circle- 13/22 standing stones, 12m dia.; central burial cist surrounded by stone circle 3m dia.; N-circle- smaller w/river stones; star stones- Hydra; Kilmartin Glen)
· Thurayya Tuilyies [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Pleiades; Perth, Fife, Edinburgh)
· Timshemath Memsie Hirezym [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Lyra; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Tigh Cliche [Latv. “fishing net” (tiklis)][MA](Neolithic; star stones- Scorpio-Antares; Stone of Eyre- Scorpio, Lupus, Centaurus are net and hook; N Uist)
· Tomnaverie Recumbent Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle; Aberdeenshire)
· Tordarroch [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: star stones- Ursa Major line of the Equinoxes; Inverness)
· Torhousekie [MA](Neolithic; stone circle; star stone circle- Eridanus; Dumfries-Galloway)
· Torran Rocks [MA](Bronze Age; star stones- Hydra; Mull i.)
· Torrylin [MA](Neolithic Age; star stones- Orion; Arran i.)
· Tullos [Gaelic root: “hill” (tulach”] Hill [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Cassiopeia; Grampian m.; Aberdeen)
· Twelve Apostles Stone Circle [MA](Neolithic: stone circle-11 stones, 89m dia.; btwn. Holywood and Newbridge; Dumfries and Galloway)
· Ullinish [Gaelic: (uilinis); Old Norse: “promontory of wolves”] [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Centaurus; Skye i.)
· Unstan Chambered Cairn [MA](Neolithic; Orkney i.)
· Vatten [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Lupus; Harlosh, Skye i.)
· Vord Hill Fetlar [MA](Neolithic; star stones- Hydra; Shetland Islands)
· Wideford Hill [MA](Neolithic; marilyn-hill; star stones- Sagittarius-The Bow; main island of Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Yarso [MA](Neolithic; tomb; Rousay i.; Orkney <Lat.: “bow” (arcus); Latv.: “bowstring” (virkne)>)
· Yoxie [MA](Neolithic; standing stones; star stones- Octans; Whalsay i., Shetland Islands)
Wales:
· Afon y Dolau Gwynion [MA](Neolithic: chambered round cairn; Llanwddyn/Lake Vyrnwy, Powys)
· Arthur’s Stone [Welsh: Maen Ceti] [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: burial ground; star stone- Serpens Caput; 60+ cairns w/in Cefn Bryn; from Cilibion to Reynoldston; Gower Peninsula; Swansea, S Wales)
· Bachwen [MA](Neolithic: long chambered cairnl star stone- Sagittarius; Clynnog Fawr; N Wales)
· Bangor Cathedral (525 CE: St.Deiniol’s monastery; 634; 1073 CE: sacked; 1102 CE: restored; 1211 CE: destroyed; 14th c.-1532 CE: nave rebuilt; 1868 CE: Gothic; Bangor, Gwynedd)
· Barclodiad y Gawres [Welsh: “apronful of the giantess”](The Globe Stone)[MA](Neolithic; burial chamber; star stone markings- Africa, Crocodile; Lancashire; Anglesey i.; N Wales)
· Bodowyr [MA](Neolithic; dolmen; star stone- Sagittarius; Anglesey i.; North Wales)
· Bontnewydd (230k BP: most northwesterly hominid remains in Eurasia; proto-Neanderthal; Llanelwy; Denbighshire)
· Brecon (Roman: Cicucium)
· Bryn Cader Faner [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze Age: stone circle- 18 jagged pillars which jut inclined up from low cairn; 8.7m dia.; Talsarnau, Ardudwy, Gwynedd)
· Bryn Dyfrydog Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Bryn yr Hen Bobl [MA](Neolithic: stone circle henge- stones removed during Bronze Age; chambered round cairn; earth barrow; -3000 BCE: postholes; summer solstice marker; star stone- Sagittarius; Llanddaniel Fab, Anglesey i./Ynys Mon)
· Cae’rarfau [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Ophiuchus; S Wales)
· Caer-Dynni [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: chambered long cairn-7 menhirs w/13 cup marks; 4th c.BCE: Celtic; Cardigan Bay; Cricieth, Eifionydd, Gwynedd)
· Caerleon (Iron Age: Roman hill fort; Newport)
· Capel Garmon, Bro Garmon [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; star stone- Sagittarius; Conwy; N Wales)
· Carreg Coetan Arthur [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen/quoit; star stone- Scorpio; near Newport; S Wales)
· Carreg Samson [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Cardiff (6000 BP: Neolithic; Bronze Age: tumuli at summit of The Garth; Iron Age: 4 hillforts; Roman-Sillure; Norman)
· Carneddau Hengwm [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; Dyffryn Ardydwy, Gwynedd)
· Castell Henllys (Iron Age: hill fort; Newport; Cardigan)
· Cefnamwlch [MA](Neolithic: chambered round cairn; Tudweiliog, Gwynedd)
· Cefn Bryn [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; Arthur’s Stone; Bronze Age: 60+ cairns; Llanilltud Gwyr)
· Clegyr Boia [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Clorach Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey)
· Coetan Arthur/Arthur’s Quoit [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; on hillside neat St.Davids Head in Pembrokeshire)
· Cors-y-Gedol [MA](4000 BCE: Neolithic: chambered long cairn/cromlech; Dyffryn Ardydwy, Gwynedd)
· Cremlyn Stones [MA](Neolithic: menhirs; Anglesey i.)
· Din Dryfol [MA](Neolithic; chambered long cairn; star stone- Sagittarius; Aberffraw, Anglesey i.; N Wales)
· Dschubba [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Dyffryn [MA](4000 BCE: Neolithic: chambered long cairn/cromlech; Dyffryn Ardydwy, Gwynedd)
· Gelli [MA](Neolithic: chambered round cairn; Llanfair-ar-y-bryn, Sir Gaerfyrddin/Carmarthenshire, S Wales)
· Gorllewin Bron-y-Foel [MA](4000 BCE: Neolithic: chambered long cairn/cromlech; Dyffryn Ardydwy, Gwynedd)
· Gower Peninsula [MA](33000 BP: Upper Paleolithic: Red Lady of Paviland- male skeleton dyed in red ochre, oldest ceremonial burial discovered in W Europe; Neolithic: Seven-Cotswold type of chambered long barrow; near 6000 BP: megalithic burial chamber-cromlech; Sweyne Howes on Rhossili Down, Penmaen Burrows Tomb/Pen-y-Crug, Nicholas Long Cairn; Bronze Age: Tooth Cave at Llethryd, Culver Hole, Cat Hole Cave; Paviland, Wales)
· Gwal y Filiast [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· The Hanging Stone [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Harold’s Stones Trellech [“town of slates”; “three slates”] [MA](Bronze Age site: star stones- Ursa Major, Hindu Atri, Virgo-Spica, Head of Regulus; near Monmouth)
· Hen Domen [t.Welsh: “old mound”] (1070 CE: Montgomery castle; Powys)
· Hendre-Waelod [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; Llansanffraid Glan Conwy)
· Hirdre-Faig [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Liech y Tribedd [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Ligwy [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Sagittarius; N Wales)
· Llandaff Cathedral (550 CE: pre-Norman; Celtic cross; Diocese; 1107 CE: monastery secular canons; 1120-1290 CE: Gothic; 1942 CE: damaged during WWII; Llandaff, Cardiff)
· Llandegfan [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Llandonna Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Lledwigan Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Llety’r Filiast [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; Llandudno, Conwy County Borough)
· Maenaddwyn Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey)
· Maen y Bardd [MA](Neolithic: long chambered cairn; star stone- Sagittarius; Caerhun; S Henryd; N Wales)
· Maen Chwyf [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Moel Ty Uchaf (Neolithic: stone circle-41 stones w/cist in center w/outlying stone NE; 12m dia.; Llandrillo, Denbighshire)
· Newport (Bronze Age: Celtic Silure: hillforts; 75 CE: Roman)
· Newport Cathedral (5th c.CE: pre-Norman; Diocese; Newport)
· Parc Cwrm/Parc le Breos [MA](5850 BP: Neolithic: chambered long cairn/cromlech; star stone- Serpens Caput; Gower Peninsula; Llanilltud Gwyr, Swansea, Paviland, S Wales)
· Paviland Cave/Merlin’s Summer Cave/Merlin’s Grave [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Serpens Caput; Gower Peninsula; S Wales)
· Penmaen Burrows [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Serpens Caput; Gower Peninsula; Gower Peninsula; Paviland, S Wales)
· Pentre Ifan [MA](3500 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; largest and best preserved dolmen in Wales; capstone-16 tons; star stone- Scorpio; 6km Newport; Nevern, N Pembrokeshire, W Wales)
· Pen y Wyrlod [MA](4000 BCE: Neolithic: chambered long cairn; bone flute; Talgarth, S Powys)
· Presaddfed [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Sagittarius; Lancashire; North Wales)
· Red Lady of Paviland (33000 BP: Upper Paleolithic: Red Lady of Paviland- male skeleton dyed in red ochre, oldest ceremonial burial discovered in W Europe; Gower Peninsula; btwn. Port Eynon and Rhossili, S Wales)
· Rhiw [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; 4th c.BCE: Celtic; Llyn Peninsula; Aberdaron)
· Saint Asaph Cathedral (553 CE: pre-Norman; Diocese; 13th c.-1282 CE: burned; 15-19th c.CE: Gothic; Saint Asaph)
· Saint David Cathedral (589 CE: pre-Norman; Diocese; 645-1097 CE: Viking raids; 1181-1793 CE: Gothic; star stone location- Scorpio; Pembrokeshire)
· Saint Lythans burial chamber [MA](33000 BP: Paviland- Gower Peninsula; 4000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; star stone- Ophiuchus; Wenvoe; Vale of Glamorgan, SE Wales)
· Swansea (Stone Age; Bronze Age; Iron Age; Roman; Viking: trading post)
· Tan-y-Coed [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; legend: 1170 CE: Madog ap Owain Gwynedd, Welsh Prince sailed to America- Madoc, MO; Llandrillo, Rhos-on-Sea, Conwy)
· Tinkinswood Burial Chamber/Castell Carreg/Llech-y-Filiast/Maes-y-Filiast [MA] (4000 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen; capstone-40 tons; findings: 920 human bones, nearly all broken-40 people, Bell-Beaker pottery; legend: petrifaction- women turned to stone for dancing on the Sabbath; star stone- Ophiuchus; near St.Nicholas and Barry; Vale of Glamorgan; S Wales)
· Trefignath [MA](Neolithic site; cairn- Sagittarius; star stone; Lancashire; N Wales)
· Twlc y Filiast [MA](Neolithic; star stone- Scorpio; S Wales)
· Tyddyn Bleiddyn, Cefn Meiriadog [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn)
· Tynewydd [MA](Neolithic site: star stone- Sagittarius; Lancashire; N Wales)
· Whetstones [MA](Neolithic/Bronze: stone circle beneath Corndon Hill; on border btwn.Powys and Shropshire, England; W White Grit, near Priestweston; near Hoarstones and Mitchell’s Fold circles)
· Wrexham (8000 BP)
· Ynys Fawr Stone [MA](Neolithic: menhir; Anglesey i.)
· Ystum-Cegid [MA](Neolithic: chambered long cairn; Llanystumdwy, Eifionydd, Llyn Penin. of Gwynedd)
JERSEY Island: (UK-off the coast of Britanny)[MA](Paleolithic-Neanderthals; 4800-2250 BCE: Neolithic-Chalcolithic: dolmen)
· Faldouet [MA](4000-3200 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen/passage grave; Channel Islands)
· La Cotte de St. Brelade [MA](100000-40000 BCE: Paleolithic-Mesolithic; Channel Islands)
· La Hougue Bie [Jerriais/Norman: “mound” (haugr); Scottish: “new year” (hogmanay)] [MA](4000-3200/3117 BCE; Neolithic: tumulus/mound, 5 passage graves w/side chambers; star stones- Sagittarius, Spring Equinox, Celestial Meridian; Channel Islands)
· La Hougue Boete [MA](Neolithic: 4-sided chamber cist w/round mound; Celtic finds: man/chief burial? lying on a horse, skeletons, greenstone axe; St.John, Channel Islands)
· La Hougue des Geonnais [MA](Neolithic: D-shaped chamber/dolmen; ruined in 1929 by quarrying; finds: pottery, flint scrapers, arrowheads, broken querns; St.Ouen, Channel Islands)
· La Pouquelaye de Faldouet [MA](Neolithic: long passage grave/dolmen; several smaller side chambers and cists; finds: human bones, pottery, stone axes, flints; Channel Islands)
· La Sergente [MA](4500 BCE: Neolithic: circular chamber; ruins of corbelled, bee-hive shaped vault; St.Brelade, Channel Islands)
· La Table des Marthes [MA](3000-2500 BCE: Neolithic/Bronze: dolmen-large flat granite slab supported by end stone pillars and earth; finds: pottery, burnt stones, broken stone axes; place of signing contracts; St.Brelade, Channel Islands)
· Le Couperon [MA](3000 BCE: Neolithic: long chambered dolmen; surrounded by stone circle-18 stones, originally covered by mound; finds: flint flakes, pottery ashes; St.Martin, Channel Islands)
· Le Mont Ube [MA](4000-3200 BCE: Neolithic: passage grave/dolmen; capstone blasted by quarrymen for building materials; finds: human bones, urns, stone axes, stone pendant; St.Clemente, Channel Islands)
· Le Pinacle [MA](natural formation resembling gigantic menhir; 4500 BCE: Neolithic: 2 earth and rubble ramparts circular chamber; Bronze/Iron Age: 3rd rampart; Gallo-Roman: temple; finds: flints, hammers, rubbers, polishing stones, copper arrow head, bronze spear head, wheel turned pottery, Roman coin; Channel Islands)
· Les Monts de Grantez [MA](4000-3200 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen/passage grave; finds: 7 articulated skeletons; St.Ouen, Channel Islands)
· Les Trois Rocques [MA](Neolithic; Channel Islands)
· The Broken Menhir [MA](3000-1500 BCE: Neolithic: menhir; Channel Islands)
· The Great Menhir [MA](3000-1500 BCE: Neolithic: menhir; Channel Islands)
· The Little Menhir [MA](3000-1500 BCE: Neolithic: menhir; Channel Islands)
· The Ossuary [MA](Neolithic: Channel Islands)
· Ville-es-Nouaux [MA](Neolithic: 3250-2850 BCE: dolmen/gallery grave; 2800-2000 BCE: cist in circle; Channel Islands)
Malta: (UK)[MA](3600 BCE: Neolithic: dolmen)
[NOTE 13] The ante-dilivian Titanic-Giant (instance defn.: titans/dragons, the parents of the ancient-astronaut-“gods,” anunaki, designing hybrid demigod navigator priest-kings in remote antiquity of Sumeria), Neolithic-Bronze Age dragon-boat-seed-people of alchemy and technology of civilization, Essene-(navigator-priest cult of the pantheonic-trinity, Isis/Osiris/Horus, Hathor/mother goddess, Thoth <human patriarch oracle of neutrality>, Baal/Dionysios)-Phoenician-Celtic-Druid-Punic-Gnostic-Cathar-Viking-Basque-Norman-Brit-secret pagan plutarchy, utilized earth grid stone circles as electro-magnetic energy conductors into gaia-pan/earth-gaia, at specific astrological orientations and times (ie.solstice-equinox temples that time the divine return of cosmos), circum-navigated the oceanic globe, with bronze-riveted immortal dragon anti-gravity vessels, via the trans-dimensional ouroboros lei line highways of the magnetosphere and beyond..., pulling the strings of kings; water sorcery is opening space-time portals.
[NOTE 14] The struggle between the secret pagan plutocracy (ie.13 wealthy illuminati families) vs. the Roman Catholic church is a hidden farce.
· Birgu (prehistoric; Phoenician; Greek; Roman; Byzantine; Arab; Norman; Angevine; Aragonese; 1436 CE: Saint Lawrence Church; Knights of Malta)
· Borg-in-Nadur (2000 BCE: Neolithic-Bronze Age settlement; Birzebbuga)
· Chapel of the Good Sheperd (Knights of Malta; Birzebbuga)
· Chapel of Our Savior (1487 CE: Knights of Malta; Kalkara)
· Clapham Junction (2000 BCE: Bronze Age; cart rut marks; Gozo, Busewdien, Naxxar, San Gwann, Bidnija, Sannat; Dingli cliffs)
· Cospicua (Neolithic; 600 BCE: Phoenician; Knights of Malta: dockyard in 1776)
· Fgura (prehistoric; 4th-3rd c.BCE: Phoenician)
· Ggantija [Malt.: “Giants’ Tower”][MA](3600-2500 BCE: Neolithic: fertility cult temple; animal sacrifice; Gozo)
· Ghar Dalam [Malt.: “cave of darkness”](Ice Age: stranded animals- bones: elephants, hippopotamus; 7400 BP: earliest human settlement on Malta; Birzebbuga)
· Gozo Island (1500 BCE: Neolithic-Bronze Age: fortification; Phoenician; Roman: acropolis; Aragonese; Knights of Saint John; Victoria)
· Hagar Qim (Qrendi)[MA](3600-3200 BCE: trilithon entrance; animal sacrifices, burnt offerings, ritual oracles; forecourt, dwelling houses and bastion; women’s chamber; main temple; the niche; Il-Misqa, “the watering place”)
· Hypogeum of Hal-Saflieni/Paola Malta [Gk.: “underground”] (Prehistoric: 1st level-underground necropolis; 2nd level- Main Room, Holy of Holies- trilithon framed w/in a trilithon w/in a trilithon, Oracle Room, Decorated Room- petrosomatoglyph, Snake Pit; 3rd level- storage; Xemxija)
· Iklin [MA](Tar-Raddiena; Roman villa)
· Kercem (5000 BCE: Ghar Dalam phase; Dawwara menhir; Roman baths; early Christian cemetery: Ghar Gerduf; Gozo i.)
· Kirkop [MA](menhir; Hal Kirkop)
· Marsaskala (Neolithic-Bronze Age; Christian catacombs; Roman: villas and baths; Knights of Malta: Saint Thomas Tower fortification)
· Marsaxlokk [Phoen.: “bay of the sirocco”(Xlokk)][MA](Neolithic: Tarxien on Tas-Silg hill; 9th c.BCE: 1st Phoenician landing place on Malta; 6th c.BCE-1st c.CE: Temple of Astarte/Hera; 4th c.CE: early Christian monastery)
· Mdina/”Silent City” (700 BCE: Phoenician-Punic; Roman; 1091 CE: Norman; 1530 CE: Knights of the Hospital of Saint John in Jerusalem; 1639 CE: earthquake- Baroque designs; Saint Agatha’s Chapel, Saint Nicholas’ Chapel, dungeons, Carmelite church and convent, Benedictine monastery)
· Mellieha (Neolithic: tombs, ruins; 870: Arab; 1530: Knights of Malta: fortifications; 16th c.: Sanctuary of Our Lady of Mellieha)
· Mnajdra (Qrendi)[MA](4th m.BCE: solstice-equinox temple; near Hagar Qim)
· Mtarfa/Imtarfa (Roman: temple of Prosperine)
· Nadur Parish Church (1688 CE: Baroque; Nadur)
· Naxxar [MA](Neolithic-Bronze Age: caves- Tal-Qattara, Ta’San Brinkaw; megaliths- Tal-Qadi, Qaliet Marku; Punic tombs; 1436 CE: Naxxar Parish Church)
· Our Lady of Victories Parish Church (1580 CE: Baroque; Senglea)
· Qala [MA](menhir; Gozo)
· Qormi (1500-800 BCE: Bronze Age: Stabal: pottery; Punic tombs; Roman)
· Rabat (Roman settlement; catacombs of Saint Paul and Saint Agatha; Saint Paul shipwreck in 60 CE; outside Mdina)
· Safi (Neolithic; Phoenician; Roman; 1592 CE: Saint James Parish)
· Saint George’s Church (1575 CE: Knights of Malta; Birzebbuga)
· Saint George’s Basilica (1670s CE: Baroque Basilica; dmg.earthquake 1693; 1818: new façade; Victoria, Gozo)
· Saint Helen’s Basilica (1436 CE; Birkirkara)
· Saint John’s Co-Cathedral (1572 CE: Baroque; Knights of Malta; Valletta)
· Saint Mary’s Tower (1416 CE; Comino)
· Saint Paul’s Cathedral (11-12th c.CE: Norman; d.in 1693 earthquake; 1697-1702: rebuilt Baroque; frescoes; Albrecht Durer designed coins; Mdina)
· San Gwann (2300-1000 BCE: Bronze Age: cart ruts)
· Skorba [MA](Neolithic; Zebbiegh)
· Ta’Hagrat [MA](3800-3600 BCE: Mgarr phase; Ggantija phase: major temple; Saflieni phase: minor temple)
· Tarxien [MA](2800 BCE: Bronze Age; animal sacrifice; cremation; Tarxien)
· Xaghra Stone Circle/Brochtorff Circle [MA](4100-3000 BCE: Ggantija temple; Gozo)
· Wied Ghomar [MA](menhir; Rabat)
· Xemxija [MA](menhir; St.Paul’s Bay; Xemxija)
· Zejtun (Roman remains- villas; church- Saint Catherine of Alexandria)
· Zurrieq (Phoenician tombs: ta’Danieri, tal-Hlewwa, tal-Gharghariet; Roman temple: tal-Bakkari
NORTH AMERICA:
Bahamas:
· N. Bimini is. [MA] [GP18](ancient Atlantis?; 1968: archeologist Jay Manson Valentine discovered submerged structures: roads, paths); western edge of Bermuda triangle
BELIZE: (Maya: pyramids)
· Actun Polbilche
· Adventura
· Altun Ha (200 BCE: Classic Mayan; Belize City)
· Baking Pot
· Barton Ramle
· Black Man Eddy
· Blue Creek
· Buenavista del Cayo
· Cahal Pech (900 BCE; San Ignacio)
· Caracol (Classic Maya; Cayo)
· Cerros (400 BCE; Chetumal Bay)
· Chan Chich
· Chau Hiix
· Chicawate
· Colha
· Cuello
· Dos Hombres
· El Pilar (Cayo)
· El Porito
· False Cay
· Frenchman’s Cay
· Honey Camp
· Indian Church
· Kendal
· Kichpanha
· Kunahmul
· La Milpa
· Lamanai (1600 BCE: Preclassic Maya; Orange Walk)
· Louisville (400 BCE; Corozal)
· Lubaantun (730 CE; Toledo)
· Moho Cay
· Mountain Cow
· Muenal Tunich
· Mun Diego
· Nim Li Punit (500 CE; Toledo)
· Nohmul
· Nohoch Ek
· Pacbitun
· Petroglyph Cave
· Pomona
· Potts Landing
· Pulltrouser Swamp
· Pusilha
· Rio Frio Cave
· San Antonio Rio Hondo
· San Estevan (800 BCE; New River)
· San Jose
· Sand Hill
· Santa Rita (Post classic Maya)
· Sarteneja
· Shipstern
· Tiger Mound
· Tipu (Post classic Maya)
· Uxbenka (250 CE; Toledo)
· Xnaheb
· Xunantunich (200 CE: Classic Maya; Cayo)
CANADA:
NEWFOUNDLAND:
· Brador
· Cape Ray
· Curtis
· Eskimo Island
· Hopedale
· Indian Point
· Island-Sandy Cove
· La Matre
· L'Anse Aux Meadows (1000 CE: Viking settlement; St.Anthony)
· Mingan
· Northwest River Sites
· Port Au Choix
· Rattler's Bright
· Wigwam Brook
NEW BRUNSWICK:
· Cow Point
· Deadman's Pool
· Minister's Island
· Portland Point
· Teacher's Cove
NOVA SCOTIA:
· Debert
· McEvoy
· Merigomish
· Shubenacadie
YUKON:
· Canyon Creek
· Chimi
· Engigstciak
· Gladstone
· Klo-kut
· Little Arm
· Old Crow Flats
· Otter Falls
· Pelly Farm
· Rat Indian Creek
· Taye Lake
· Trout Lake
BRITISH COLUMBIA:
[NOTE 70] Chinese Legendary Fuxiang described by Shi Huang (219 BCE) and Hui Shen (499 CE), who described it 20000 li/8700 km E of China; described on French world map by Philippe Bauche (1753)
[NOTE 71] Region of many big foot (Sasquatch; Halkomelem: sasq’ets) sightings (Alaska has most)
· Bell (Mount Cayley)
· Black Tusk/Mount Garibaldi [V] [Squamish: “Landing Place of the Thunderbird;” mountain derived zig-zag shape from Thunderbird’s lightning]
· Blue Jacket Creek
· Callison
· Chapperon Lake
· Chinlat
· Duncan <CC: 2008: ‘herringbone swirls’>
· Drynoch Slide
· Esilao (Mount Garibaldi)
· Grant Anchorage
· Hagwilget
· Honna River
· Ice Mountain
· Kitselas Canyon
· Kwatna
· Lawn Point
· Lochnore Creek (Mount Cayley)
· Marpole
· Marron Valley
· Miliken (Mount Garibaldi)
· Montague Mayne
· Mount Cayley [V] [Squamish: “Landing Place of the Thunderbird;” mountain derived zig-zag shape from Thunderbird’s lightning]
· Namu
· Natalkuz Lake
· Nesikep Creek (Mount Cayley)
· Pedder Bay
· Poplar Grove
· Potlatch
· Prince Rupert Harbor Sites
· Standing Stones of Lougheed [MA](stone circle-5 stones; Sky Train station at Lougheed Town center; Burnaby, Vancouver)
· Stselax
· Tezli
· Yuquot
ALBERTA:
· Bayrock
· Big Bay
· British Block Cairn
· Calling Lake
· Castor Creek
· Cluny Earth Lodge Village
· Fletcher
· Freeland
· Head-Spashed-In Buffalo Jump (3500 BCE: Fort Macleod, Alberta)
· Johnston Locality
· Morkin
· Narrows
· Old Women's Buffalo Jump
· Rabbit Hill
· Red Deer <CC: 2009: simple circles and rings; golden mean spiral geometry; UVG-8>
· Writing-On-Stone
SASKATCHEWAN:
· Aneroid <CC: 2005>
· Bakken-Wright
· Buffalo Pound Lake
· Bulyea Midden
· Estuary
· Garratt
· Gray
· Gull Lake
· Long Creek
· Morris Church
· Mortlach
· Pelican Narrows
· Stony Beach
MANITOBA:
· Avery
· Brockinton
· Calf Mountain
· Cemetery Point
· Clearwater Lake
· Evans
· God's Lake
· Harris Bison Runs
· Larter
· Linear Mounds
· Lockport
· Neck
· Scott
· Seahorse Gully
· Shethanei Lake
· Tailrace Bay
· Thyazzi
· Westbourne Mound
ONTARIO:
· Abitibi Narrows
· Brohm
· Cahiague
· Donaldson
· Drunkard's Point [SM](High Rock; Lake Temagami)
· Eaka
· Frank Bay [SM](High Rock; Lake Temagami)
· Goessens
· Heron Bay
· Inverhuron [Gaelic: (inbhir) “confluence of the waters”](6000 BP: indigenous Ojibway; Highland Scot settlement; confluence of Little Sauble r. and “Godmother l.,” Heron L.)
· Krieger
· Mac Gillivary
· Maple Mountain [SM] (Temagami)
· McCollum
· Michipicoten
· Miller
· Mississaugi
· Potato Island
· Quimet
· Roebuck
· Serpent Mound
· Sheguiandah
· Teiaiagon (Iroquois village; Toronto)
· Thompson Island
· Uren
· Wabinosh River
QUEBEC:
· Allumette
· Arnapik
· Berube
· Bourassa
· Great Whale River
· Hochelaga (Iroquoian fortified village; Montreal)
· Imaha
· Ivugivik
· Lanoraie
· Metabetchouan
· Mistassini
· Morrison's Island
· Oka
· Payne Lake
· Richmond Gulf Hazard
· Stadacona (16th c.CE: St.Lawrence Iroquoian village; Quebec City)
· Tobacco Bay & Kempt
NORTHWEST TERRITORIES:
· Aberdeen
· Acasta Lake
· Aurora
· Baker Lake
· Bloody Falls
· Button Point
· Dismal Lake
· Dot Island
· Dundas Island
· Ekalluk River Sites
· Frank Channel
· Grant Lake
· Great Bear River Sites
· Grinnel Peninsula
· Holman
· Igloolik
· Jackson
· Joss
· Kamut Lake
· Kapuivik
· Kittigazuit
· KjNb-6,7
· Kopuk
· Lemming
· Lockhart River
· Malernalik
· Mitimatulik
· Naujan
· Pelly Bay
· Resolute
· Schultz
· Silumiut
· T-1
· Taltheilei Narrows
· Umingmak
· Whirl Lake
· Yellow Lake
COSTA RICA:
· Aguas Buenas
· El Hacha
· Guayabo (1000 BCE: mounds; gold artifacts; San Jose)
· Las Mercedes
· Las Pilas
· Nacascolo
· Stone Spheres/Petrospheres [MA](200 BCE; Isla del Cano/Diquis Delta)
CUBA:
[NOTE 84] Submerged Atlantean? site w/pyramid [MA] and track at S.Bimini (over ½ mile down), off west coast of Cuba, western edge of Bermuda triangle; 30 submerged (2200 ft. below surface of water) megalithic structures- streets, buildings, tunnels, pyramids (6000 years ago?)
· Bani
· Cayo Redondo
· Guayabo Blanco Sites
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC:
· Boca Chica
· Casimira & Mordan
· Meillac
· Samana Sites
LESSER ANTILLES:
[NOTE 80] Many maps of the Middle Ages showed maps of the Atlantic and Antilla, or the ‘Antilles,’ a region associated with Atlantis. Aristotle called the Phoenicians, ‘Antil haus,’ who called themselves the Cana anu (defn.: ‘offspring of the Canaan’); accd. to Biblical chronology, the ancient navigators (ie. Phoenicians) were operating as the Atlantean Empire at the end of the ice age, which seems to have ended around 1500-2000 BCE (coincides with Biblical Exodus), rather than 10000 BCE (conventional) (Childress)
· Arnos Vale (St.Vincent)
· Chancery Lane (Barbados)
· Coral Bay (St.John)
· Esperanza
· Grand Anse (St.Lucia)
· Bay (St.Thomas)
· La Salle & Vive (Martinique)
· Magens Bay (St.Thomas)
· Morrel (Guadeloupe)
· Paquemar (Martinique)
· Pearls (Grenada)
· Pointe des Cailles (St.Lucia)
· Salt River (St.Croix)
· Savonne Suazey (Grenada)
EL SALVADOR: (Maya- pyramids)
· Acajutla
· Asanyamba
· Atiquisaya
· Azacualpa
· Campana-San Andres
· Cara Sucia
· Ceren
· Cerro Zapote
· Cihuatan
· Conchagua Vieja
· Coroban
· El Carmen
· El Trapiche & Tazumal
· Igualtepeque
· Izalco
· Joya de Ceren (900 BCE: buried by volcanic ash, 250 CE by Lago Ilopango, and 400 CE by Loma Caldera)
· La Rama
· Los Llanitos
· Quelepa
· Rio Gualacho
· San Andres (900 BCE: buried by Lago Ilopango; La Libertad)
· Santa Leticia
· Santa Rosa
· Tazumal [Kiche:”the place where the victims were burned”](100 CE: Preclassic Maya; Chalchuapa)
· Tula
GREENLAND:
· Angmagssalik
· Brattahlid
· Curtis
· Igdlorssuit
· Independence Sites
· Indian Point
· L’Anse aux Meadows (1000 CE: first Viking settlement in America)
· Quilakitsoq (1475 CE: mummies buried; Uummannaq)
· Sarqaq
· Thule
GUATEMALA: (Maya- pyramids)
· Abaj Takalik
· Aguateca
· Altar de Sacrificios (Classic Maya)
· Anna
· Aquas Calientes
· Asuncion Mita
· Atiquipuque
· Balberta
· Bejucal
· Beleh
· Bilbao
· Castillo de San Felipe (Lago de Izabal)
· Cenote
· Cancuen (7th c.CE: Classic Maya)
· Cahyup
· Chalchitan
· Chacula
· Chama
· Chinautla
· Chocola
· Chuitinamit
· Chukumuk
· Chutixtiox
· Copoja
· Cotzumalhuapa
· Dos Pilas (Late Classic: 629 CE)
· El Balsamo
· El Baul
· El Caribe
· El Chayal
· El Jobo
· El Mesak
· El Mirador (Preclassic Maya: pyramid)
· El Peru/Waka (500 BCE: Classic Maya)
· El Tintal
· El Manantial
· El Peru
· El Porvenir
· El Zotz
· Finca Arizona
· Finca Toliman
· Flores/Tayasal
· Guaytan
· Holmul
· Itzan
· Itzimte
· Iximche (1470 CE: Postclassic Maya)
· Ixkun
· Ixlu
· Ixpone
· Ixtepeque
· Ixtutz
· Juan Noh
· Kaminaljuyu (1500 BCE: Preclassic Maya; figurines; monument)
· Kinal
· La Amelia
· La Blanca
· La Corona
· La Florida
· La Honradez
· La Muralla
· La Nueva
· La Selva
· La Victoria (Preclassic Maya)
· Laguna Perdida
· Las Tinajas-Pueblo Viejo/Chacujal
· Machaquila
· Mactum
· Michiquirtlan
· Mixco Viejo (12th c.CE: Postclassic Maya)
· Monte Alto (400 BCE: Preclassic Maya; stelae, altars, pyramids)
· Motul de San Jose
· Naachtun
· Naj Tunich Cave (100 BCE: Classic Maya)
· Nakbe (1400 BCE: Preclassic Maya)
· Nakum
· Naranjo
· Nebaj
· Ocos (Preclassic Maya)
· Pantaleon
· Pantzac
· Paso Caballos
· Piedras Negras (7th c.BCE: Classic Maya; Peten)
· Polol
· Poptun
· Pueblo Nuevo Tiquisate
· Quen Santo
· Quirigua Stela D [MA](200 CE: Tikal; Motagua r.)
· Rio Azul (400 CE: Classic Maya)
· Rio Jesus
· Sakajut
· Salinas la Blanca
· San Augustin Acasaguastlan
· San Bartolo (300 BCE: Preclassic Maya; pyramid)
· San Diego
· San Jose Chacaya
· Seibal
· Sin Cabezas
· Tacuilula
· Tajumulco (pyramid; volcano)
· Takalik Abaj (9th c.BCE: Olmec-Preclassic Maya)
· Tamarindito
· Tikal (Classic Maya)
· Tayasal (Postclassic Maya)
· Tres Islas
· Topoxte
· Uaxac Canal
· Uaxactun [Maya: “Eight Stones”]/Siaan K’aan [Maya: “Born in Heaven”] (Classic Maya)
· Ucanal
· Uolantun
· Uspantan
· Utatlan/Qumarkaj (1400 CE: Postclassic Maya)
· Vista Hermosa
· Xolcol
· Xunantunio
· Xutilha
· Yaxchilan
· Yaxha
· Yaxox
· Zaculeu (Postclassic Maya; Huehuetenango)
HAITI:
Cabaret
Couri
HONDURAS:
· Calamuya
· Cerro Palenque
· Copan [MA](500 CE: Classic Maya)
· El Paraiso
· El Puente
· El Tesoro
· Gualjoquito
· Jaral (Naranjos)
· La Ceiba
· La Florida
· La Ola
· La Sierra
· Las Flores
· Las Vegas
· Lo de Vaca
· Los Higos
· Los Naranjos
· Naco (Postclassic Maya)
· Nispero
· Playa de los Muertos
· Rio Amarillo
· Salitron
· San Marcos
· Santa Ana
· Santa Rita
· Santa Rita de Copan
· Tenampua
· Travesia
· Wankybila
· Yarumela
GREATER ANTILLES:
JAMAICA:
· Fairfield
· Little River
· White Marl
· Windsor
MEXICO: (pyramids)
[NOTE 72] Original homeland <root civilization> of the Aztecs was a mysterious lost land of Atlan (‘Atlan’-tis; Dutch call their lost civilization, Atland); commerce-trade connecting America w/Europe, and vice-versa via trans-Atlantic navigation; c.2000 BCE: Olmec-Egyptian; Phonecians routinely visiting America; megalithic cyclopean temple ruins at Teotihuacan and other Mayan sites are similar to those of Lixus (Larache, Morocco) and others in s.Spain; curious similarity between the Basque and Aztec languages (combinations of “x”, “atl” sounds); [Aztec: “water” (atl); original homeland (atlan), “across the water” to the eastern Atlantic]
· Abejas and Purron Caves
· Acanceh
· Acapetagua
· Acapulquito
· Achiutla
· Agua Cancuan
· Agua Escondida
· Aguacatal
· Aguada Grande (Isla Cozumel)
· Ahualulco
· Ake
· Akumal
· Alta Vista de Chalchihuites
· Altar de Sacrificios
· Amapa
· Apanquetzalco
· Apatzingan
· Aquiles Serdan
· Arenitas
· Arroyo el Concho Caves
· Arroyo Pesquero
· Atasta
· Atilhuayan
· Bacalar
· Balakbal
· Balamku
· Balancan
· Balankanche Cave (Postclassic Maya)
· Barrancon
· Becan (550 BCE: Pre-Classic Maya)
· Bellote
· Bolonchen
· Bonampak (590 CE: Chiapas)
· Buena Vista (Isla Cozumel)
· Cacaxtla (Tlaxcala)
· Caguama and Metate Caves
· Calakmul (500 CE: Classic Maya)
· Calderitas
· Calixtlahuaca
· Campanario
· Canajaste
· Cantona (Cofre de Perote)
· Canyon Diablo Caves
· Canyon Infiernillo Caves
· Casas Grandes (Paquime)
· Castillo de Teayo
· Cave Valley Sites
· Celba Grande
· Centla
· Cerrillos
· Cerrito Blanco
· Cerro Chavin
· Cerro Cuevoso
· Cerro de las Mesas
· Cerro de los Monos
· Cerro de Moctehuma
· Chacchoben
· Chacmool
· Chacmultun
· Chakanputun
· Chalcatzingo
· Chamax
· Chametla
· Chanal
· Chanchopa
· Chantuto
· Chauacah
· Chiapa de Corzo (1400 BCE: Preclassic Mayan)
· Chicanna (Classic Maya)
· Chichen Itza (600 CE: Postclassic Maya; calendar: 4 stairways of 91 steps x4 directions = 364 + 1 castillo-summit platform = 365 steps/days; main axis SE-NW targets the rising point of the Sun during the winter solstice and the setting point of the Sun during the summer solstice; light-shadow feature: step descent of the serpent during spring equinox; dedicated to Kulkukan, the plumed serpent; Characo: astronomical observatory- diagonal site lines frame views of certain stars during rising and setting; Temple of Warriors: thousands of human sacrifices)
· Chichmuul
· Chilapa
· Chilpancingo
· Chinikiha
· Chinkultie
· Cholula (2nd c.BCE)
· Chumal
· Chunchucmil
· Chupicuaro
· Cilvituk (Laguna of Silvituk)
· Cinnatan
· Coapexco
· Coba (500 CE: Pre-Classic Maya)
· Coixtlahauca
· Comalcalco
· Copanaguastla
· Copilco
· Coxcatlan Cave
· Cuajilote
· Cuicuileo
· Culiacan
· Culuba (Classic Maya)
· Dainzu (700 BCE: Zapotec; Oaxaca)
· Dry Lake Chapala
· Dzibanche
· Dzibilchaltun (Classic Maya: equinox temple; Merida)
· Dzibilnocac
· Dzitnup
· Ecab/Gran Cairo (Postclassic Maya)
· Edzna (400 BCE: Classic Maya; Campeche)
· Ejutla
· El Arenal & San Sebastian
· El Azuzul
· El Cayo
· El Cedral (Isla Cozumel)
· El Cuyo
· El Dos
· El Infiernillo
· El Manati
· El Meco (Cancun)
· El Ocote
· El Openo
· El Pabellon
· El Palmar
· El Pital
· El Ramonal
· El Rey
· El Riego (Tehuacan)
· El Suspiro
· El Tajin (1st c.CE: Veracruz)
· El Tigre
· El Viejon
· El Zapotal
· Ek’Balam (Classic Maya; Valladolid)
· Etzna
· Frightful Cave
· Guachimontones/Huachimontones (300 BCE-900 CE: Aztec?; Teuchitlan, Jalisco)
· Guajilar
· Gualupita
· Guasave
· Guiengola (Quiengola)
· Guila Naquitz
· Hochob
· Hormiguero (Classic Maya)
· Huajuapan de Leon
· Huamelulpan
· Huexotla
· Hueyatlaco (Pre-Clovis: arrival of humans in New World; 1960’s- arch. Cynthia Irwin- 22,000 BP w/C-14 carbon dating strat-column at Caulapan; mastadon bones w/carvings; bifacial/unifacial spear points; 250,000-700,000 BP w/uranium-238 dating; Valsequillo; 4-500,000 BP: Uranium-Thorium-Helium dating: )
· Hun Chabin
· Huntichmul
· Ichmul de Morley
· Ichpaatun
· Ikil
· Isla Cerritos
· Isla Chantuto
· Isla Piedra
· Isla de Sacrificios
· Ixil
· Ixtlan del Rio
· Izamal
· Izapa (600 BCE: stelo- galactic alignment <12/21/2012>: center of milky way, celestial pole, Sun deity; Chiapas)
· Jaina (Classic Maya)
· Jiguhingo
· Jmetic Lubton
· Juarez <CC: 2007: circles and rings>(14 mi. E Monterrey, Nuevo Leon)
· Juchitan
· Juxtlahuaca Cave (700 BCE: cave paintings)
· Kabah/Kabahuacan [Maya: “strong hand”/”royal snake in the hand”] (3rd c.BCE; Uxmal; Yucatan)
· Kantunil Kin
· Kiuic
· Kohunlich (200 BCE: Classic Maya)
· Komchen (350 BCE: Pre-Classic Maya)
· Labna (Uxmal; Yucatan)
· La Aguada
· La Candelaria
· La Conchita
· La Mar
· La Muneca
· Lacanha
· Lagartera
· Laguna de los Cerros
· Lambityeco (Yeguih <Zapotec: “small hill”>; Mitla; Oaxaca)
· Landeros
· La Playa
· La Quemada (Chicomostoc)
· La Sabana (Acapulco)
· Las Bocas
· Las Higueras
· Las Limas
· Las Panteras
· Las Ranas
· Las Trincheras
· La Venta [MA](1200 BCE: Olmec; Hancock: <20> colossal heads (60 tons)- features Africans and Caucasian portrayals in relief; bearded gods are associated with plumed serpents; 1500 BCE: oldest image of plumed serpent in Mexico; civilization of sky-watchers and astronomers; pyramid site alignment w/ 1950s: destroyed by oil industry; Tabasco)
· Leona Vicario
· Loltun Cave
· Loma del Zaptore
· Lomo San Gabriel
· Los Alzati
· Los Cimientos
· Los Guarixes
· Los Monos
· Majahual
· Malinalco
· Mani
· Marco Gonzalez
· Mario Ancona
· Mayapan (1220 CE: Postclassic Maya; Tecoh)
· Mezcala
· Miahuatlan
· Mirador
· Mitla (500 BCE; Oaxaca
· Monte Alban (500 BCE; Oaxaca)
· Monte Flor
· Monte Negro
· Moral
· Mount Tlaloc [SM][V][Nahuatl: “Tlalocatepetl”](Aztec shrine for human sacrifice to raingod Tlaloc; Mexico City)
· Morett
· Muyil/Chunyaxche
· Navacoyan
· Necaxa
· Nochixtlan
· Nocuchich
· Nohcacab
· Nopiloa
· Ojo de Agua
· Okop
· Olinala
· Oxkintok [Maya: “three day gone”](475 CE: Classic Maya)
· Oxpemul
· Oxtotitlan Cave (700 BCE: cave paintings)
· Oztuma
· Pachuca
· Palenque [MA] [Sp: “fortification;” Maya: Otolum “land of the strong houses;” Classic Maya: Lakam Ha “big water”; sim.Venus/Mercury; ancient capital of B’aakal/B’aak (“bone”)](Chiapas)
· Pajon
· Panuco
· Pared de los Reyes
· Pasion del Cristo
· Paso del la Amada
· Payan
· Penitas
· Pescadero
· Piedras Negras
· Piedra Parada
· Pijijiapan
· Planchon de las Figuras
· Playa de Tesoro
· Pobileuc
· Pomona
· Potrero Nuevo
· Punta Cerritos
· Punta Laguna (Postclassic Maya)
· Pustunich
· Quiahuiztlan
· Quiotepec
· Ramonal
· Rancho Viejo
· Remojadas
· Resbalon
· Rio Bec
· Rio Chiquito
· Rio Huach
· Rio Indio
· Rio Verde
· Rosario
· Sabancuy
· Saci
· San Angel
· San Borjita Cave
· San Carlos
· San Enrique
· San Fernando
· San Francisco Arriba
· San Gervasio (1000 CE: Postclassic Maya; Cozumel i.)
· San Jose Mogote
· San Lorenzo Tenochtitlan [MA](1400 BCE: Olmec; colossal head; Veracruz)
· San Miguel Amuco
· Santa Catalina Mission
· Santa Cecilia Acatitlan [nahuatl: “place among the reeds”](Tlalnepantla de Baz; Mexico City)
· Santa Cruz
· Santa Elena Poco Uinic
· Santa Isabel Iztapan
· Santa Isidro
· Santa Luisa
· Santa Marta Cave
· Santa Rosa Xtampak
· Santo Ton
· Sayil (800 CE: Uxmal; Yucatan)
· Schroeder
· Solferino
· Sonora Coast Figurine Sites
· Suum
· Tabasqueno
· Tahcob/Tohcok
· Tamaulipas (8000 BP: Vera Cruz)
· Tampalam
· Tamuin
· Tancah (Postclassic Maya)
· Tecolpan
· Tehuacan Valley
· Tehuantepec
· Telantunich
· Templo Mayor (1390 CE: Aztec; Tenochtitlan)
· Tenam Puente
· Tenayuca (1224 CE: Aztec)
· Tenochtitlan (1320 CE: Aztec); Aztec Calendar Stone
· Teopantecuanitlan
· Teopanzolco (2000 BCE: Toltec; Aztec)
· Teotenango
· Teotihuacan [“the place where men became gods”](200 BCE: Olmec-Toltec; Aztec; Water Deity on Pyramid of the Moon [MA](1000 BCE); Hancock: myth- the pyramids are instruments for soul transformation after death; pyramid base length is equal to the base length of Great Pyramid at Giza; sacred lava tunnel- oldest part beneath the Pyramid of the Sun, accessible from an entrance at W base; the pyramid and the mouth of the tunnel are aligned with the setting of the Pleiades, when the pyramid was built; causeway offset from true N by 15½°; causeway may have been filled with water; Hausten: 9000 measurements; surveys reveal STU-Standard Teotihuacan Unit- 9000 measurements- code: repeating numbers: dimensions of citadel represent the circumference of Earth: 100,000/1); site of main structure represents the radius of the Earth; earth measuring-geometry)
· Tepetitan
· El Tepozteco (Aztec)
· Tequixquiac
· Texpa
· Texcoco
· Ticul
· Tierra Nueva
· Tila
· Tilantongo
· Tiradero
· Tixchel
· Tizatlan (Aztec; Tlaxcala)
· Tlacuachero
· Tlapacoya (25000 BP: bones; curved obsidian blade; 1500 BCE: Toltec/Olmec; Tlatilco)
· Tlatelolco (1300 CE: Aztec)
· Tonala
· Tonina (200 CE: Olmec; Classic Maya; Chiapas)
· Tortuga
· Tortuguero
· Totoate
· Trapiche
· Tres Zapotes
· Trutruculi
· Tula (Toltec)
· Tulancingo
· Tulum/Zama [Yucatec: “fence;” “city of dawn”] (564 BCE: Postclassic Maya)
· Tumba del Caracol (Isla Cozumel)
· Tupak
· Tututepec
· Tuxtepec
· Tuzaptepetl
· Tzebtun
· Tzendales
· Tzintzuntzan
· Uaacbal
· Uci
· Uxmal [Maya: “built 3x”] (500 CE: Classic Maya)
· Uxul
· Valsequillo (250,000-700,000 BP: Pre-Clovis; Uranium-Thorium-Helium dating)
· Varajonal
· Vega de la Pena
· Xcach
· Xcalak
· Xcalumkin
· Xcambo
· Xcaret [Maya: “small inlet”] (Yucatan)
· Xcopte
· Xelha
· X-Hasil
· Xicalango (Postclassic Maya)
· Xico
· Xkichmook
· Xkukic
· Xlacah
· Xlapak (Maya; Yucatan)
· Xnoha
· Xoc
· Xochicalco [Nahuatl: “in the house of flowers”] (200 BCE; Cuernavaca)
· Xochimileo
· Xochitecatl [Nahuatl: “flower person”](1000 BCE; Tlaxcala)
· Xpuhil
· Xpukil Cave
· Xtacumbilxunan Cave
· Xtelhu
· Xuenkal
· Yagul [Zapotec: “old tree”](3000 BCE: cliff paintings; 500 BCE: Zapotec; Oaxaca)
· Yalsihon
· Yatachio
· Yaxchilan [Maya: “green stones”](6th c.BCE: Classic Maya; Chiapas)
· Yaxcopoil
· Yaxuna
· Yerba Buena
· Yoactun
· Yucunudahul
· Zaachila (1100 CE: Zapotec/Mixtec)
· Zempoala
NICARAGUA:
· Isla De Ometepe
· Isla Momotombito
· Isla Zapatera
· Laguna De Apoyo
PANAMA:
· Barriles
· Cerro Mangote
· El Hatillo
· Giron
· La Concepcion
· Monagrillo
· Pueblo Nuevo
· Sitio Conte
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA: (mounds, cliff dwellings, and petroglyphs)
[NOTE 85: Recent plasma studies have suggested that petroglyphs indicate evidence of plasma discharge streams stretching between planets; plasma formation w/synchrotron radiation at a toroidal center; radio/electro-magnetic discharge, expressing through the number of radial streams and structure, changes with intensity; sim. Tib.: “lightning bolt” (vajra)> (Talbot)]
ALABAMA:
· Apalachicola Fort S (1690: Spanish Fort; Lower Creek; Holy Trinity)
· Bessemer
· Bottle Creek (Prehistoric; 1200 CE: 18 mounds; Mobile)
· Cathedral Caverns (8000 BCE; Woodville)
· Guntersville Basin Sites
· Indian/Shell Mound Park (1100 CE; Dauphin Is.)
· Kinlock Shelter (Thousands BP: solstice temple; Yuchi, Cherokee; Double Springs)
· Liddell (9000 BCE: Prehistoric; Wilcox)
· McQuorquodale
· Moundville (11th c.CE: swastikas found; Tuscaloosa)
· Quad
· Russel Cave (9000 BP; 1000 BCE: Woodland; 500 CE: Mississippian; Bridgeport)
· Stanfield-Worley Bluff Shelter (7000 BCE; Colbert)
· Tennessee River Gorge (10000 BP; Bridgeport)
· William B. Bankhead National Forest (petroglyphs; Double Springs)
· Willstown (Cherokee town; Fort Payne)
· Wheeler Basin Sites
· Yuchi Town Site (1650 CE: Apalachicola/Yuchi; Ft. Benning; Ft. Mitchell)
ALASKA:
· Adamagan (Aleut village)
· Afognak (7500 BP: village; Kodiac)
· Amalik Bay (Katmai NP, Kodiac)
· Amchitka
· Anangula (8400 BP; Umnak i., Aleutian)
· Barrow (500 CE: Inupiat; 800 CE: Birnirk mounds)
· Birnirk (Barrow)
· Brooks River (2500 BCE; Katmai NP)
· Cape Krusenstern (9000 BP)
· Cape Prince of Wales Sites
· Chaluka (Aleut: mound; Nikolski)
· Chitina (Athabaskan; Valdez-Cordova)
· Crow Village (Anvik; Deloy Ges/Hawk Bluff [SM])
· Daxatkanada (Angoon)
· Diomede Islands
· Dixthada
· Dry Creek (Healy)
· Gallagher Flint Station
· Gambell Sites
· Glacier Bay
· Healy Lake
· Homer (Alutiq culture)
· Ipiutak
· Iyatayet (6000 BCE; Nome; Cape Denbigh)
· Kachemak Bay
· Katmai NP (King Salmon)
· Kenai Fjords NP (Seward)
· Kijik (Denaina Athabaskan culture)
· Kodiak Archipelago
· Krugloi Point
· Mount McKinley/Denali [Koyukon-Athabaskan: “the high one” (Dinali); Denaina: “the big one” (Dghelay Ka’a); Aleut: (Traleika); highest elevation in North America]
· Naknek Sites
· Noatak NM
· Ocean Bay
· Okvik
· Onion Portage
· Palugvik (Cordova)
· Pedro Bay
· Port Moller
· Ratekin
· Shaktoolik (Nome)
· Sterling (Denaina pits; Kenai penin.)
· Takli
· Tangle Lakes
· Trail Creek Caves (8500 BP; Seward penin.)
· Uelen (USSR)
· Wrangell-St.Elias (Anchorage)
· Yukon Island (Homer)
· Yukon-Charley Rivers (Paleontological)
ARIZONA:
· Agate House Pueblo (900 CE; Holbrook)
· Awatovi Ruins (16th c.CE; Keams Canyon)
· Besh-Ba-Gowah
· Betatakin
· Bradshaw Mountains (Kwevkapaya- 1100 CE: Yavapai: forts, copper mines; 1800: Apaches)
· Broken K
· Canyon de Chelly NM (White House Ruin; Anasazi)
· Carter Ranch
· Casa Grande Ruins NM (1200 CE; Coolidge)
· Casa Malpais [t.Basque: “House of the Badlands”](1250 CE; Springerville)
· Double Adobe (11000 BP: Clovis culture; mammoth; Douglas)
· Gatlin (800 CE: Hohokam; mounds, pit houses, ball courts, middens, prehistoric canals; Gila Bend)
· Grasshopper
· Hohokam Pima NM/Snaketown (Hohokam village: ball court; miles of canal; Gila River IR; Sacaton)
· Kanab Creek Wilderness (1100 CE; San Manuel)
· Keet Seel
· Kinishba Ruins (1200 CE: Anasazi-Mogollon; Whiteriver)
· Kitt Peak [SM](Tohono O’oodham)
· Lehner Mammoth-Kill site (9000 BP: Clovis)
· Mesa Grande (1300 CE: Hohokam mound; Mesa; Phoenix)
· Montezuma Castle NM (700 CE: Sinagua; Camp Verde)
· Mount Trumbull Wilderness (Anasazi; Fredonia)
· Murray Springs
· Naco-Mammoth kill site (10000 BP: Clovis; Naco)
· Navajo NM [SM](1250 CE: Anasazi; Kiet Siel and Betatakin cliff dwellings, and Tsah Bii Kin Inscription House; Kayenta; El Capitan/Agathla Peak)
· Painted Rocks (petroglyphs; Theba)
· Palatki (6000 BP: petroglyphs; 1100 CE: Sinagua; Sedona)
· Palo Parado
· Paria River (petroglyphs; Page)
· Petrified Forest NP (Agate House; Holbrook)
· Pipe Spring NM (Paiute/Puebloan; Mormon; Fredonia)
· Point of Pines NM (Anasazi-Mogollon-Hohokam; Morenci)
· Presidio Santa Cruz de Terrenate (Hohokam; Sobaipuri; 1776: New Spain; Tombstone)
· Pueblo Grande Ruin and Irrigation Sites (Hohokam-Pima; Phoenix)
· Puerco
· Point of Pines
· Red Rock-Secret Mountain Wilderness (prehistoric rock art; cliff dwellings; Sedona)
· San Francisco Peaks/Humphreys Peak [SM] [V] [Navajo: (Dook’o’oosliid)] (demarks western boundary of Dinetah; sacred to 13 Native American nations; Flagstaff)
· Sierra Ancha (1280: Salado-Mogollon; cliff dwellings; Gila co.)
· Sikyatki [Hopi: “Yellow House”](14th c.CE: Hopi village; Navajo co.)
· Snaketown
· Tonopah [Apache: “water for us/you”](Yavapai-Apache; Maricopa co.)
· Tonto NM (13th c.CE: Salado; Phoenix)
· Topock Gorge (petroglyphs; Lake Havasu)
· Tres Alamos
· Tumacacori NP (1691: Jesuit missions; 1700s: Franciscan churches; Nogales)
· Tusayan ruins (1200: Pueblo kiva; Grand Canyon NP)
· Tuzigoot NM [Apache: “crooked water”](1125: Sinagua; Flagstaff)
· Unkar Delta
· Ventana Cave (11300 BP: Clovis; Santa Rosa; near Kitt Peak)
· Walnut Canyon NM (Sinagua; Flagstaff)
· Winona site (1066 CE: Sunset Crater eruption; Winona)
· Wupatki NM [Hopi: “Big House”](Sinagua ball court and citadel; Flagstaff)
ARKANSAS:
· Arkansas Post National Memorial (Quapaw; 1783: Revolutionary War sitr; Pine Bluff; Gillett)
· Baytown (300 BCE: mounds; Monroe co.)
· Bluff Shelter Sites
· Crenshaw
· Eaker Site (Quapaw-Nodena; Blytheville)
· Helena Crossing
· Island 35 Mastodon (4m BP: Blytheville)
· Menard Hodges Site/Casqui (2 mounds; DeSoto d.1540; Watson)
· Mineral Springs
· Natural Steps (1500 CE: Quapaw; Kinkead-Mainard site; Pulaski co.)
· Nodena/Pacaha (1400 CE: Mississippian; mastodon; Wilson)
· Old Davidsonville SP (4000 BCE; 1100 CE: mounds; Black Rock)
· Parkin SP (1350 CE: mounds)
· Toltec/Knapp Mounds SP (600 CE: Plum Bayou; Scott)
CALIFORNIA:
· Acuragna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Achasta (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Ahapchingas (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Alyeupkigna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Santa Anita; Los Angeles)
· Anderson Marsh SP (10000 BP: Pomo; Clearlake)
· Apyu (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Arekw (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.; Orick)
· Arlington Springs Man/Woman (13000 BP; Santa Rosa i.)
· Aranimokw (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Astakiwi (Shastan settlement; Modoc co.; Canby)
· Awigna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; La Puente)
· Azucsagna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Azusa)
· Bamom (Maidu settlement; El Dorado co.)
· Bauka (Maidu settlement; Gridley)
· Bayu (Maidu settlement; Powers)
· Blossom
· Blythe Intaglios (2000 BP: gigantic ground figures; Blythe)
· Bokea (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.)
· Borax Lake (Paleo-Clovis-Post Pattern; Clearlake)
· Browne
· Buldam (Pomo settlement; Mendocino)
· Burro Flats Painted Cave (500 CE/1400s?: Chumash: 2 human stick figures wearing headdresses w/lines radiating from; Boeing-Rocketdyne lab.; Simi Valley/San Fernando valley)
· Burton Mound
· Cahuenga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Calico Early Man (200000 BP: 60000 prehistoric stone tools; first American migrations 11000 BP?; Barstow; Mojave d.)
· Chinits (Karok settlement; Tsofkara; Humboldt co.)
· Chokishgna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Chomchadila (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.; Calpella)
· Chowigna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Palos Verdes)
· Chumash Painted Cave SP (200-1000 BP?: cosmology depictions; Santa Barbara)
· Chumawi (Shastan settlement; Modoc co.)
· Corn Springs (Archaic; Chemehuevi-Desert Chuilla-Yuma; petroglyphs; Desert Center)
· Coso Rock Art D/Big and Little Petroglyph Canyons (10000 BP: Coso: 20000 petroglyphs; China Lake)
· Cucamonga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; San Bernadino; Rancho Cucamonga)
· Dahnohabe (Pomo settlement; Lake co.; Clear Lake)
· Dapishul (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.; Redwood Valley)
· Death Valley NP (10000 BP: Nevares Spring People; 5000 BP: Mesquite Flat; 2000 BP: Saratoga Spring; petroglyphs; Pahrump, NV)
· Emeryville Shellmound (1769)
· Erner (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Ertlerger (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Eshpeu (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Eskini (Maidu settlement; Durham)
· Eslanagan (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Farmington
· Fernandez
· Fort Ross (1812: Russian/N.Pacific natives settlement; Healdsburg)
· Guayusta (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Gunther Island S67 (Wiyot: Tolowat village; large shell midden, 11 house middens, burial sites; Eureka)
· Hahamongna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Glendale)
· Harasgna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Harris
· Hokokwito (Miwok settlement; Yosemite Falls)
· Hokomo (Maidu settlement; Mooretown)
· Holhoto (Maidu settlement; Mooretown)
· Honkut (Maidu settlement; Yuba co.)
· Honmoyoausha (Chumash settlement; San Pedro)
· Honsading (Hupa settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Hopitsewah (Pomo settlement; Lake co.; Clear Lake)
· Indak (Maidu settlement; Placerville)
· Isanthcogna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Mission Vieja)
· Joshua Tree NP
· Juyubit (Serrano settlement; Los Angeles)
· Kaci-badon (Pomo settlement; Lake co.)
· Kakonkaruk (Rumsen settlement; Monterey co.; Big Sur)
· Kalindaruk (former settlement; Monterey co.)
· Kalkalya (Maidu settlement; Butte co.)
· Keshlakchuis (Modoc settlement; Rhett l.)
· Keuchishkeni (Modoc settlement; Modoc co.)
· Khawina (Pomo settlement; Lake co.)
· Khoonkhwuttunne (Tolowa settlement; Del Norte co.)
· Khwunrghunme (Yurok settlement; Del Norte co.)
· Kokaman (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Koloma (Nishinam settlement; Coloma)
· Koi (Pomo settlement; Lake co.; Lower Lake is.)
· Kowanga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Kulaiapto (Maidu settlement; Butte co.)
· Kule Loklo [“Bear Valley”](Coast Miwok village; Marin co.)
· Kulul (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Kumaini (Awani settlement; Yosemite Falls)
· Kuya’mu (Chumash village; Santa Barbara)
· Kworatem (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· La Jolla Complex (6000 BCE; San Diego)
· Lake Manix
· Lake Mohave
· Lava Beds NM (petroglyphs; Modoc co.; Klamath Falls, OR; Medicine Lake volcano)
· Little Harbor
· Little Sycamore
· Lolsel (Wintun settlement; Lake co.; Clear Lake)
· Loolego (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Lukaiasta (Kalindaruk settlement; Monterey co.)
· Macheto (Awani settlement; Mariposa co.; Calpella)
· Malaga Cove
· Masut (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.)
· Maugna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Meadow Lake (1500 BCE: Martis; petroglyphs; French Lake)
· Medicine Lave Volcano [SM] (near Mt.Shasta)
· Michopdo (Maidu settlement; Butte co.)
· Mikiw (Chumash village; Santa Barbara; Dos Pueblos Creek; adjacent Kuyamu)
· Mission San Jose (1797)
· Mitchell Caverns (Chemehuevi tools and fire pits; Providence Mountains SRA)
· Moaning Cave (Miwok burial ground: bones; Vallecito)
· Moiya (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.; Hopland)
· Nacaugna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Notomidula (Awani settlement; Mariposa co.; just E of Macheto)
· Oak Grove
· Oketo (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.; Trinidad)
· Okowvinjha (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Ololopa (Maidu settlement; Oroville)
· Olposel (Wintun settlement; Lake co.; Cache Creek)
· Olumpali/Olompali SHP (6000 BCE; 1200 CE: Coast Miwok main center; Petaluma)
· Onchomo (Maidu settlement; Placerville)
· Opegoi (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Opok (Maidu settlement; Nashville)
· Oreq (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Otaki (former settlement; near Michopdo; between Chico creeks)
· Painted Rock (2000 BCE: Chumash/Yokut pictographs; San Luis Obispo co; Taft)
· Paisin (former Kalindaruk settlement; Monterey co.)
· Paki (Maidu settlement; Butte co.)
· Panamenik (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Pasara (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Pasinogna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Pauma Complex (Holocene; San Diego)
· Pekwan (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Pekwuteu (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Petroglyph Canyons
· Pimocagna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Pinto Basin
· Post Pattern (13000 BP: pre-Hokan; Clear l.; Borax l.)
· Presidio (1782: mission; Santa Barbara)
· Pubugna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Alamitos)
· Quapa (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Quasil (Chumash village; Santa Barbara)
· Quina (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Red Rock Canyon SP (Coso; Kawaiisu; petroglyphs; Bakersfield)
· Rekwoi (Yurok settlement; Del Norte co.; Requa)
· Sakaya (former native settlement; Mariposa co.)
· San Onofre SB (8000 BP: Juaneno/Achachemen-Panhe village; San Diego)
· San Dieguito Complex (8200 BCE: projectile points; Escondido)
· San Luis Rey Complex (500 CE; San Diego)
· Santa Clara River (LA)
· Santa Monica Mts (Tongva-Chumash; LA)
· Santa Rosa Island (13000 Arlington Springs man; Chumash)
· Sapaywis (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Saway-yanga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Sawuara (Karok settlement; Del Norte co.; Orleans)
· Seama (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Serra Springs/Kuruvungna [“a place where we are in the sun”](400 BCE: Tongva; LA)
· Shalawa Meadow (13000 BP: Chumash burial site; Montecito)
· Shanamkarak (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Shasta [SM][V][Karuk: “White Mountain”](7000 BP; Tribes: Shasta, Okwanuchu, Modoc, Achomawi, Atsugewi, Karuk, Klamath, Wintu, Yana; Siskiyou co.)
· Shegoashkwu (Karok settlement; Del Norte co.)
· Shiegho (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.; Hopland)
· Shishuchii (Chumash village; Santa Barbara)
· Shregegon (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Shumig (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Sibagna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Sisitcanogna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Pear Orchard)
· Siwim (Maidu settlement; Kelsey)
· Soccorondo (Esselenian settlement; Monterey)
· Sonagna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Steloglamo (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Suangna (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles; Palos Verdes)
· Subazama (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Sunusi (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Jacinto)
· Tadoiko (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Durham)
· Taikus (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Cherokee)
· Taisida (Maidu settlement; Marysville)
· Tajiguas (Chumash village; Santa Barbara)
· Takuyumam (Chumash settlement; New Hall; Santa Clarita; Los Angeles)
· Tatlatunne (Tolowa settlement; Del Norte co.)
· Tchikimisi (Maidu settlement; El Dorado co.)
· Tecolom (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Tcose
· Teshaya (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Tetachoya (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Tisechu (Yokuts-Choinimni settlement; Fresno co.)
· Tiubta (Kalindaruk village; Monterey co.)
· Tolowot
· Topanga
· Totoma (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Yankee-Hengy)
· Toviseanga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Trinity Reservoir Sites
· Tsofkara (Karok settlement; Humboldt co.)
· Tsuka (Maidu settlement; Butte co.)
· Tsurau (Yurok settlement; Humboldt co.; Trinidad)
· Tukutnut (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Tuyunga (Tongva-Gabrieleno settlement; Los Angeles)
· Ubakhea (Pomo settlement; Mendocino co.)
· Wachanaruka (Costanoan settlement; Monterey)
· Waikosel (former native American settlement; Colusa co.)
· Whiskeytown Reservoir Sites
· Willow Creek
· Windmiller
· Wiskala (Awani settlement; Mariposa co.)
· Yalisumni (Maidu settlement; El Dorado co.)
· Yauko (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Chico)
· Yuman (Maidu settlement; Butte co.; Oroville)
· Yusumne (Maidu settlement; Ione)
· Zassalete (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
· Zumblito (Salinan settlement; Monterey co.)
COLORADO:
· Agate Bluff
· Bent’s Old Fort NHS (1833; La Junta)
· Blanca Peak [SM] [Navajo: “Sacred Mountain of the East,” “the Dawn,” or “White Shell Mountain” (Sisnaajini/Tsisnaasjini)] (demarks E boundary of Navaho sacred homeland, Dinetah; Alamosa)
· Canyons of the Ancients NM (10000 BP: Clovis; Anasazi; Dolores)
· Chimney Rock (Anasazi; Durango)
· Cliff Palace (1190 CE: 23 kivas; Mesa Verde NP)
· Cliff Swallow Cave
· Cowboy Wash (9 Anasazi Sites; Ute Mt.; Montezuma co.)
· Curecanti NRA (6000 BP: dwellings; Gunnison)
· Dent
· Dinosaur NM (dinosaur fossils; petroglyphs; Vernal, UT)
· Dutton
· Frazier and Jurgens
· Great Sand Dunes
· Hesperous Peak [Navajo: “Sacred Mountain of the North” (Dibentsaa)] (demarks N boundary of Navaho sacred homeland, Dinetah; Durango)
· Hovenweep NM (14000 BP: paleo-indians; 1150 CE: Anasazi; Cortez)
· Jones Miller
· Lamb Springs
· Limon Breaks
· Lindenmeier (8710 BCE: Folsom culture campsite; Fort Collins)
· Lowry Pueblo (1060 CE: Anasazi; Canyons of the Ancients NM; Pleasant View)
· Ludlow Tent Colony (1913)
· Mesa Verde NP (1200 CE: Cliff Palace; House of Many Windows; Spruce Tree House; Square Tower House; Cortez)
· Olsen-Chubbuck
· Phillips-Williams Fork Reservoir (11000 BCE: paleoindian)
· Rocky Mountain NP (10000 BP: paleo; Ute; Arapaho; Estes Park)
· Tabeguache Caves
· Talus Slope
· Trinidad Pueblos
· Yucca House NM (900 CE: Anasazi; Cortez)
CONNECTICUT:
· Fort Shantok (17th c.CE: Mohegan; Montville; New London)
· Gungywamp (2000 BCE: astronomical stone circle; stone chamber; Groton; New London)
· Mashantucket Pequot Reservation (Ledyard; New London)
DELAWARE:
· Island Field
· Koens-Crispin
FLORIDA:
· Airport Clear Zone AS (18th c.CE: Smyrnea settlement; New Smyrna Beach)
· Alachua culture (700 CE: mounds)
· Anhaica (Apalachee; Tallahassee)
· Atsena Otie Key (1500’s: Spain)
· Barley Barber Swamp (1100 CE: sand mound; pottery; Okeechobee l.)
· Bay Pines S (mounds)
· Bear Lake Mounds AD (Flamingo)
· Big Heart West
· Big Mound City (mounds; Canal Point; Okeechobee l.)
· Big Mound Key-Boggess Ridge AD (850 BCE: John Quiet mound; Placida)
· Blanchette AS (Smyrnea settlement; New Smyrna Beach)
· Bowers Bluff Middens AD (mounds; Astor; Lake co.)
· Bubba Midden (mounds; Green Cove Springs)
· Bulow Plantation Ruins HSP (sugar mill; Flagler Beach)
· Burns Lake S (mounds; Ochopee)
· Butcherpen Mound (mounds; Gulf Breeze)
· Carrabelle
· Cayson Mound and Village S (Blountstown)
· Cedar Key (500 BCE: mound; Levy co.)
· Cockroach Key
· Crystal River ASP (400 BCE: 6 mounds)
· DeLeon Springs SP (8000 BCE; 6000 BCE: canoe)
· De Soto NM (1539; Tampa)
· Demere Key (Fort Myers)
· Devil’s Den (subterranean river/cave: artifacts)
· Dunlawton Plantation and Sugar Mill (destroyed by Seminoles; Port Orange)
· Edward Ball Wakulla Springs SP (12000 BP: paleo-indians; Tallahassee)
· Escambe (17th c.CE: Spanish Franciscan mission; Tallahassee)
· Everglades NP (10-20000 BP: Tequesta; Calusa; shell mounds)
· Fig Springs mission S (17th c.CE: Spanish mission; Fort White)
· Fort Center
· Fort King (6500-2000 BCE; Ocala)
· Fort Walton
· Galt Island AD (shell midden; burial mound)
· Garden Patch AS (Horseshoe Beach)
· Grange AS (New Smyrna)
· Grant Mound
· Green Mound (800 CE: Ponce Inlet)
· Halfway Creek S (Carnestown)
· Otis Hare AS (Bristol)
· Hawks AS (Smyrnea: Edgewater)
· Melbourne (10000 BP: paleo-indians)
· Lake Hell’n Blazes (8000 BP; Melbourne)
· Hickory Ridge Cemetery AS (Pensacola)
· Hinson Mounds (Miles City)
· Horr’s Is. AS (4000 BP: 4 mounds)
· Capt. John Foley Horr House (Marco i.)
· Indian Fields (Titusville)
· Indian Temple Mound (1100 CE; Fort Walton Beach)
· J&J Hunt Submerged AS (Pleistocene; 14000 BP: Clovis; stone tools; 6km off coast; Ft Walton Beach)
· Janet’s AS (New Smyrna Beach)
· Josslyn Is. S (Pine i.-Cayo Costa; Ft. Myers)
· Jungle Prada S (mounds; St.Petersburg)
· Jupiter Inlet HAS (mounds)
· Key Marco (Prehistoric: 1000 wooden artifacts)
· Kimball Is. Midden AS (mounds; Astor)
· Lake Hell’n/Helen Blazes (8000 BCE: Clovis points; Melbourne)
· Lake Jackson Mounds ASP (1100 CE: Ft Walton culture; Tallahassee)
· Lake Pithlachocco Canoe S (4000 BCE; Gainesville)
· Leon-Jefferson culture (1100-1550 CE: Ft.Walton culture; mounds)
· Letchworth Mounds (200 CE: state’s largest ceremonial mound-46’; Montecello)
· Little Salt Spring (13450 BP: tortoise bone; 6800 BP: burial mounds; North Port)
· Madira Bickel Mound SAS (2000 BP; Terra Ceia i.; Bradenton)
· Mala Compra Plantation AS (1816-36; Palm Coast)
· McKeithen Weeden Is. Culture (200 CE: mounds, plaza, artifacts; Santa Fe r.-Aucilla r.)
· Melbourne Bone Bed (20000 BP: paleontological)
· Miami Circle (2000 BP: 24 holes in Oolitic limestone bedrock)
· Mission San Luis de Apalachee (1633 CE: Spanish Franciscan; Tallahassee)
· Mound Key ASP (2000 BP: Calusa; Ft. Myers Beach)
· Mount Elizabeth AS (mound; Jensen Beach)
· Mount Royal (mounds; Welaka)
· Mount Taylor (4000 BCE; DeBary)
· Mullet Key (Crystal River)
· Naval Live Oaks R (Gulf Breeze)
· New Smyrna Sugar Mill Ruins
· Offshore Reefs AD (Key Biscayne)
· Old Fort Park AS (New Smyrna)
· Old Stone Warf AS (New Smyrna)
· Ormond Mound (800 CE: St.Johns culture; Ormond Beach)
· Osprey AHS (mound; Osprey)
· C.J.Ostl S (Ochopee)
· Page-Ladson prehistory S (14500 BP: Clovis; Aucilla r.)
· Mark Pardo Shellworks S (mounds; Bokeelia)
· Persimmon Mound (Rockledge)
· Pierce Mounds S (Apalachicola)
· Pineland AD (1300 CE: Calusa: mounds; Pineland)
· Platt Is. (Miles City)
· Plaza S (Ochopee)
· Portavant/Snead I. Temple Mound (Palmetto)
· Porter’s Bar S (Eastpoint)
· Princess Mound (Green Cove Springs)
· Rock Mound AS (Key Largo)
· Rookery Mound (Everglades City)
· Ross Hammock S (mounds; New Smyrna)
· Safety Harbor S (500 BCE: capital of Tocobaga)
· San Joseph de Ocuya (17th c.CE: Spanish Franciscan mission; Lloyd)
· San Juan de Aspalaga (17th c.CE: Spanish Franciscan mission; Wacissa)
· San Juan del Puerto (1587 CE: Roman Catholic mission; Jacksonville)
· San Marcos de Apalache HSP
· San Miguel de Asile (17th c.CE: Spanish Franciscan mission; Lamont)
· Sanchez Powder House S (St.Augustine)
· Santa Fe de Toloca Sebastian Inlet SP (1606 CE: Spanish mission)
· Shell Bluff Landing (Ponte Vedra Beach)
· Silver Springs
· Sleepy Hollow AS (New Smyrna)
· Spruce Creek Mound Complex (Prehistoric; Timucuan; Port Orange)
· St.Augustine
· St.Johns Culture (500 BCE; St.Johns r., Oklawaha r.)
· Sugar Pot S (Ochopee)
· Terra Ceia
· Third Gulf Breeze
· Thomas Creek AD (Chumuckla)
· Turnbull Colonists’ Houses AS (New Smyrna)
· Turner River S (Ochopee)
· Turtle Mound (prehistoric Timucuan; 800 CE; New Smyrna)
· Twin Mounds AD (Sorrento)
· Upper Tampa Bay Park (mounds)
· Useppa Is./Toampe (8000 BCE: paleo-indians; Calusa: burial mound; Fort Myers)
· Velda Mound (1450: Apalachee province w/Lake Jackson, and Anhaica; Tallahassee)
· Vero Beach (8000 BCE: Clovis points; Melbourne)
· Waddells Mill Pond S (mounds; Marianna)
· Warm Mineral Springs (10000 BP: human remains; North Port)
· Weeden Is. Preserve (St.Petersburg)
· White Fox House AS (New Smyrna)
· Windover AS (8000 BCE: 168 peat pond burials; Titusville)
· Yent Mound (St. Teresa)
· Yon Mound and Village S (Bristol)
· Yulee Sugar Mills Ruins SHS (1851 CE; Homosassa)
GEORGIA:
· Bilbo
· Deptford
· Etowah Mounds (1000 CE: Mississippian mounds; Cartersville)
· Hollywood
· Irene
· Jim Woodruff Reservoir Sites
· Kolomoki Mounds HP (250 CE: Swift Creek/Weeden Is. culture; Blakely)
· Lamar
· Leake Mounds (300 BCE: Swift Creek; Cartersville)
· Mandeville
· Nacoochee Mound [Cherokee: “evening star”](100 BCE: prehistoric; Woodland/Mississippian culture; Chattahoochee r.)
· New Echota/Gansagiyi (-1819 CE: Cherokee town; Calhoun; Resaca)
· Ocmulgee NM (10000 BP; 900 CE: Mississippian mounds; Creek; Macon)
· Rock Eagle Effigy Mound (2000 BCE?: Woodland; Eatonton)
· Rock Hawk Effigy Mound (2000 BCE?: Woodland; Eatonton)
· Roods Landing/Creek Mounds S (Woodland: mounds; Omaha)
· Santa Isabel de Utinahica (17th c. CE: Spanish mission; Telfair co.)
· Sapelo
· Soapstone Ridge (1000 BCE: quarry; Atlanta)
· Stallings Is. (4500 BP: ceramic sherds; Augusta)
· Track Rock (8000 BCE?: petroglyphs; Chattahoochee NF)
· Tugaloo (Cherokee town; Toccoa; Tugaloo r.)
HAWAII QIGONG VORTEX:
[Heiaus, pohaku stones, caves, fish ponds/healing pools, petroglyphs]
[NOTE 1] Kahuna Momi Mo’okini Lum, traces lineage back to Kuamo’o Mo’okini, to ancient temples in Fiji, India, and Kapakapa’au’a’kane/Sumeria.
[NOTE 2] Haw./Tahitian/Polynesia Myth.: Kane/Tane-creator god; Lono-g.storms, rain, fertility; Ku-g.war, strenuous activity; Kanaloa/Taaroa-g.sea, death.
· Ahu A Umi Heiau [HI: “mound/temple of Umi] (16th c.CE; North Kona)
· Ahuena Heiau (1813-9: K.Kamehameha personal temple; Kailua-Kona, Hawaii)
[NOTE 89: Ahu pua’a definition- word derives from the boundary marker, a pile (ahu) of stones surmounted by an image of a pig (puaʻa), to indicate where tribute was laid on the altar as tax to the chief; each ahupua'a contained nearly all the resources that were required for survival; land division; estate]
· Ahu pua’a Makaha
· Ahu pua’a Ohikilolo
· Ahu pua’a Makua
· Ahu pua’a Kahanahaiki
· Ahu pua’a Keawe’ula
· Ahu pua’a Ka’a’awa
· Ahu pua’a Hakipu’u
· Ahu pua’a Waikane
· Ahu pua’a Ka’alaea
· Ahu pua’a Kahalu’u
· Ahu pua’a Kailua
· Ahu pua’a Waimanalo
· Alala Heiau (1400-1600 CE: K.Kakuhiewa; large pohaku stones; spotting site for fishing; luakini?; Kailua, Oahu)
· Bobcat Trail Habitation Cave (16th c.CE; North Kona)
· Halawa (H3)
· Halulu Heiau (Lanai)
· Hawaii Volcanoes NP (petroglyphs)
· Halekii-Pihana Heiau (reded.by Kahekili as war temples; Wailuku, Maui)
· Hale O Lono Heiau (1470-1700 CE; d.Lono, god of agriculture, weather, sports, medicine; Waimea v., Oahu)
· Hawaii Kai Heiau (1400s CE; can get there from behind Kokohead; Hawaii Kai, Oahu)
· Hikiau Heiau (r.1917; Kealakekua Bay, Hawaii)
· Hikina’akala Heiau (Wailua Complex of Heiau; Wailua r.; Kauai)
· Holomakani [Haw.: “Running Wind”] Heiau (500 CE?: 96’x48’; priv.prop, Ulumawao ridge; Kawainui marsh; Kapa’a Quarry rd., Oahu)
· Honokohau Settlement Kalokohonokohau NHP (300 BP: petroglyphs, aquaculture, stone slides, heiaus)
· Hokukano-Ualapue Complex (6 temples, 2 fishponds; Ualapue, Maui)
· Holualoa Bay (1300 CE: Kamoa Point Complex; Kailua-Kona)
· Huilua Fishpond/HASS-50-OA-FS-1 (Kane’ohe)
· Ili’iliopae Heiau (310’x120’; luakini heiau; ancient kahuna school; 2nd largest heiau in Hawaii; Molokai)
· Kahalu’u Bay (500 BP: Ku’emanu Heiau, Pa o ka menehune/”wall of the ancients”; Kahaluu-Keauhou)
· Kahea Heiau (Lanai)
· Kahoolawe (1000 CE: petroglyphs)
· Kalalea Heiau (ancient settlement, fishponds, platforms, petroglyphs, heiau; Kaloko-Honokohau NHP, Kona, Hawaii)
· Kalaupapa Peninsula Heiau (Molokai)
· Kaloko-Honokohau NHP (ancient settlement, fishponds, platforms, petroglyphs, Kalalea heiau; Kona, Hawaii)
· Kaneaki Heiau (1470-1700 CE; d.Lono, god of agriculture; Makaha Valley; Mauna Olu Estates; Oahu)
· Kaneana Cave (near Makua, Oahu)
· Kaena Point (Spirit Gate; menehune trail; army fort and shaft, and bunkers; satellite tracking station and observatory; monk seal and albatross sanctuary; Oahu)
· Kaniakapupu/Summer Palace of King Kamehmeha III (built over existing heiau; 1825 CE; Nu’uanu, Oahu)
· Kaunolu Village Site (largest surviving fishing village ruins; Lana’i)
· Kaupo Village (130'x 150'; was where Sea Life Park area is; 1853: during the small pox epidemic in Hawaiian Islands, many Hawaiians moved here to escape quarantine; most of the site was destroyed when the present hwy. was built; Makapuu, Oahu)
· Kawela AS (21 sites; Molokai)
· Kea’iwa Heiau [Haw.: “temple of healing”](16th c.CE?: Hawaiian Healing Herb Center- kahuna kapa’ao; near Ho’ola Heiau; Aiea, Oahu)
· Kealakowaa Heiau (Sadie Seymour BG; Kailua-Kona)
· Keikipuipiu Heiau (Quarry Hill Rd., Kalaniole, across from Olomana Golf Course; near unnamed heiau on Waimanalo side of Olomana ridge facing the Koolau range: 2 terraces, 50' x 130'; Kaneohe-Kailua, Oahu)
· Kuamoo/Lekeleke Burials (North Kona)
· Kuemanu Heiau (Kona)
· Kuilioloa Heiau (3-terraced platforms; plaque: “Malaea: Malama I Ko Makou Aina”; Kaneilio Point (midpoint of W side); Maili, Waianae; Lualualei Homestead Rd. and Pokai Bay Rd.; Oahu)
· Kukaniloko Birthstones SHS (1100-1795 CE: Birthstones: birthplace of chiefs; navel of Oahu, symbolic of navel cord/piko; key battles fought here for control of Oahu; solstice temple astro-time keeper w/Wai'anae Range; assoc. w/ Ho'olonopahu Heiau, now destroyed; 1400-1500 CE: near royal center of Lihu'e; Wahiawa, Oahu)
· Kuka’o’o Heiau (17th c.CE: legend: built by menehune; Manoa, Oahu)
· Kunawai (mo’o healing waters; Kuakini, Oahu)
· Laaloa Bay [HI: “very sacred”](Haukalua Heiau; Kailua-Kona)
· Leahi (built by Maui King Kahekili; 1856 CE: destroyed; built over with condos.; near La Pietra school: Roman sarcophagus; Diamond Head, Oahu)
· Loaloa Heiau (1730 CE: luakini heiau; built by Kekaulike, k. of Maui; Kaupo, Maui)
· Makaha Heiau (Lahilahi Ln.; Makaha Beach; Pokai Bay, Oahu)
· Makapuu Heiau Healing Pool (Makapuu, Oahu)
· Makua Heiau (Makua, Oahu)
· Mauna Kea Adz Quarry [SM][V](prehistoric: quarry; heiau, petroglyphs; Hilo)
· Moku’ula (moated palace; piko; Lahaina)
· Mo’okini Heiau (480 CE; d.Ku, built by Kuamo’o Mo’okini; luakini heiau/temple of human sacrifice; 1000 CE: reded.by Pa’au, kahuna chief from Samoa; 1000 CE: Samoan-Tahiti arrival/invasion- kapu sys. until 1819; accd.to Kahuna Momi Mo’okini Lum, traces lineage back to Kuamo’o Mo’okini, to ancient temples in Fiji, India, and Kapakapa’au’a’kane/Sumeria; 2006: earthquake dmg.; Upolu pt.; N.Kohala, Hawaii)
· Na Pohaku O Hauwahine (1000 CE: fishing pond; mo’o temple; Kawainui SP; Kaneohe-Kailua, Oahu)
· Nihoa/Bird Is./Moku Manu
· Pahua Heiau (1400 CE: agricultural heiau; 2 zones of 3 platforms at base of ridge trail; pohaku stone throne on ridge above by Outdoor Circle; restored 1984-5; center of Hawaii Kai valley, oriented towards Hawaii Kai Bay; Kokohead Crater; L Lunalilo Home Rd.-L Hawaii Kai Dr.at Kaiser High School-R Wai’oli-L Makahu’ena; Hawaii Kai, Oahu)
· Pahukini Heiau (Kawainui SP; Kaneohe-Kailua, Oahu)
· Piilanihale Heiau (16th c.CE: b.Riilani; platform; largest heiau in Hawaii; Kahanu Garden, Hana, Maui)
· Pohakunui Heiau (50'x90'; on hill at base of Koolau mts; on Ekahi farms; between Kaulukanu and Mahailua St.; possible heiau at stone ruins above Kaikaina St.: 130' x 110'; possibly more back further in the valley; Waimanalo, Oahu)
· Poliahu Heiau (Wailua Complex of Heiau; Wailua r.; Kauai)
· Pueo Heiau (130'x 150'; above University Experimental Farm on Waikupanaha Rd., Waimanalo, Oahu)
· Pu’ukohola Heiau NHS [HI: “Temple on the Hill of the Whale”] (1580; Kawaihae)
· Pu’u O Mahuka Heiau (17th c.CE; Waimea, Oahu)
· Pua’a-2 Agricultural Fields AD (stone platform, heiau)
· Pu’uhonua Heiau (sanctuary; on coral hill near Bellows Field main entrance; Waimanalo, Oahu)
· Pu’uhonua o Honaunau NHP (Hale O Keawe Heiau; sanctuary; Holualoa)
· Queen Emma Summer Palace (Nu’uanu, Oahu)
· Russian Fort Elizabeth (1815; Waimea)
· Ulupo Heiau (900 CE; fishery; Kawai Nui Marsh, Kailua, Oahu)
· Wahaula Heiau (1000 CE: b.Samoan kahuna chief Pa'au; Puna, Hawaii)
· Waimea Valley (Haleiwa): near Iliohu (fishing shrine); pohaku
· War Memorial (pohaku; Kaimana beach; Diamond Head- Leahi; Oahu)
Magnetic Anomolies: (Manoa Cliffs trail, Makiki Hts.; Halona Blowhole)
IDAHO:
· Crane Creek
· Craters of the Moon NMP (12000 BP: Paleoindian; Arco; Snake River Plain)
· Hells Canyon
· Midvale Quarry
· Nez Perce NHP (38 sites; Lewiston)
· Shoup Rockshelters
· Veratic and Bison Caves
· Wasden
· Weis Rockshelter
· Wilson Butte Cave (Hunt)
ILLINOIS:
· Albany Mounds SHS (Albany)
· Beattie Park Mound Group (Late Woodland; Rockford)
· Cache River (Little Egypt)
· Cahokia <CC: 2006: Belleville circles; plants damaged; sightings of strange aerial lights; soybean; hoax?>(650 CE: Woodland; 900 CE: Monks Mound; Collinsville)
· Center for American Archeology (Kampsville)
· Coles County <CC: 2005: circle; heat on node in corn; many witnesses saw balls of light>
· Crable
· Dickson Mounds (12000 BP; burial mound complex; Lewistown)
· Faulkner
· Gentleman Farm
· Fort Defiance (Cairo)
· Grand Village/Old Kaskaskia Village (Illini confederacy; Kaskaskia; agricultural village; Ottawa; Utica)
· Hatchery
· Kincaid Mounds SHS (Miss; Paducah, KY)
· Knight
· Knoll Spring
· Koster
· Kuhn Station S (Mississippian: low earthen mound, small village, artifacts; Edwardsville)
· Little Rock Village (Potawatomi village; Kankakee r.)
· Macoupin
· Modoc Rock Shelter (Woodlands)
· Piasa (before 1673: Piasa Bird/Thunderbird cliff murals; Alton)
· Riverton
· Rutherford
· Scovill
· Sinnissippi (Havana Hopewell; Sterling)
· Steuben
· Starved Rock
· Weaver
· Zimmerman
INDIANA:
· Angel Mounds (1000 CE: Mississipian; 1400 CE: Caborn-Welborn; Evansville)
· Angel Phase (1050 CE; mouth of Anderson cr.)
· Huntingburg <CC: 2006: circles and rings; unusual appendages; hidden geometry>
· Mann
· Mounds SP (160 BCE: Adena; Hopewell; “Great Mound”; Anderson)
· Potts Creek Rockshelter AS (Paleo-indians; Crawford co.)
· Swan’s Landing AS (Early Archaic; Harrison co.)
· Wyandotte Caves (8000 BCE; Leavenworth)
IOWA:
· Blood Run S (8500 BP: Hochunk, Ioway, Otoe, Missouri; Quapaw; Kansa; Osage; Omaha; civic, ceremonial, effigy, burial mounds; Granite)
· Boone
· Chanyata S (1100 CE: Mill Creek culture; Linn Grove)
· Cherokee Sewer S (Prehistoric bison processing site; Cherokee)
· Coralville Reservoir Sites
· Edgewater Park S (3800 BP: Late Archaic campsite; Coralville)
· Effigy Mounds NM (500 BCE: Woodland; Marquette)
· Fish Farm Mounds SP (prehistoric cemetery; New Albin)
· Folkert Mound Group (Steamboat Rock)
· Fort Atkinson SP (1830: Treaty of Prairie du Chien)
· Goodhue
· Hartley Fort SP (Woodland: fortified settlement; Driftless Area)
· Indian Village S (1000 CE: Mill Creek culture: 20 dwellings; Sutherland)
· Little Maquoketa River Mounds SP (700 CE: Woodland: 32 mounds; Sageville)
· Maquoketa Caves SP
· Phipps S (1100 CE: Mill Creek culture; earthlodges; Cherokee)
· Simonsen
· Slinde Mounds SP (Waukon)
· Toolesboro Mound Group (Hopewell; Wapello, Toolesboro)
· Turin
· Wittrock
KANSAS:
· Beloit <CC: 2006: 133’ circle- largest circle in North America; sorghum>
· Buresh
· Doniphan
· Eagle Creek
· El Quartelejo Ruins (1696: Taos, Picuris; Pueblo Revolt; Scott City)
· Fanning
· Glen Elder Sites
· Great Bend Sites
· Griffing
· Infinity
· Lansing Man (35000 BP: human remains)
· Lewis
· Paint Creek
· Pottorff
· Pratt
· Quindaro Townsite (1856; Kansas City)
· Sharps Creek AS (Lindsborg)
· Snyder
· Tobias-Thompson Complex (1500 CE: Wichita; Geneseo)
· Trowbridge <CC: 2007: Mission>(200 CE: Hopewell; Kansas City)
· Twelve-Mile Creek
· Whiteford (Price) AS (1000 CE: Smoky Hill culture; 12-15 house sites and burial area; Salina)
· Woodruff
KENTUCKY:
· Blue Licks Battlefield SP (1782: final Revolutionary War battle)
·
Green River Shell Middens AD (Late Archaic; Morgantown)
Indian Knoll (Paradise)
· Fox Farm
· Indian Knoll
· Jonathan Creek
· Mammoth Cave NP (6000 BP: mummies; Brownsville)
· Mount Horeb
· Parrish
· Portsmouth Earthworks (100 BCE: Hopewell mound complex)
· Round Hill (Adena; Berea; Richmond)
· Salts Cave
· Shannon (prehistoric mound; unincorporated; near Fleminsburg)
· Slack Farm (1400 CE: Mississippian; Uniontown)
· Wickliffe Mounds (Mississippian)
· Wright
LOUISIANA:
· Avery Island
· Belcher
· Crooks Mound (Marksville culture: burial mound; 1150 remains; La Salle Parish)
· Fredericks
· Gahagan
· Greenhouse
· Los Adaes (1729-1770: frontier of New Spain)
· Marksville PIS/SHS (Marksville; Natchez-Avoyle)
· Medora S (1300 CE: Plaquemine; 2 mounds and plaza; West Baton Rouge Parish)
· Peck
· Poverty Point <CC: 2007; also at Epps- 25 circles in ¼ mi.arc>(1650-700 BCE: 6 concentric circle earthworks; platform mounds; magnetic field variations; Epps)
· Tchefuncte S (500 BCE: 2 oval shaped shell middens; Mandeville)
· Troyville
· Watson Brake (3400-2800 BCE: oval formation of 11 mound complex; oldest known mounds in North America; Monroe; owned by Gentry family)
MAINE:
· Cushnoc AS (1628 Plymouth colony trading post)
· Damariscotta
· Ellsworth Falls
· Goddard S (1180 CE: Penobscot; Maine penny/Norwegian silver penny/Goddard coin - minted: 1067-1093 CE; Brooklin; Maine State Museum)
· Hirundo
· Mount Katahdin [SM][Penobscot: “The Greatest Mountain”] (Piscataquis)
· Nevin
· Norridgewock AD/Old Point/ Norridgewock Mission S (1724: Jesuit mission)
· Pemaquid AS (17 sites)
· Pentagoet AD (Abenaki-Penobscot; fortified trading post; Castine)
· Spirit Pond runestones (3 stones with runic inscriptions; Phippsburg)
· Turner Farm
MARYLAND:
· Accokeek Creek S (2000 BCE)
· Aisquith Farm E AS (Woodland; Riva)
· Antietam Furnace Complex AS (1768-1775: iron furnace; Hagerstown)
· Arundel Cove AS (prehistoric summer camp; Baltimore)
· Barton Village S (1000 CE: Woodland; Cumberland)
· Beck Northeast S (Late Archaic-Middle Woodland; Algonquian; Davidsonville)
· Biggs Ford S (prehistoric; Frederick)
· Brinsfield I S (900 CE: Late Woodland; prehistoric village; Cambridge)
· Broad Creek Soapstone Quarries/Orr Prehistoric Steatite Quarry AS (1700 BCE: manufactured vessels from boulders; Whiteford)
· Buckingham AS (Woodland village; Assateague; Berlin)
· Buckingham House and Industrial School Complex (Woodland sites; 1870: trade school; Buckeystown)
· Bumpstead AS (stone tools; Elkton)
· Cumberland Bone Cave (Pleistocene fossils)
· Doncaster Town S (1658; Easton)
· Elkridge S (Woodland village)
· Folck’s Mill (grist mill; Cumberland)
· Fort McHenry (1798; Baltimore)
· Grear Prehistoric Village S (Late Woodland; Crystal beach)
· Heath Farm Camp/Jasper Quarry AS (stone tools; Elkton)
· Hoye S (1000 CE: Woodland; Oakland)
· Iron Hill Jasper Quarry AS (stone tools; Elkton)
· Katchef AS (Clovis-Late Woodland; Crofton)
· L’Hermitage Slave village AS (Frederick)
· Magothy Quartzite Quarry AS (Middle Archaic; Pasadena)
· Martins Pond S (Woodland; Annapolis)
· Mattapany-Sewall AS (1663; 1689: Protestant Revolution)
· McCandless AS (stone tools; Elkton)
· Meyer S (Late Prehistoric; Westernport)
· Monocacy S (1145 BCE: Archaic-Woodland; projectile points, pottery, soapstone vessels; Dickerson)
· National Archives AS (4000-1500 BCE: stone artifacts; College Park)
· Nolands Ferry I AS (prehistoric; Tuscarora)
· Nottingham S (6000 BCE-1600 CE: Middle Archaic-Late Woodland; Upper Marlboro)
· Port Tobacco/Potopaco Village (Charles co.)
· Old Colony Cove Site (shell midden; Rose Haven, Annapolis)
· Patterson’s AD (Wallville)
· Piscataway
· Sandy Point S (Woodland; shared w/Buckingham AS; Ocean City)
· Shawnee Old Fields Village S (Woodland; Shawnee; Oldtown)
· Shoemaker III Village S (900 CE: pottery, projectile points; Emmitsburg)
· Skipworth’s Addition (17th c.CE: Quaker; Harwood)
· Walker Prehistoric Village AS (circular houses, cylindrical pits; Poolesville)
· Qillin Village AS (Archaic-Woodland; Eldorado)
· Woodyard AS (1711; Clinton)
· Wye House (1650: Welsh Puritan; Easton)
MASSACHUSETTS:
· Boylston Street Fishweir
· Bull Brook
· Nashoba Brook Stone Chamber/Potato Cave (ceremonial stone landscape structure; Acton)
· Nauset AD (1620: early European contact w/Native Americans; Eastham)
· Parting Ways (African-American freedmen settlement; Plymouth)
· Saugus Iron Works NHS (1646)
· Tantiusques (graphite mines for ceremonial paint; Sturbridge)
MICHIGAN:
· Apple Island (2000 BP; Orchard Lake)
· Brooks
· Burch
· Butterfield
· Feeheley
· Fort Michilimackinac (1671: Jesuit mission)
· Gibaltar
· Holcombe
· Isle Royale
· Juntunen
· Kantzler
· Keweenaw NHP (5000 BCE: copper mines; Calumet)
· Mackinac Island SP
· Moccasin Bluff
· Naomikong Point
· Norton Mound Group (400 BCE: Hopewell; Grand Rapids)
· Sanilac Petroglyphs HSP (300-1000 BP; Bad Axe)
· Schultz
· Skegemog Point
· Younge
MINNESOTA:
· Anderson
· Browns Valley
· Cambria
· Frontenac SP (400 BCE: Hopewell; Dakota-Fox; In-Yan-Teopa “Rock with opening”)
· Indian Mounds P (2000 BP: Hopewell; 37 burial mounds; Saint Paul)
· Inyan Ceyaka Otonwe (19th c.CE: Dakotah/Wahpeton village; tomahawk; several centuries BP: just south- 29 effigy mounds; Jordan)
· Itasca SP (7-8000 BP: hunting; Woodland: burial mounds; Park Rapids; headwaters of Mississippi r.)
· Jeffers Petroglyphs (Late Archaic?: turtle petroglyph- sim. to Indian Knoll, KY; 900-1750 CE: Otoe-Sioux-Iowa: thunderbirds, dragonflies, turtles, shamans)
· Kaposia Park/Little Crow’s Village (1750: Mdewakanton Dakota village; St.Paul)
· Kathio
· Malma
· Mille Lacs Kathio SP (3000 BCE: Archaic mounds; Sioux-Ojibwe; Vineland)
· Minnesota Woman (10000 BP; Pelican Rapids)
· Mooney S (1000 CE: Archaic-Woodland; pottery; Red River Levee, Norman co.)
· Pelican Rapids
· Pike Bay
· Pipestone NM (Woodland: burial mounds; Dakota, Lakota; catlinite quarry for ceremonial pipes)
· Shakopee HD (pre-Dakotah: burial mounds)
· Silvernale
· Viking Altar Rock (Viking?: glacial erratic; Sauk Center)
· Voyageurs NP (10000 BP: Paleo-indian; International Falls)
MISSISSIPPI:
· Aden S (Coles Creek: mounds; Valley park)
· Alligator
· Anna S (Plaquemine; Natchez)
· Bynum
· Crippen Point S (1050 CE)
· Denton
·
Emerald Mound S (1200 CE: Plaquemine-Mississippian; Stanton)
Hester/Hester-Standifer Creek/ Beachum-Harrison S (Amory)
· Fatherland
· Holly Bluff S (Plaquemine-Mississippian; mound complex)
· Jaketown S (2000-600 BCE: Poverty Point culture: artifacts; regional trade center; 1100 CE: Mississippian: earthwork mounds; Belzoni)
· Kings Crossing S (Mississippian: mounds; Vicksburg)
· Nanih Waiya/Nunih Waya [Choctaw: “leaning hill,” “stooping hill,” or “place of creation”](2000 BP: Middle Woodland; Choctaw-Chickasaw-Creek-Cherokee sacred origin location, “mother mound”; emerged from a cave/mound; or final destination; Fearns Springs)
· Owl Creek
· Shiloh NMP (Late Woodland-Mississippian: mounds; Corinth)
· Teoc Creek
· Tishomingo SP (7000 BCE: paleo-indians)
· Walls
· Winterville S (1000 CE: Mississippian: mounds; Greenville)
MISSOURI:
· Big Eddy S (14000 BP: Clovis; Archaic; artifacts; Sac r.)
· Big Mound
· Carrington Osage Village S (1775-1825: Big Osage; Nevada)
· Dalton Sites
· Gordon Tract AS (prehistoric village; Columbia)
· Graham Cave (10000 BP: Archaic; Mineola)
· Jacobs Cavern (Archaic: skeletons, pottery, horn awls, pictographs; Pineville)
· Malden
· Mathews and New Madrid
· Mastodon SHS (14000 BP: Clovis: spear points; mastadons; Imperial)
· Nebo Hill
· Old Forte
· Renner Village AS (Kansas City Hopewell; Riverside)
· Research Cave (8000 BP; Portland; Jefferson City)
· Sac River (10000 BP: Clovis)
· Steed-Kisker
· Towosahgy SHS (Mississippian: mound; Mississippi co.)
· Utz S (1400 CE: Missouri; Marshall)
· Vista Shelter
MONTANA:
· Ash Coulee
· Barton Gulch (9400 BP: Clovis; Madison co.)
· Billings Bison Trap
· Chief Mountain [SM] [Black Feet: “Great Chief” (Ninastiko)]
· Ethridge
· Galata
· Hagen S (Crow-Hidatsu; Glendive)
· Little Bighorn BNM (Billings)
· MacHaffie
· Madison Buffalo Jump
· Malta
· Nez Perce NHP (Lewiston)
· Pictograph Cave (3500 BP: 30000 artifacts; Billings)
· Pompeys pillar NM (petroglyphs; Billings)
· Sorenson & Mangus
· Wahkpa Chugn
NEBRASKA:
· Ash Hollow SHP (1000 BCE: Late Archaic; Woodland; Apache; Lewellen)
· Birdwood
· Burkett
· Cabannes Trading Post (1822; Omaha)
· Coufal
· Dismal River Sites
· Fort Atkinson (1819; Omaha)
· Fort Kearny (1848)
· Fort Lisa (1812)
· Lawson
· Leary S (Rulo)
· Lime Creek Sites
· Logan Creek
· Lovitt
· Lynch
· Meserve
· Palmer S/Skidi Pawnee Village
· Pike-Pawnee Village S (Guide Rock)
· Ponca Fort/Nanza (1700; Niobrara)
· Schultz S (Woodland-Hopewell; North Loup)
· Scottsbluff
· Signal Butte (middle prehistoric; Gering)
· Stanton
· Sterns Creek
· Sweetwater
· Walker Gilmore S (2000 BP: Creek Woodland; Weeping Water; Murray)
· White Cat
· White River Sites
· Woodcliff Burials (Inglewood)
NEVADA:
· Brownstone Canyon AD (petroglyphs; Las Vegas)
· Corn Creek Campsite (5000 BCE; Las Vegas)
· Etna Cave
· Fishbone Cave
· Gatecliff
· Grapevine Canyon Petroglyphs (Laughlin)
· Gypsum Cave
· Humbolt Cave
· Leonard Rockshelter (6710 BCE; Lovelock)
· Lovelock Cave
· Mormon Well Spring (1000 CE; Las Vegas)
· Pueblo Grande de Nevada/Nevada’s Lost City (8000 BCE; 100-1150 CE: Anasazi; Overton)
· Red Rock Canyon NCA (11000 BCE: Paleoindians; San Dieguitol Pito-Gypsum; Anasazi; Patayan; Paiute; petroglyphs; Las Vegas)
· Rocky Gap
· Sheep Mountain Range AD (Las Vegas)
· Sloan Canyon NCA (Archaic petroglyphs; Las Vegas)
· South Fork Shelter
· Spirit Mountain/Newberry Peak [SM](Laughlin)
· Sunshine Locality (Long Valley)
· Tonopah
· Tule Springs AS (13000 BCE; Las Vegas)
NEW HAMPSHIRE:
· America’s Stonehenge (2000 BCE: Late Archaic-Early Woodland; astronomical stone circle; Salem)
· Neville AS (8000 BP: Middle Archaic; Manchester)
NEW JERSEY:
· Abbott Farm HD (500 BCE: Middle Woodland; Trenton)
· Brielle (Lenape settlements)
· Minisink AS (Munsee community; Buskkill, PA)
· Plenge S (12000 BP; Musconetcong r.)
· Rosencrans Ferry
NEW MEXICO:
· Abo (Salinas Pueblo Missions NM)
· Adolfo Canyon S (Navajo pueblito; Tierra Amarilla)
· Ake S (11000 BCE: Clovis; 8000 BCE: Folsom; Datil)
· Arroyo Hondo
· Aztec Ruins NM (Anasazi)
· Bandelier NM (10000 BP; 1150 CE: Anasazi; Los Alamos)
· Bat Cave
· Big Bead Mesa (1700: Navajo village; Casa Salazar)
· Blackwater Draw (Late Pleistocene mammals; 13000 BP: Clovis: stone/bone weapons; Clovis)
· Burnet Cave (Clovis)
· Casa Chiquita [“small house”] (Chaco)
· Chaco Culture NHP (10000 BCE: Archaic-Clovis; 490 CE: Basketmakers; 900 CE: Anasazi: 15 major complexes; kivas; Hopi-Pueblo; Pueblo Bonito; Wijiji; Farmington)
· Christmas Tree Ruin (18th c.CE: Navajo fortification; Farmington)
· Conkling Cavern (Pleistocene fauna; Dona Ana co.)
· Coronado SM (1300 CE: Kuaua pueblo: 6 kivas; Bernalillo)
· El Malpais NM (Grants)
· El Morro NM [Zuni: Atsina “place of writings on the rock”] (Anasazi: Inscription Rock: petroglyphs; Ramah)
· Fajada Butte (Anasazi: cliff dwellings; three slab site- summer solstice/equinox sun dagger piercings on spiral petroglyph; Chaco)
· Feather Cave
· Folsom S (9000 BCE: paleo-indian)
· Gallina (1050 CE: Rosa culture; Anasazi-Pueblo; Los Alamos; Jemez Mts.)
· Gila Cliff Dwellings NM (1275 CE: Mogollon; Silver City)
· Gobernador
· Gran Quivira
· Hawikuh
· Hungo Pavi (Chaco)
· Kinishba SU
· Kuaua
· Ladron Peak (10000 BP; Mogollon-Anasazi; Albuqueque)
· Lucy
· Milnesand
· Mount Taylor [SM][V][Dine: “Turquoise Mountain”(Tsoodzil)](Navajo mythological abode of Black God, Turquoise Boy and Girl; sacred to Navajo, Acoma, Laguna, Zuni; demarks the southern boundary of Dinetah; Grants; San Mateo Mts.)
· Old Fort Ruin (Navajo pueblito; Tierra Amarilla)
· Pecos NHP (14th c.CE; Santa Fe)
· Pendejo Cave (Clovis)
· Petroglyph NM (25000 images; Albuquerque)
· Picuris
· Pottery Mound (1350 CE: 17 kivas; Los Lunas)
· Pueblo Bonito (Chaco)
· Puye Cliff Dwellings (1200s; Santa Fe)
· Quarai
· Salinas Pueblos Missions NM (early 17th c.CE: Spanish Franciscans; Gran Quivira)
· Salmon Ruins (1088 CE: Anasazi; Farmington)
· San Lazaro AS (2 pueblos; Santa Fe)
· Sandia Cave (prehistoric; Bernalillo)
· San Jon
· Shelter Cave (Dona Ana; Pleistocene fauna fossils)
· Swartz
· Three Rivers Petroglyph Site (1000 CE: Mogollon: 21000 petroglyphs; Tularosa-Carrizozo)
· Tsankawi [Tewa: “village between two canyons at the clump of sharp round cacti”](15th c.CE: pueblo ruins; petroglyphs; Bandelier)
· Tsirege [Tewa: “bird place”](1325 CE: Anasazi: 800 rooms, 10 kivas, petroglyph panels; White Rock; Los Alamos National Lab-closed)
· Tularosa
· Wild Horse Arroyo (Pleistocene bison; Folsom)
NEW YORK:
· African Burial Ground (NYC)
· Bluff Point Stoneworks (Norse/Celt?; Keuka l.; Finger Lakes)
· Canajoharie/Upper Castle (Mohawk town; Fort Plain)
· Catherine’s Town (Iroquois town; Montour; Walnut-Glen)
· Chonodote (18th c.CE: Cayuga Iroquois village; Aurora)
· Claud No.1 AS (Groveland)
· Crooked/Keuka Lake Outlet HD (Penn Yan)
· Davis
· Dutchess Quarry Cave S (12000 BP: paleo-indian fluted points, stone tools; Town of Goshen; Middletown)
· Eaton S (8000 BCE: Archaic; 1200 CE: Woodland; 1550 CE: Iroquoian village; West Seneca)
· Finger Lakes NF (10000 BP)
· Fort Corchaug AS (1600s: contact between Corchaug and Europeans; Cutchogue)
· Fort Hunter (2 Mohawk settlements: Teantontalago and Canajoharie)
· Fort Massapeag AS (Oyster Bay)
· Fort Orange (1617; Albany)
· Fort de La Presentation (1749)
· Frontenac Island
· Ganondagan SHS (17th c. CE: Seneca village; Victor)
· Hiscock S (10000 BP: paleo-indian artifacts; mastadons; Byron)
· Kanadaseaga/Seneca Castle (Seneca settlement; Geneva)
· Kanatsiohareke (Mohawk-Kanienkahaka settlement; Fonda)
· Kipp Island
· Kleis S (17th c. CE: Iroquoian village; Hamburg)
· Lake Rockshelter
· Lamoka S (3500 BCE: Archaic-Woodland hunting-gathering; Tyrone)
· Lewiston Mound (200 BCE: Hopewell: burial mound)
· Little Beard’s Town/Genesee Castle (18th c.CE: Seneca town; Leicester)
· Lower Landing AD (Lewiston)
· Mohawk Upper Castle HD (1769: colonial Indian missionary church; Danube)
· Morganville Pottery Factory S
· Mount Sinai (4000 BP; Long Is.)
· R.P. Kemp No.1 S (W. Sparta)
· Onaquaga (Iroquois village; Windsor)
· Onoville
· Point Peninsula
· Potts & Vinette
· Roundtop
· Schuyler Flatts (6000 BP; Menands)
· Wadsworth (1540 CE: Iroquois; Geneseo)
· Ward’s Point AS (Tottenville, Staten Is.)
· West Athens Hill
NORTH CAROLINA:
· Beachtree
· Doerschuck
· Fort Neoheroka (1711: Tuscarora fort; Snow Hill)
· Garden Creek
· Gaston
·
Hardaway S (Badin)
Joara (1000 CE: Mississippian mounds; Morganton)
· Kituwa (ancient Cherokee mound settlement; hereditary priesthood called “ani-kitu-hwagi/anikutani;” Bryson City; Tuskasegee r.)
· Nikwasi (1000 CE: Mississippian mound; Cherokee town; Franklin)
· Town Creek Indian Mound (1100 CE: Mississippian-Pee Dee: mounds; Mount Gilead)
NORTH DAKOTA:
· Arvilla
· Biesterfeldt
· Crowley Flint Quarry
· Fire Heart Creek Fort Clark (1822: Mandan-Arikara; Washburn)
· Fort Lisa (1809)
· Huff AS (Mandan: fortified village; Lake Oahe)
· Knife River Indian Villages NHS (Hidatsa villages; Bismarck)
· Like-A-Fish-Hook (Mandan-Hidatsa-Arikara sanctuary village)
· Little Muddy Creek
· Huff
· Menoken/Verendrye/Apple Creek S (1200 CE: earthen dwellings; Bismarck)
· Northwood <CC: 2005: simple circle>
· Paul Brave
· Slant Village
· Sully's Hill
OHIO:
· Aberdeen Mound
· Adena Mound (Chillicothe)
· Alligator Effigy Mound (800 CE: Fort Ancient culture: underwater panther [Ojibwe: ”mishupishu”] effigy?; Granville)
· Arledge Mounds I and II (Circleville)
· Armco Park Mound I-II (Otterbein)
· Benham Mound (Cincinnati)
· Blanchard River Sites
· Burchenal Mound (Woodlawn)
· Conrad Mound AS (village site; burials; Cleves)
· D.S. Rose Mound (Huntsville)
· Demoret Mound (Ross)
· Dunns Pond Mound (300 BCE: Hopewell; Huntsville)
· Edwin Harness
· Flint Ridge
· Fort Ancient (100 BCE: Hopewell: prehistoric hilltop enclosure; Lebannon)
· Great Hopewell Road (connects monumental Hopewell culture centers from Newark to Chillicothe)
· Hopeton Earthworks (near Mound City group; Hopetown)
· Hopewell Culture NHP/Mound City Group NM (200 BCE: Hopewell earthworks, burial mounds; Chillicothe; Scioto r.)
· Inscription Rock
· Lake Ridge Island Mounds/Wolf Mounds I-IV (Hopewell; near Dunns Pond Mound; Russells Point)
· Lower Shawnee Town/Sonnontio (1738: Shawnee settlement; Portsmouth)
· Madisonville
· Mann Mound (Jacksonburg)
· Matthew Mound (Evendale)
· Miamisburg <CC: 2004: juxtaposed circles; corn>
· Moorehead Circle (40 BCE: Hopewell: triple woodhenge; Fort Ancient)
· Mound Cemetery (Hopewell; Revolutionary War cemetery; Marietta)
· Newark Earthworks (100 BCE: Hopewell: earthen mounds; lunar observatory octagon earthworks-tracking 18.6 year lunar cycle; similar to Chimney Rock, CO)
· Norwood Mound
· Odd Fellows’ Cemetery Mound (Newtown)
· Pickawillany (1748: Miami village; Piqua)
· Portsmouth Earthworks (100 BCE: Hopewell)
· Seip
· Serpent Mound (-1200 BCE: Archaic-Allegheny?; 1200 BCE: Adena; 1070 CE: Fort Ancient; astronomy- Crab nebula? Draco? Halley’s Comet? aligned to summer solstice? Lunar alignments? star Thuban/Alpha Draconis/Pole Star?; Peebles)
· Shawnee Lookout (Fort Hill)
· Story Mound (Cincinnati)
· Sun Watch Indian Village (Fort Ancient culture; Dayton)
· Tower S (1000 CE: Monongahela village; Barnesville)
· Tremper mound and Works (100 BCE: Hopewell: earthen enclosure; irregular shaped mound; West Portsmouth)
· Upper Sandusky/Half-King’s Town (19th c.CE: Wyandot/Huron settlement)
· Wakatomika (18th c.CE: 2 Shawnee village; Dresden)
· Zimmerman Kame (glacial kame; Roundhead)
OKLAHOMA:
· Brackett
·
Cooper Bison Kill S (10900 BCE: Folsom tradition; arrowheads; Fort Supply)
Deer Creek S (fortified village of the Wichita; Newkirk)
· Deer Creek
· Domebo
· Eufalfa
· Fourche Maline Sites
· Grove
· Hughes
· Kenton Caves
· McLemore S (1000 CE: prehistoric village; Colony)
· Norman
· Rock Saline
· Spiro Mounds (950 CE: Mississippian: platform, burial mounds, woodhenge)
· Stamper S (Optima)
OREGON:
· Ashland <CC: 2007>
· Catlow Cave
· Collier Pithouse
· Columbia River Gorge (13000 BP: Folsom-Marmes; Celilo Falls)
· Five Mile Rapids
· Fort Rock Cave (13200 BP; 10000 BP: sandals, oldest footwear)
· Grande Ronde River (Nez Perce-Umatilla-Walla Walla-Cayuse)
· Greaser Petroglyph S (12000 BP: Clovis; Paiute; Lakeview)
· Harney Basin (10000 BP; Paiute)
· Netarts Sand Spit
· Paisley Caves (14290 BP: Clovis coprolite)
· Roaring Springs Cave
· Sunken Village AS (700 BP: Chinookan village; Portland; Sauvie is.)
· Wildcat Rapids
PENNSYLVANIA:
· Independence Hall (Philadelphia)
· Meadowcroft Rockshelter (19000 BP: Clovis; Avella)
· Minisink AS (Munsee community; Bushkill)
· Fort Necessity NB (1754: French and Indian War; Uniontown)
· Logstown (1725: Shawnee settlement; Ambridge)
· McFate
· Meadowcroft
· Mohr
· Murdering/Murthering Town (Lenni Lenape village; Harmony)
· Oley Hills S (Berks co.)
· Shackamaxon (1600s: Delaware Lenape village; Philadelphia)
· Shamokin (Iroquois-Shawnee-Lenape trading village; Sunbury)
· Shawnee Minisink
· Sheep Rock
· Shelter
· Shoop
· Shriver
· Valley Forge (1777-8: Continental Army camp; Washington’s headquarters)
RHODE ISLAND:
· Bristol Soapstone Quarries
· Mount Hope Farm (1680; Bristol)
· Newport Tower (Norse?; 17th c.CE: windmill; Newport)
· Nine Men’s Misery (1676: King Philip’s War; Central Falls)
· Smith’s Castle (1678; Newport)
· Wanton-Lyman-Hazard House (1697; Newport)
SOUTH CAROLINA:
· Charlesfort-Santa Elena S (1562-1566: French-Spanish; Beaufort)
· Cowpens Furnace S (19th c. CE: iron furnace; Gaffney)
· Fig Island (shell rings; plazas; Rockville)
· Fort Sumter (1827)
· Isunigu/Seneca (18th c.CE: Cherokee town; Seneca; submerged beneath Lake Hartwell)
· Keowee (18th c.CE: Cherokee town; Clemson)
· Lake Springs
· Mulberry S (Cofitachequi: large mound; Camden; Pine Tree creek-Wateree r.)
· Scott's Lake (Ft.Watson)
· Sewee
· Stallings
· Thoms Creek
· Topper (50000 BP; Allendale co.)
SOUTH DAKOTA:
· Arzberger S (1500 CE: Arikara; fortified village; 44 circular house rings, 24 bastions; Pierre)
· Badlands NP (11000 BP: paleo-indians; Arikara; Lakota; Rapid City)
· Bear Butte (10000 BP; Cheyenne-Lakota-Sioux; Sturgis)
· Big Bend Reservoir Sites
· Black Hills [SM](7000 BCE; 1500 CE: Arikara; Cheyenne-Crow-Kiowa-Pawnee; Harney Peak)
· Blood Run S (8500 BP; Ho-Chunk, Ioway-Otoe-Missouri-Quapaw-Kansa-Osage-Omaha: civil, ceremonial, effigy, burial earthworks; Sioux Falls; Shindler; Granite, IA)
· Bloom S (1000 CE: Mandan ancestry: 25 rectangular houses, 50 burial mounds; Bloom)
· Crow Creek R (just E of Big Bend Reservoir)
· Demery & Leavenworth
· Dodd
· Fort Pierre Chouteau (1832)
· Fort Randall Reservoir Sites
· Fort Thompson Mounds (800 CE: Woodland; Crow Creek R)
· Hosterman
· Langdeau S (Lower Brule)
· Larson
·
Mitchell AS (1000 CE: Woodland-Mississippian)
Molstad Village (Mandan-Arikara-Hidatsa; Mobridge)
· Pipestone Quarry
· Ray Long
· Thomas Riggs
· Vanderbilt AS (1000 CE: Mandan-Hidatsa; Pollock)
· Verendrye S (1743; Fort Pierre)
· Wind Cave NP (Lakota: sacred place of emergence from the underworld; Rapid City)
TENNESSEE:
· Anderson S (Archaic; Franklin)
· Apple Barn S (Archaic; Woodland; Miss.; Cherokee; Townsend)
· Audubon Acres (Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Ausmus Cave (Miss.; Tazewell)
· Austin Peay Bridge S (Archaic; Gainsboro)
· Bacon Farm S (Archaic; Knoxville)
· Bacon Bend S <CC: 2006: Madisonville>(Archaic-Woodland; Madisonville)
· Bat Creek S (Miss.: burial mound; paleo-Hebrew? inscription; Knoxville)
· Big Bone Cave (1050 BCE: Woodland; Bone Cave)
· Birdwell S (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Greenville)
· Bledsoe’s Station
· Bowman Farm S (Miss.; Jacksboro)
· Brentwood Library S (Miss.; Franklin)
· Bull Bluff S (Woodland-Mississippian; Knoxville)
· Bussell Island (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.-Cherokee; Knoxville)
· Calloway Island (Archaic-Woodland; Madisonville)
· Cardwell Mountain (Archic-Woodland-Miss.; McMinnville)
· Carson-Conn-Short S (Paleoindian; Camden)
· Castalian Springs (Paleoindian-Archaic-Woodland-Miss.)
· C.H. Nash Museum (Chucalissa)
· Chatata (Cherokee; Cleveland)
· Cheek S (Archaic-Woodland; Claiborne co.)
· Cherry Creek Mound (Archaic-Woodland-Miss; Sparta)
· Chestnut Flats (Archaic; Knoxville)
· Chiaha
· Chickamauga and Chattanooga NMP
· Chihowee (Cherokee town)
· Chilhowee (submerged Cherokee town; Knoxville; Little Tennessee r.)
· Chota (Cherokee town; Vonore; Little Tennessee r.)
· Chucalissa (Miss.; Memphis)
· Citico (1000 CE: Miss.-Cherokee town; Vonore; Little Tennessee r.)
· Clinton S (Woodland; Knoxville)
· Coats-Hines S (Paleoindian; Franklin)
· Cochran S (Archaic-Woodland; grouped w/Pinson; Jackson)
· Cox S (Mississippian; Knoxville)
· Crawford Farm Mound (Woodland; Knoxville)
· Dallas Island (Woodland-Miss.; Chattanooga; submerged)
· David Davis S (Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Davis-Noe Site (Miss.; Kingston)
· Davy Crockett Birthplace (Woodland; Greenville)
· Denmark Mound Group (Miss.; Jackson)
· Doug Young S (Woodland; Tazewell)
· Drennon S (Archaic-Woodland; Nashville)
· Dunbar Cave (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Clarksville)
· East Nashville Mounds (Miss.; Nashville)
· Ensworth School (7000 BCE: Paleoindian-Archaic-Miss.: Nashville; destroyed)
· Essary S (Archaic; Tazewell)
· Eva AS (6000 BCE: Archaic; Camden)
· Fewkes Group AS (Miss.; Franklin)
· Fort Pillow SP
· Fort Southwest Point
· Freels (Woodland; Knoxville)
· French Lick (Archaic-Woodland; Davidson co.)
· Foxhole S (Miss.; Tiptonville)
· Gas Company S (Woodland; Townsend)
· Gordon S (Paleoindian-Archaic-Woodland; Centerville)
· Great Tellico/Chatuga (Cherokee; Madisonville)
· Gregory Cave (Woodland-Miss.; Knoxville)
· Halfway Town (Cherokee; Madisonville; submerged)
· Hampton Place AS (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Harris Farm S (Miss.; Jacksboro)
· Harrison Branch (Archaic-Woodland; Madisonville; submerged)
· Heatherly Stone Mounds (Woodland; Jacksboro)
· Hermitage Springs (Archaic-Woodland; Nashville)
· Hiwassee Island (Miss.; Decatur)
· Hixon S (Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Icehouse Bottom (7500 BCE: Archaic-Woodland; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· Iddins S (Archaic; Knoxville)
· Indian Cave (Woodland-Miss; Sparta)
· Irvin Village (Miss.; Jacksboro)
· Island 35 Mastadon (Tertiary; Memphis)
· Johnson May S (Woodland; Pulaski)
· Johnston Mound Complex (Woodland; Jackson)
· Kelley’s Battery (Miss.; Nashville)
· Kellytown (Miss.; Franklin)
· Kimberly-Clark S (Miss.; Knoxville)
· Kinzel Springs S (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Cherokee; Townsend)
· Lake Hole Cave (Miss.; Mountain City)
· Lecroy S (Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Ledford Is. (Miss.; Cleveland)
· Link Farm S (Miss.; Waverly)
· Lucky 7 S (Woodland; Somerville)
· MacLellan Island (Archaic-Woodland; Chattanooga)
· Mallards Dozen AS (Archaic-Woodland; Chattanooga)
· Martin Farm Site (Miss.; Madisonville; submerged)
· Mayberry S (Paleoindian-Archaic-Woodland; Centerville)
· McCroskey Island (Miss.; Sevierville)
· McMahan Indian Mounds (Miss.; Sevierville)
· Mialoquo (Miss.; 1760: Cherokee town; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· Moccasin Bend (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Montgomery S (Woodland; Knoxville)
· Moore Bottom (Archaic; Gainsboro)
· Morganton (1800; submerged; Tellico Lake)
· Mound Bottom (950 CE: Miss.: mound complex, burial mounds, plaza; Kingston Springs; Harpeth r.)
· Mouse Creek S (Woodland-Miss.; Athens)
· Mud Glyph Cave (Mississippian)
· Myers Mound (Archic-Woodland-Miss.; McMinnville)
· Neas S (Archaic-Woodland; Greenville)
· Norris Basin
· Nuckolls S (Paleoindian; Waverly)
· Obion Mounds (Miss.; Paris)
· Ocoee (Woodland-Miss.-Cherokee; Benton)
· Oldroy S (Paleoindian-Archaic-Woodland; Centerville)
· Old Stone Fort (80 CE: Woodland: 2 pedestal mounds; Manchester; Little Duck River)
· Old Town AS (Miss.; Franklin)
· Pack S (Miss.; Mound Bottom)
· Parker’s Pasture (Miss.; Pulaski)
· Pierce S (Paleoindian; Henderson)
· Pinson Mounds (1 CE: Woodland: 17 mound complex; grouped w/Cochran; Jackson)
· Plum Grove AS (Woodland-Miss.; Jonesborough)
· Pony Ride S (Woodland-Miss-Cherokee; Townsend)
· Post Oak Island (Miss.; Knoxville; submerged)
· Prison Hill Site (Woodland-Miss.; Wartburg)
· Rankin S (Woodland; Newport)
· Red Velvet Spider Rockshelter (Woodland; Kingston)
· Regions Center (Pleistocene: fauna; 2390 BCE: Paleoindian-Woodland; Nashville)
· Rose Island (Archaic-Woodland; Madisonville; submerged)
· Rutherford-Kiser Mound Group (Miss.; Gallatin)
· Rymer S (Miss.; Bradley co.)
· Saltpeter Cave (Woodland; Campbell co.)
· Sellars Farm S (Miss.; Lebanon)
· Shiloh Indian Mounds (Woodland-Miss; Savannah-Corinth, MS)
· Stardust S I-III (Archaic-Woodland; Celina)
· Starnes-Kahite (Cherokee; Madisonville; submerged)
· Tallassee (Cherokee town; Knoxville)
· Tanasi (1600 CE: Cherookee; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· Tellico Blockhouse (1795; Vonore)
· Tipton-Dixon House (Woodland; Knoxville)
· Tomotley (1000 CE: Archaic-Miss.; 1751: Cherokee; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· Toqua (900 CE: Miss.; Cherokee; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· Tuskegee (Cherokee; Vonore; submerged; Little Tennessee r.)
· University of Tennessee Agriculture Farm Mound (1000 CE: Woodland; Knoxville; exact loc. restricted)
· Vulcan AS (Archaic-Woodland-Miss.; Chattanooga)
· Wear Bend S (Cherokee; Knoxville)
· Widemeier S (Paleoindian-Archaic; Nashville)
· Woodland Mound AD (Woodland; Chattanooga)
· Zimmerman’s Island (Miss.: ancient Chiaha; Dandridge)
TEXAS:
· Alibates Flint Quarries NM (Paleoindian; Amarillo)
· Big Bend NP (9000 BP: Paleoindian; Alpine; Rio Grande r.)
· Bonfire Shelter
· Burro Mesa Quarry
· Chimney Rock
· Devils Mouth
· Enchanted Rock (11000 BP: Tonkawa sacred site; Fredericksburg-Llano)
· Gas Plant
· George C. Davis
· Hale
· Harrell S (1200 CE; South Bend)
· Horn Rockshelter
· Hot Wells
· Hueca Tanks
· Jonas Short
· Keystone Wetlands (4000 BP: village; El Paso)
· Kyle
· Landergin Mesa (Adrian; Vega)
· Levi Rock Shelter (10000+ BP: Clovis points; Austin)
· Lewisville
· Lipscomb
· Lone Wolf Creek
· Lubbock Lake (12000 BP: Paleoindian)
· Malakoff
· McLean
· Miami
· Midland (Scharbauer)
· Mission Concepcion (1716: Spanish Franciscan; San Antonio)
· Mission Espada (1690: Spanish Franciscan; San Antonio)
· Mission San Jose (1720: Spanish Franciscan; San Antonio)
· Mission San Juan Capistrano (1716: Spanish Franciscan; San Antonio)
· Morhiss Mound
· Paint Rock
· Panther Cave
· Plainview S (7800 BCE)
· Polvo
· Rocky Dell
· Sanders
· Shelby Brooks
· Spanish Fort
· Stansbury
· Steadman
· Stone
· Texarkana Reservoir Sites
· Vinson
· White
UTAH:
· Alkali Ridge (900 CE: Pueblo II: pit dwellings, multi-story buildings, kivas, ceramics; Monticello)
· Arches NP (Ute pictographs; Moab)
· Black Rock Cave
· Canyonlands NP (2000 BCE: Late Archaic; Anasazi; petroglyphs; rock painting; False Kiva; Horseshoe Canyon; Newspaper Rock; Moab; Colorado-Green r.)
· Danger Cave (9500 BCE; Wendover)
· Deadman Cave
· False Kiva (Canyonlands NP; Moab)
· Glen Canyon
· Grand Staircase Escalante NM (500 CE: Fremont-Anasazi; rock art; Kanab)
· Hogup Cave
· Hovenweep NM (14000: Paleoindian hunters; Anasazi; Blanding; Cortez, CO)
· Millsite Rock (pictograph; Ferron)
· Moon House (1150 CE: Anasazi: kivas; pictographs; Cedar Mesa)
· Natural Bridges NM (Anasazi; Navajo-Hopi; sacred site; Blanding)
· Newspaper Rock SHM (largest known collection of petroglyphs; Moab-Monticello)
· Nine Mile Canyon (Archaic; 950 CE: Fremont culture; 1000 rock art sites, petroglyphs, pit-houses, rock shelters, granaries, pottery; Myton; Fremont r.)
· Paria River (petroglyphs)
· Pilling Figurines (900 BP: Fremont culture; Range Creek)
· Promontory
· Quail rock art panel (Fremont culture: pictographs; Emery)
· Rainbow Bridge (Anasazi)
· Rochester Rock Art Panel (Fremont culture: petroglyphs; Emery)
· Ruin Arch (Fremont culture: kiva, rock art; San Rafael Swell)
· Snow Canyon SP (250 CE: Anasazi; Paiute; Ivins)
· Thorne Cave
· Turner-Look
· White Canyon (Anasazi: cliff dwellings; rock art; Natural Bridges NM; Sipapu Bridge)
· Zion
VIRGINIA:
· Cactus Hill (17000 BP: Clovis-Archaic; Richmond; Nottoway r.)
· Clarksville
· Colonial Williamsburg (1699)
· Flint Run
· Gala
· Jamestown Settlement (1607-1699)
· Kecoughtan/Kikotan (1607: Algonquian)
· Keyser Farm
· Mount Vernon (1757; Alexandria)
· Powhatan’s Chimney (1607: Werowocomoco- capital village; Wicomico)
· Thunderbird AD (Paleoindian-Archaic; Fifty S; Fifty Bog; Limeton)
· Thompson's Shelter
· Thunderbird
· Tollifero
· Werowocomoco (1200 CE: Woodland; Powhatan Confederacy <30 Algonquian speaking tribes> political center; artifacts, earthworks; Gloucester co.; Jamestown; York r.; Tsenacommacah coastal plain)
· Williamson
WASHINGTON:
· Ash Cave
· Columbia River Gorge (13000 BP: Folsom-Marmes people)
· Congdon, Indian Well
· Duvall
· Duwamish Number 1 S (670 CE: Duwamish: shell midden, village; Seattle)
· East Wenatchee Clovis S (11000 BP: Clovis bone and stone tools)
· Ginkgo Petrified Forest SP/Wanapum RA (300 petroglyphs; Vantage)
· Grande Ronde River (Nez Perce-Umatilla-Walla Walla-Cayuse)
· Hoko River AS (3800 BP: Makah; 2500 BP: fishing camp; Pysht)
· Indian Dan
· Kennewick Man (9300 BP)
· Lake Lenore Caves
· Lake Roosevelt Sites
· Lind Coulee AS (7450 BCE: stone tools; bone tools: 24 needles, points; Warden)
· Manis Mastadon S (Sequim)
· Marmes Rockshelter (10000 BP: human bones; Lyons Ferry; Snake-Palouse r.)
· Marymoor Prehistoric Indian S (4000 BCE; 1000 BCE; Redmond; Sammamish r.)
· McNary Reservoir Sites
· Mt.Rainier NP (8000 BP: Nisqually-Puyallup-Muckleshoot-Yakama-Taidnapam)
· Olcott
· Old Man House (2000 BP: Suquamish winter village; Suquamish)
· Ozette Indian Village AS (2000 BP: Makah village; La Push)
· Ryegrass Coulee
· Tse-whit-zen (2700 BP: Klallam village: 10000 artifacts, 335 skeletons; Port Angeles)
· Whitman Mission NHS (1836: Presbyterian mission; Cayuse Ware; Walla Walla)
· Wilbur <CC: 2009: circles and rings>
· Windust Caves AD (8500 BCE: Clovis points)
· Wishram village (10000 BP; Upper Chinook; Yakama-Nez Perce; trading village; Wakemup mound; petroglyphs; The Dalles, OR; near Five Mile Rapids)
WEST VIRGINIA:
· Clover S (400 BP: Fort Ancient culture; Lesage)
· Cresap
· Criel Mound (250 BCE: Adena: 2 sacred circle earthwork enclosures; South Charleston)
· Dixon
· Grave Creek Mound (250 BCE: Adena: largest conical burial mound in US; Moundsville)
· Indian Mound Cemetery (Hopewell; Romney)
· Marcy Creek
· Oak Mounds (100 BCE: Hopewell: flint tools, pottery; mounds; Clartksburg)
· Rohr
· St. Albans
WISCONSIN:
· Aztalan SP (900 CE: Woodland-Mississipian; mounds; houses, stockades, pottery; Lake Mills; Rock Lake)
· Calumet County Park Group (6 effigy mounds of panthers; Stockbridge; Lake Winnebago)
· Clam Lake Sites
· Copper Culture SP (6000 BP: Old Copper culture; Oconto)
· Cyrus Thomas
· Diamond Bluff
· Durst Rockshelter
· Ferry Road
· High Cliff State Park (500 CE: conical effigy mounds; Sherwood; Lake Winnebago)
· Indian Mounds P (200 CE: effigy mounds; Whitewater)
· Karow
· Lake Nakomis
· Lake Wingra [Ho-chunk:”duck”](mounds; Madison)
· Lawton
· Lizard Mound CP (500 CE: effigy mound; West Bend)
· Mero
· Natural Bridge SP (9000 BCE: Paleoindian; Baraboo)
· Neale
· Oconto
· Osceola
· Porte des Morts
· Renier
· Roche-a-Cri Petroglyphs (Friendship)
· Rock Island
· Ross
· Silver Mound AD (Hixton; Alma Center)
WYOMING:
· Agate Basin
· Birdshead Cave
· Bottleneck Cave
· Brewster Bridger Antelope Trap (Paleoindian hunting; Evanston)
· Devils Tower NM [SM][Lakota: Mato Tipila “bear lodge”](Lakota-Arapaho-Crow-Cheyenne-Kiowa-Shosone; Hulett)
· Horner S (Cody)
· McKean S (Moorcroft)
· Mummy Cave (7280 BCE: Early Archaic: human burial site; lanceolate projectile points; Cody; Yellowstone NP; Shoshone r.)
· Ruby
· Signal Butte
· Spring Creek Cave
· White River Hell Gap
PUERTO RICO:
Canas
Capa
Cuevas & Hacienda Grande
Ostiones
SOUTH AMERICA:
ARGENTINA:
· Cueva de las Manos (8000 BCE: wall painting; Santa Cruz)
BOLIVIA:
· Chanapata
· Chiripa (1000 BCE; Lake Titicaca)
· Pumapunku [MA]
· Tiwanaku/Tiahuanaco [MA] [GP35](13000 BCE? Posnansky; 1500 BCE; accd.local Amara legends- submerged city of Wanaku w/in l.Titicaca; ocean-boat builders (sim. To Egyptian boats); 2000: Italian archeologists have discovered submerged paved road, stone terrace, ½ mi. long wall, large sculptured stone head sim. to those found at Tiwanaku- Viracocha; sea horses habitation w/in l.Titicaca; legends of lights coming and going from lake; Oswaldo Rivera: tracker for rising and setting of Sun, solar year; gateway aligned with spring equinox; ancient harbor constructions, port city on l.Titicaca)
BRAZIL:
· Macupiri
· Mangueiras
CHILE:
· Fell Cave
· Monte Verde (14500 BCE: pre-Clovis; mastodon bone; coprolites; Llanquihue)
· Pali Aike
· Pukaras
· Camina
· Nama
· Quitor (pre-Columbian: San Pedro de Atacama)
· Turi
· Easter i. (Hancock: place of refuge from deluge; facing rising sun on; Rapa Nui/Isla de Pascua)
· Rano Raraku (volcanic crater w/Moai); Orongo village (Rano Kau); Moai [MA](1250 CE)
COLUMBIA:
· Barlovento
· Betanci
· Bogota (pre-Columbian: Muiscas; early animal domestication site)
· Canapote
· Catanguero
· Cienaga de Ora
· Crespo
· Cuidad Perdida/Buritaca/Teyuna (800 CE)
· Cupica
· Garzon
· La Pitia
· Malagana (300 BCE: gold artifacts)
· Malambo
· Momil
· Monsu
· Puerto Hormiga
· San Augustin [MA](Huila)
· San Nicolas
· Tamalameque
· Tierradentro (pre-Columbian hypogea; Inza, Cauca)
· Zambrano
· Zapatosa
ECUADOR: (Valdivia culture)
· Agua Blanco
· Cerro Narrio
· El Encanto (Amazonas)
· Machallla
· Real Alto
· Valdivia (3500 BCE: Las Vegas culture; Valdivia)
PERU:
· Acaray (900 BCE: fortified hill top; Huacho, Lima)
· Buena Vista (2200 BCE: Temple of the Fox observatory; Lima)
· Cahuachi (1 CE: Nazca)
· Canamarca (ruin; Yauri)
· Caral (3000 BCE: Norte Chico pyramid; Huacho)
· Chan Chan (850 CE: Chimu; Trujillo)
· Chavin de Huantar (900 BCE: Chavin; San Marcos)
· Choquequirao [Quechua: “Cradle of Gold”] (1450 CE: Abancay)
· Cumbe Mayok [Quechua: “well made water channel” (Kumpi Mayu)] (1500 BCE; Cajamarca)
· Guitarrero Cave (12500 BP; 1000 BCE; Ancash)
· Jiskairumoko [Aymara: “small-bunch grass-small hill”](3200 BCE: Puno)
· Kuelap (6th c.CE: Chachapoyas;
· Machu Pichu [Quechua: “old peak”][MA][SM](Urubamba, Cuzco; Putucusi) “Happy Mountain”)
· Nazca Lines (200 BCE: geoglyphs; Spider: replica of Orion constellation; Nazca; Palpa)
· Ollantaytambo/Ullantaytampu [MA](Urubamba, Cuzco)
· Pachacamac [Quechua: “Creator of the World/Earth”](200 CE; 600 CE: Huari; Lima)
· Pikillacta [Quechua: “city of fleas”] (500 CE: Huari; Cusco)
· Pikimachay [Quechua: “flea cave”](20000 BCE; Ayacucho Valley)
· Pisac (Cuzco)
· Raqchi (Inca; Sicuari; Cuzco)
· Sacsayhuaman [MA](900 CE: Killke; Cuzco)
· Sayhuite (monolith; Abancay)
· Sillustani (Incan burial ground; Puno)
· Sipan (Moche; Chiclayo)
· Tambo Colorado (Incan adobe; Pisco)
· Tambomachay [Quechua: “resting place”](Inca; Cusco)
· Tucume (800 CE: Lambayeque/Sican; 1350 CE: Chimu; 1450: Inca; pyramids/mounds; Lambayeque)
VENEZUELA:
· Aerodromo
· Agua Blanca
· Arauquin
· Barrancas
· Betijoque
· Camoruco
· Cano del Oso
· Capacho & La Mulera
· Cerro Iguanas
· Cerro Machado
· Chipepe
· Cotua
· Dabajuro
· El Agua
· El Heneal
· El Jobo
· El Mayal
· El Morro
· El Palito
· El Penon
· Guarguapo
· Guavaguao
· Guayabita
· Guaribe
· Hato de la Calzada
· Irapa
· La Betania
· La Cabrera
· La Ceiba
· La Mata
· La Pitia
· Los Caros
· Manicuare
· Manzanillo
· Memo
· Mirinday
· Muaco
· Nericagua
· Ortoire
· Pedro Garcia
· Peludo
· Punta Gorda
· Rio Chico
· Ronquin
· Saladero
· San Fernando
· Santa Ana
· Sarare
· Tabay
· Tocuyano
· Topo
AUSTRALIA/PACIFIC:
· Bala Uru (Mudginberri; Woolwonga Aboriginal Reserve; Deaf Adder Creek)
· Conondale <CC: 2006>(Queensland)
· Kolondjorluk Creek (Jim Jim Falls; Mudginberri; Woolwonga Aboriginal Reserve; Deaf Adder Creek)
· Lake Mungo (40000 BCE: Mungo Man- oldest human remains found in Australia; Mungo Lady- oldest human remains in world to be ritually cremated; Pan Ban)
· Murujuga (10000 BCE: standing stone rock art; 1 million petroglyphs; Burrup/Dampier penin.)
· Ngarrabullgan cave (40000 BCE: rock shelter; Mulligan mt.)
· Nourlangie Rock (monoliths and skulls; Mudginberri; Woolwonga Aboriginal Reserve; Deaf Adder Creek)
Associated shelter sites: (N-S)
o Initiation Cave
o Gorge Creek Shelter
o Waterhole Cave
o Ngarrabullgan Cave
o Nonda Rock
o Quinine Bush Shelter
o Kookaburra Rock
o Courtyard Rock
o Dragonfly Hollow
o Fig Tree Shelter
o Hand Shelter
o Grass Tree Shelter
o Lookout Shelter
o Painted Ell
o Tunnell Shelter
o Bush Peg Shelter
o Devil’s Lair (30000 BCE)
o Mandu Mandu Creek
o Rottnest Island (70000 BCE)
o Upper Swan Bridge (40000 BCE)
SOUTH PACIFIC ISLANDS:
· Easter i. (Hancock: 144° E Angkor Wat, 144° W Giza; 2° of precession; Rapa Nui/Isla de Pascua)
· Rano Raraku (volcanic crater w/Moai); Orongo village (Rano Kau); Moai [MA](1250 CE)
· Malakunanja
· Nawalabila (60000 BCE)
· Nawamoyn
· Puritjarra (21000 BCE)
· Sepik River sites (Jaya pk.) of Tifalmin (Neolithic); (ancient Chamorro migrations)
PALAU:
· Aemiliik
MICRONESIA:
· Nan Modol [MA][“spaces between”] (1st c.CE; Hancock: myth of underwater city nearby; stone structures; perfectly oriented to cardinal directions-NSEW; ghost stories; myth: place to prepare soul’s journey after death (underwater); Pohnpei)
· Chuuk (2000 BP; Truk)
TONGA:
[Langi (tombs); Esi (mound)]
· Ha'apai Tombs [MA] (mound-tombs; Tongatapu)
· Hehea Mound (near Namoala tomb; Tongatapu)
· Langi Tombs [MA] (mound-tombs; royal village; Lapaha, Tongatapu)
· Mu'a Tombs [MA] (mound-tombs; Tongatapu)
· Namo'ala tomb (pyramid tomb)
· Paepae 'o Tele'a/Uluakimata I (16th c.CE: pyramid tomb; coral sandstone; near 'Esi Ai Kona mound)
· Vava'u Tombs [MA] (mound-tombs; Tongatapu)
ANTARCTICA:
LEGEND
B = BALANCED
C = COLD/YIN
H = HOT/YANG
MRP = Magnetic Reversal Point
VV = Vile Vortice
UVG# = Earth Grid Point Number of Unified Vector Grid
VS = Vital Statistics (Earth Extremes)
EC = Earth Crust
OC = Ocean Currents; (+)=Warm; (-)=Cold; (directions)
WC = Wind Currents; (directions)
NT = Nearest Topology
HE = Human Extreme
[V] = Volcano
[SM] = Sacred Mountain
NC = Nearest Civilization/City/Town/Village
AS = Archaeological Site(s)
[MA] = nearby/associated Megalithic Architecture
[SR] = Silk Road settlement
AD = Archeological District
AS = Archeological Site
ASP = Archeological State Park
HD = Historic District
HP = Historic Park
HSP = Historic State Park
NBP = National Battlefield Park
NCA = National Conservation Area
NHP = National Historic Park
NHS = National Historic Site
NM = National Monument/National Memorial
NMP = National Military Park
NP = National Park/National Preserve
RA = Recreation Area
S = Site
SHP = State Historic Park
SHS = State Historic Site
SP = State Preserve/State Park
IR = Indian Reservation
<CC> = Crop Circle